Neuroanatomy & neurophysiology for speech-language pathology
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
What is the CNS responsible for?
Processing, integration, and initiating responses
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
cranial and spinal nerves
What is the PNS subdiveded into
Somatic and Autonomic
Somatic
voluntary skeletal muscles
Autonomic
involuntary control of smooth muscle, glands, and viscera
What does the Automatic nervous system (ANS) contain?
Sympathetic division and Parasympathetic division
sympathetic division
fight, flight, or fear reponse
Parasympathetic division
rest and digest
Spinal cord function
Transmits signals between brain and body.
Foramen magnum
the hole in the base of the skull that the spinal cord passed through
cervical and lumbar enlargements
sites where nerves serving the upper and lower limbs emerge.
conus medullaris
end of spinal cord
cauda equina
"horse's tail", a fan of nerve fibers below the spinal cord
filum terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
meningeal layers
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater (DAP)
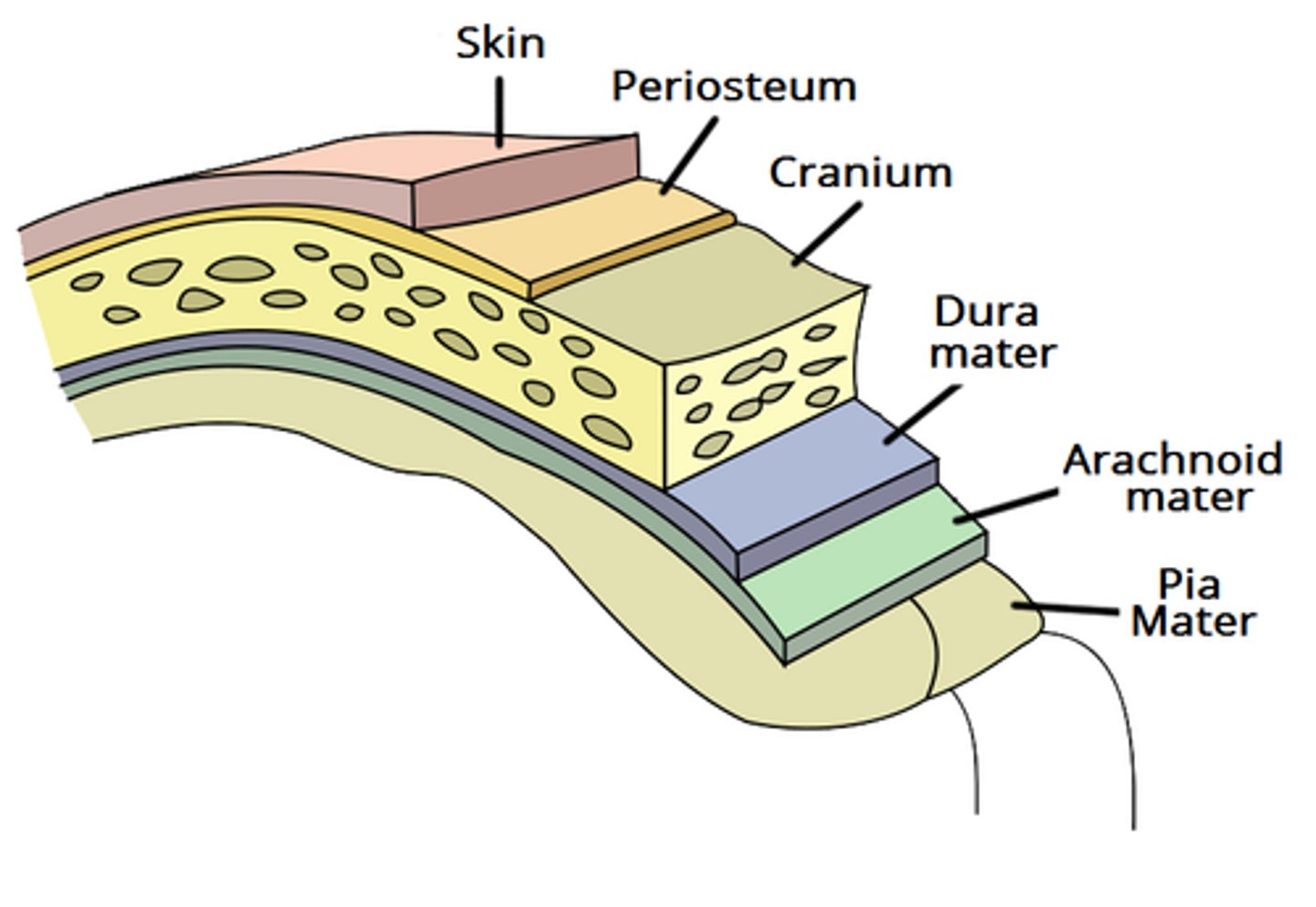
What does the pia mater adhere to directly?
Spinal cord
What does the subarachnoid space contain?
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
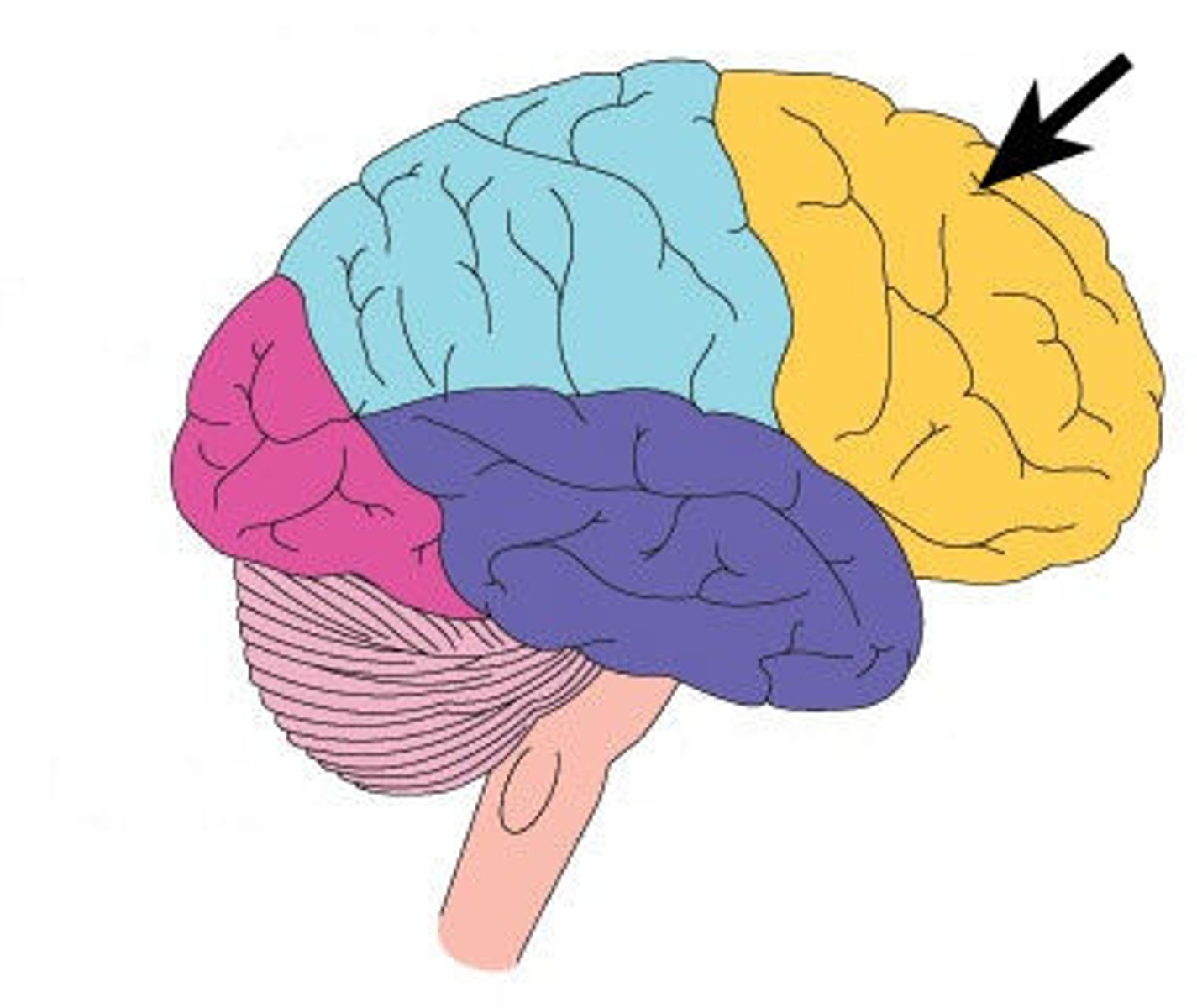
frontal lobe
primary motor cortex (area 4), premotor areas for planning and initiation (areas 6-8), executive functions, personality, speech (broca's)
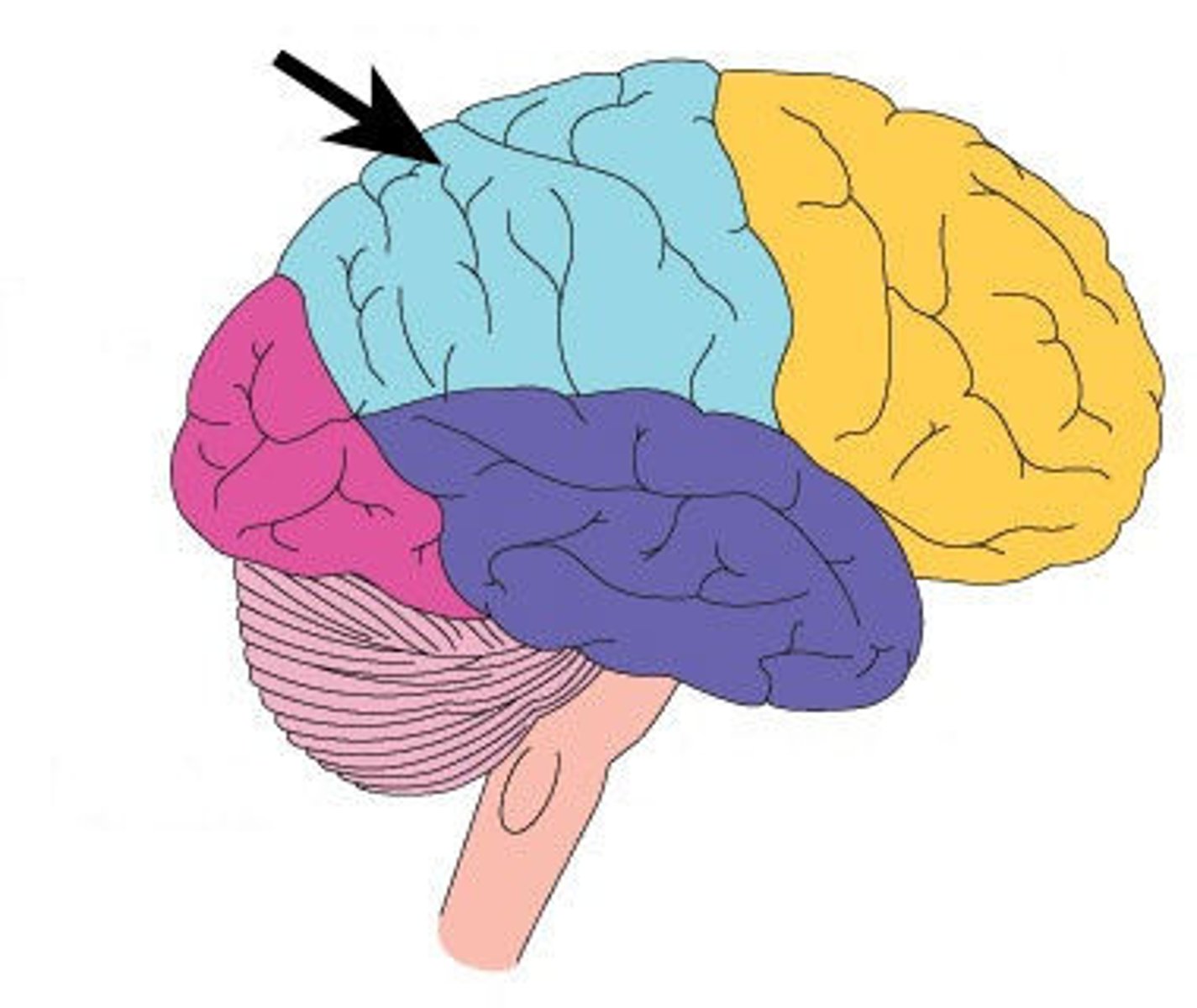
Parietal lobe
primary somatosensory cortex (areas 3, 1, 2), spatial awareness, constructional tasks(building, drawing, etc.)
somatosensory cortex
area of the parietal lobes that processes touch, temperature, pain, and pressure
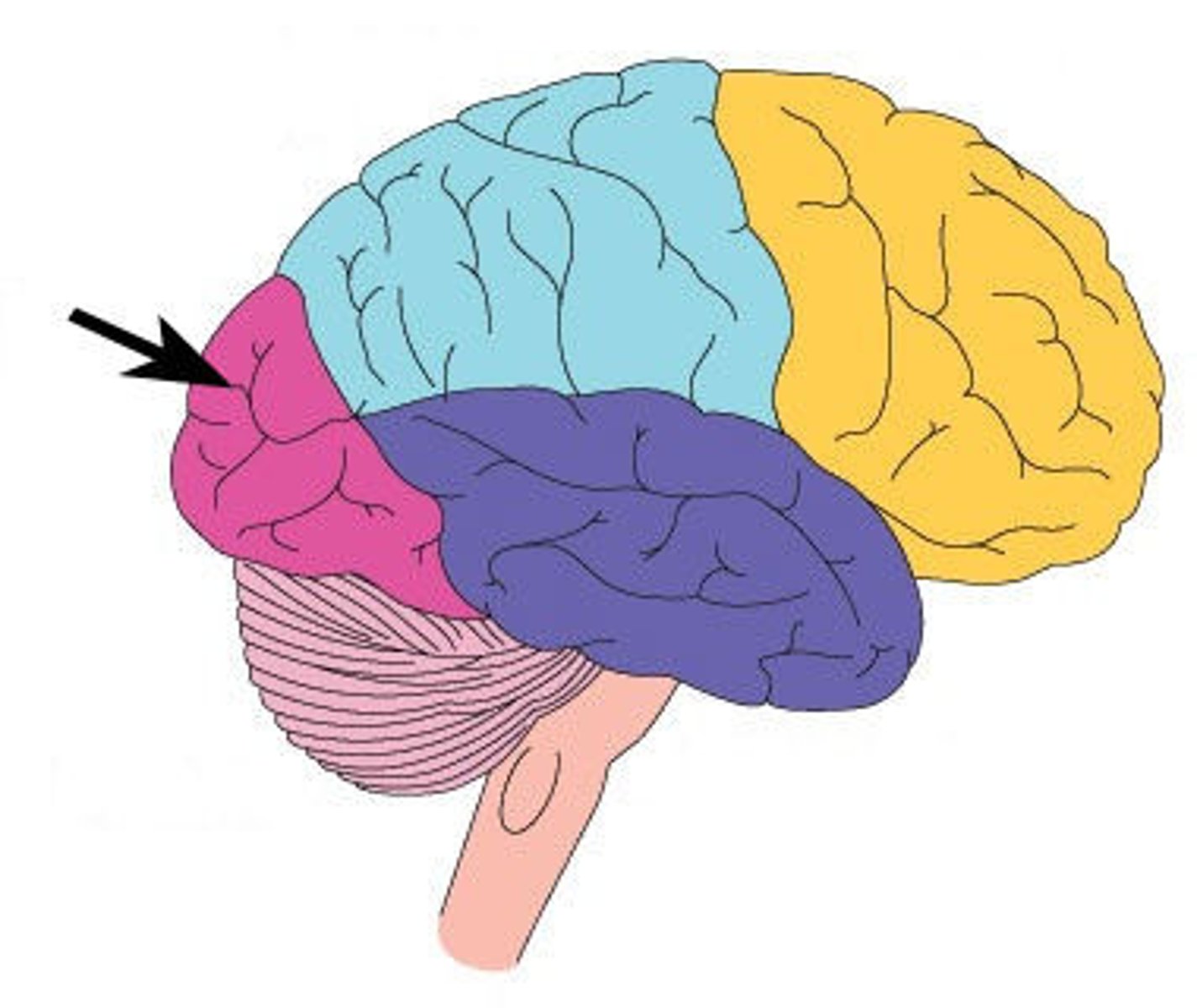
temporal lobe
auditory processing, wernicke's area (area 22), memory (hippocampus), emotion (amygdala)

occipital lobe
vision (area 17), visual recognition (area 18-19)
Lateralization and specilization
the brain's left and right sides do different jobs
left hemisphere
language, analytical reasoning, sequential processing
right hemisphere
pragmatics, prosody, visual-spatial functions, environmental orientation.
planum temporale
is involved in language processing and is also studied in relation to developmental disorders like dyslexia (larger on left)
Each hemisphere controls the _________ side.
opposite
topographical representation
specific cortical areas map to specific body regions
functional networking
specialized yet integrated systems
dorsal pathways
convey sensory information (touch)
ventral pathways
"what pathways"from occipital to temporal lobe, identifying objects
ventral horn
motor neurons
dorsal horn
sensory input
Where are the sensory neuron cell bodies located?
dorsal root ganglia
dermatomes
an area of the skin supplied by nerves from specific spinal root
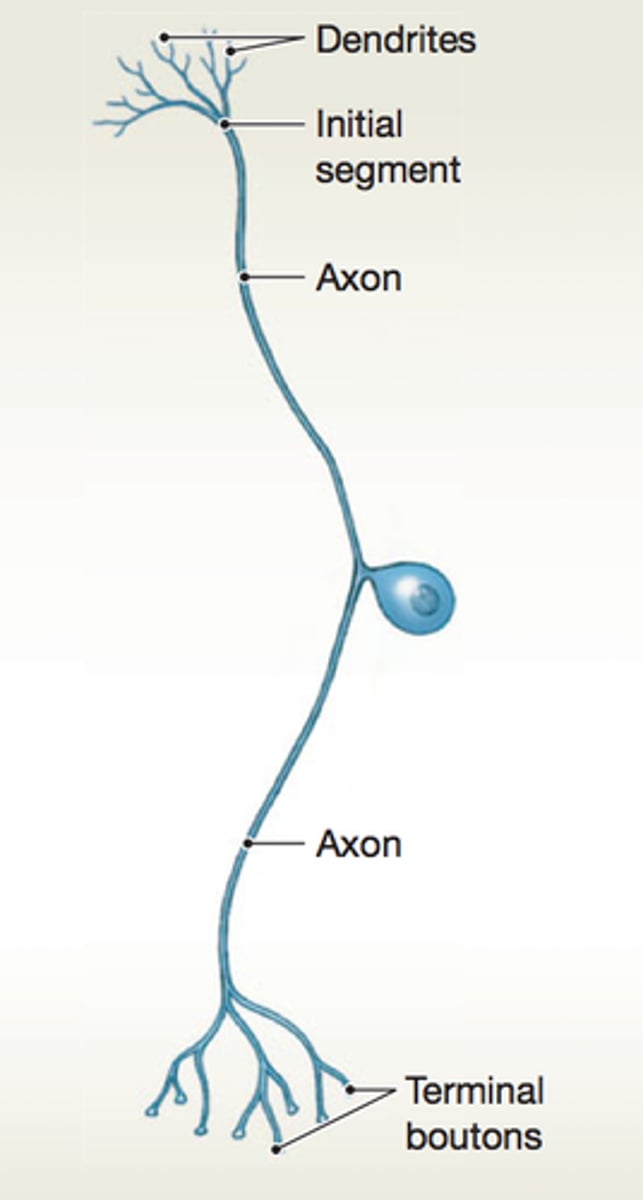
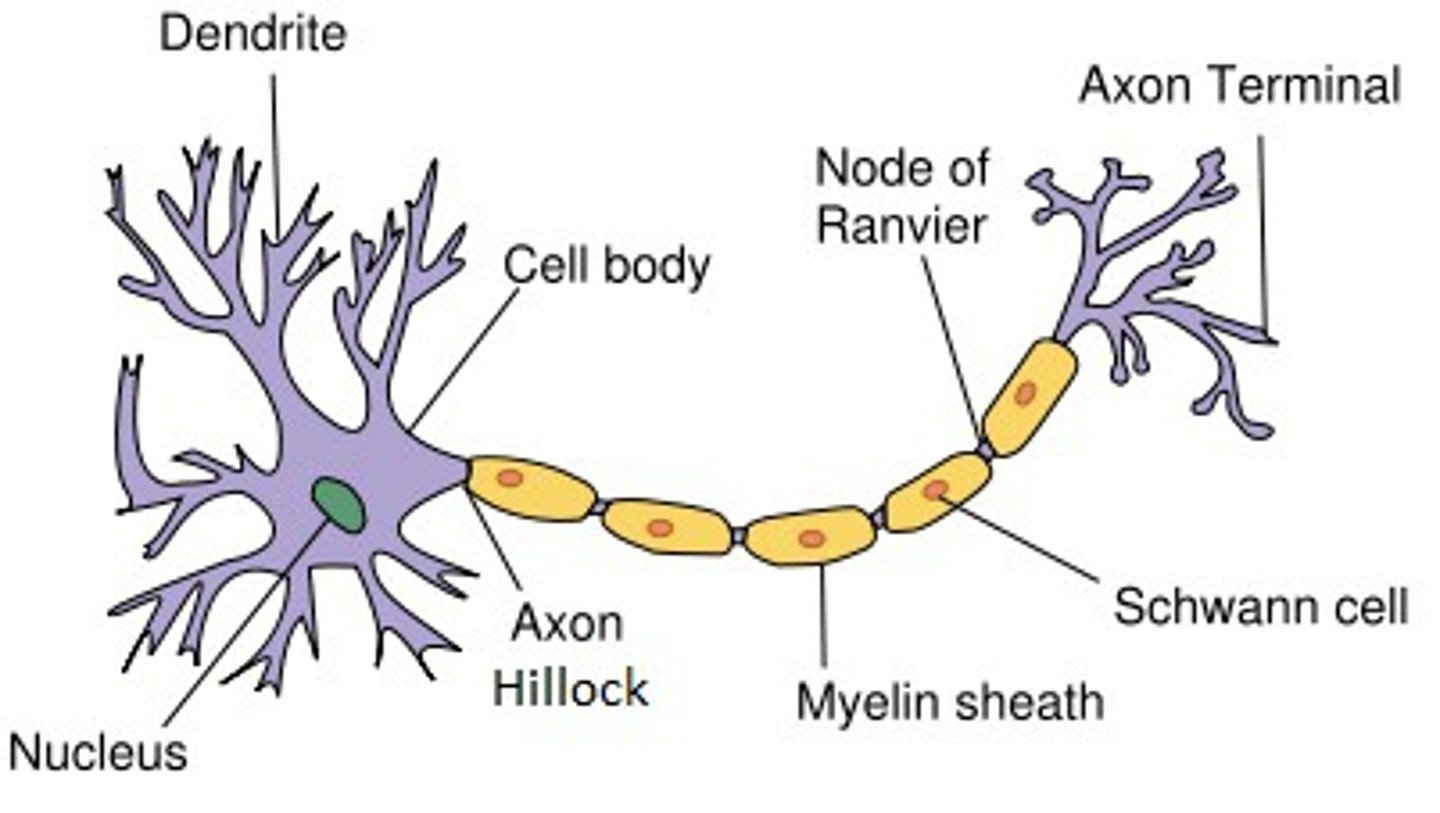
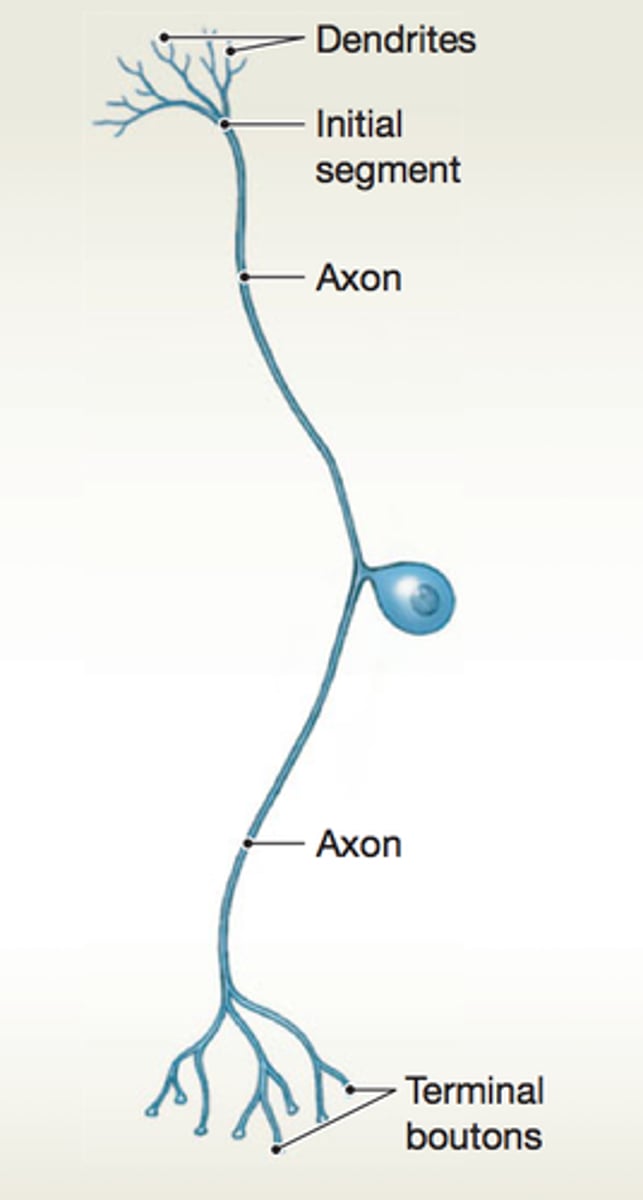
Dendrites
receive signal
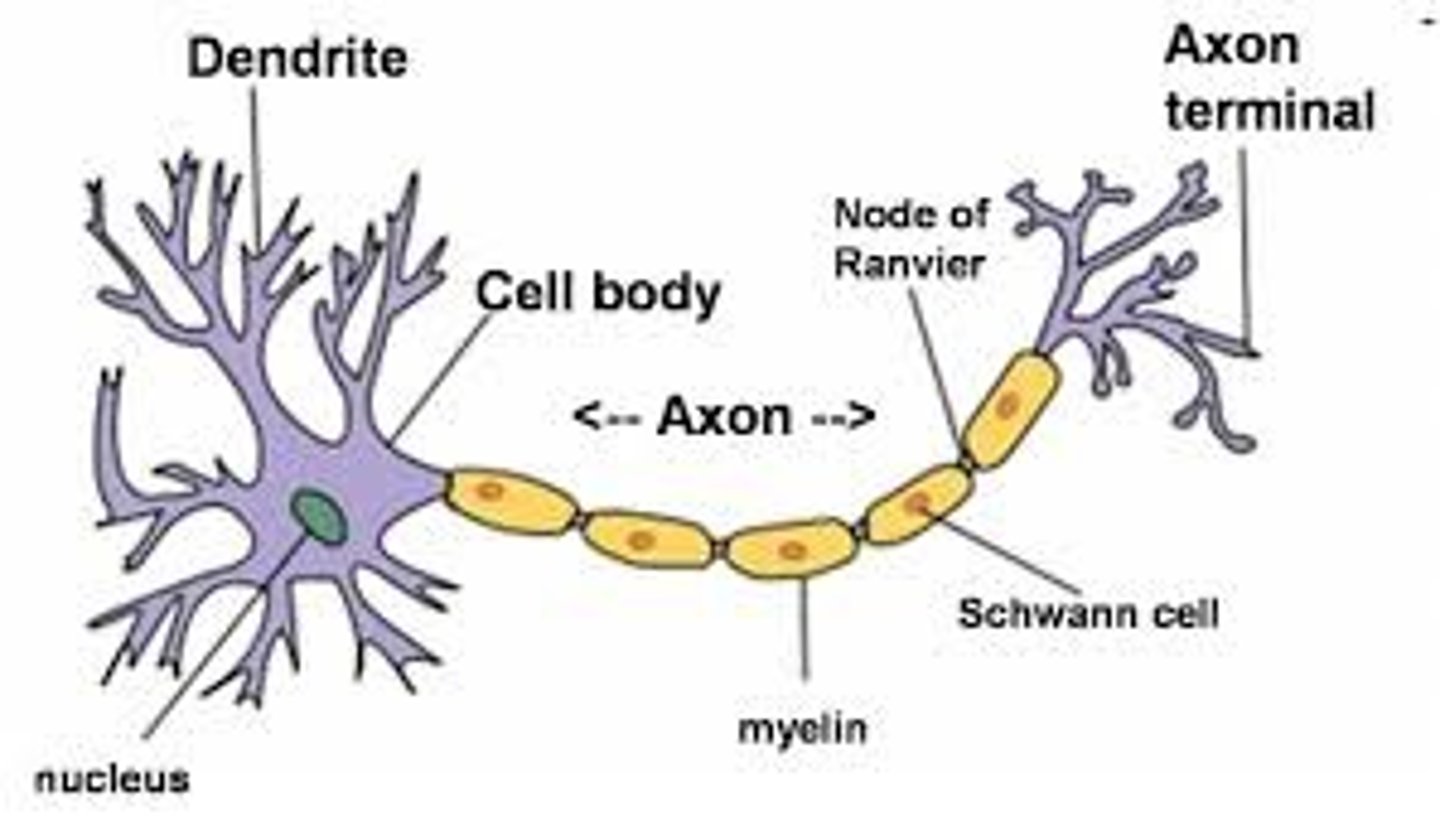
axon hillock
initiates action potential
axon terminals
release neurotransmitters
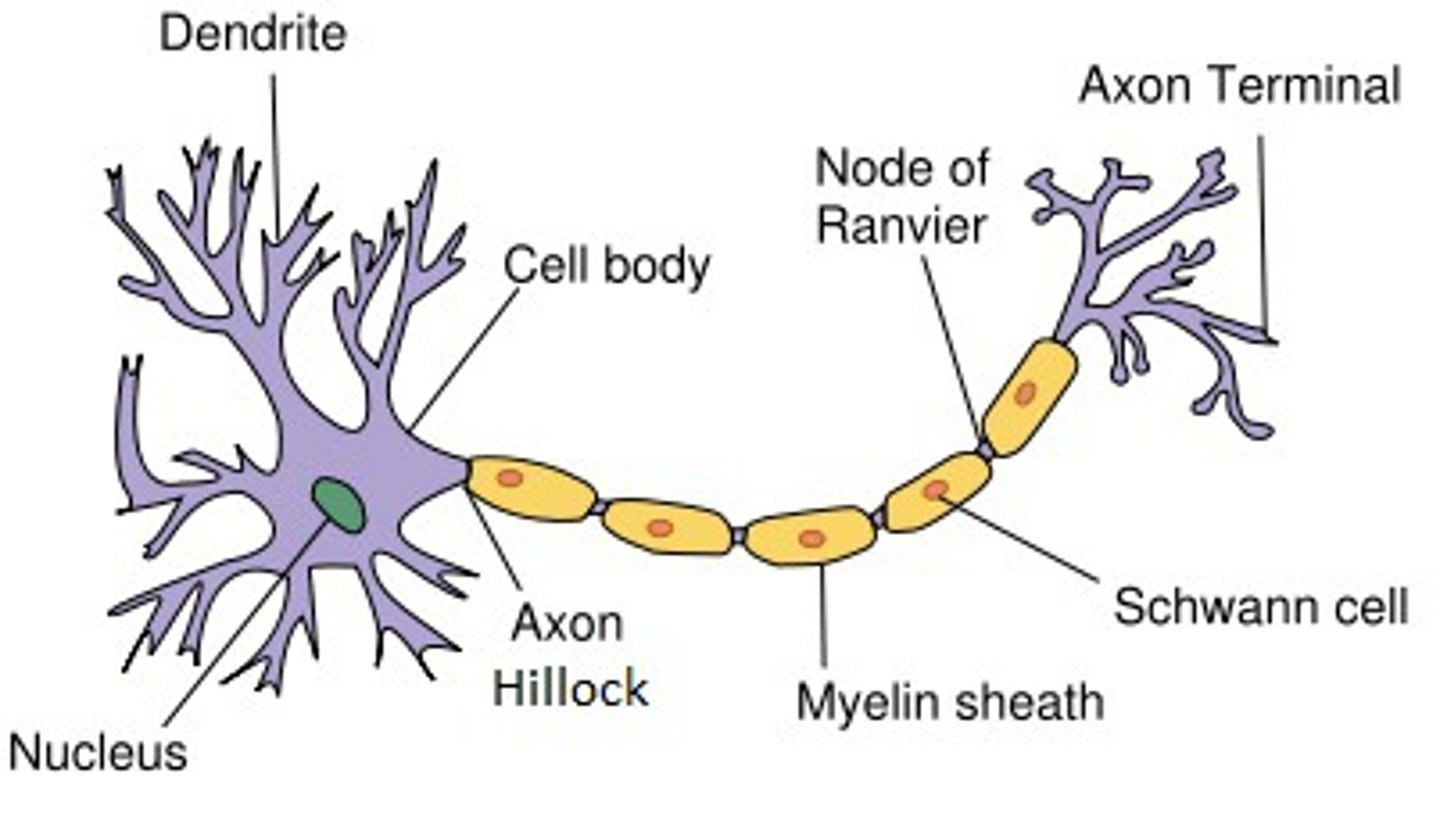
schwann cells
produce myelin in PNS
Oligodendrocytes
produce myelin in CNS
myelin
enables saltatory conduction
Nodes of Ranvier
facilitate action potential propagation
Resting Membrane Potential
depends on high K+ inside and high Na+ outside
irritability
ability to respond to a stimulus and generate impulse
Conductivity
ability to transmit impulses
absolute refractory period
(8 ms) neuron cannot refire
Exocytosis
vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
postsynaptic bonding
generates excitatory or inhibitory effects
Neurotransmitters diffuse and bind to what>
postsynaptic receptors, altering ion channels
neuroplasticity
Brain's ability to reorganize after injury.
Hebbian learning
repeated motor/swallowing tasks strengthen synaptic efficacy
limbic system
amygdala, hippocampus, cingulate gyrus, thalamus, fusiform gyrus
Amygdala
fear and agression
Hippocampus
memory consolidation
cingulate gyrus, thalamus, fusiform gyrus
emotion and recognition
dorsal pathway (where)
spatial location
ventral pathway (what)
object and face recognition
tactile agnosia
failure to recognize objects by touch
hemineglect
non-dominant inferior parietal lesion
Prosopagnosia
face recognition deficits
contralateral
opposite side
Ipsilateral
same side
pseudounipolar neuron
The cell body is off to one side of the axon
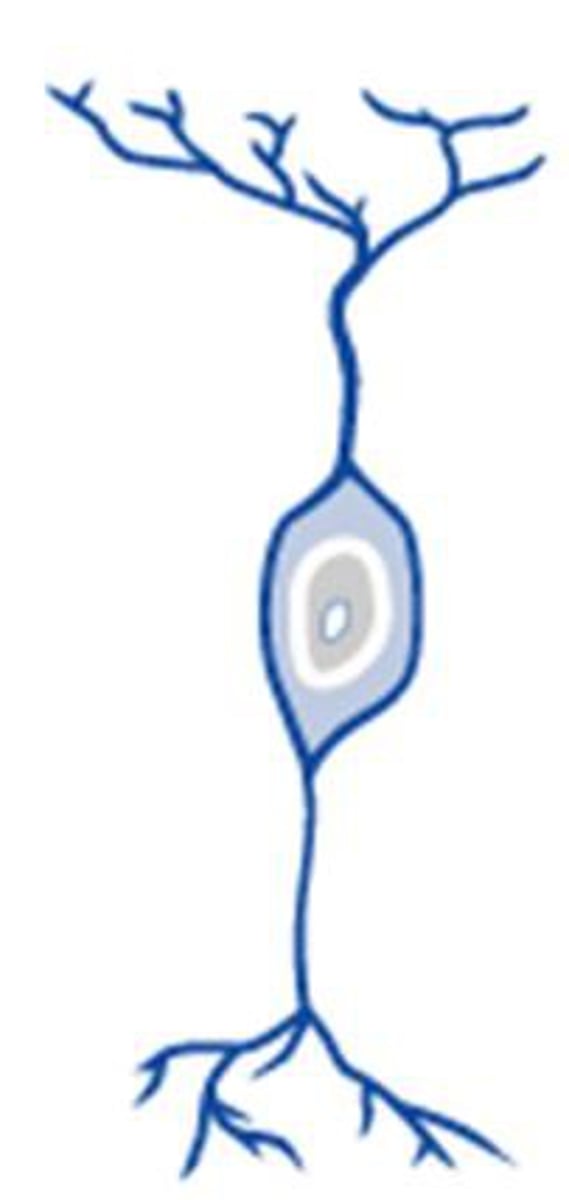
bipolar neuron
one axon and one dendrite
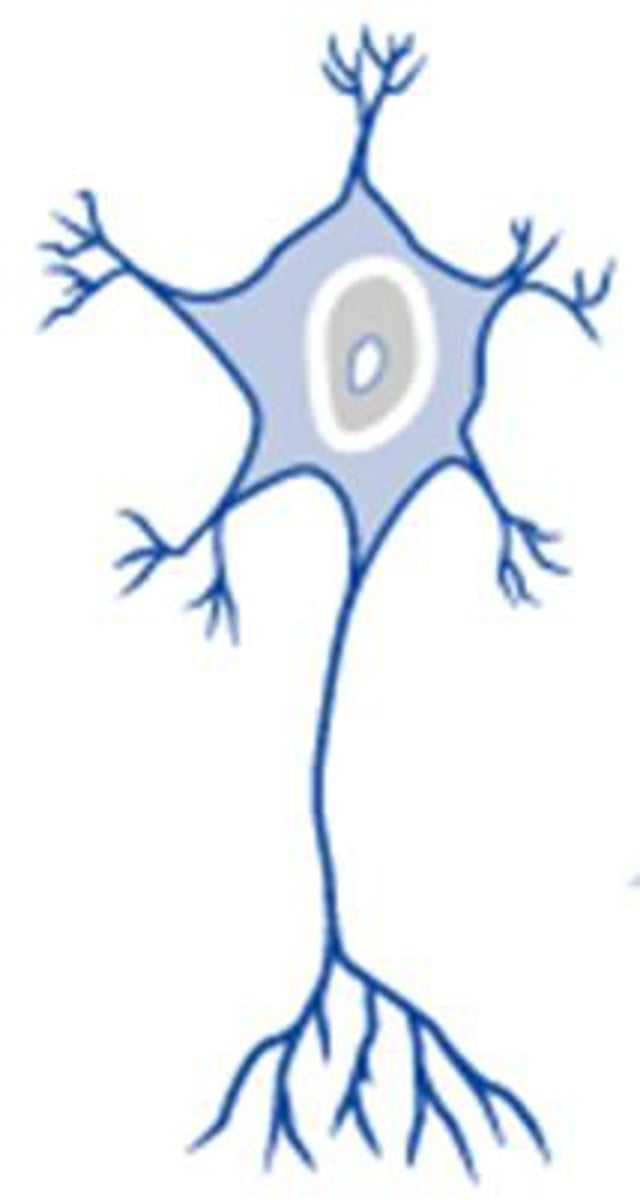
mulitpolar neuron
a nerve cell that has many dendrites and a single axon
saltatory conduction
the jumping of action potentials from node to node