art quiz reveiw
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
which style is considered more masculine due to its simplicity and mass?
doric
which style is considered more feminine due to its lightness, delicacy, and fanciful carving
ionic
which style is considered the most ornate
corinthian
which style has the leaves and scrolls on its capitals?
corinthian
corinthian
which style has the shell-like spirals on its capitals?
ionic
which style has alternating blocks on its frieze?
doric
which style has one continuous frieze?
ionic
which style has more flutes, or vertical grooves, on its shafts
ionic
which style has less flutes, or vertical grooves, on its shafts
doric
which style has a plain architrave?
doric
which style has an architrave made up of 3 horizontal bands?
ionic
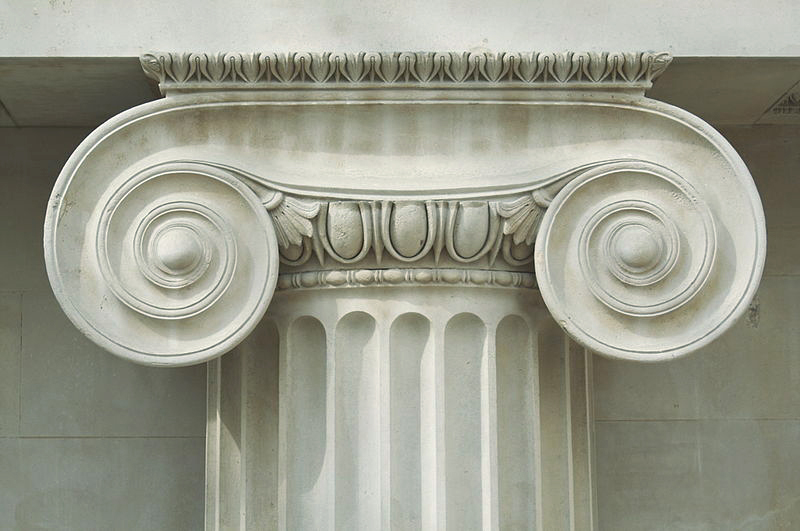

which style is this capital?
ionic
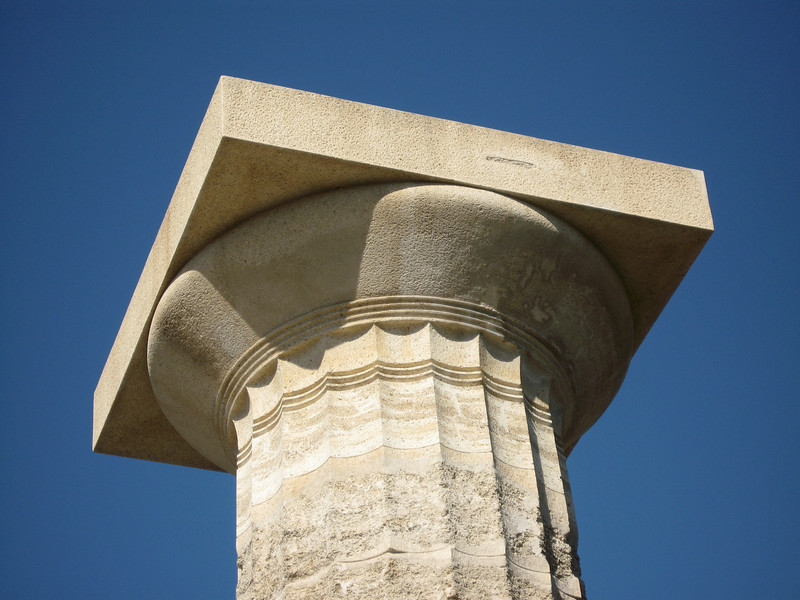

which style is this capital?
doric
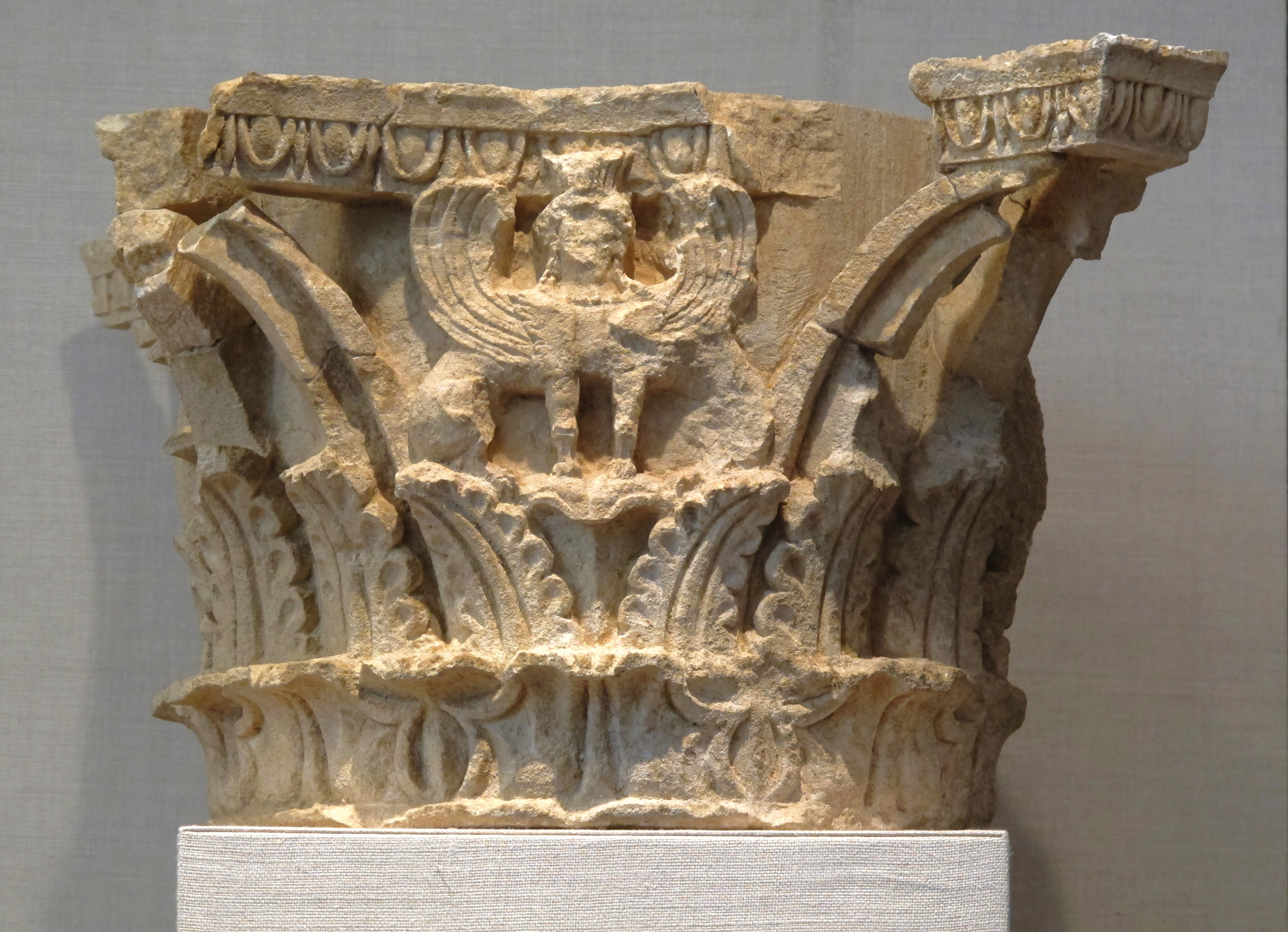

which style is this capital?
corinthian
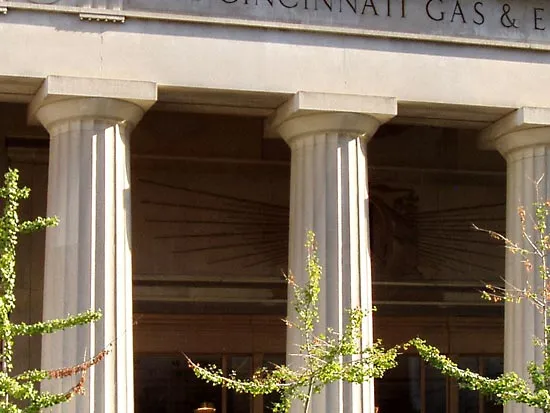

what style is this building?
doric
the triangular space on top, often filled with sculpture
pediment
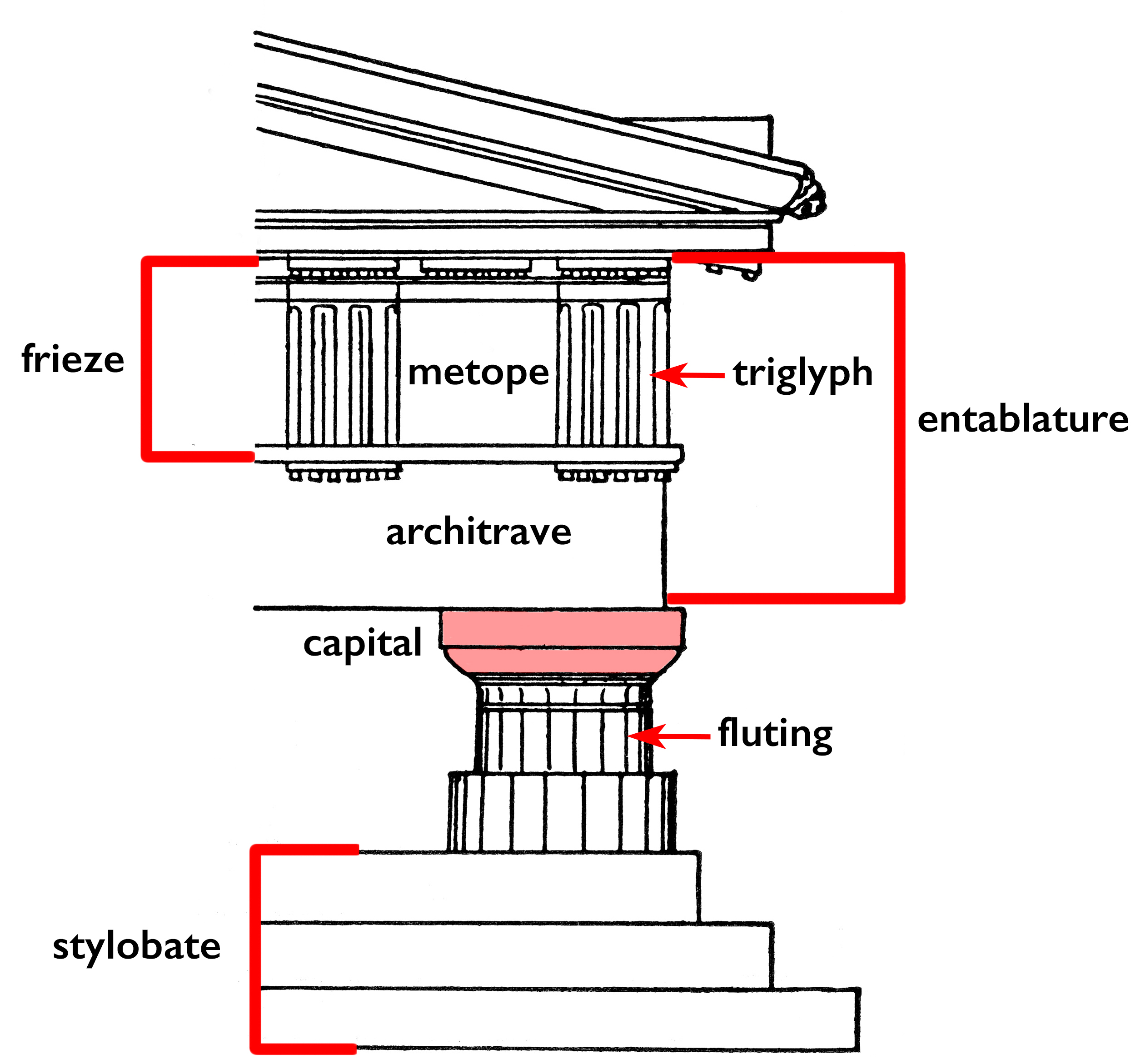
on doric friezes, this is the block with vertical bands
triglyph
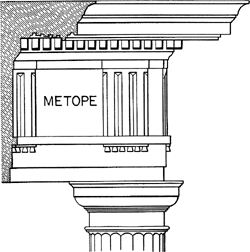
on doric friezes, this is the block that is either plain or has images on it
metope
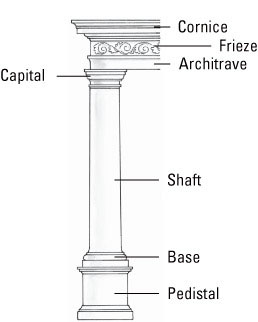
decorative head of the shaft is called the
capital
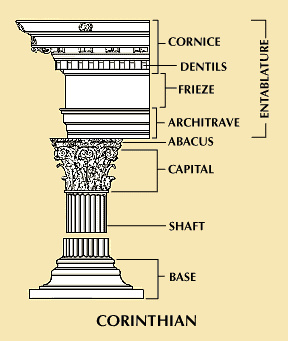
bottom part of the entablature, this is plain in the doric order and has 3 horizontal bands in ionic order
architrave
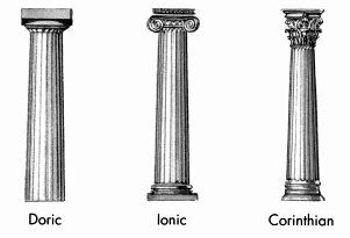
this is made up of the base (or podium), shaftm and capital
column

this band of carved decoration may consist of alternating triglyphs and metotopes (doric) or a continuous scene or pattern
frieze

the long, fluted part under the capital on a column
shaft
what style is the parthenon
doric
what style is the temple of athena
ionic
where in the city is the acropolis located
high up in the center of the city
brief history of parthenon and acropolisP
480 BC-persians sacked acropolis and two temples of athena
479 BC-greeks take oath not to rebuild but let ruins serve as reminder of “impiety of the barbarian”
450 BC-peace with persia makes oath seem less binding
447-432 BC-parthenon is constructed
parthenon
448-432 BC, acropolis, athens
main figures in rebuilding of acropolis
pericles-leader of dominant political faction in athens, led athens from 461 to 429 BC
Pheidias-architect and sculptor, in charge of design’
iktinos-architect of parthenon
ionic order
luxury, refinement, intellectualism
doric order
somber, stioic simpicity
metope details
92 in all-most extensive of any doric temple
employed a series of archetypal myths and legends to celebrate the victory of forces of civilization over chaos and barbarism
-Greeks vs. Amazons (who attacked Athens)
-Greek sack of Troy (badly damaged)
-Lapith vs. Centaurs (Greeks vs.half human beasts)
- -Celebration of general themes – celebration of ancestors over
savage and foreign enemies
-Clearly allusion to victory over Persians
east pediment, parthenon
birth of Athena from the head of her father, Zeus
Central figures are now lost, but they included Zeus and Athena,
grown and fully armed, representing the new Athens
west pediment, parthenon
The struggle between Poseidon and Athena for
control of Athens
athena
Reproduction of votive statue in Parthenon
Chryselephantine - architectural term
given to statues which were built upon a
wooden frame, with slabs of ivory representing
the flesh and gold leaf representing the
garments, armor etc
Here Athena is a warrior goddess. She’s called
Athena Parthenos ("virgin"),.because she was believed to remain perpetually a virgin.
5th century AD
Cult figure of Athena is looted by roman Emperor and taken to Constantinople where it is destroyed, perhaps during the 4th Crusade (13th C)
6th century AD
Parthenon was converted into a Christian church
dedicated to the Virgin
- Christians interpret some sculpture as reflecting Christian themes, westernmost north metope viewed as Annunciation
- interior sculptures are reinterpreted,removed or destroyed
1456
Ottoman conquest of Athens, Parthenon is converted into a Mosque
-Ottomans were generally respectful of ancient monuments in their territories, and did not destroy the antiquities of Athens, however they did scavenge them for building materials
1687
venetian bombardment ignites ammunition stored in parthenon which is severely damaged; venetians loot the site, sculptures suffer heavily
1806
lord elgin, then british ambassador to turkey (greece was under turkish control) removes surviving south metopes, parts of frieze and some pedimental sculptures
1816
Lord Elgin sell sculptures to british museum where they are now displayed
1832
greece gains control of acropolis and removes all ottoman and medieval structures
1975
greek government begins restoration effort, project later attracts funding from EU
geometric period
9th-7th century BC
archaic period
6th century BC
classical period
5th century BC
late classical period
4th century B
humanism
is an approach in study, philosophy, world view
or practice that focuses on human values and concerns,
attaching prime importance to human rather than divine or
supernatural matters.
ethos
the values or character of a community, society.
pathos
a quality or experience when viewing a work of art that arouses pity, sympathy or sorrow.
contrapposto
shifting from one leg to another, casual standing position, not stiff