GI Pharmacology 1- Khan
1/38
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Name of 3 mediators used in gastric acid secretion:
gastrin
histamine
ACh
What cell type is involved in GI secretion?
parietal cells
Where is ACh released from?
vagus nerve terminal
What histamine receptor subtype is present in the parietal cells?
H2 receptors
Discuss the entire signal transduction following H2 receptor activation:
histamine binds to H2 receptor
H2 receptor activates AC
AC converts ATP to cAMP
cAMP activates PKA
PKA causes vesicle containing H+/K+ ATPase to move to surface of parietal cell
Following the fusion of the vesicles with the apical membrane, how is the proton released?
active transport!
K+ moves into the cell, H+ move out of the cell
needs ATP to do this
What is the role of the apical membrane K channel?
how acid gets into the stomach?
What is the role of mucin against GI acidity?
an insoluble gel that coats the mucosal surface and protects
What is the role of somatostatin against acidity? Include it’s direct effect.
somatostatin DIRECTLY inhibits parietal cell gastric secretion
What is the role of PGs against acidity?
inhibits acid secretion by increasing bicarb secretion and increases mucus production
Answer the following about SUCRALFATE:
How is it activated?
How does it work as a coating agent?
What, if any, effect does it have on gastric pH?
Does it cause constipation or diarrhea?
activation- in acidic pH undergoes cross-linking and polymerization to form a VISCOUS GEL
works to protect from pepsin and acid
NO EFFECT ON GASTRIC pH
causes CONSTIPATION
Answer the following about Bismuth Subsalicylate:
What does the drug do in the stomach?
What are its antimicrobial effects?
What are the ADRs?
What is the BBW?
undergoes DISSOCIATION in the stomach
DIRECT antimicrobial effect against H.PYLORI
ADRs- BLACKENING of stool, DARKENING of tongue, TINNITUS
(think Bismuth= black)
BBW- REYE’s SYNDROME associated w/ salicylate in kids/teens
Answer the following about MISOPROSTAL:
What type of derivative is it?
What is its indication?
What is the BBW?
synthetic PG E1 derivative
indicated in NSAID INDUCED ULCERS ONLY
BBW- ABORTION (can cause uterine contractions)
What are the names of the agents that neutralize acids? (brand/generic)
Antacids
Aluminum Hydroxide+Mg+simethicone (Maalox)
Magnesium Hydroxide (milk of magnesia)
Calcium Carbonate (Tums)
Sodium Bicarbonate/aspirin/citric acid (ALKA-SELTZER)
Alginic Acid
Answer the following about ANTACIDS:
What is their effect on gastric acidity, pH, and pepsin inactivation?
They can cause acid _________.
What is the reason for their drug interactions?
neutralize acid, increase gastric pH, inactivate pepsin
they can cause acid REBOUND
reasons for DI- can affect absorption of other drugs by binding to the drug OR altering the pH
ex: some drugs need acidic environment to be absorbed
What is acid rebound? Which antacids cause high acid rebound? Which cause low acid rebound?
acid rebound- persistent acid secretion even though pH is normal
low acid rebound- Al and Mg (Maalox, milk of magnesia)
high acid rebound- NaHCO3 (sodium bicarb) and CaCO3 (calcium carb) (Tums, Alka-Seltzer)
What are the ADRs of calcium carbonate, magnesium, and aluminum?
calcium carbonate- belching, hypercalcemia, constipation
magnesium- diarrhea
aluminum- constipation
What 2 drug classes suppress acid secretion?
H2 blockers
PPIs
What are the names of the H2 blockers? (brand/generic)
Cimetidine (Tagamet)
Ranitidine (Zantac)
Nizatidine
Famotidine (Pepcid)
Answer the following about Cimetidine:
What is the role of the CH3 group in imidazole ring?
What is the role of the 4 atom linker?
What is the S role in potency?
Where does hydroxylation take place in the molecule?
What is the problem with the imidazole ring?
What are the endocrine ADRs?
What are the effects of the endocrine ADRS?
role of CH3- H2 SELECTIVITY
role of 4 atom linker- extends guanidine group into antagonist binding region
S role- has higher potency then C or O
Hydroxylation occurs on the CH3 GROUP OF THE IMIDAZOLE RING
Problem with the ring? DRUG INTERACTIONS! Inhibit CYP450 enzymes
endocrine ADRs-
inhibit binding of DHT to androgen receptor
inhibits estrogen metabolism
increases prolactin levels
effect of endocrine ADRs- gynecomastia and impotence in men
What group does Cimetidine have that NO OTHER H2 blocker has?
IMIDAZOLE RING
Answer the following about Ranitidine:
The imidazole is replaced with a furan. What is the advantage?
What happens when the S of 4-atom linker is replaced by O?
advantage- less/no drug interactions
less activity
Answer the following about all H2 BLOCKERS (Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Nizatidine, Famotidine:
MOA of H2 blockers
ADRs of H2 blockers
Why is fluconazole/itraconazole absorption reduced when taken with H2 blockers?
MOA- COMPETITIVE H2 RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST
ADRS- confusion and vit b12 deficiency
Can’t be taken bc they need an acidic gut for absorption and H2 blockers inhibit the acid
What are the names of the PPIs? (brand/generic)
Omeprazole (Prilosec)
Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
Dexlansoprazole
Pantaoprazole (Protonix)
Esomeprazole (Nexium)
What is the structure of benzimidazole?
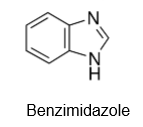
Given the structure, be able to identify where omeprazole is protonated in acidic pH?
Drug is protonated on the “N” of benzimidazole
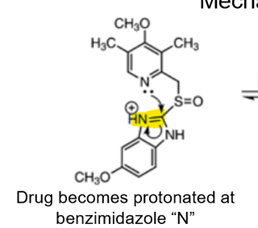
What is the MOA of PPI?
“proton pump inhibitor” DUH
basically: Sulfenamide reacts with Cys residue H+/K+ ATPase, forms disulfide linkage (covalent bond) and irreversibly inactivates the enzyme
If PPI’s are prodrugs, how do they reach parietal cells? What is the drug converted into?
enteric coated tablets
once in intestine, coating is dissolved and drug is absorbed and diffuses to parietal cells
then converted into SULFENAMIDE
Answer the following about PPIs (-prazoles):
What enzymes are involved in metabolism?
What are the drug interactions?
What is the specific drug reaction with clopidogrel?
What are the complications with long term use?
What are the ADRs
enzymes: CYP2C19, CYP3A4
DI: inhibit CYP2C19 (increase warfarin/phenytoin), increase GI pH (-azoles, iron)
CLOPIDOGREL+ PPI (esomeprazole/omeprazole)= DECREASED CLOPIDOGREL EFFECT
long term complications: osteoporosis, hypomagnesemia, vit B12 deficiency
ADRs- acute interstitial nephritis, increase risk of C.difficile associated diarrhea, increase risk of pneumonia in hospitalized pts.
What are the 3 main causes of PUD?
H. pylori bacteria
chronic NSAID use
Stress
How does H. pylori survive in an acidic environment?
by increasing pH
produces urease which converts urea to ammonia
ammonia buffers H+
What is the role of H.pylori in PUD?
overall effect: increase gastrin = increase parietal cell proliferation and acid secretion= PUD
What systemic effects are produced by NSAIDs?
inhibit COX= decrease PGs
increase gastric acid secretion
decrease bicarb/mucus production
decrease blood flow
mucosal damage
What topical effects are produced by NSAIDs?
cell damage
NSAID enters cells in non-ionized form and in cytoplasm becomes trapped and ionized= cell damage
What mechanisms do the following antibacterial drugs eliminate bacteria?
Amoxicillin
Tetracycline
Clarithromycin
Metronidazole
Amoxicillin—> inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
Tetracycline and Clarithromycin—> inhibit bacterial protein synthesis
Metronidazole—> damage bacteria DNA
What are the tx options for GERD?
antacids
PPIs
H2 blockers
metoclopramide
What is a prokinetic drug?
drug that increases MOTILITY/movement
What is the dopaminergic mechanism of metoclopramide?
DOPAMINE ANTAGONIST!!!!!!!!!!
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonist (central and peripheral)
Central dopamine antagonism—> anti-nausea effect
Dopamine antagonism in the GIT—> increase prokinetic effect
Dopamine decrease motility in GIT
What are the ADRs of metoclopramide? What is the BW?
ADRs- drowsiness, restlessness, dystonic reactions
BBW- tardive dyskinesia