AP Human Geography Unit 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
spatial
relating to space
absolute location
the precise point where a place is located on Earth
cartography
The science of making maps
cultural ecology
Geographic approach that emphasizes human-environment relationships.
relative location
where a place is located in relation to another place
geographic information system (GIS)
a computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data
latitude
Distance north or south of the equator
equator
the imaginary center line of latitude that divides the northern and southern hemispheres.
longitude
Distance east or west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees
prime meridian
Imaginary line drawn from the North Pole through Greenwich, England, to the South Pole
International Date Line
the line of longitude that marks where each new day begins, centered on the 180th meridian
place
specific human and physical characteristics of a location
region
a group of places on Earth with similar human and/or physical features
site
The characteristics of a place (immediate location), Ex: soil type, climate, labor force, human structures
situation
the location of a place relative to other places and its surroundings
toponym
place name
time-space compression
the shrinking of time distance between locations because of improved methods of transportation
distance decay
decline of activity or function with increasing distance from its point of origin
density
number of something in a specifically defined area Ex: population density is the number of people per square mile
human-environment interaction
connection and exchange between humans and the natural world
culture
Beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.
environmental determinism
the idea that human behavior is controlled by the physical environment
possibilism
the natural environment constrains human activity, but humans can adapt to some environmental limits by modifying it using technology
scale
the ratio between the size of things in the real world and the size of those same things on a map
projection
The system used to transfer locations from Earth's surface to a flat map.
diffusion
The process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time
formal region
An area in which everyone shares in one or more distinctive characteristics
GPS
a system that determines accurately the precise position of something on Earth through satellites, tracking stations, and receivers
location
The position of anything on Earth's surface.
movement
an act of changing physical location or position or of having this changed.
remote sensing
process of gathering data about Earth from instruments far above the planet's surface
spatial analysis
The analysis of geographic data about a certain place.
time zone
any of the 24 longitudinal areas of the world within which the same time is used
physical geography
One of the two major divisions of systematic geography; the spatial analysis of the structure, processes, and location ex: of items studied: climate, soil, plants, animals, and topography.
human geography
One of the two major divisions of Geography; the spatial analysis of human population, its cultures, activities, and landscapes.
connectivity
how well two locations are tied together by roads or other links . This is often used when describing relative location.
sense of place
The feeling that an area has a distinct and meaningful character
friction of distance
as distances increase, it requires more time, effort, and cost for interactions between places to occur; measures the degree to which distance affects the interaction between two places
distribution
The arrangement of something across Earth's surface.
spatial association
connection between phenomena that tend to occur in proximity to each other ex: the distribution of malaria matches the distribution of the mosquito that carries it
landscape analysis
the task of defining and describing landscape
field observation
the act of physically visiting a location, place, or region and recording, firsthand, information there
spatial data
data about the size, shape and location of objects and features; information about relationships between them
aerial Photography
professional images captured from planes within the atmosphere
built environment
part of the physical landscape that represents material culture; the landscape created by humans ex: buildings, roads, signs, fences etc.
cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity on the landscape
scale (relative scale)
the amount of territory that a map represents ex: global scale means the entire planet
reference maps
Maps designed for people to refer to for general information about places
political map
A map that shows man-made features such as boundaries, countries, and cities.
physical map
a map that shows natural features such as mountains, rivers and deserts
choropleth map (thematic)
uses various colors, shades of one color, or patterns to show the location and distribution of data
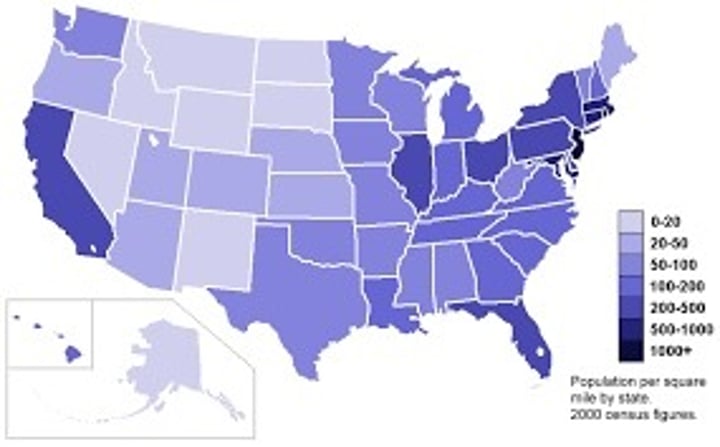
thematic map
a map that shows a particular theme, or topic ex: choropleth, dot distribution, graduated symbol, isoline
dot distribution map
A map where dots are used to demonstrate the frequency or intensity of a particular phenomena
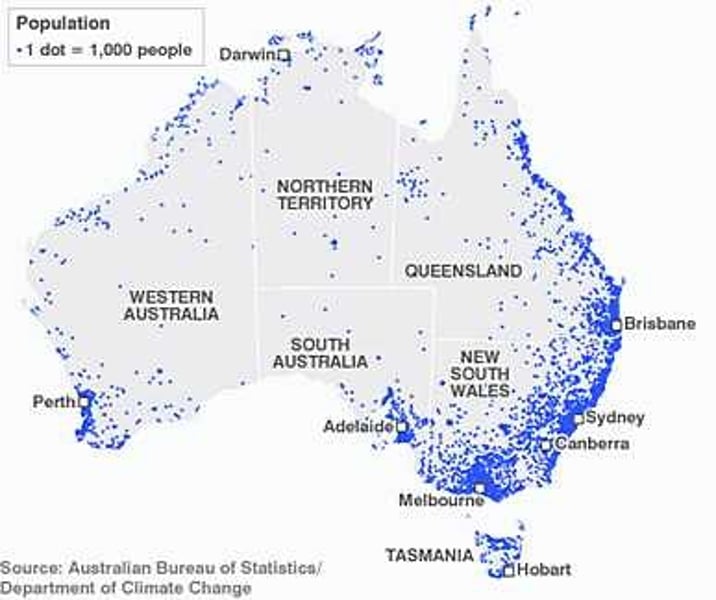
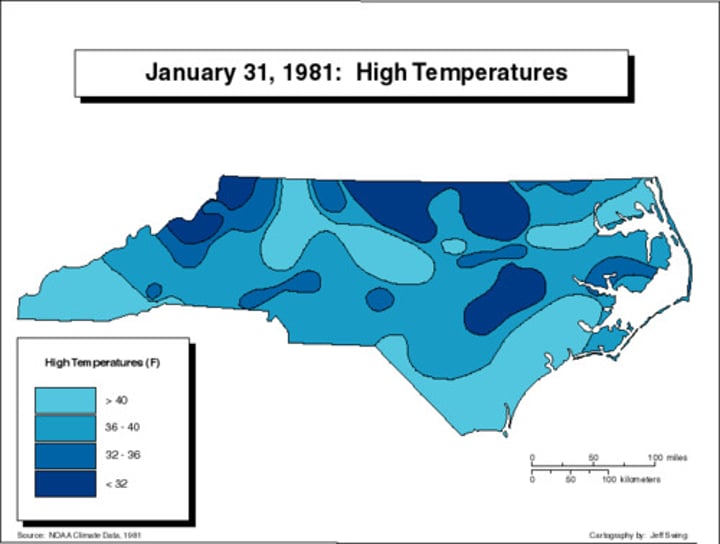
isoline map
A thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value.
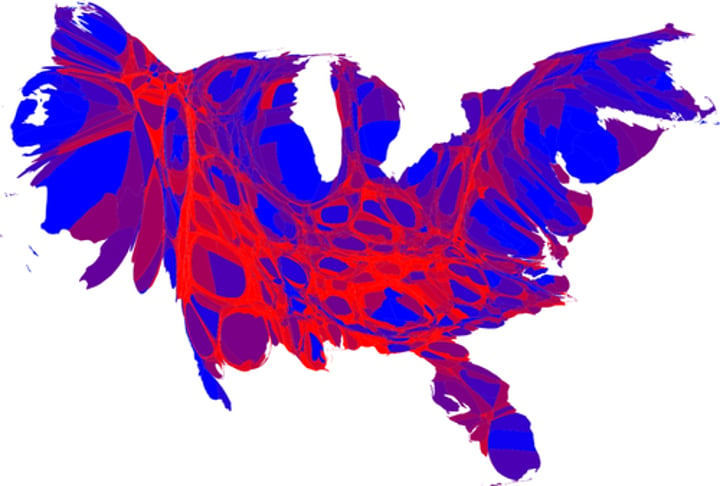
cartogram (thematic)
the sizes of countries are shown to some specific statistic
Mercator projection
a projection of a map of the world onto a cylinder in such a way that all the parallels of latitude have the same length as the equator, EX: used especially for marine charts and certain climatological maps.
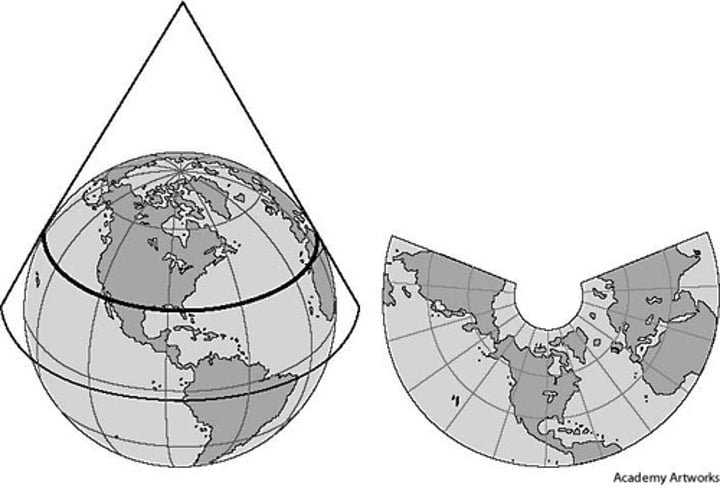
conic projection
a map projection that is made by moving the surface features of the globe onto a cone
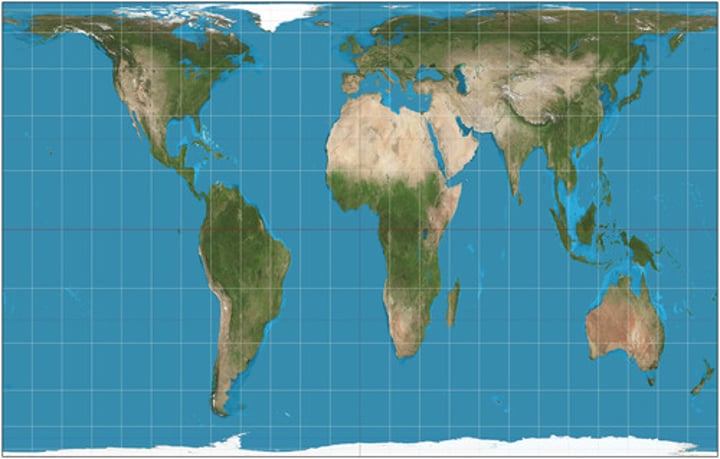
Peters projection
focuses on keeping landmasses equal in area. As a result, the shapes are distorted, and the map looks unfamiliar to viewers
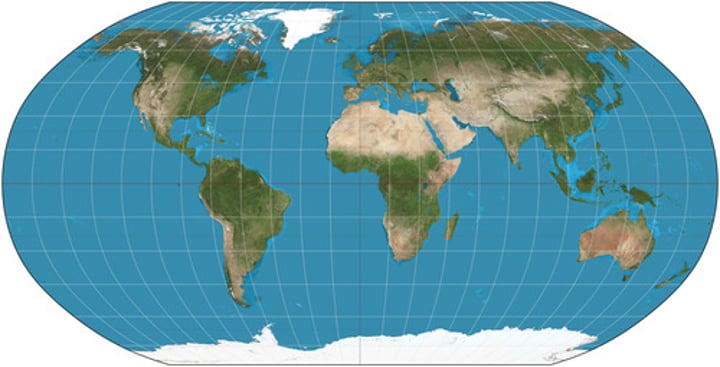
Robinson projection
Projection that attempts to balance several possible projection errors. It does not maintain completely accurate area, shape, distance, or direction, but it minimizes errors in each.
graduated symbol map
A map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent.
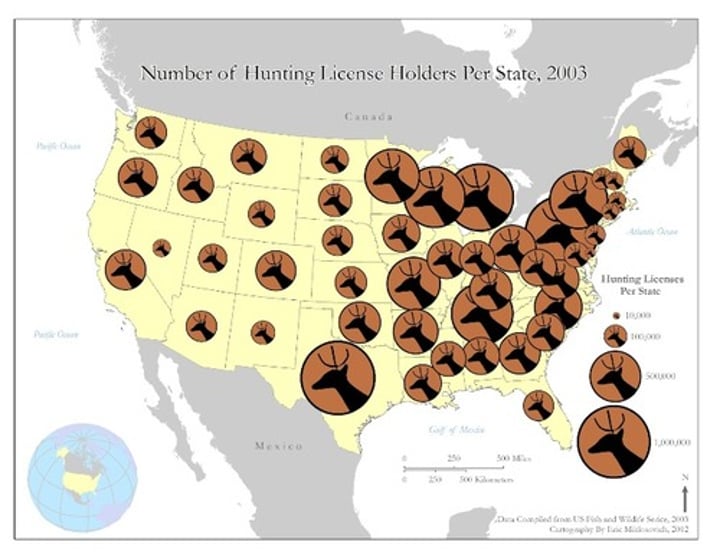
homogenous Region
another name for formal region or uniform region
mental Map
maps that people create in their minds based on their experience and knowledge
placelessness
the loss of uniqueness of place in the cultural landscape so that one place looks like the next ex: Walmart- everyone of them looks the same
quantitative data
numerical data ex: distribution of people based on income
qualitative data
Data associated with a more humanistic approach to geography, often collected through interviews, empirical observations, or the interpretation of texts, artwork, old maps, and other archives.
regionalization
process by which specific regions acquire characteristics that differentiate them from others within the same country; certain economic activities may dominate in particular regions.
topographic map
a map that shows the surface features of Earth

scale of analysis
level at which the data is collected; global, regional, national, local (includes supranational and county)
cartographic scale
the ratio of a distance on Earth compared to the same distance on the map
spatial perspective
the "why" of "where"