Biology Unit 3 Test (Chapters 11, 12, 13)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
The primary function of DNA
store and transmit genetic information
The physical appearance of an organism
Phenotype
Heredity
The transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring
Mutation
Change in the DNA
AGTTCG
What is the complementary DNA sequence for TCAAGC?
Codon
During translation, each nucleotide triplet codes for an amino acid is referred to as a(n)____________________.
X^R Y
In fruit flies, red eyes are X-linked. Red is dominant to white. What would a red eyed male genotype be?
hh
In dogs, black hair is dominant to brown hair. What is the genotype for a dog with brown hair? (H-dominant; h-recessive)
ribosome
tRNA brings the amino acids to what organelle?
Watson & Crick
Who is credited for the discovery of the structure of DNA?
Double Helix
What is the shape of DNA?
5 Amino Acids
How many amino acids are coded by this DNA strand?
TACCCAGGATATGCG
AUG
Start Codon
TT
What is the genotype for a homozygous dominant Tall Plant? (use the letter Ts)
Nondisjunction
Example: Down Syndrome; Down syndrome is also known as trisomy
Point mutation
A mutation where you change one nucleotide is called a(n)
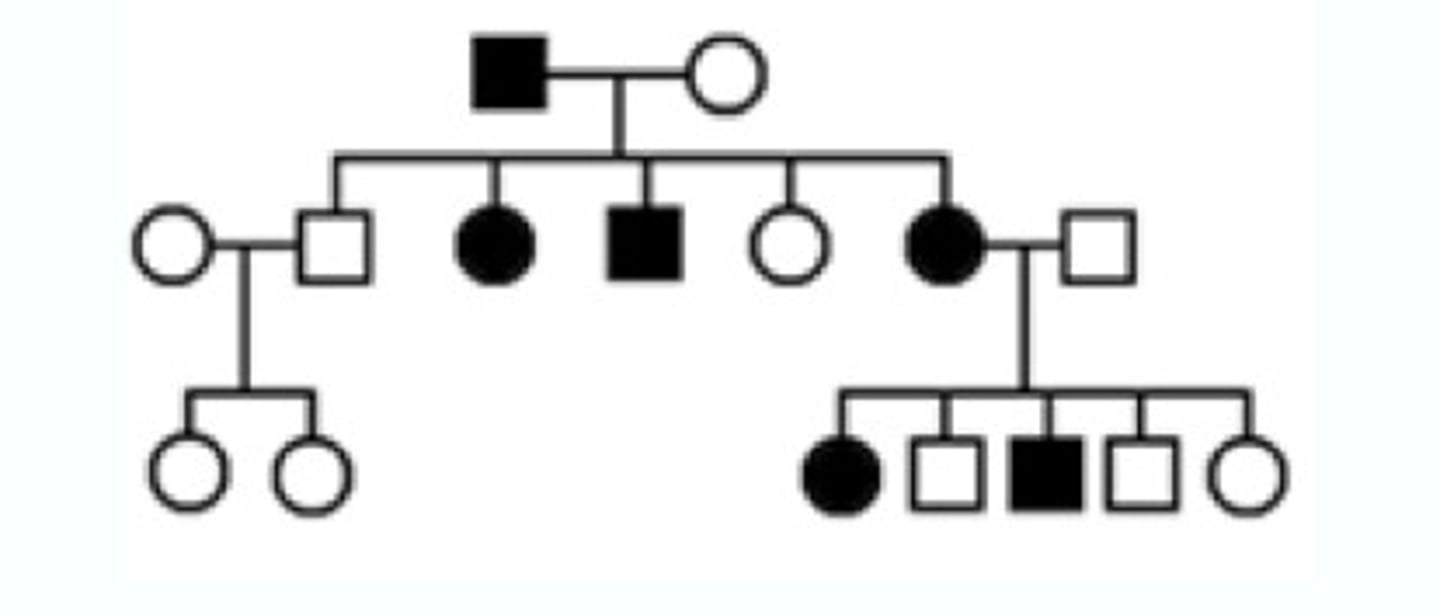
The diagram shows a recessive trait being passed through generations. What is the genotype for the man in the first generation?
rr
Human Genome Project
What project in 1988 helped with discovering where certain genes were found on each chromosome?
Incomplete Dominance
The heterozygous trait shows a combination of the two traits (example: pink flower)
Codominance
Blood type AB is an example of what type of genetic pattern?
X-linked trait
Colorblindness is what type of trait?
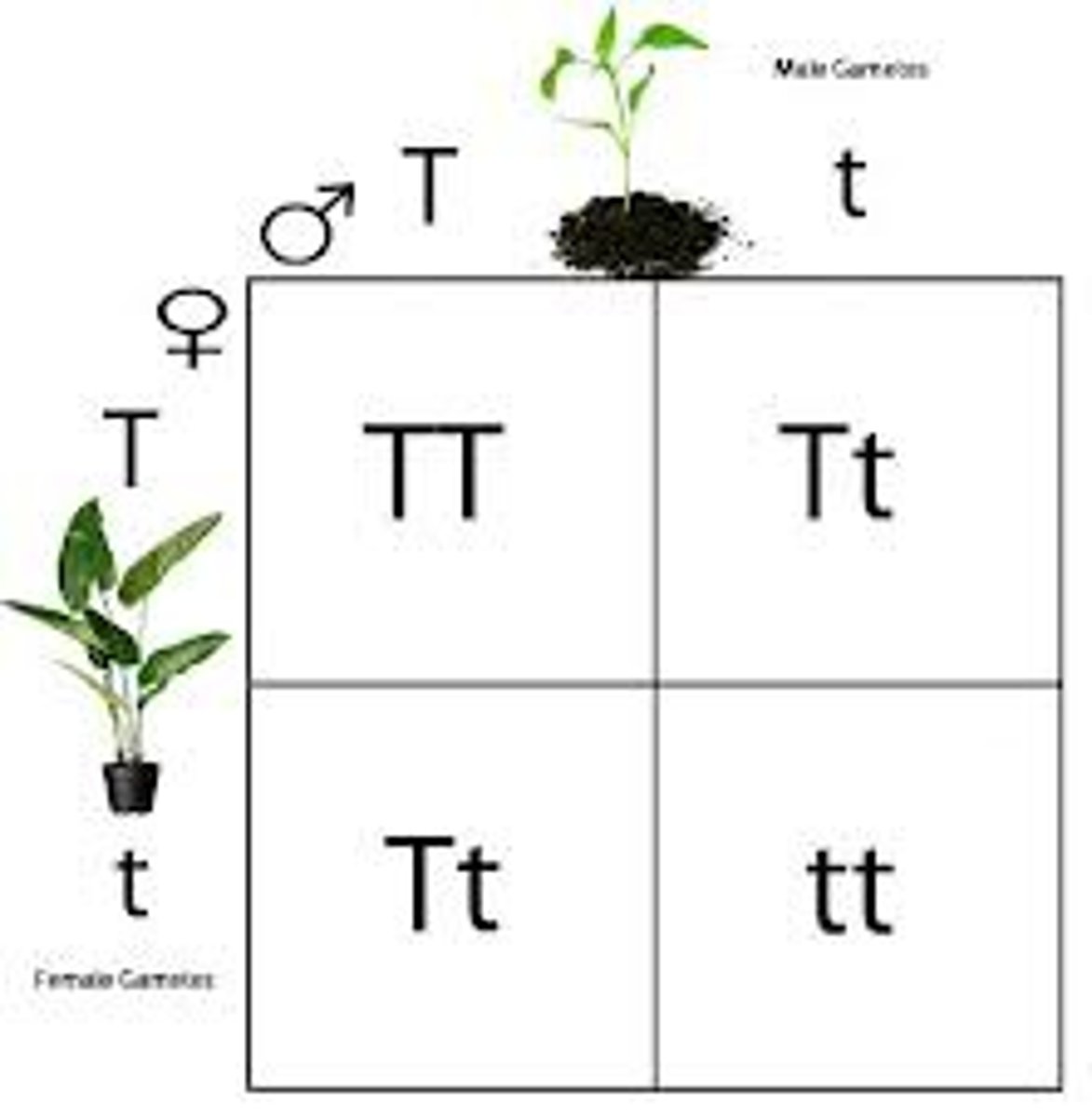
Punnett Square
Diagram to help you determine the probability of having a trait
mRNA
The type of RNA that helps with transcribing the DNA strand
rRNA
The type of RNA that makes up the ribosome
tRNA
The type of RNA that brings the amino acid to the ribosome
Letters that represent the phenotype
Genotype
Helicase
What enzyme breaks the Hydrogen bonds during DNA replication?
Ligase
The repair enzyme during DNA replication
DNA polymerase
The enzyme that adds complimentary DNA nucleotides during DNA replication
Division of the Cell
Why is DNA replication important?
Chromosomal Mutation
Deletion is an example of what type of mutation?
Pedigree
Diagram used by genetic counselors for tracking the genetic disorder that runs in a family.
25%
Crossing parents Tt and Tt. What is the probability of having a genotype TT?
AUGGGCCAU
What is the complimentary mRNA strand to the following DNA strand?
TACCCGGTA
Anticodons
tRNA are the Codons or Anticodons?
purines A & G
What structures are similar in both DNA and RNA?
Heterozygous form for blood type A.
I^A i
Carrier
Term for being heterozygous without having the trait but could pass the trait on
X-Link Traits Affect
Men express X-Linked Traits more frequently
Frameshift Mutation
Addition or deletion of a nucleotide base that affects the rest of the strand of mRNA; multiple codons affected
Central Dogma
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
Gel Electrophoresis
Procedure used to separate and analyze DNA fragments by placing a mixture of DNA fragments at one end of a porous gel and applying an electrical voltage to the gel
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited; this is an example of albinism
polygenic traits
traits controlled by two or more genes; example; human height, eye color
Carrier
A person whose genotype includes a gene that is not expressed in the phenotype.