Cognitive models and Cluster C disorders (L4)
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
Schemas
Knowledge representation of the self, others, the world
2
New cards
Explicit and implicit beliefs
* Explicit - can be verbalised
* Implicit- Non-verbal knowledge, like attachment representations
* Implicit- Non-verbal knowledge, like attachment representations
3
New cards
What are Early Maladaptive Schemas?
Schemas that originate in childhood and contain maladaptive beliefs about the world (maladaptive only if they last into adulthood, because they were functional at the time)
4
New cards
Core beliefs
Basic beliefs about the world (I am inferior)
5
New cards
Conditional beliefs
(if x, then y) (If others get to know me, they will reject me)
6
New cards
Strategic/ instrumental beliefs
(Do A to get B) (To feel less anxious about doing a presentation, don't do the presentation)
7
New cards
There are different beliefs in different disorders. What are the core beliefs in AVPD, BPD, DPD, PPD?
**Avoidant**:
Core: I'm unwanted and unskilled
**Dependent:**
Core: I am weak
**Paranoid**:
Core: I am a target
**Borderline**
Core: I am evil, victim, helpless, lost
Core: I'm unwanted and unskilled
**Dependent:**
Core: I am weak
**Paranoid**:
Core: I am a target
**Borderline**
Core: I am evil, victim, helpless, lost
8
New cards
What is the difference between assimilation and accommodation?
**Assimilation**: New information is manipulated in such a way it still fits with the existing schema
**Accommodation**: The schema is changed to fit new information
9
New cards
Why is assimilation easier than accomodation?
It’s easier to think of something as an exception if it doesn’t fit with your schema than to change the entire schema
10
New cards
What happens according to the cognitive model when you are feeling insecure and then have to give a lecture?
Get information
**Attention bias**: Pay attention more to critical faces
**Selection bias**: seeing more critical face
**Interpretation bias**: Interpreting it in a negative way (People looking critically means they hate the lecture)
**Evaluation**: "People hating the lecture means they think I'm a loser”
**Response:** Not give a lecture the next time (avoidance behaviour), crying, getting anxious. This reflects
**Encoding bias**: Remembering it as worse than it actually was, encoding that version of events into long-term memory
**Memory bias**: Remembering the situation in similar situations (giving a speech) and then restarting the whole process
**Attention bias**: Pay attention more to critical faces
**Selection bias**: seeing more critical face
**Interpretation bias**: Interpreting it in a negative way (People looking critically means they hate the lecture)
**Evaluation**: "People hating the lecture means they think I'm a loser”
**Response:** Not give a lecture the next time (avoidance behaviour), crying, getting anxious. This reflects
**Encoding bias**: Remembering it as worse than it actually was, encoding that version of events into long-term memory
**Memory bias**: Remembering the situation in similar situations (giving a speech) and then restarting the whole process
11
New cards
Know the order of this
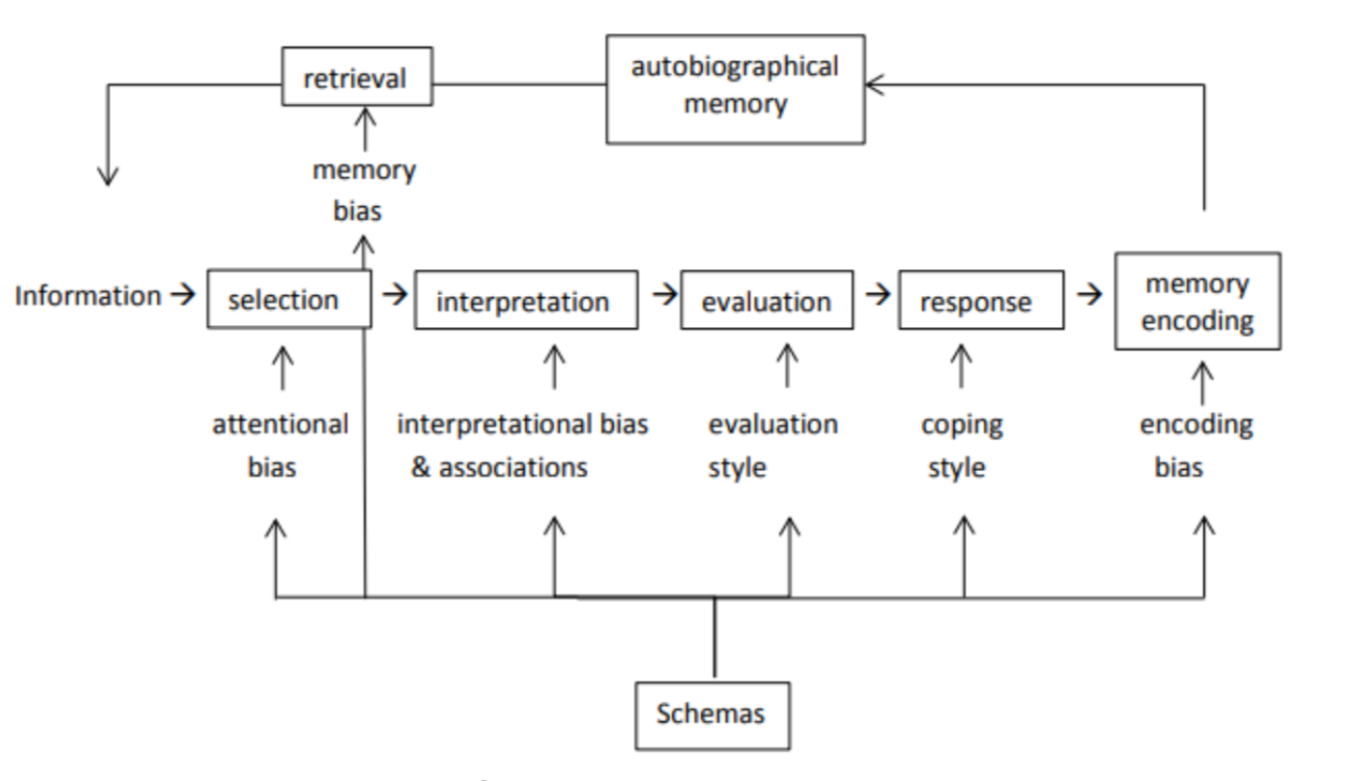
12
New cards
How can you test attention bias?
With an Emotional Stroop Task
13
New cards
What are the results of an Emotional Stroop Task with people with personality disorders?
If the person has an attentional bias towards the word, they will respond slower, because they are focusing more on the content of the word than the colour
Especially the case in borderline personality disorder
Especially the case in borderline personality disorder
14
New cards
How can you test interpretation bias?
using a short story with a forced response
15
New cards
What were the results of using a short story with a forced response?
Response were made so that they matched the disorder (dependent responses - dependent personality disorder)
For dependent & AV (Cluster C) and BPD, they picked the interpretation that most matched their disorder and also believed in it more
For OCPD, this wasn't the case, and non-clinical controls actually picked the OCPD response more than people with OCPD (probably because OCPD traits are "valued" by society
For dependent & AV (Cluster C) and BPD, they picked the interpretation that most matched their disorder and also believed in it more
For OCPD, this wasn't the case, and non-clinical controls actually picked the OCPD response more than people with OCPD (probably because OCPD traits are "valued" by society
16
New cards
What attachment style is often found in people with Avoidant PD?
(preoccupied) avoidant attachment style
17
New cards
Etiology of AVPD?
Biological: Vigilance is explained by the dominant sympathetic nervous system and lowered autonomic arousal threshold, which allows for irrelevant impulses on logical associations
Often no healthy emotion expression in family, avoidant parents
Parental and peer rejection lead to hypervigilance
Often no healthy emotion expression in family, avoidant parents
Parental and peer rejection lead to hypervigilance
18
New cards
What core beliefs do people with AVPD have?
Core belief of rejection and hypersensitivity to being rejected. Core view of self as socially inept and others as defective
19
New cards
How do people with AVPD come across in therapy?
Guarded, circumstantial, and respond with single-word answers. Empathy and reassurance are needed for a therapeutic relationship
20
New cards
What is the general treatment goal for people with AVPD and how can that be achieved?
Increasing their tolerance for feedback and increasing their (selective) trust towards others.
\
Can be achieved through:
CBT (Addressing automatic thoughts and improving social skills)
Schema therapy: Addressing the 4 core schemas people with AVPD have (effectiveness, social isolation, self-sacrifice and approval seeking) and changing these schemas into more adaptive ones
Group therapy: To overcome social anxiety, build interpersonal support and increase the capacity to mentalize
\
Can be achieved through:
CBT (Addressing automatic thoughts and improving social skills)
Schema therapy: Addressing the 4 core schemas people with AVPD have (effectiveness, social isolation, self-sacrifice and approval seeking) and changing these schemas into more adaptive ones
Group therapy: To overcome social anxiety, build interpersonal support and increase the capacity to mentalize
21
New cards
What are common comorbidities of AVPD?
Mood and anxiety (PTSD, panic, GAD), alcohol use
BPD, OCPD
BPD, OCPD
22
New cards
Why is seeking treatment often hard for people w AVPD?
they often think they are not worthy of treatment or that treatment cannot help them
23
New cards
What are similarities and differences between AVPD and SAD?
**Similar**: Also fear social situations where they could be exposed to possible scrutiny
**Differences**: AVPD also difficulties in intimate relationships, not just social situations
AVPD is ego-syntonic
Feelings of inferiority a lot stronger in AVPD
People with SP are more likely to panic
AVPD comes with introversion, much more general avoidance strategy and feelings of inferiority, as well as heavier deficits in metacognitive skills
**Differences**: AVPD also difficulties in intimate relationships, not just social situations
AVPD is ego-syntonic
Feelings of inferiority a lot stronger in AVPD
People with SP are more likely to panic
AVPD comes with introversion, much more general avoidance strategy and feelings of inferiority, as well as heavier deficits in metacognitive skills
24
New cards
What two hypotheses exist about the comorbidity between AVPD and SAD?
The hypothesis that social phobia is always present in people with AVPD, that these disorders exist on a spectrum, and AVPD is just the more extreme manifestation of it
Hypothesis that there is some overlap but the disorders don't always co-occur
Findings are still inconclusive
Hypothesis that there is some overlap but the disorders don't always co-occur
Findings are still inconclusive
25
New cards
Why do people often not seek treatment for OCPD?
The criteria of OCPD is valued in Western societies, also because this leads to increased wealth and higher status
Therefore, people often do not seek treatment for OCPD, but for things like depression and burnout
Therefore, people often do not seek treatment for OCPD, but for things like depression and burnout
26
New cards
What is the etiology of OCPD?
* Focus on production, rigid rules, lot of responsibility early in life (parentification)
* Punitive parenting or overprotecting parenting style
* Lack of focus on relaxation, fun, playtime
* Punitive parenting or overprotecting parenting style
* Lack of focus on relaxation, fun, playtime
27
New cards
What are the comorbidities of OCPD and how does it differ from syndrome OCD?
**Overlap w other disorders**
* OCD and OCPD are only moderately correlated (25%), but symptom overlap makes correlation analyses difficult
* Ego-syntonic thoughts in CPD - This is just how I am/ do things. Thoughts and intrusions seem to "make sense"
* Hoarding disorder: Don't want to throw stuff out
* OCD and OCPD are only moderately correlated (25%), but symptom overlap makes correlation analyses difficult
* Ego-syntonic thoughts in CPD - This is just how I am/ do things. Thoughts and intrusions seem to "make sense"
* Hoarding disorder: Don't want to throw stuff out
28
New cards
What trait correlates positively with DPD?
Elevated levels of interpersonal dependency
29
New cards
Why are people with DPD often in abusive relationships?
People w DPD go to great lengths to keep their partner around, do whatever partner wants, stays with abusive partner cause they cannot stand being alone
30
New cards
What are the four components of dependency as found in DPD?
* Motivational (Need for guidance, support, approval)
* Cognitive (perception of oneself as weak)
* Affective (anxiety when asked to work autonomously)
* Behavioural (use strategies to get taken care of)
* Cognitive (perception of oneself as weak)
* Affective (anxiety when asked to work autonomously)
* Behavioural (use strategies to get taken care of)
31
New cards
Cognitive interactionist model of DPD
Dependency is the intermingling of motivational, cognitive, affective and behavioural features, and this dependency is goal-directed and proactive
32
New cards
What does the Relationship Profile Test (RPT) measure?
Healthy and unhealthy dependency. unhealthy dependency is characterized by intense uncontrolled dependency across various situations
33
New cards
People with DPD are traditionally viewed as very passive. When is this not the case?
Some can be very pro-active and aggressive, for example if they are competing with someone for the approval of someone else (boss, teacher)
* Also pro-active in searching for someone
* Also pro-active in searching for someone
34
New cards
What does DPD stem from, according to Bornstein’s model and what does it lead to?
DPD often stems from overprotective (teaching children that they are weak), authoritarian (teaching children you have to accede to others to get by in life) parenting
Gender role socialisation (people see women as more dependent)
Cultural attitudes regarding achievement/relatedness (higher dependency in collectivist culture)
**Cognitive consequences:** Schema of the self as powerless and ineffectual
**Motivational effects:** Desire to obtain and maintain nurturing, supportive relationships
Gender role socialisation (people see women as more dependent)
Cultural attitudes regarding achievement/relatedness (higher dependency in collectivist culture)
**Cognitive consequences:** Schema of the self as powerless and ineffectual
**Motivational effects:** Desire to obtain and maintain nurturing, supportive relationships
35
New cards
What is the prevalence of Cluster C disorders and who suffers from it most?
Avoidant PD: 2.5% healthy population, 25% clinical population
Dependent PD: 1% healthy population, 15% clinical population
OCPD: Around 2% population, 10% clinical population
\
More in women and low SES except OCPD, which is more high SES
Dependent PD: 1% healthy population, 15% clinical population
OCPD: Around 2% population, 10% clinical population
\
More in women and low SES except OCPD, which is more high SES
36
New cards
There was a pilot study at the UVA into Cluster C disorders. What did the results show?
People with DPD make almost no progress during treatment but then learn in the follow-up (because the therapist gets taken away and they're forced to implement the tools they learn during therapy)
37
New cards
Cognitive theories of PDs
theories that propose that cognitive structures (schemas) and processes (biases) underlie the development and maintenance of personality disorders
38
New cards
Schema modes
transient state-related patterns of schematic activation, which are a combination of an activated schema and coping with this activation. In other words, the activation of schemas by external or internal cues.
39
New cards
What are the origins of schemas?
Schemas for PDs are assumed to develop during childhood, from the interaction of biological and environmental influences (attachment, parenting). Children differ in their innate sensitivity to the environment and in how they respond to stressors
40
New cards
Schema theory
the idea that PD-related schemas arise from experiences during early childhood when basic needs are not met (early maladaptive schemas; EMSs)
41
New cards
What coping styles are there to deal with EMSs?
• Overcompensation (fight): the person behaves and thinks in a way that is the opposite of the triggered EMS, to keep it out of awareness as much as possible (a narcissistic person with underlying inferiority and loneliness schemas that acts superior and popular).
• Avoidance (flight): the person tries to prevent triggering EMSs or avoids the emotions and thoughts that are aroused when they are triggered (avoiding situations that might trigger EMSs).
• Surrender (freeze): the person submits to what the EMSs dictate, leading to the person completely believing it is true (believing to be inferior and giving up any attempt to change these feelings).
• Avoidance (flight): the person tries to prevent triggering EMSs or avoids the emotions and thoughts that are aroused when they are triggered (avoiding situations that might trigger EMSs).
• Surrender (freeze): the person submits to what the EMSs dictate, leading to the person completely believing it is true (believing to be inferior and giving up any attempt to change these feelings).
42
New cards
How can you measure interpretation bias?
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) = a task that is used to measure interpretational bias. Participants are asked to interpret a series of ambiguous pictures.
43
New cards
what is characteristic of schemas in PDs?
They are relatively inflexible, even when they cause problems
44
New cards
What happens if you train people towards/away from focusing on threats
It increases/reduces stress responses
\
Similar effects have been found for interpretation biases
\
Similar effects have been found for interpretation biases
45
New cards
Criteria for AVPD
Social inhibition as characterised by 4 or more of the following
\
* Avoids interpersonal contact in occupational activities for fear of rejection
* Unwilling to get involved with people unless certain of being liked
* Restrained in intimate relationships because of fear of being shamed or ridiculed
* Preoccupied with being criticised or rejected in social situations
* Inhibited to new interpersonal experiences bc of feelings of inadequacy
* Low feelings of self-worth (feels inferior to others)
* Reluctant to take risks or engage in new activities because they may prove embarrassing
\
* Avoids interpersonal contact in occupational activities for fear of rejection
* Unwilling to get involved with people unless certain of being liked
* Restrained in intimate relationships because of fear of being shamed or ridiculed
* Preoccupied with being criticised or rejected in social situations
* Inhibited to new interpersonal experiences bc of feelings of inadequacy
* Low feelings of self-worth (feels inferior to others)
* Reluctant to take risks or engage in new activities because they may prove embarrassing
46
New cards
How do people with DPD present in therapy?
They have pseudo-emergencies, request more after-hours contact and have a harder time quitting therapy. They are also prescribed higher levels of medicatio
47
New cards
What are the DSM-Criteria for DPD?
Pervasive, excessive need to be taken care of, as indicated by 5 or more of the following
\
* Has difficulty making everyday decisions w/o advice or reassurance
* Needs others to assume responsibility for most major areas of their life
* Doesn’t express disagreement for fear of rejection
* Can’t do things on their own
* Goes to excessive lengths to obtain nurturance and support from others
* Urgently seeks another relationship when one ends
* Unrealistically preoccupied with fears of being left to care for themselves
\
* Has difficulty making everyday decisions w/o advice or reassurance
* Needs others to assume responsibility for most major areas of their life
* Doesn’t express disagreement for fear of rejection
* Can’t do things on their own
* Goes to excessive lengths to obtain nurturance and support from others
* Urgently seeks another relationship when one ends
* Unrealistically preoccupied with fears of being left to care for themselves
48
New cards
What is DPD comorbid with, and why can it be difficult to diagnose?
It’s comorbid with depression, somatic disorders, social anxiety disorder and agoraphobia
In personality disorders it’s often comorbid with avoidant, borderline, and histrionic pd
\
It’s hard to diagnose because underlying dependency also plays a role in other disorders
In personality disorders it’s often comorbid with avoidant, borderline, and histrionic pd
\
It’s hard to diagnose because underlying dependency also plays a role in other disorders
49
New cards
What biological, genetic and neurobiological underpinnings are there for DPD?
Genetic factors: 30% risk
Temperament: Withdrawal, low adaptability, high reactivity
Insecure attachment
Temperament: Withdrawal, low adaptability, high reactivity
Insecure attachment