Alevel Biology
1/426
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
427 Terms
Where do the light-dependent reactions take place
thylakoid membrane
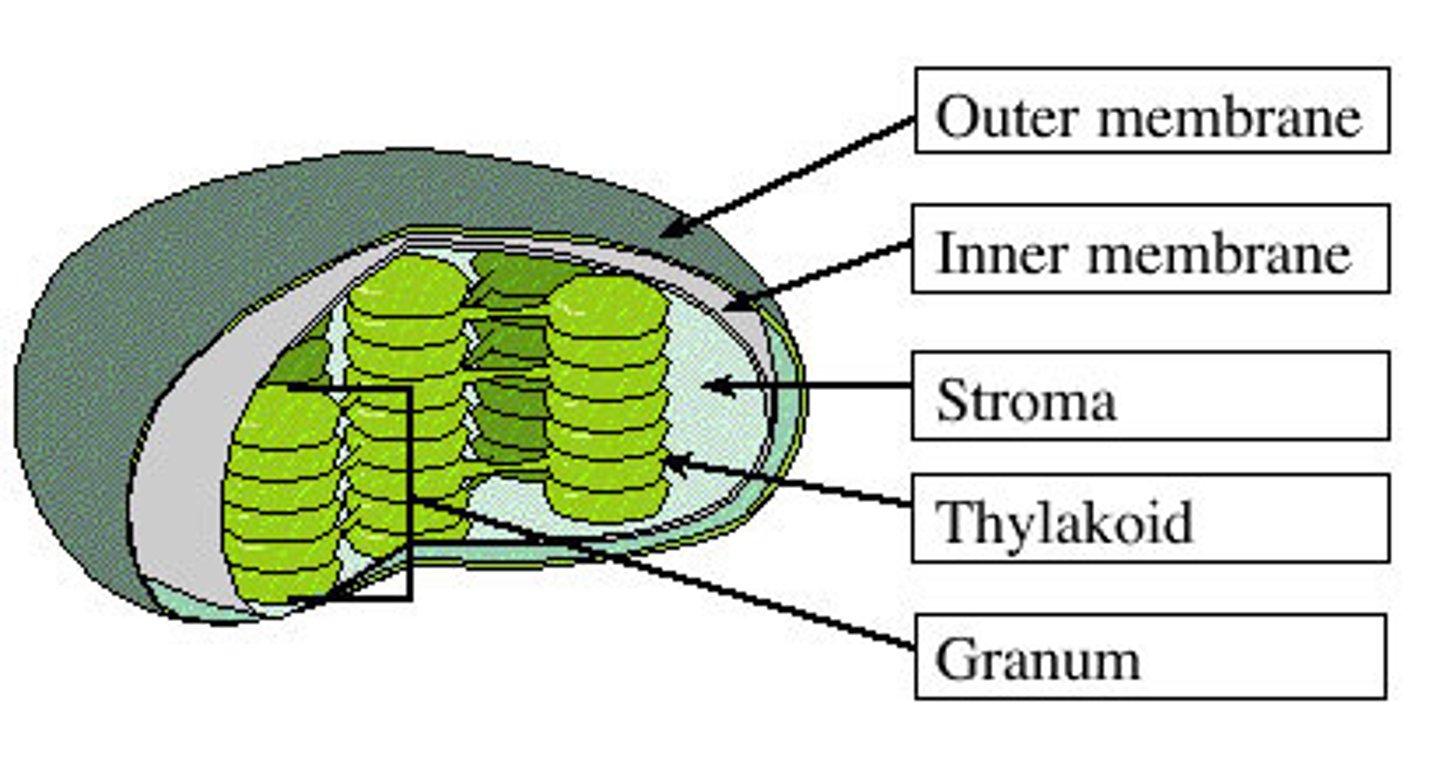
A stack of thylakoid membranes is called
granum (grana)
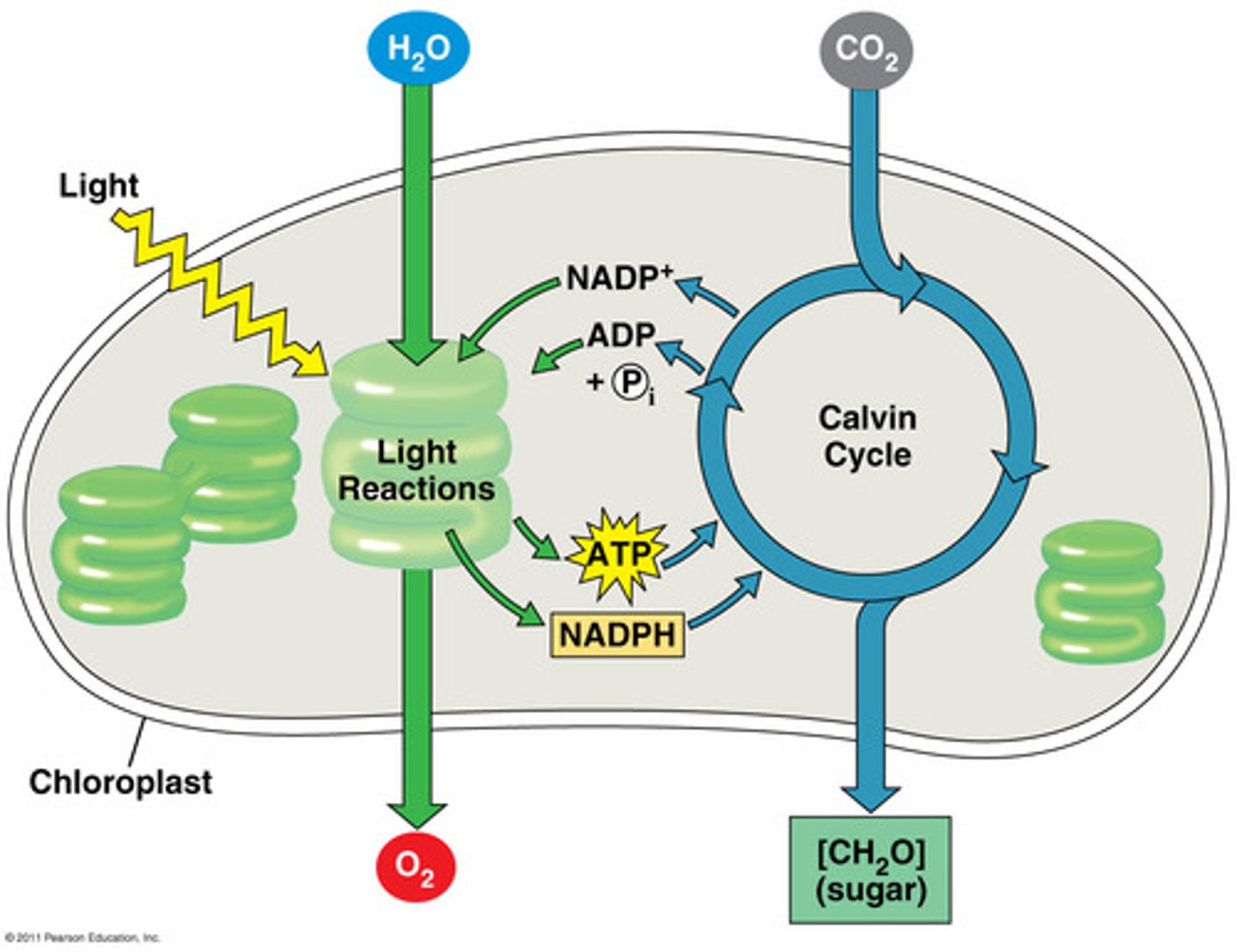
1st stage of light dependent reaction
Photolysis
(Water moves in to the thylakoid and is broken down into H+ ions Oxygen and electrons when a photon of light hits the chlorophyll molecule in photosystem 2)
2nd stage of light dependant reactions
Photoionisation
(When a photo of light hits the chlorophyll molecule at photosystem 2 it 'excites' the electrons, these high energy electrons then move down the electron transport chain)
3rd stage of light dependant reactions
Electron Transport Chain
(The high energy electron move through the thylakoid membrane via a series of carrier proteins which act as proton pumps, using the energy from the electrons to actively transport H+ ions into the thylakoid membrane.
4th stage of light dependant reactions
Chemiosmosis via ATP Synthase
(The combined effect of the photolysis of water and the ETC form a electrochemical gradient of H+ ions from a high concentration in the thylakoid to a low concentration in the Stroma, this causes the facilitated diffusion of H+ ions out of the thylakoid via ATP Synthase causing it to spin and this movement allows ATP to be synthesised)
5th stage of light dependant reactions
Re-exicted Electrons
(Another photon of light hits the chlorophyll molecule at photosystem 1 causing the electrons to be re-excited, these high energy electrons are then picked up by a molecule of NADP+ forming a molecule of Reduced NADP)
Products of light dependent reactions
ATP (used in Clavin Cycle)
Reduced NADP (used in Clavin Cycle)
Oxygen (used in Respiration or released as waste product)
The Process of the Calvin Cycle (3 Steps)
1. RuBP (a 5 carbon compound) is combined with a molecule of Carbon Dioxide forming 2 molecules of GP. This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme Rubisco.
2. GP (3 carbon) is then reduced into TP (3 carbon) using (2x) ATP and (2x) Reduced NADP form the Light Dependant Reactions.
3. From the (2x) TP molecules 1 carbon is used to make useful organic substances (glucose) the other 5 carbons are recycled into RuBP using an ATP molecule
Number of ATP and Reduced NADP needed to produce one molecule of glucose
18 x ATP
12 x Reduced NADP
Where does the Calvin cycle occur
The stroma of the chloroplast
Where does glycolysis occur
The cytoplasm
1st Stage of Glycolysis
Phosphorylation :
Glucose is phosphorylated twice forming Glucose Phosphate and the Hexose Bisphosphate (this use 2 ATP molecules). The Hexose Bisphosphate molecule then splits into (2x) TP molecules .
2nd Stage of Glycolysis
Oxidation :
The (2x) TP molecules are oxidised forming (2x) Pyruvate molecules. This produces (2x) Reduced NAD and (4x) ATP
Net Products of Glycolysis
2 x Pyruvate
2 x Reduced NAD
2 x ATP
Anaerobic Respiration in Animals
Lactate Fermentation
(Pyruvate is converted into Lactate reforming NAD+ from Reduced NAD)
Anaerobic Respiration in Plants
Alcoholic Fermentation
(Pyruvate is first converted into Ethanal producing Carbon Dioxide then into Ethanol reforming NAD+ form Reduced NAD)
Why is anaerobic respiration necessary
Anaerobic respiration regenerates NAD
(Allowing Glycolysis to continue allowing a small amount of ATP produced meaning the cells do not die initially in the absence of oxygen)
Where do the link reaction and Krebs cycle take place
The matrix of the mitochondria
Process of the Link Reactions (3 Steps)
1. Pyruvate is decarboxylated (one carbon atom removed forming a molecule of Carbon Dioxide)
2. Its is oxidised to form Acetate which also produced Reduced NAD
3. Acetate is combined with co-enzyme A to from Acetyl CoA
Process of Krebs Cycle (5 Steps)
Acetyl CoA combines with Oxyloacetate to form Citrate (2 carbon + 4 carbon = 6 carbon) and the CoA is recycled back into the link reactions
2. Citrate (6 carbon) undergoes decarboxylation and dehydrogenisation which involves removing 1 carbon and 1 hydrogen producing Carbon Dioxide, Reduced NAD and a 5 carbon compound.
3. The 5 carbon compound undergoes decarboxylation and dehydrogenation again producing Carbon Dioxide, Reduced FAD and Reduced NAD.
4. During the conversion from 5 carbon to 4 carbon substate level phosphorylation occurs producing ATP.
5. Oxyloacetate is Reformed
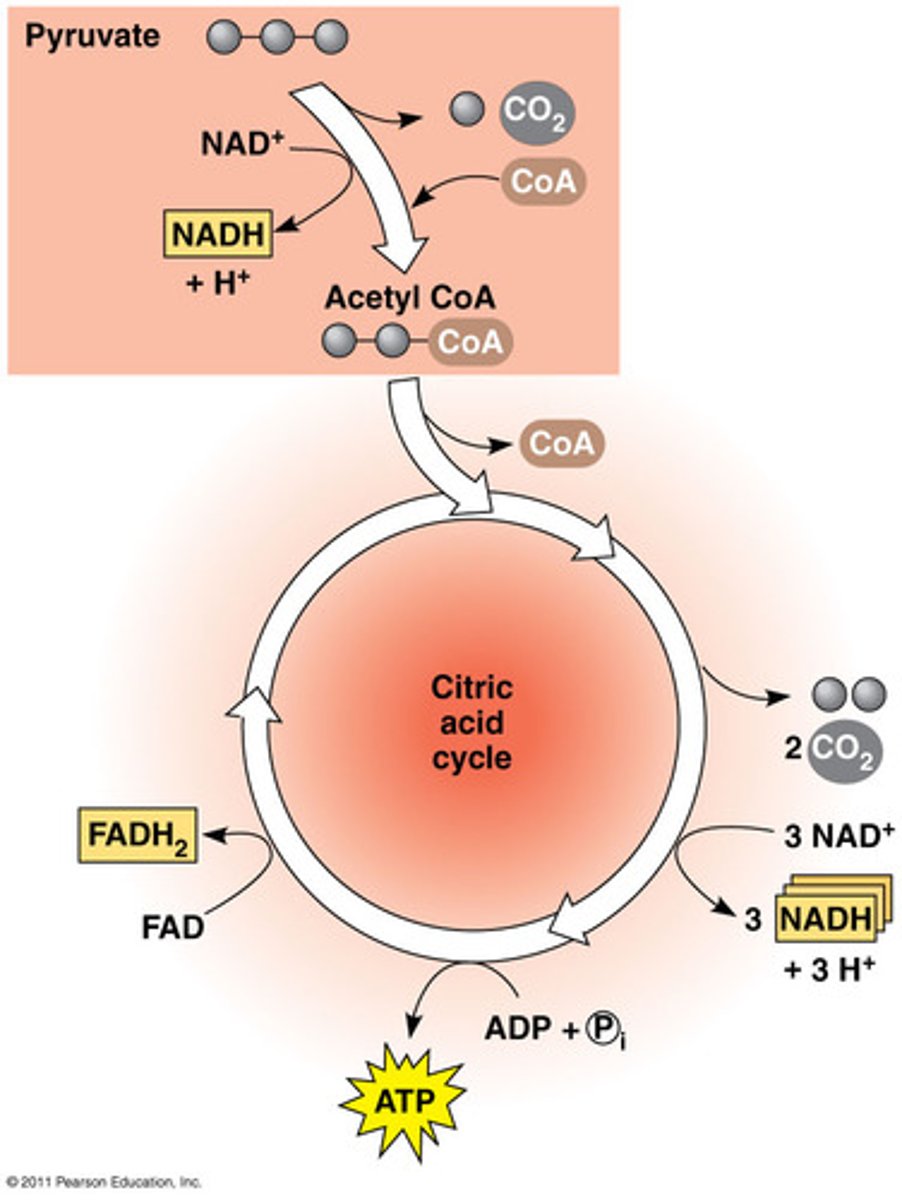
How many carbons in Acetate
2
How many carbons in Oxyloacetate
4
How many carbons in Citrate
6
Products of the Krebs cycle and their uses
CoA - Recycled in Link Reaction
2 x Carbon Dioxide - Released as waste
1 x ATP - Used for energy
3 x Reduced NAD - Used in ETC
1 x Reduced FAD - Used in ETC
1st Stage of the ETC
Oxidation
(Reduced NAD/FAD are oxidised releasing H+ ions and electrons)
2nd Stage of the ETC
ETC
(The Electrons from the hydrogen atoms move down the ETC through a series of transport proteins)
3rd Stage of the ETC
Proton Pumps
(Energy from the electrons is used by the proteins to actively transport H+ ions from the matrix into the intermembrane space Proton Pumps)
4th Stage of the ETC
Chemiosmosis
(An electrochemical gradient is formed causing H+ ions to move by facilitated diffusion back into the matrix via ATP synthase causing it to spin)
5th Stage of the ETC
ATP Synthesis
(The movement of ATP synthase allows for ATP to be synthesised from ADP and Pi)
6th Stage of the ETC
Final Electron Aceptor
(In the matrix H+ ions combine with oxygen and electrons to form a water molecule, hence oxygen is known as the final electron acceptor)
ATP produced per glucose molecule
36 - 38
(2 from glycolysis)
(2 from Krebs)
(32 - 34 from ETC)
Define Immunity
the ability of an organism to resist a particular pathogen and to show no symptoms of the disease
1st Stage of an Immune Response
Phagocytosis
(chemicals released by the pathogens attract phagocytes, the phagocyte surrounds and engulfs the pathogen trapping it in a phagocytic vacuole, lysosomes fuse to the vacuole releasing digestive enzymes)
2nd Stage of an Immune Response
Antigen Presenting Cells activates the T(H) Cells
(The Phagocyte displays the antigens of the pathogen and when T(H) cells bind they are activated, these activated T(H) cells release chemical signals which activates more phagocytes and T(C) cells
3rd Stage of an Immune Response
Clonal Selection
(When a T(H) cells comes into contact with a B cell that has already come into contact with an antigen presenting cell, the B cell becomes activated. Activated B cells either divide into identical plasma cells which produce the specific antibodies or memory cells.
Types of T cells
Helper T cells
Cytotoxic T cells
What are vaccines
Vaccines are antigens which are either free or attached to a dead/weakened pathogen. They are harmless but they trigger and immune response allowing specific memory cells to be produced and therefore protect you from symptoms on your 2nd exposure.
Structure of an Antibody
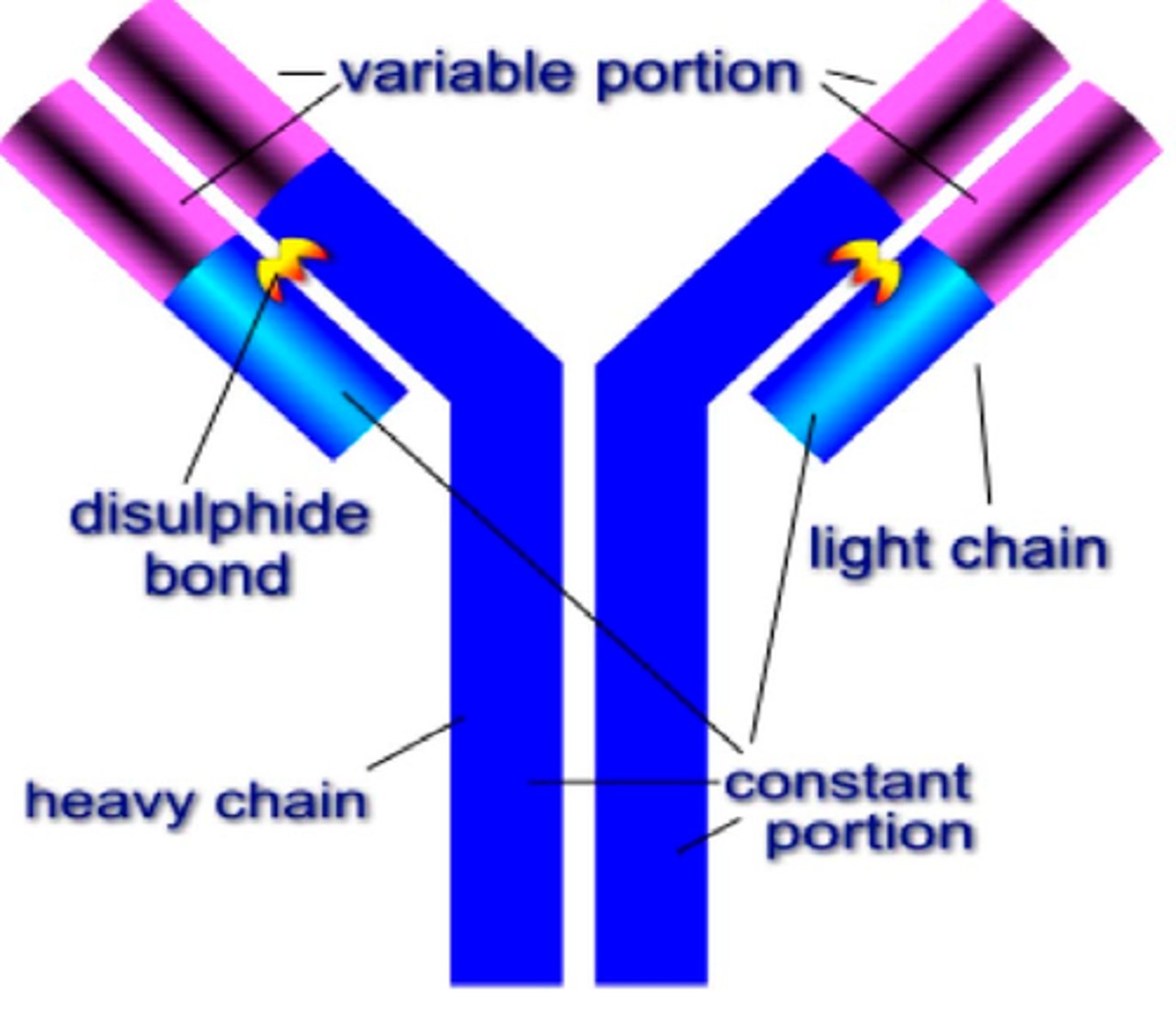
Define active immunity
the immunity that results from the production of antibodies by the immune system in response to the presence of an antigen. This can be caused artificially through the use of a vaccine.
Define passive immunity
the short-term immunity that results from the introduction of antibodies from another person or animal.
What are monoclonal antibodies
Antibodies produced from a single group of genetically identical B-cells.
Name of Hormone in a Pregnant Women's Urine
HCG Hormone
The use of Monoclonal Antibodies in Pregnancy Testing (3. Steps)
1. An antibody for HCG is located in the application area with a coloured bead attached to it, this binds to any HCG present in the urine sample.
2. This complex moves along the strip to the test area.
3. The test strip contains immobilised antibodies for HCG causing the complexes to accumulate in this area cause the strip to change colour.
The Process of ELISA Testing for HIV
1. The HIV antigen is bound to the bottom of the well, to which a sample of the patients blood is added, if there are any HIV specific antibodies in the blood they with bind and remain once the plate is washed.
- Wash -
2. As second antibody is added, this is specific and will bind to the HIV antibody if this is present.
- Wash-
3. The Second antibody added as an enzyme attached which will cause the colour change of a substate if present.
What is HIV
It is the human immunodeficiency virus which eventually leads to the development of AIDs
What is AIDs
It is the acquired immune deficiency syndrome, you are diagnosed with AIDs when an HIV patient's T(H) cell count drops bellow a certain level.
Structure of HIV

The Replication of HIV (4 Steps)
1. Attachment proteins on the HIV bind to a receptor molecule on the cell surface membrane of their Host T(H) Cell.
2. The Capsid is released into the cell where it uncoats and releases its genetic material RNA into the cells cytoplasm.
3. Reverse Transcriptase is used to make a complementary strand of DNA from the viral RNA this is then used to produce a molecule of double-stranded DNA.
4. This double-stranded DNA is inserted in to the human DNA, this is then read by the cell and viral proteins are produced and assembled into new viruses which are released from the cell.
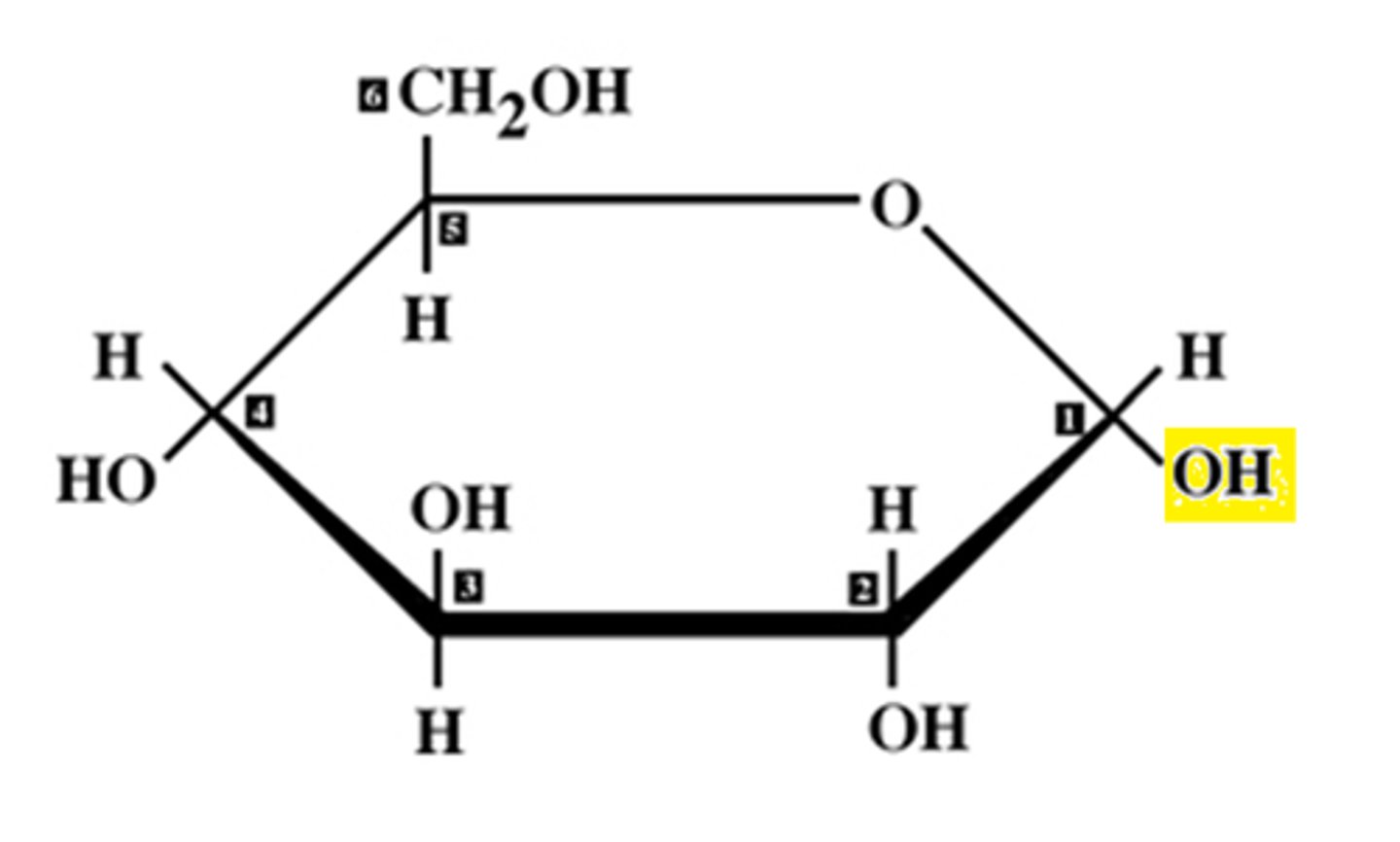
Structure of alpha glucose
OH down
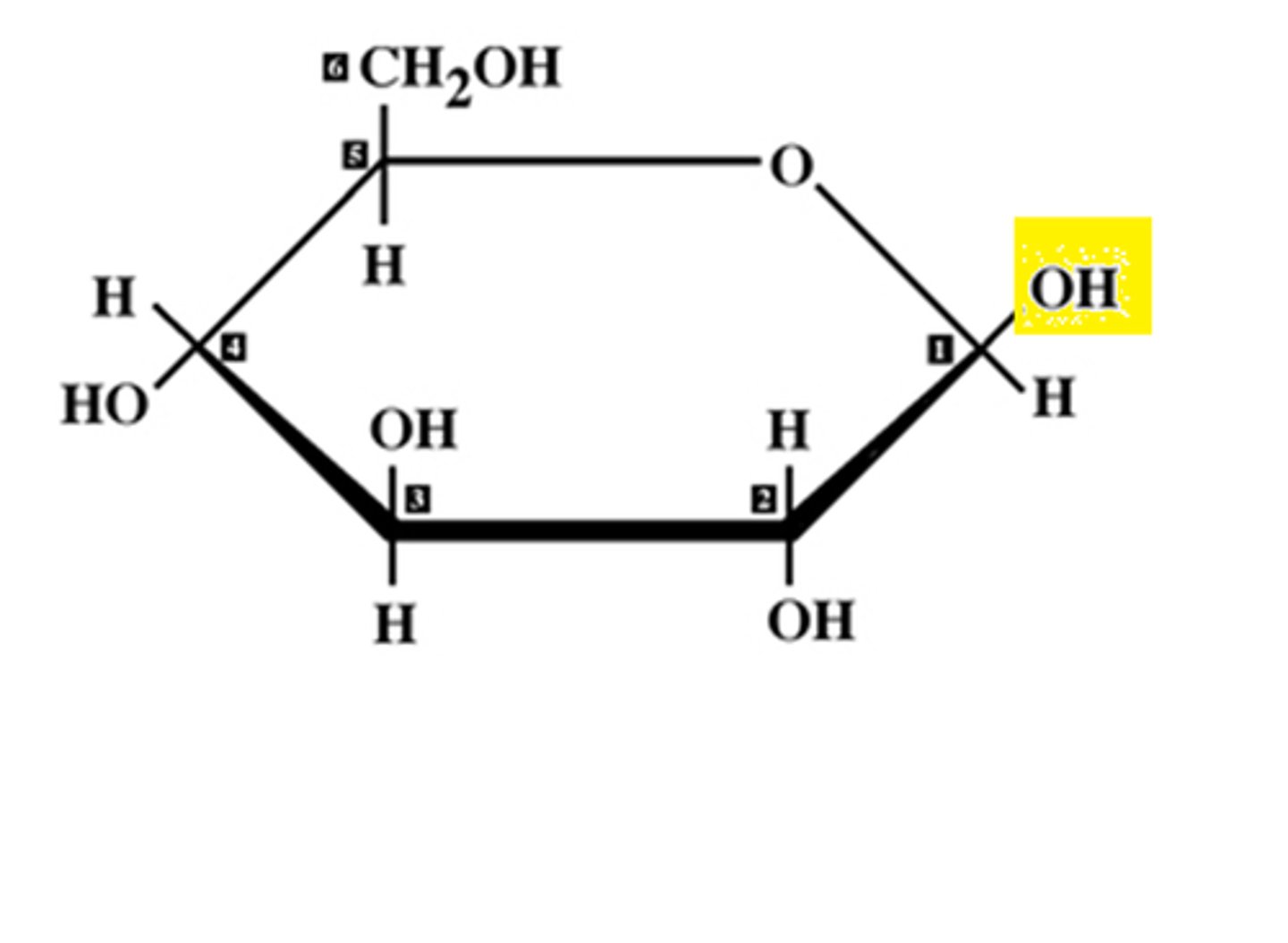
Structure of beta glucose
OH up
Maltose is made of
glucose + glucose
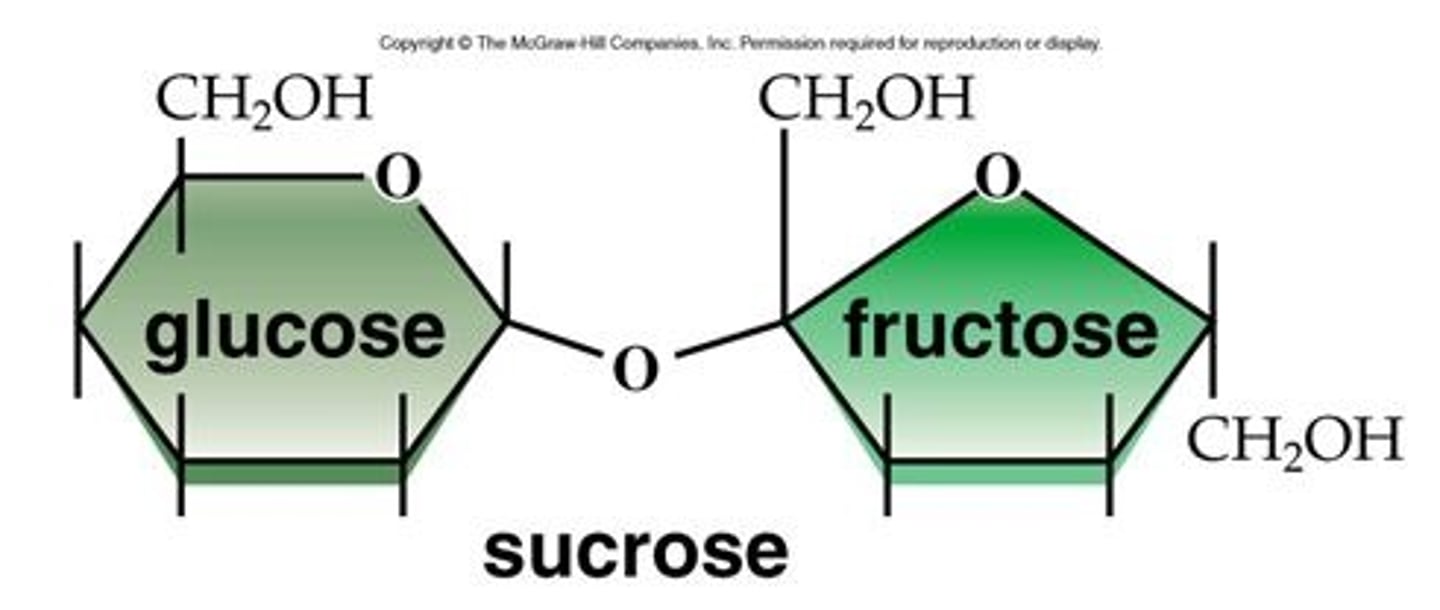
Sucrose is made of
glucose + fructose
Lactose is made of
glucose + galactose
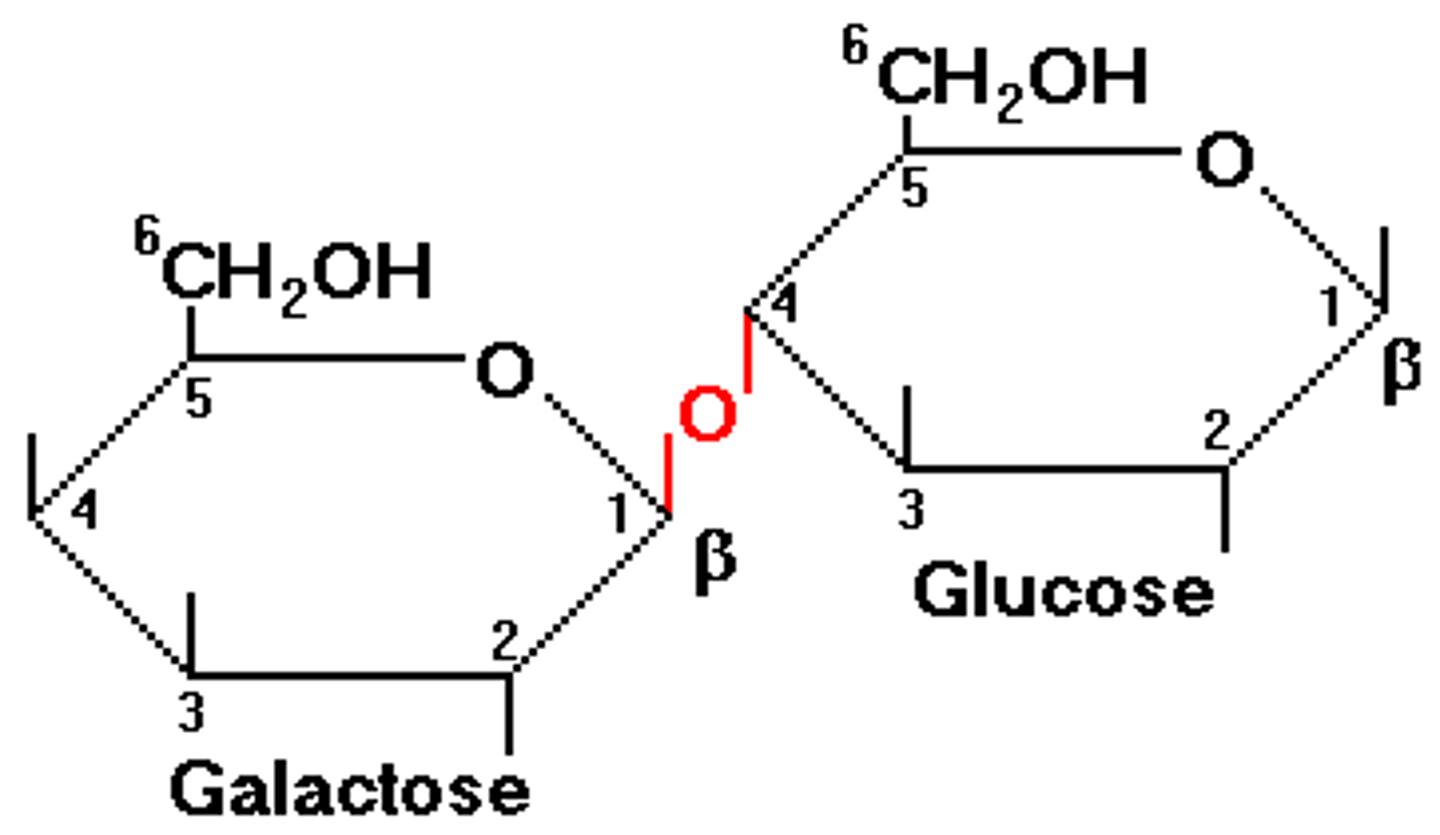
Bonds between Monosaccharides is called
Glycosidic Bonds
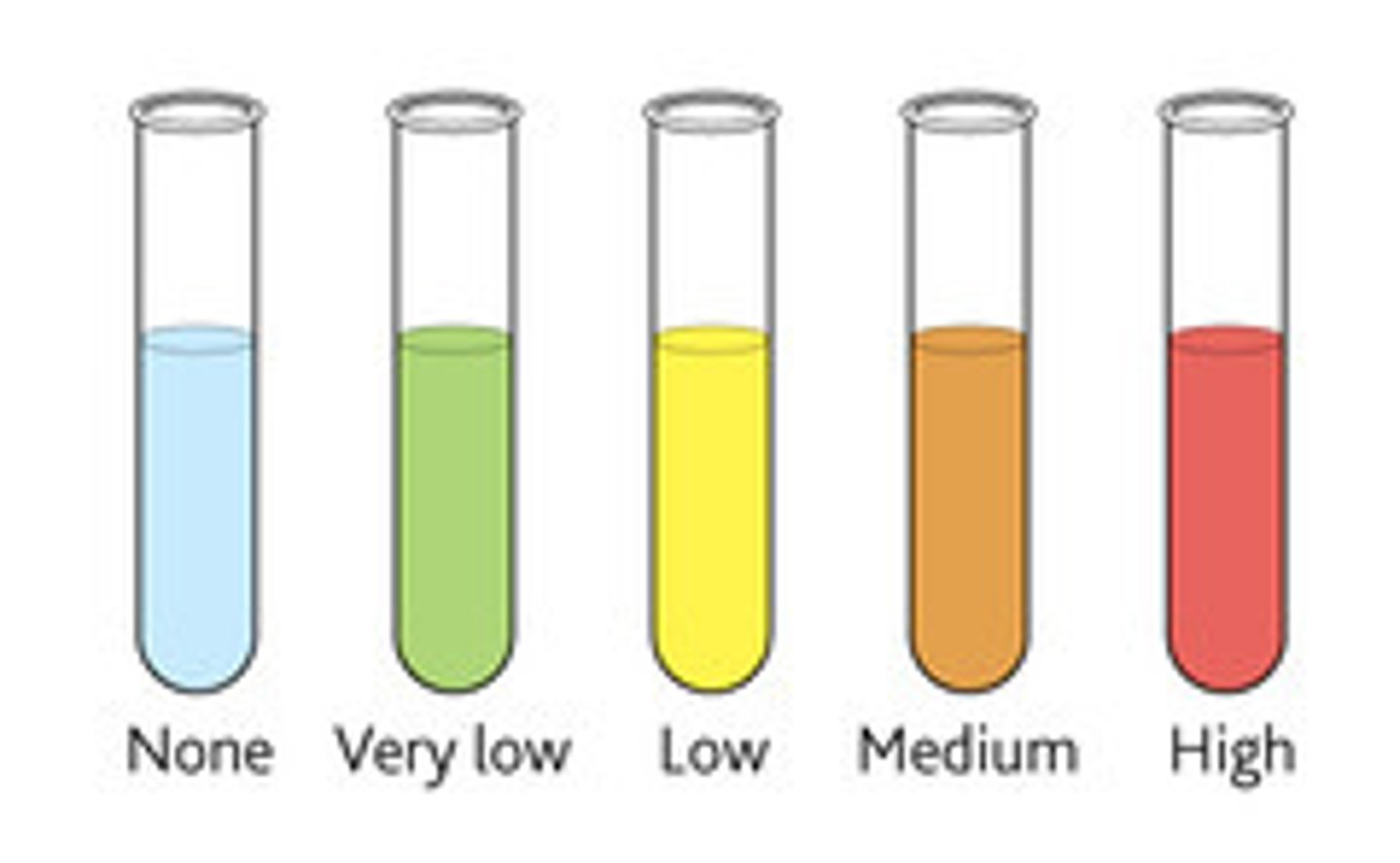
Test for reducing sugars (+ colours)
Add Benedict's Reagent (blue sol.) and heat in a water bath at a boil and observe for the formation of a coloured precipitate the colour indicates the concentration of reducing sugars.

Test for non-reducing sugars
Boil with HCL (to hydrolyse the glycosidic bonds) and the neutralise with NAHCO3 then carry out a normal Benedict's test.
What are reducing sugars
All monosaccharides and some disaccharides
Structure of a triglyceride
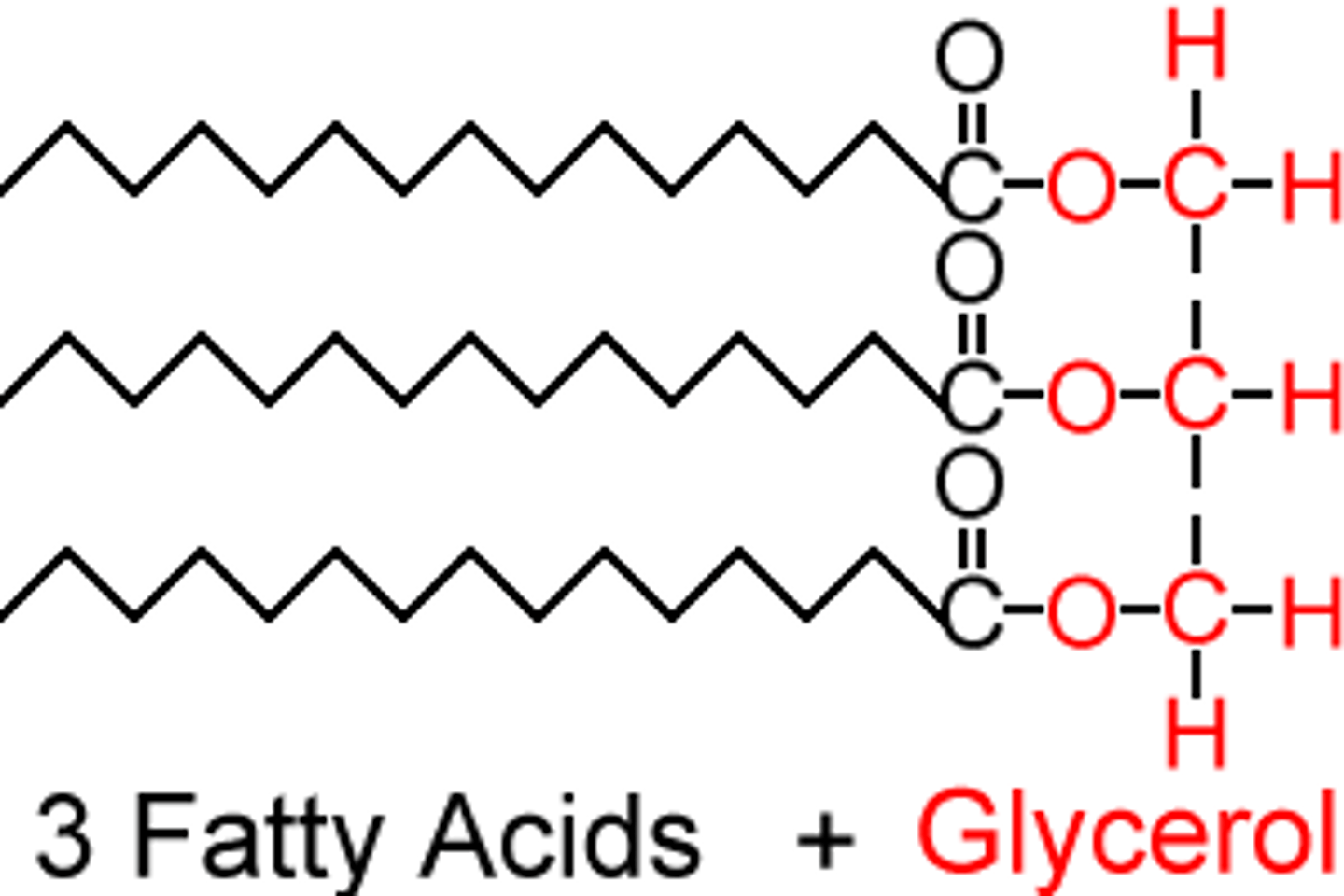
Name of bonds in lipids
Ester Bonds
Properties of triglycerides
Insoluble (Don't effect water potential)
Efficient store of chemical energy (2x as much per gram as carbohydrates)
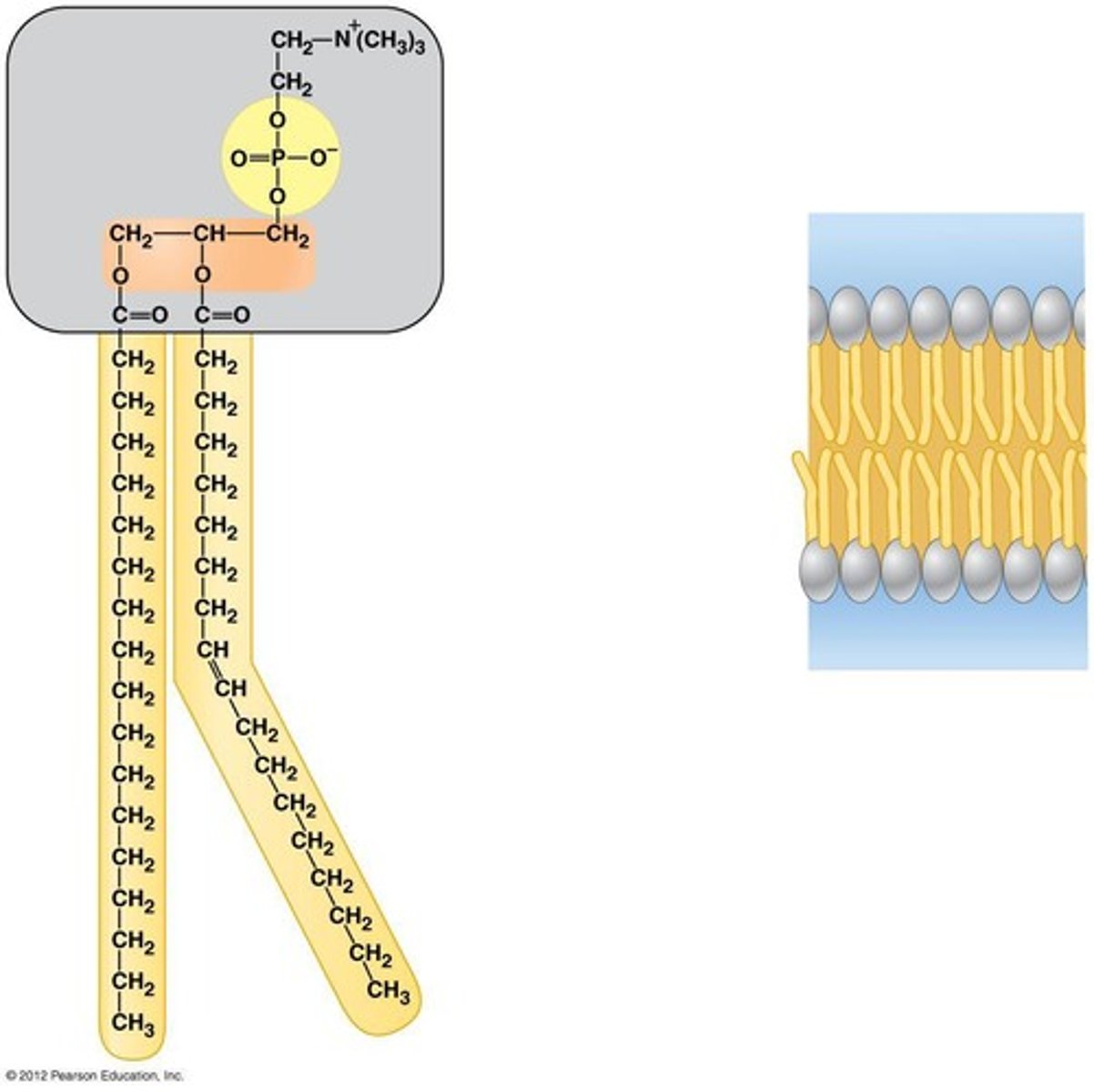
Properties of phospholipids
Hydrophilic Phosphate Head
Hydrophobic Fatty Acids Tail
Test for Lipids
Emulsion Test :
Shake substance with ethanol until fully dissolved then add the solution to water if there are any lipids then they will precipitate out of the liquid and show up as a milky emulsion

Structure of Starch
Made of (80-90%) Amylopectin and (10-20%) Amylose. (Both Alpha Glucose Polysaccharides)
Amylopectin = Long branched chain, increase the speed starch can be broken down.
Amylose = Coiled structure, unbranched, compact
Structure of Glycogen
Made of alpha glucose with both 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds (More 1,6 bonds that amylopectin)
Approx 8-12 units before each branch
Compact and easily broken down
Structure of Cellulose
Made of Beta glucose bonded with 1,4 glycosidic bonds.
Forms straight unbranched chains which are held together by hydrogen bonds which allows them to form microfibrils and fibres to give plant cells their strength
Structure of an Amino Acid
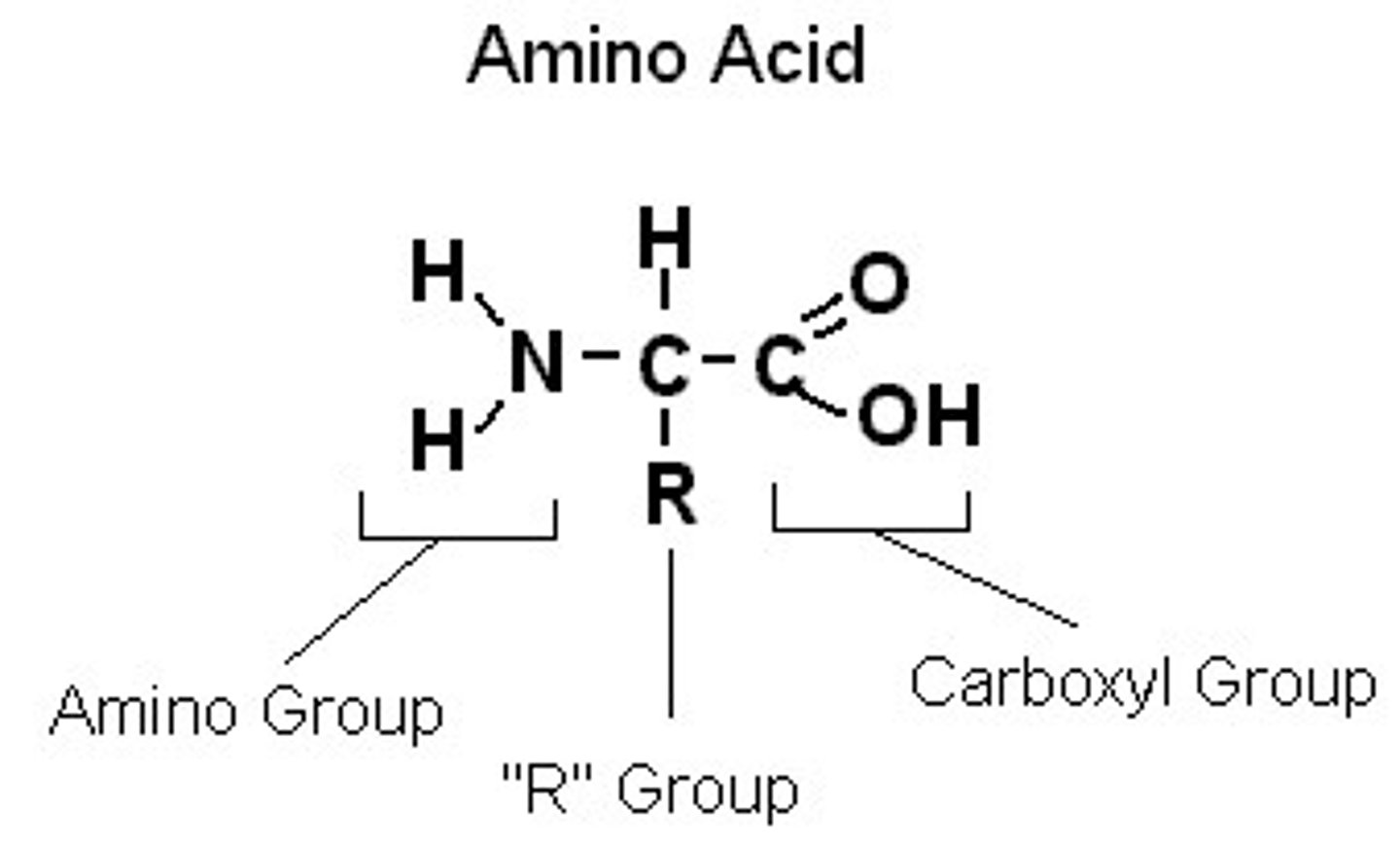
Name of bonds between amino acids
peptide bonds
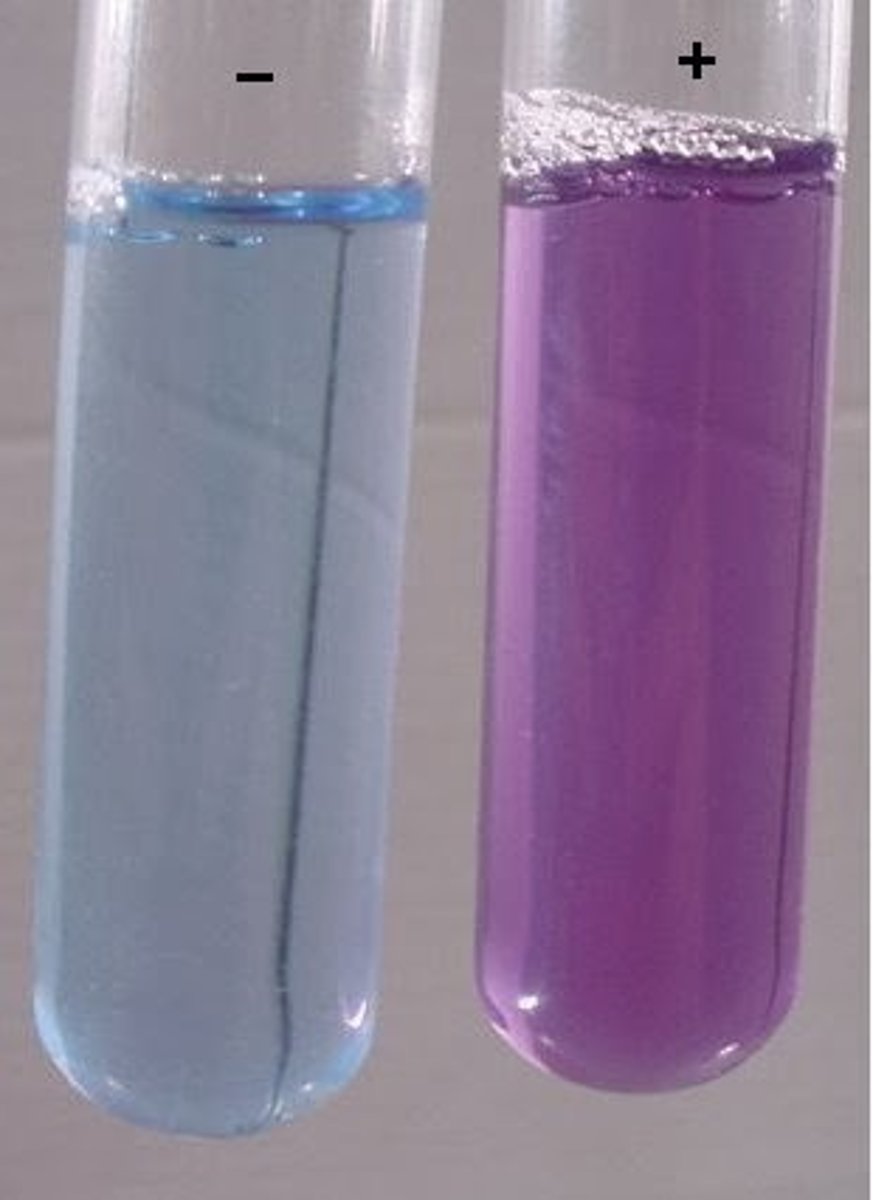
Test for Proteins
Biuret Test :
Add a few drops of NaOH (as the solutions needs to be alkaline) then add Copper (II) Sulphate solution
If the solution turns from Blue to Purple then protein is present

Primary structure of protein
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
(Defined by DNA base sequence)
Secondary structure of protein
Hydrogen bonds form between the amino acids in the chain which makes it automatically coil into an alpha helix or fold into a beta pleated sheet. The helix is held together by H bonds between every N-H group and the oxygen of the C=O.
Tertiary structure of proteins
The chain is further coiled and folded due to more hydrogen, ionic and covalent (disulphide bridges between cystine residues) bonds forming
Quaternary Structure of protein
Several Polypeptide chains some with additional groups
(e.g. Haem group in haemoglobin)
Types of enzyme inhibition
Competitive and non-competitive inhibition
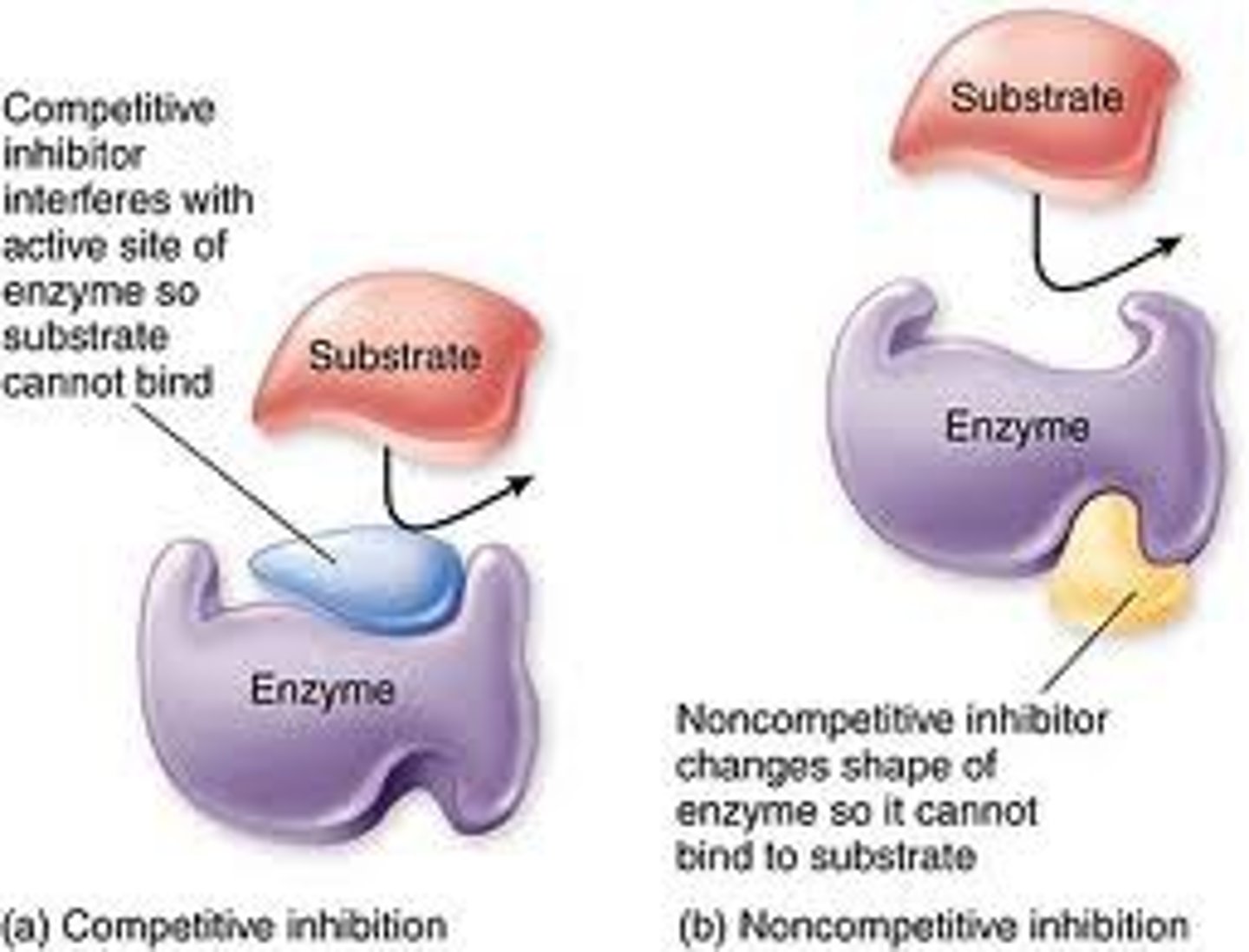
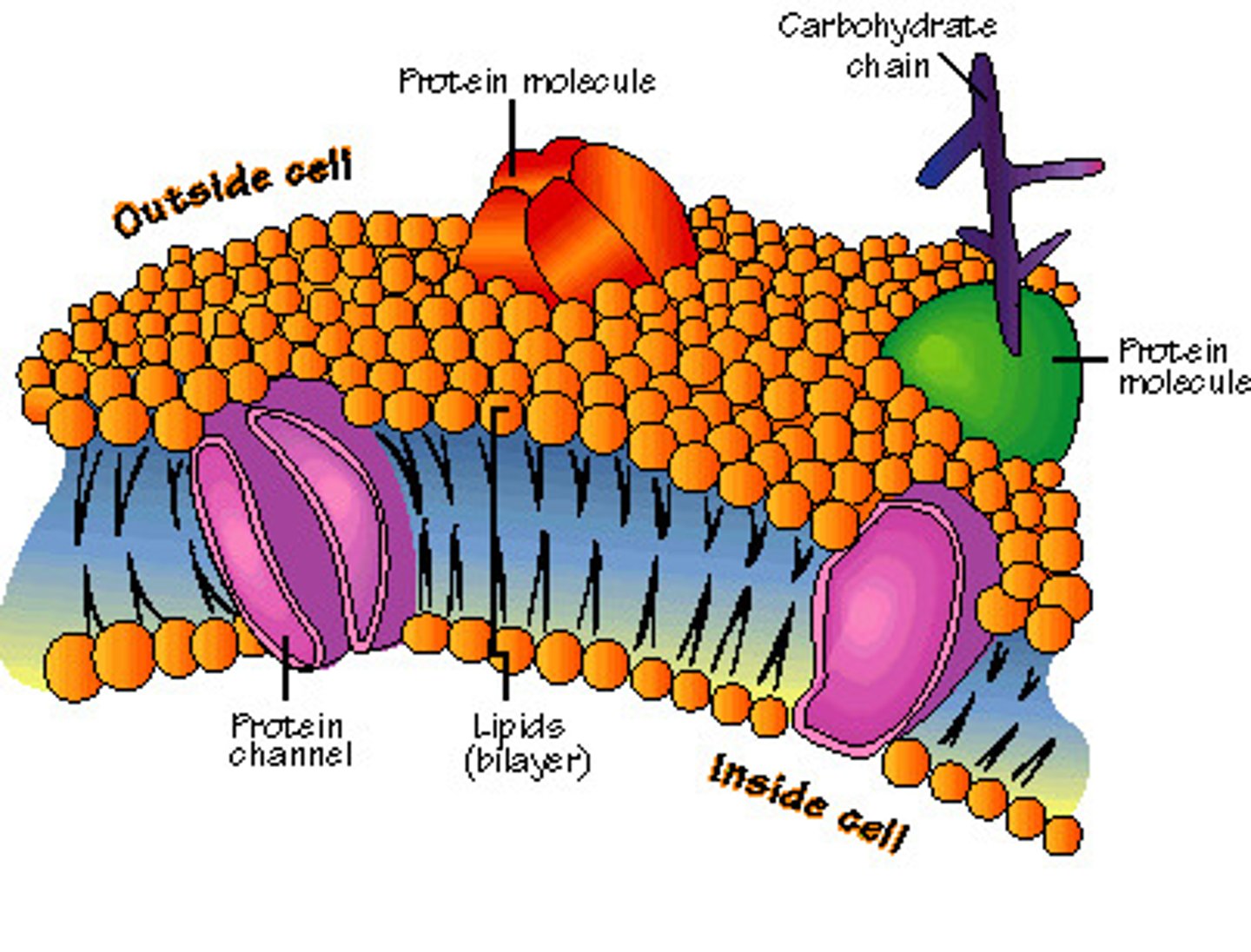
What is the model for plasma membranes
Fluid Mosaic Model
(The phospholipid bilayer is described as 'fluid' as the molecules are constantly moving)
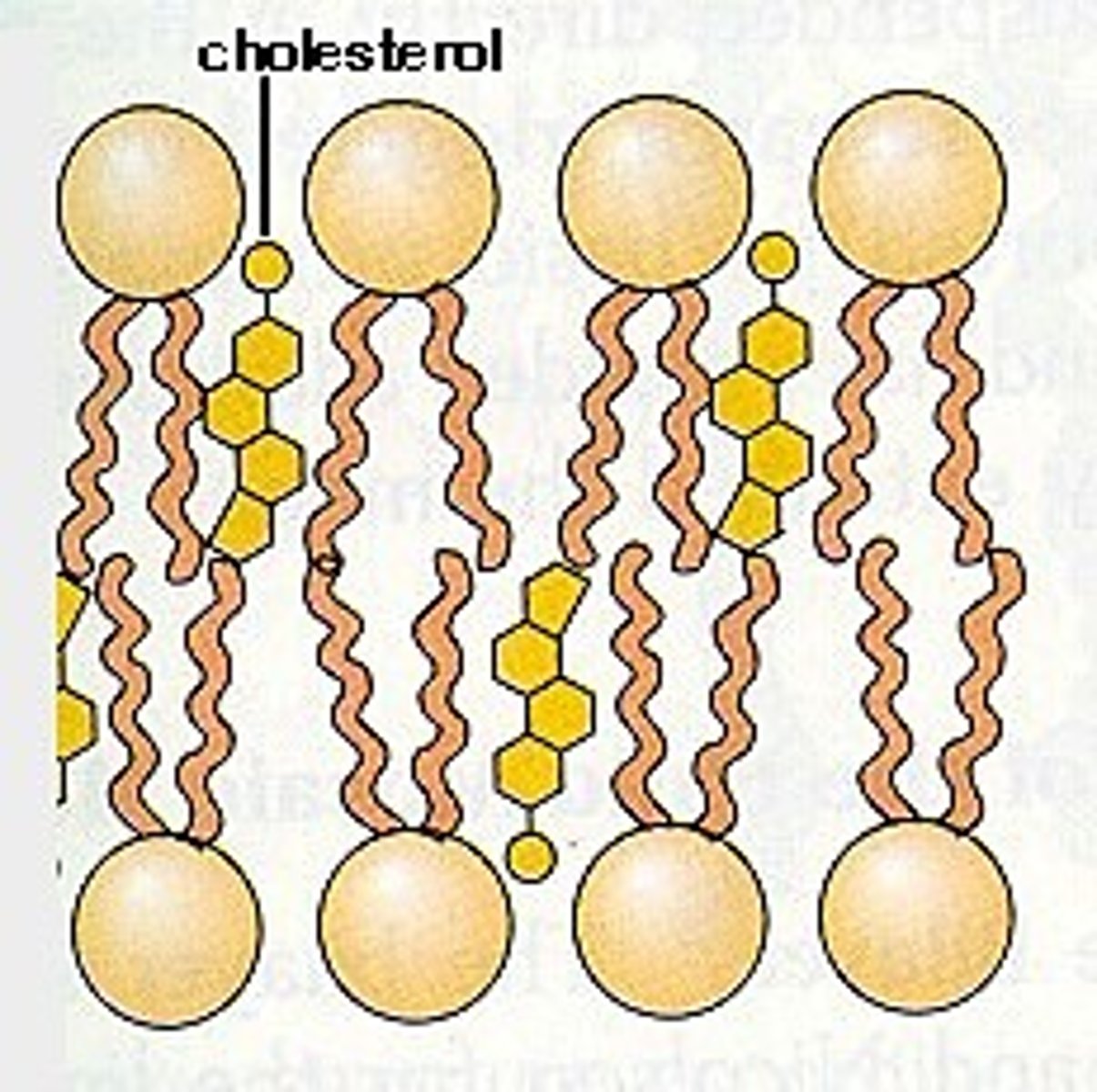
Function of cholesterol in plasma membranes
Fit between phospholipids and they bind together the fatty acid tails, this packs the phospholipids closer together restricting their movement making the bilayer 'less fluid'.
Important in animal cells to help the cell maintain its shape
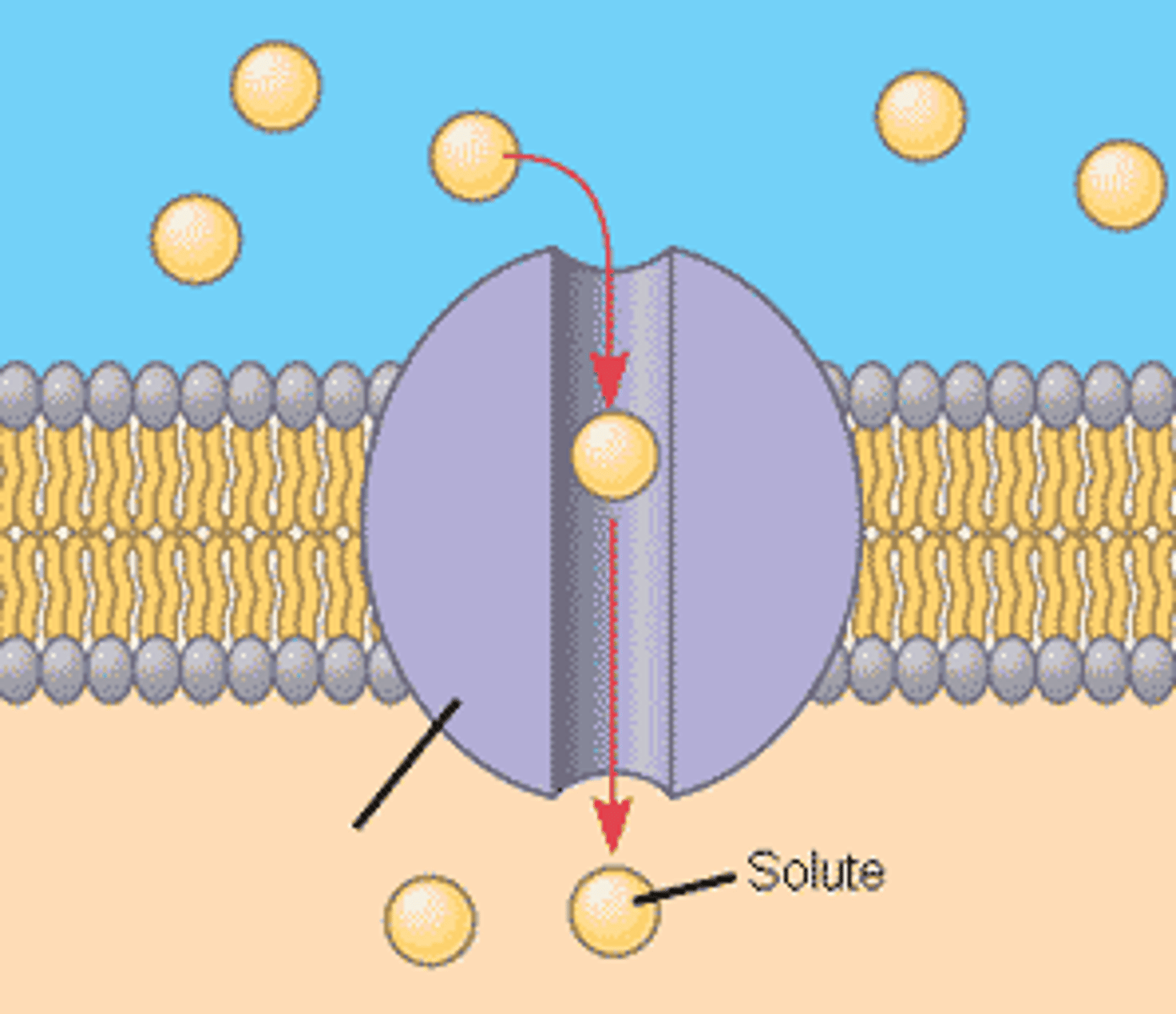
What are Channel Proteins
Transport proteins that have a water-filled hydrophilic channel that certain molecules/ions use as a tunnel through the membrane as ions are charged so they cannot pass directly through the membrane.
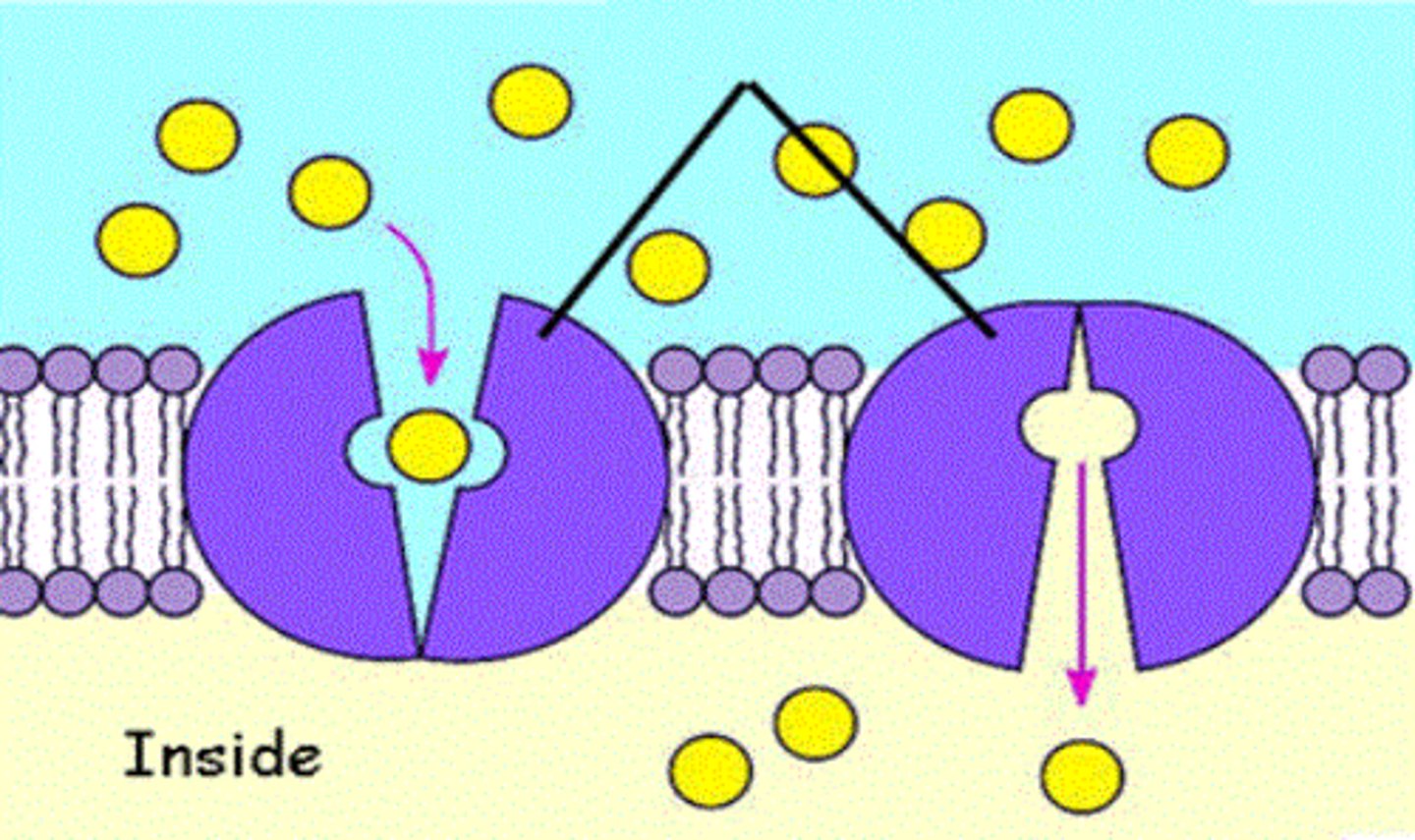
What are Carrier Proteins
A specialised membrane proteins that change shape when a certain molecule binds releasing the molecule on the other side on the membrane
(No ATP required)
Function of glycoproteins in plasma membrane
Made of a carbohydrate bound to a protein and these act as cell surface receptors allowing cells to be recognised and to join to each other.
Formula for magnification
Magnification = image size / real size
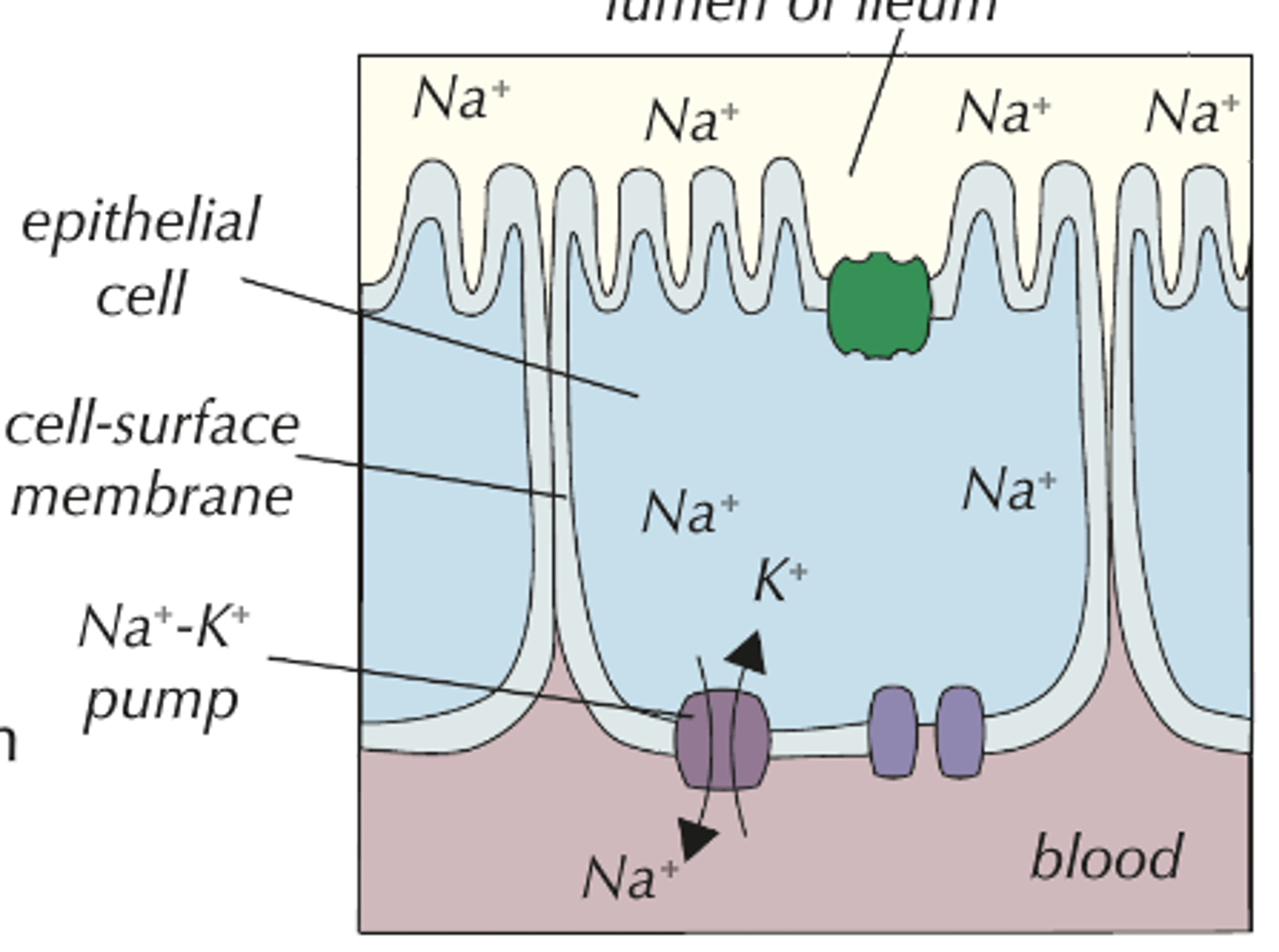
The Process of the co-transport of glucose
1. Sodium Ions are actively transported out of epithelial cells by the Sodium-Potassium Pump.
2. This lowers the concentration of Sodium Ions in the epithelial cells forming a concentration gradient from the lumen of the small intestine to the epithelial cells.
3. This causes Sodium Ions to diffuse in to the epithelial cells via the Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter protein which for every Sodium Ion moves one glucose into the cell.
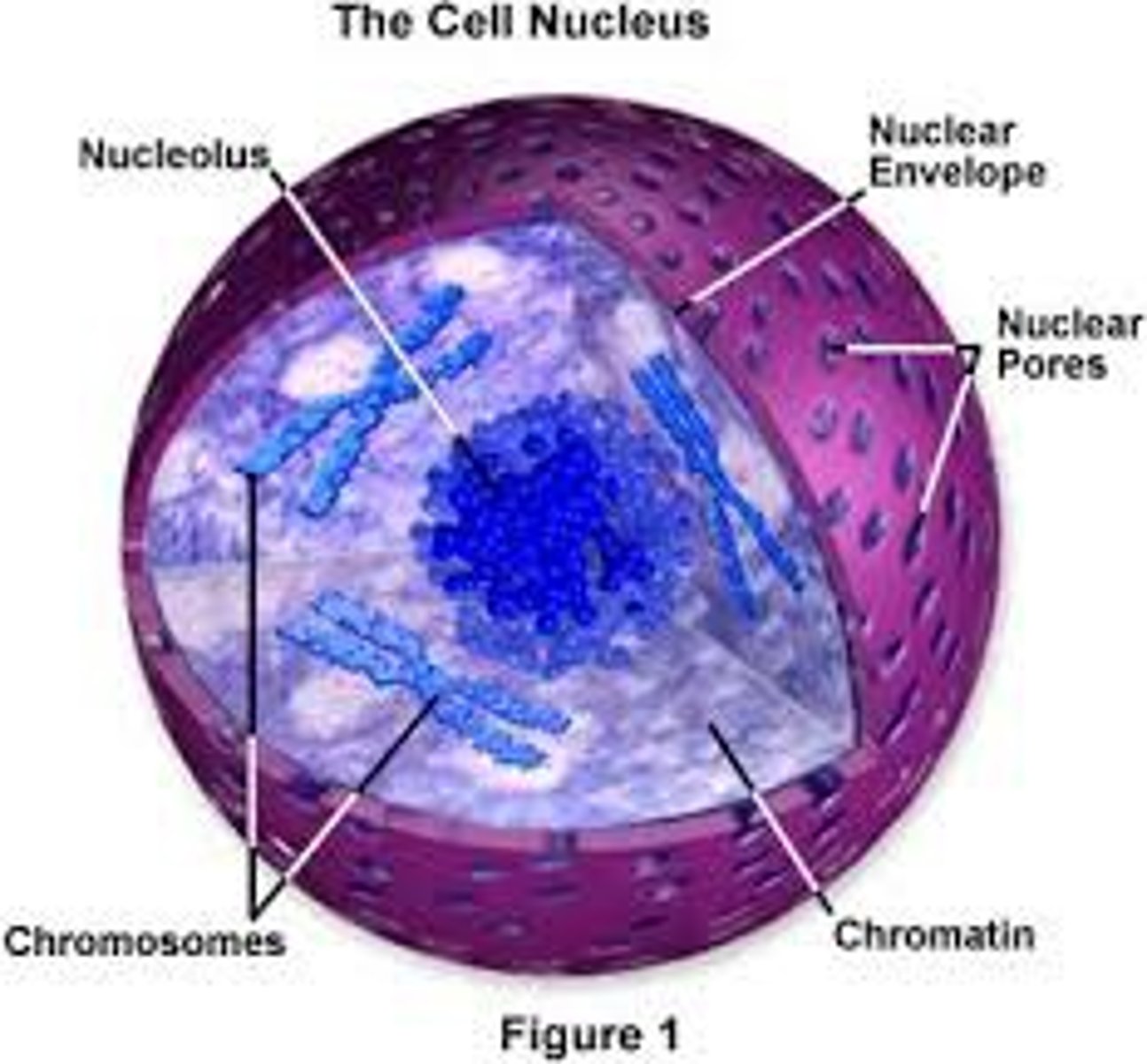
Structure and function of the Nucleus
A large organelle surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
The Nucleolus makes Ribosomes.
Contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes
What are chromosomes
Protein (Histone) bound linear DNA, each formed of two chromatids
Structure of Chloroplasts
Small flattered structure found in plant and algae cells.
They have a double membrane
They contain thylakoid membranes, which are stacked to form grana
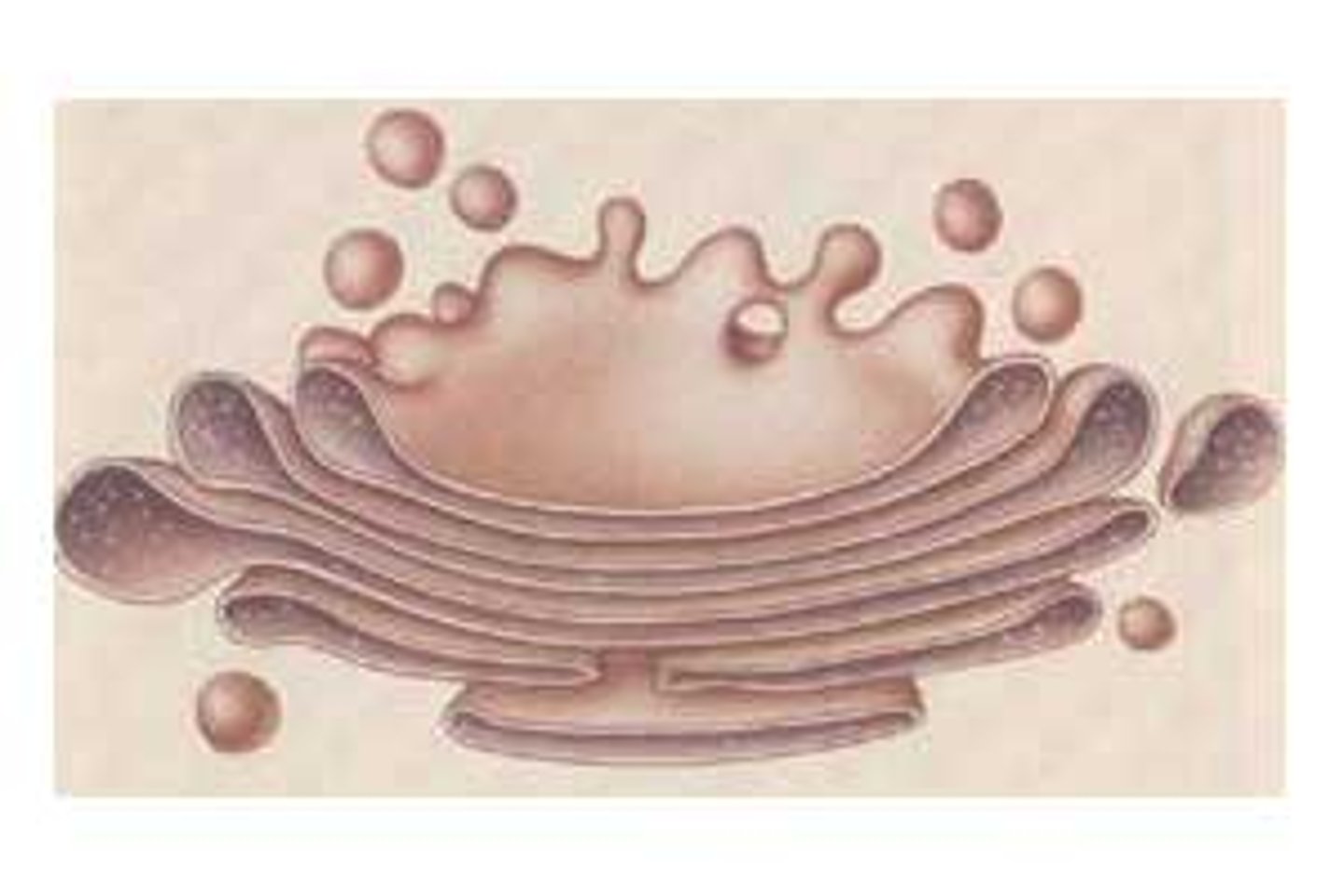
Structure and function of the Golgi apparatus
A group of fluid-filled flattered sacs with vesicles often found at the edges
Process and packages lipids and proteins and then vesicles transport them out of the cell
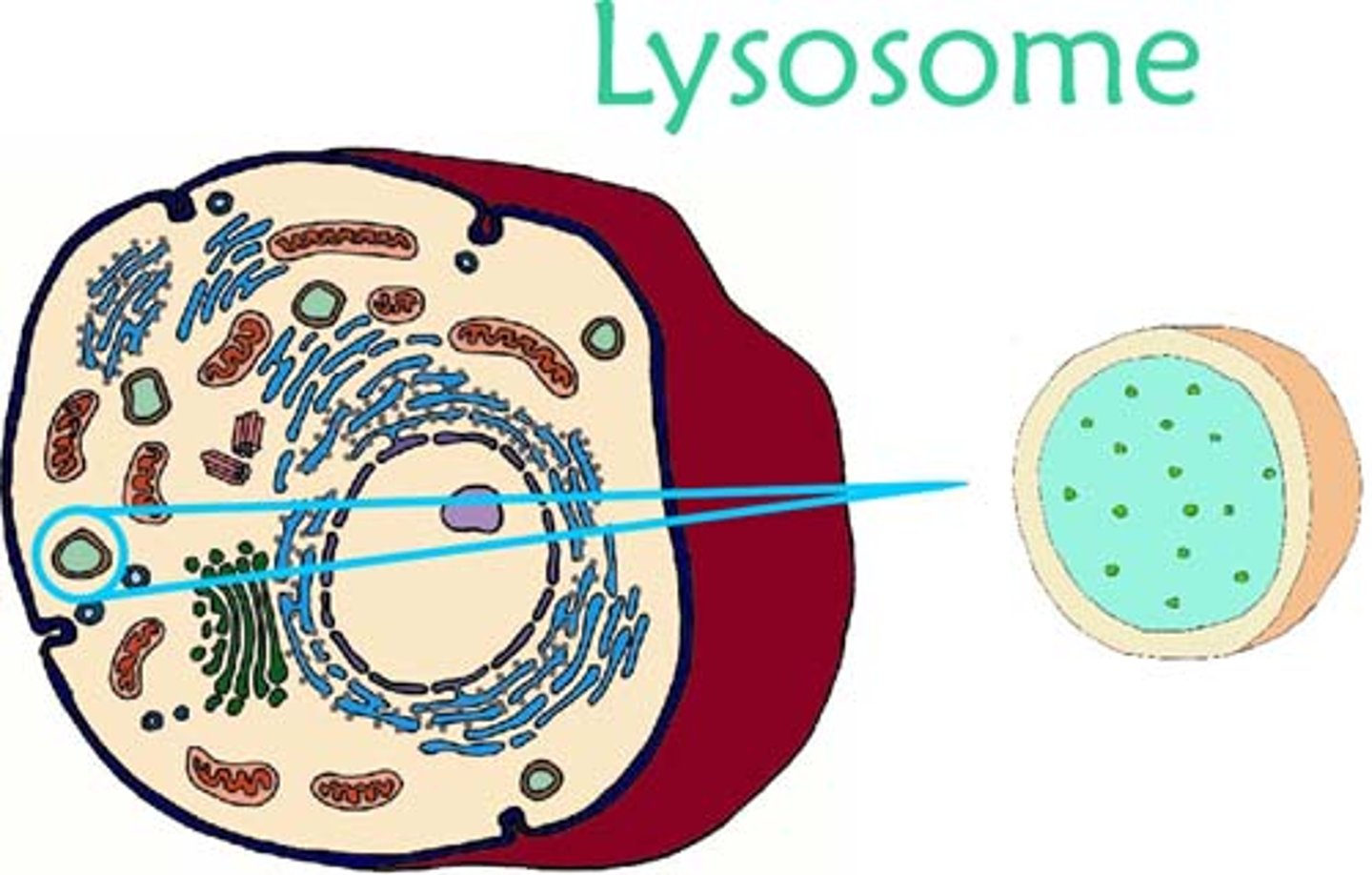
Structure and function of Lysosomes
A round organelle surrounded by a plasma membrane with no clear internal structure.
Can contain digestive enzymes
A type of vesicle
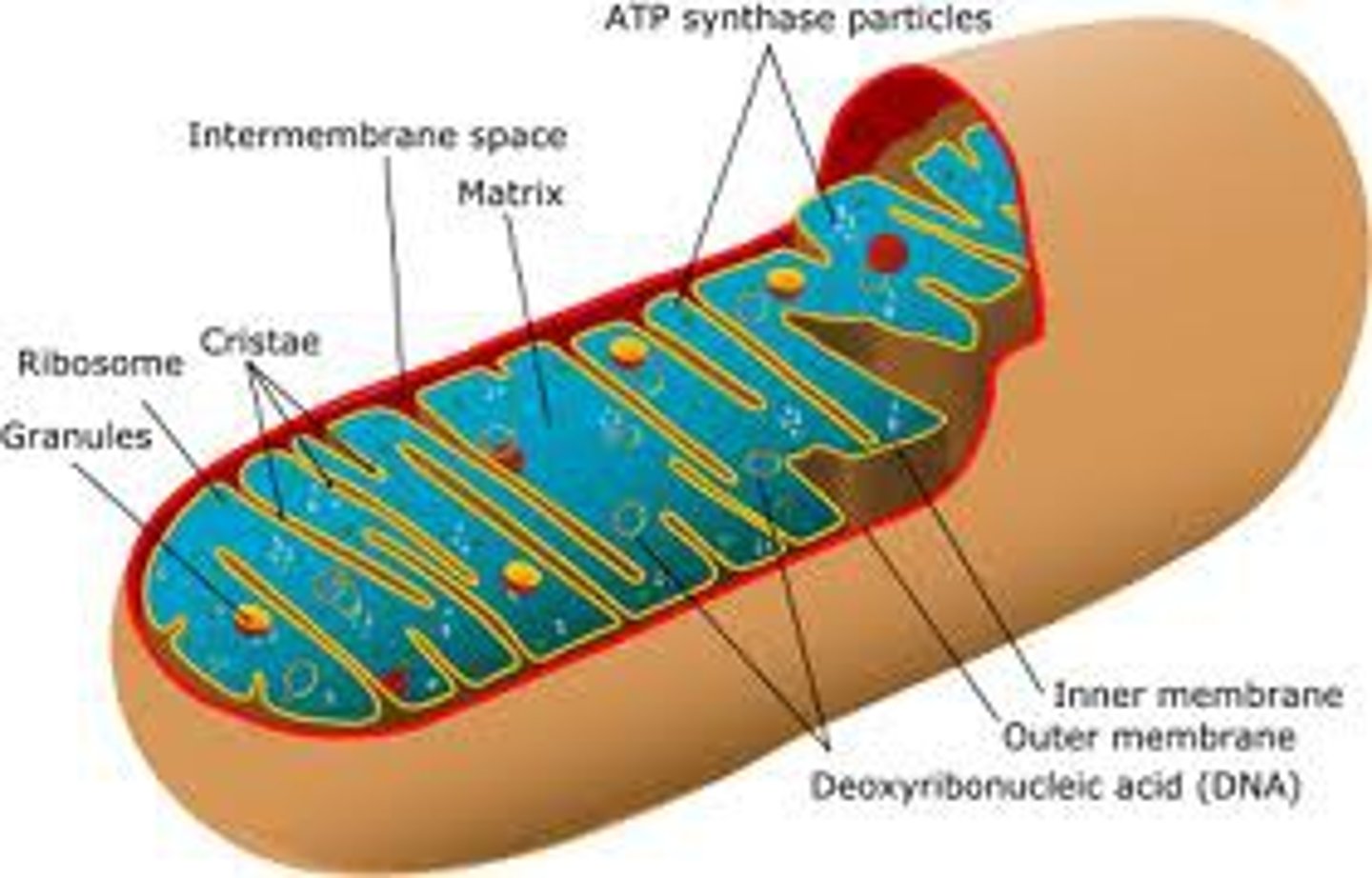
Structure of Mitochondria
Oval shaped with a double membrane, inner membrane is folded to form Cristae

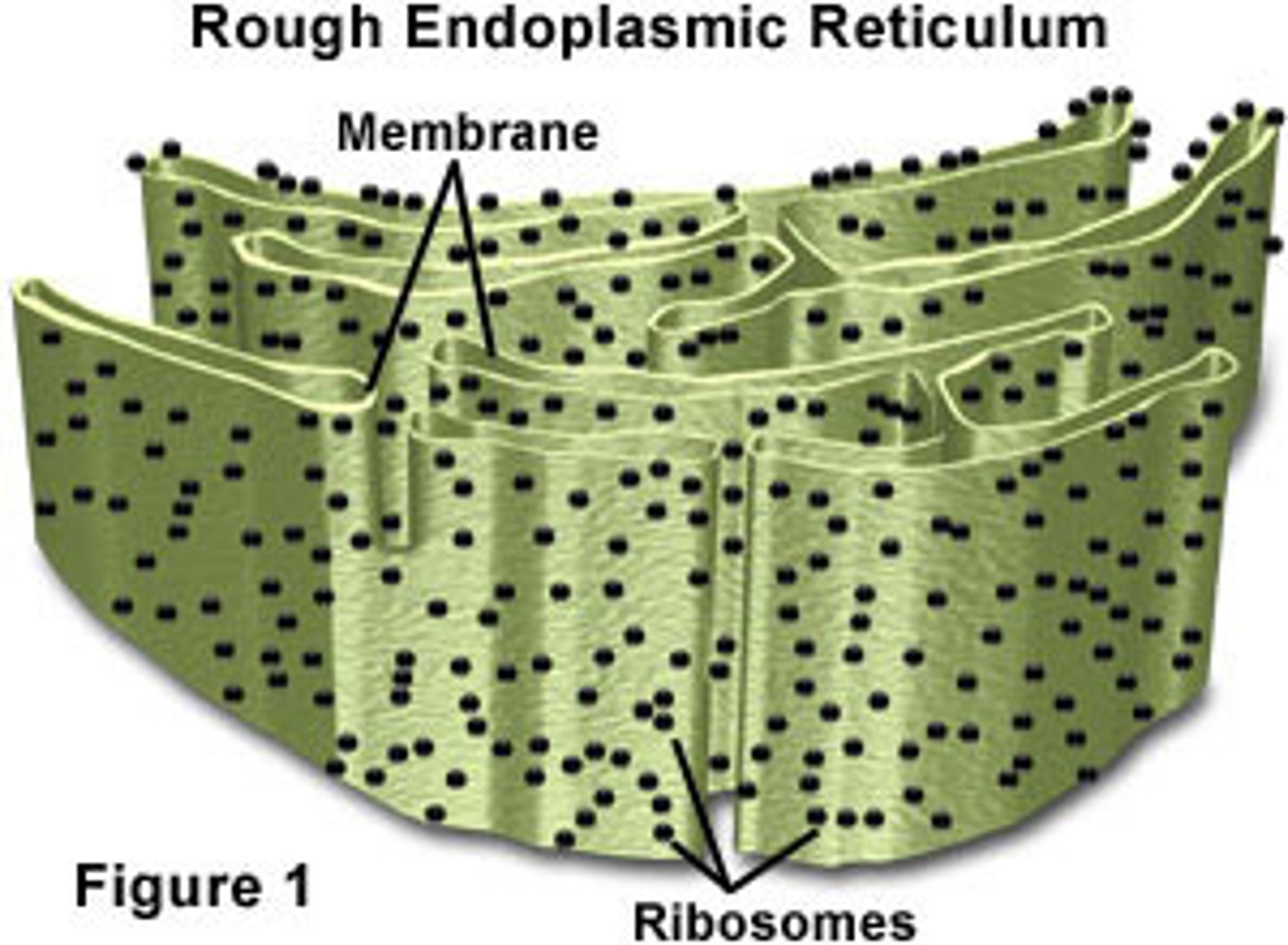
Structure and function of the RER
A system of fluid filled membrane bound sacs
Surface is covered in ribosomes
Fold and processes proteins
Structure and function of the SER
Similar structure to RER but with no ribosomes
Synthesises and processes lipids
Structure and function of the Cell Wall
A rigid structure that surround plant, algae and fungal and bacteria cells.
In plants and algae this is made of Cellulose
In fungal this is made of chitin
In bacteria this is made of murein
Structure and function of Vacuoles
A membrane bound sac found in the organelle surrounded by the TONOPLAST (a plasma membrane).
It contains cell sap (a weak salt and sugar solutions)
Important in maintain cells pressure and in the isolation of unwanted chemicals
Structure and function of Cell Membrane
a phospholipid, bilayer with embedded proteins to regulate molecules entering and leaving cytoplasm
Structure and function of Ribosomes
Organelles made of rRNA and protein
Found bound to the endoplasmic reticulum and free floating in the cytoplasm
Sites of protein synthesis
6 differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
1. Prokaryotic cells don't have a nucleus
2. Prokaryotic cells have circular DNA and no histone proteins
3. Prokaryotic cells have plasmids
4. Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles
5. Prokaryotic cells have a Murein Cell wall
6. Prokaryotic cells have 70s ribosomes compared to 80s in eukaryotes
Cell wall of fungi
Made of chitin
Conditions needed for cell fractionation
Reduced Temp
Isotonic
Buffered
3 Stages of Cell Fractionation
1. Homogenisation
2. Filtration
3. Ultracentrifugation
The Cell Cycle
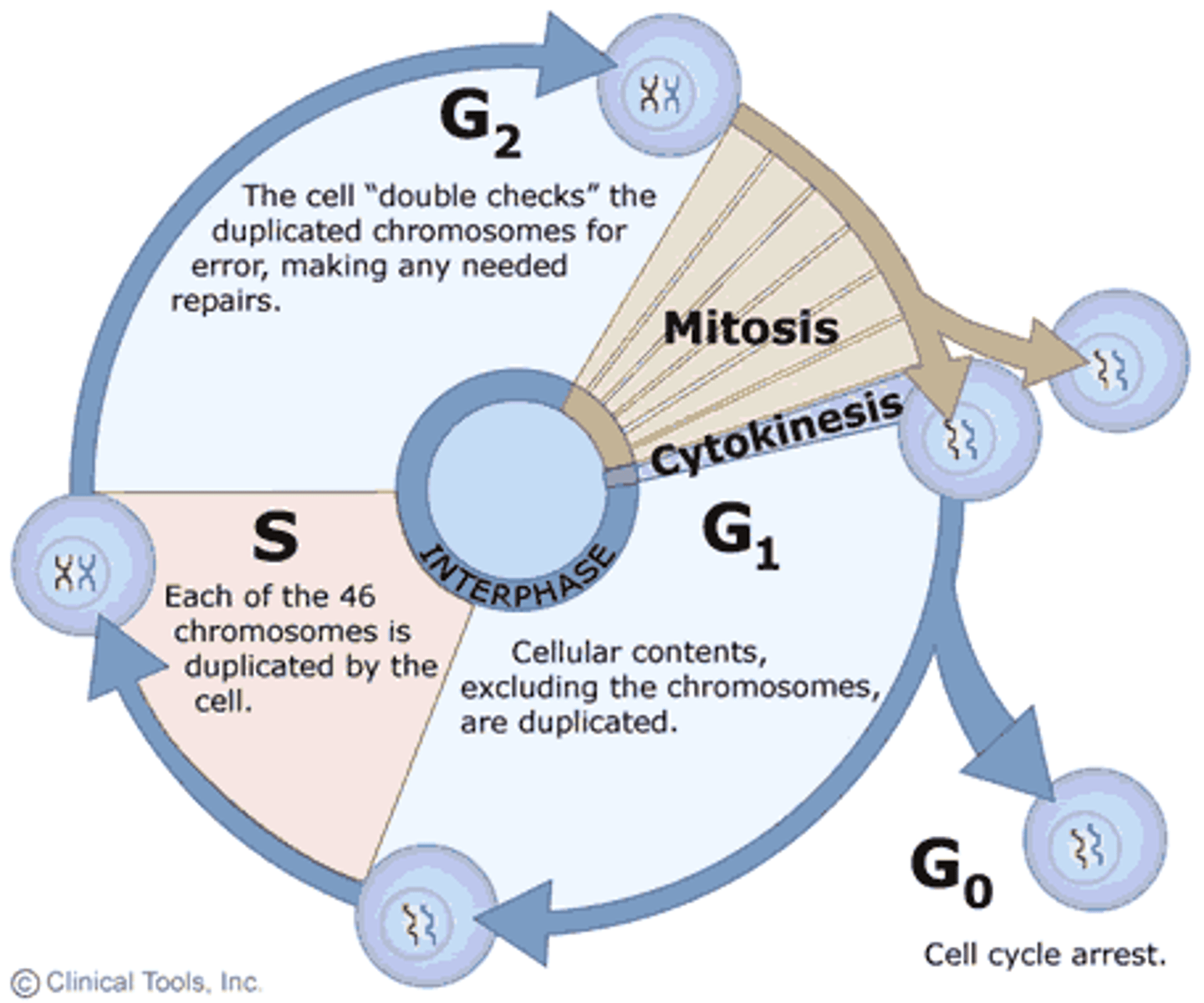
What happens in the G1 phase of interphase?
Growth
New Proteins & Organelles Made
What happens in the S phase?
DNA synthesis (or replication) occurs during this phase. At the beginning of the phase, each chromosome is single. At the end, after DNA replication, each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids.