Test 2
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:37 PM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
1
New cards
**High stiffness and strength**
can be alloyed for high rigidity, strength, and hardness
2
New cards
**Toughness**
capacity to absorb energy better than other classes of materials
3
New cards
**Good electrical conductivity**
metals are conductors
4
New cards
**Good thermal conductivity**
conduct head better than ceramics or polymers
5
New cards
**Cost**
the price of steel is very competitive with other engineering materials
6
New cards
**Cast metal**
starting form is a casting
7
New cards
**Wrought** metal
the metal has been worked or can be worked after casting
8
New cards
**Powdered** metal
starting form is very small powders for conversion into parts using powder metallurgy techniques
9
New cards
**Ferrous**
Those based on iron, steels, cast irons
10
New cards
**Nonferrous**
all other metals, aluminum, magnesium, copper, nickel, titanium, zinc, lead, tin, gold, silver
11
New cards
Alloy
a mixture or compound of two or more elements, at least one of which is metallic
12
New cards
The phase of Iron at room temperature
alpha, α, called ferrite
13
New cards
What does ferrite transform to as temperature rises?
Ferrite, alpha, to austenite, gamma, to delta
14
New cards
Steel
an iron-carbon alloy containing from 0.02% to 2.1% carbon
15
New cards
Cast iron
an iron-carbon alloy containing from 2.1% to about 4% or 5% carbon
16
New cards
**Ductile iron**
is formed by special melting and pouring treatment of gray cast iron
17
New cards
**Malleable iron**
is formed by heat treatment of white cast iron
18
New cards
THIS IS START OF CH 6 ASSIGNMENT
IGNORE
19
New cards
What are some of the general properties that distinguish metals from ceramics and polymers?
Typical metallic properties include: high strength and stiffness, good electrical and thermal conductivity, and higher density than ceramics or polymers
20
New cards
What are the two major groups of metals? Define them.
Ferrous metals, which are based on iron; and nonferrous, which includes all others.
21
New cards
What is a solid solution in the context of alloys?
A solid solution is an alloy in which one of the metallic elements is dissolved in another to form a single phase.
22
New cards
Distinguish between a substitutional solid solution and an interstitial solid solution.
A substitutional solid solution is where the atoms of the dissolved element replace atoms of the solution element in the lattice structure of the metal. An interstitial solid solution is where the dissolved atoms are small and fit into the vacant spaces (the interstices) in the lattice structure of the solvent metal.
23
New cards
What is an intermediate phase in the context of alloys?
An intermediate phase is an alloy formed when the solubility limit of the base metal in the mixture is exceeded and a new phase, such as a metallic compound (e.g., Fe3C) or intermetallic compound (e.g., Mg2Pb) is formed.
24
New cards
What is the range of carbon percentages that defines an iron‑carbon alloy as a steel?
The carbon content ranges from 0.02% to 2.11%.
25
New cards
What is the range of carbon percentages that defines an iron‑carbon alloy as cast iron?
The carbon content ranges from 2.11% to about 5%.
26
New cards
Identify some of the common alloying elements other than carbon in low alloy steels.
The common alloying elements in low alloy steel are Cr, Mn, Mo, Ni, and V. at least two
27
New cards
What is the predominant alloying element in all of the stainless steels?
Chromium
28
New cards
Besides high carbon content, what other alloying element is characteristic of the cast irons?
Silicon
29
New cards
Identify some of the properties for which aluminum is noted?
Aluminum is noted for its low density, high electrical and thermal conductivity, formability, good corrosion resistance due to the formation of a tough oxide film on its surface, and ability to be alloyed and strengthened to achieve good strength‑to‑weight ratios.
30
New cards
What are some of the noteworthy properties of magnesium?
Magnesium is noted for its very low density (lightest of the structural metals), propensity to oxidize (which can cause problems in processing), and low strength; however, it can be alloyed and strengthened by methods similar to those used for aluminum alloys to achieve respectable strength‑to‑weight ratios
31
New cards
What is the most important engineering property of copper that determines most of its applications?
Its high electrical conductivity (low resistivity).
32
New cards
What elements are traditionally alloyed with copper to form (a) bronze and (b) brass?
The elements are (a) tin and (b) zinc, respectively.
33
New cards
What are some of the important applications of nickel?
The important applications of Ni are (1) as an alloying ingredient in steel, e.g., stainless steel; (2) for plating of steel to resist corrosion; and (3) to form nickel‑based alloys noted for high‑temperature performance and corrosion resistance
34
New cards
35
New cards
What are the noteworthy properties of titanium?
Titanium is noted for its high strength‑to‑weight ratio, corrosion resistance (due to the formation of a thin but tough oxide film), and high temperature strength.
36
New cards
Identify some of the important applications of zinc.
The important applications of Zn are (1) die castings ‑ zinc is an easy metal to cast; (2) as a coating in galvanized steel; (3) as an alloying element with copper to form brass.
37
New cards
What important alloy is formed from lead and tin?
Solder
38
New cards
What is so special about the superalloys? What distinguishes them from other alloys?
The superalloys are generally distinguished by their strength and resistance to corrosion and oxidation at elevated temperatures.
39
New cards
What are the three basic methods by which metals can be strengthened?
The three basic methods are (1) alloying to form solid solutions and two‑phase structures which are stronger than the elemental metals; (2) cold working, in which the strain‑hardened metal is stronger and harder than the unstrained metal; and (3) heat treatment ‑ most of the commercial heat treatments are designed to increase the strength of the metal.
40
New cards
THIS IS START OF CH 21 SLIDES
IGNORE
41
New cards
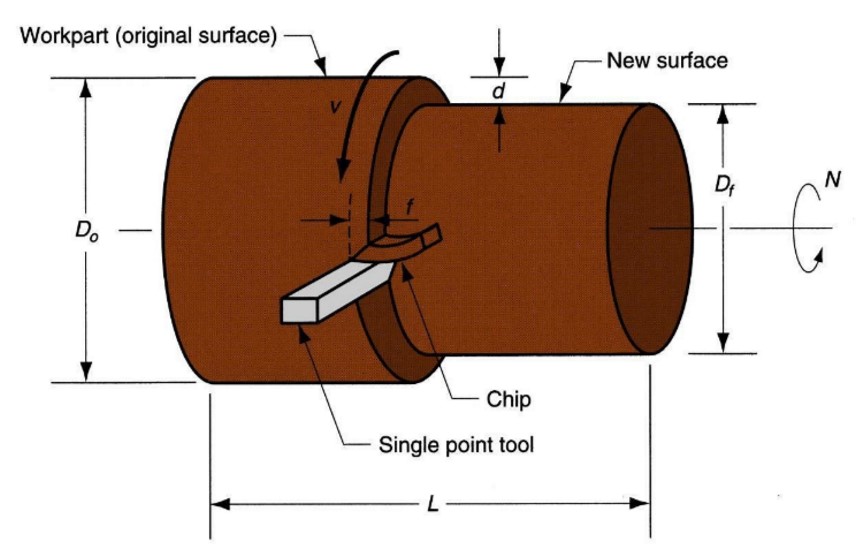
Machining
a material removal process in which a sharp cutting tool is used to mechanically cut away material so that the desired part geometry remains
42
New cards
Turning
\
43
New cards
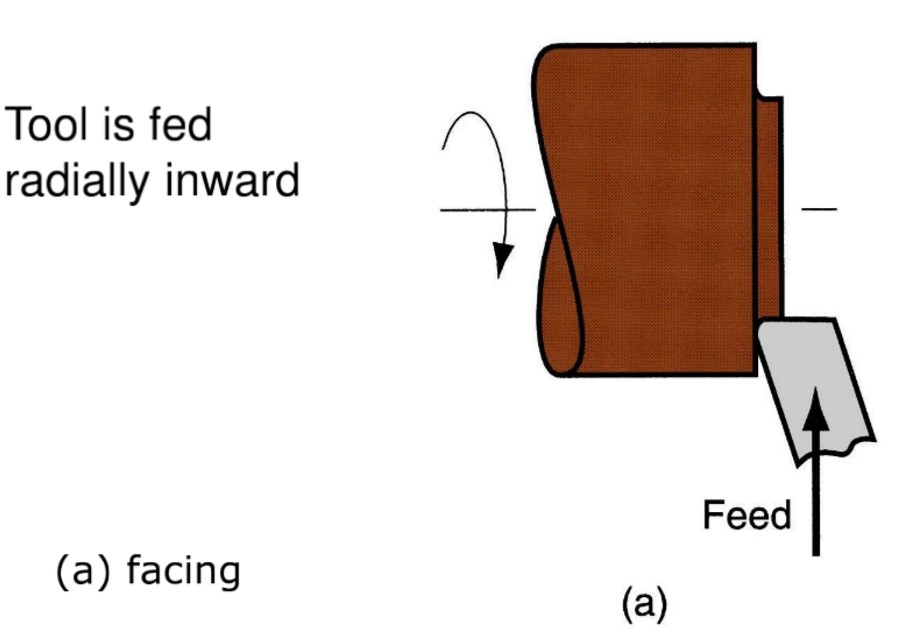
Facing
44
New cards
Contour Turning
instead of feeding tool parallel to axis of rotation, tool follows a contour that is other than straight, thus creating a contoured shape
45
New cards
Chamfering
cutting edge cuts an angle on the corner of the cylinder, former a chamfer
46
New cards
Cutoff
tool is fed radically into rotating work at some location to cut off end of part
47
New cards
threading
pointed form tool is fed linearly across surface of rotating work part parallel to axis of rotation at a large feed rate, thus creating threads
48
New cards
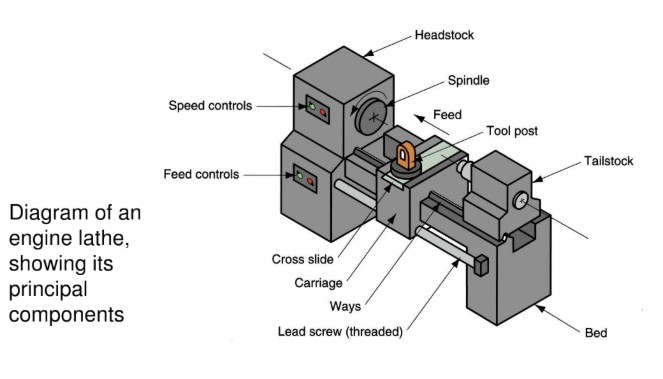
MANUAL LATHE
49
New cards
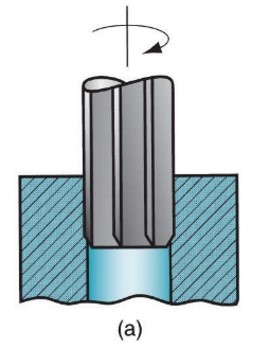
Reaming
50
New cards
tapping
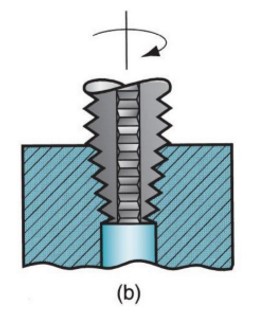
51
New cards
counterboring
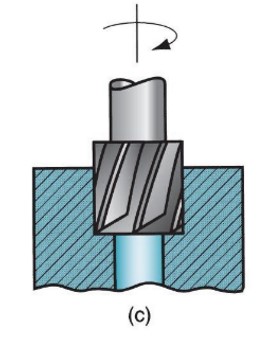
52
New cards
countersinking
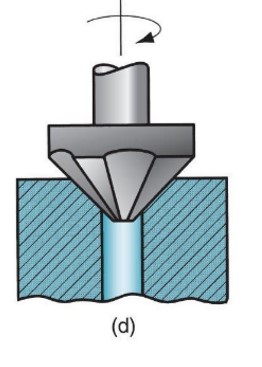
53
New cards
center drilling
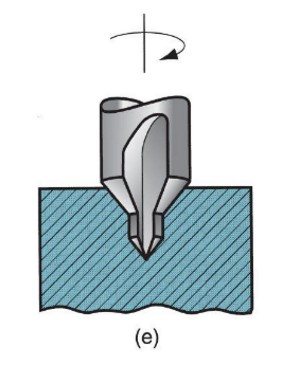
54
New cards
spot facing
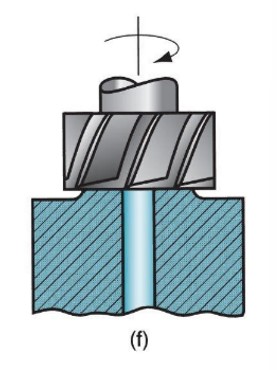
55
New cards
DRILL PRESS
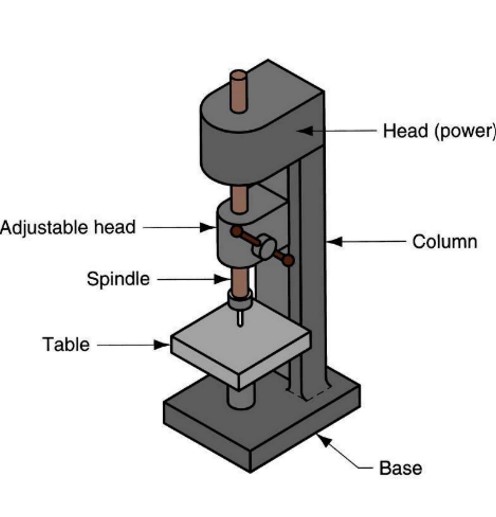
56
New cards
Vertical milling machine
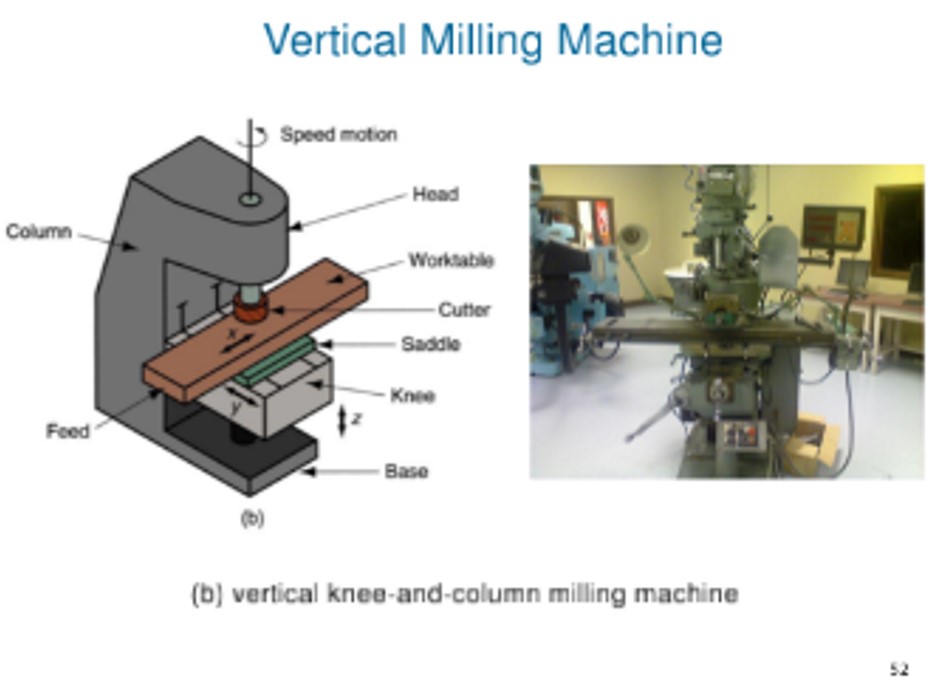
57
New cards
THIS IS START OF CH 6 QUIZ
RECHECK ANSWERS
58
New cards
Sand casting is which of the following types:
expendable mold
59
New cards
The upper half of a sand casting mold is called which of the following:
cope
60
New cards
In foundry work, a runner is which one of the following:
channel in the mold leading from the downsprue to the main mold cavity
61
New cards
A riser in casting is NOT described by which of the following:
an insert in the casting that inhibits buoyancy of the core
62
New cards
Which one of the following casting processes is the most widely used:
sand casting
63
New cards
For which one of the following reasons is a green mold named:
moisture is contained in the mold
64
New cards
Shell molding is best described by which one of the following:
casting process in which the mold is a thin shell of sand binded by a thermosetting resin
65
New cards
Which of the following qualifies as a precision casting process:
investment casting
66
New cards
Which of the following metals would typically be cast in die casting
aluminum
67
New cards
A misrun is which one of the following defects in casting:
metal solidifies before filling the cavity
68
New cards
START OF CH 39 40
69
New cards
The manufacturing engineering department in an organization is best described as which one of the following:
technical staff function
70
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a usual responsibility of the manufacturing engineering department?
marketing the product
71
New cards
Which of the following is considered a basic process, as opposed to a secondary process?
impression die forging
72
New cards
Which of the following would be considered a secondary process, as opposed to a basic process?
machining a metal casting
73
New cards
In a make or buy situation, the decision should always be to purchase the component if the vendor ’s quoted price is less than the in-house estimated cost of the component:
False
74
New cards
Which of the following is an operation to enhance physical properties?
annealing
75
New cards
A route sheet is a document whose principal function is which one of the following?
specifies the process plan
76
New cards
Which one of the following types of computer-aided process planning relies on parts classification and coding in group technology?
retrieval CAPP
77
New cards
Start of Jeopardy
jeopardy
78
New cards
For what is aluminum not noted
poor corrosion resistance. Has good corrosion resistance
79
New cards
CHECK PHOTOS
80
New cards
RANGE OF CARBON PERCENTAGES
81
New cards
the distance the tool advances into or along the workpiece each time the tool point passes a certain position in its travel over the surface is called
Feed
82
New cards
Ch 21 quiz
ch 21 quiz
83
New cards
In a turning operation, the change in diameter of the workpart is equal to which one of the following:
2 x depth of cut
84
New cards
A lathe can be used to perform which of the following machining operations:
boring
85
New cards
A facing operation is normally performed on which one of the following machine tools:
lathe
86
New cards
Knurling is performed on a lathe, but it is a metal forming operation rather than a metal removal operation:
true
87
New cards
Which one of the following cutting tools cannot be used on a turret lathe:
broach
88
New cards
Which one of the following turning machines permits very long bar stock to be used:
screw machine
89
New cards
Reaming is used for which of the following functions:
enlarge a drilled hole
90
New cards
End milling is most similar to which one of the following:
face milling
91
New cards
A planing operation is best described by which one of the following:
a workpart moves linearly past a single-point tool
92
New cards
A broaching operation is best described by which one of the following:
a tool with multiple teeth moves linearly past a stationary workpart