6. Diseases of the lens. Neoplasia of the eye.
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Describe the anatomy of the lens.
The crystallin lens is an avascular, transparent, & highly structured tissue.
It contains only a single layer of cuboidal cells, the anterior epithelium, inside the anterior lens capsule. Cortex, nucleus and posterior lens capsule.
The lens is attached to the ciliary body by fibres
Where in the eye has the most intensive refraction?
Cornea
Lens
What are examples of diseases of the lens?
Congenital abnormalities
Cataracts
Lens luxation and subluxation
Aphakia
Microphakia
Lenticonus/lentiglobus
Coloboma
Lens luxation
Vascular abnormalities (persistent pupillary membrane, PHTVL/PHPV)
What is coloboma of the lens?
Part of the lens is missing
What is lens luxation often in conjunction with?
Microphthalmia
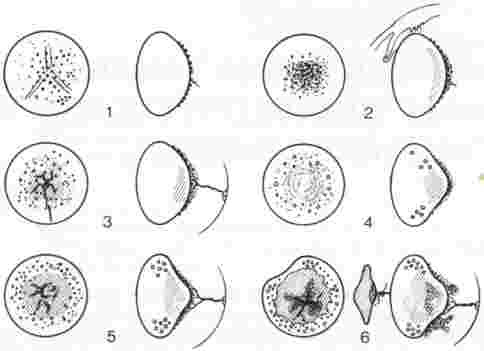
Grade 1: retro lens fibrovascular pigment/dots
Grade 2: dot + proliferation of retro lens tissue on the posterior lens capsule
Grade 3: plaque + persistent part of the hyaloid vessel
Grade 4: plaque + lenticonus
Grade 5: combination of Grades 3 and 4
Grade 6: combination of any grade with coloboma lentis, microphakia, retro lens pigment + bleeding
How can cataracts be classified?
Age
Aetiology
Consistency
Localisation
Degree of maturation
Congenital
Developmental
Juvenile
Senile
Acquired
Primary (hereditary)
Secondary (traumatic, due to intraocular diseases like uveitis, nutritional, radiation, diabetes, toxic, congenital abnormalities, senile)
Soft
Hard
Watery
Anterior capsular
Anterior subcapsular
Cortical (anterior or posterior)
Equatorial
Nuclear or perinuclear
Posterior subcapsular
Posterior capsular
Incipient
Immature
Mature
Hypermature

Wrinkling of the anterior lens capsule, crystal formation, liquefaction by proteolysis, and potential ventral settling of the lens nucleus
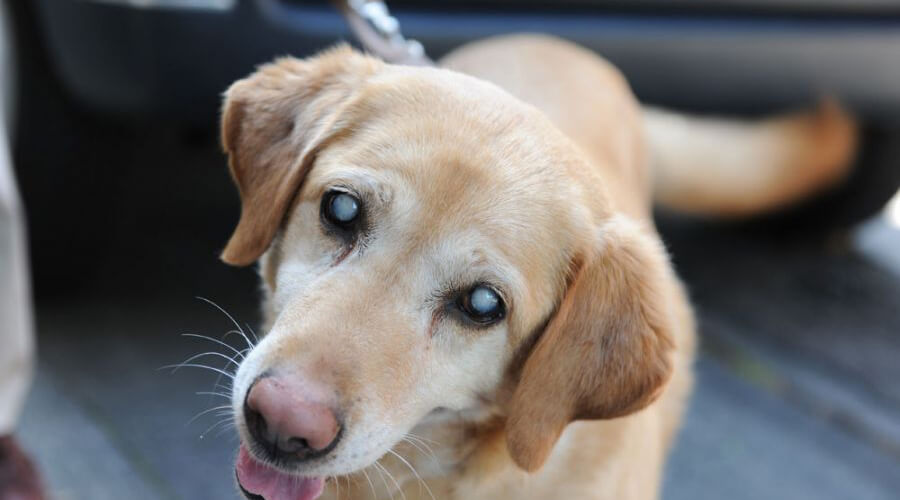

Spontaneous recovery (rare)
Conservative management (topical mydriatics, aldose reductase inhibitors)
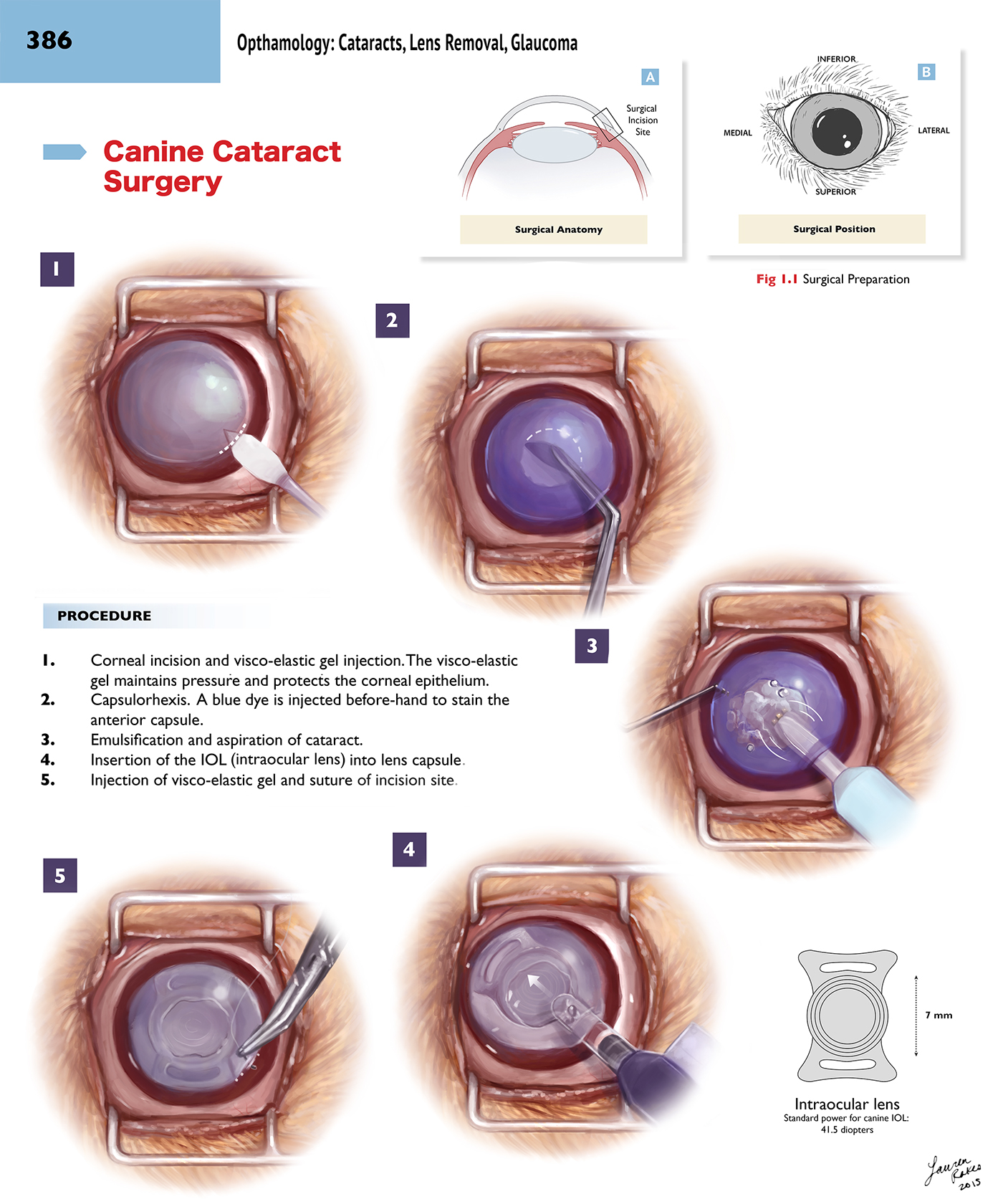
Surgical removal of the lens
Extracapsular cataract extraction (leaving the capsule)
Intracapsular extraction (removing the capsule)
Phacoemulsification (using ultrasound to break up and aspirate the lens – the gold standard) with intraocular lens implantation
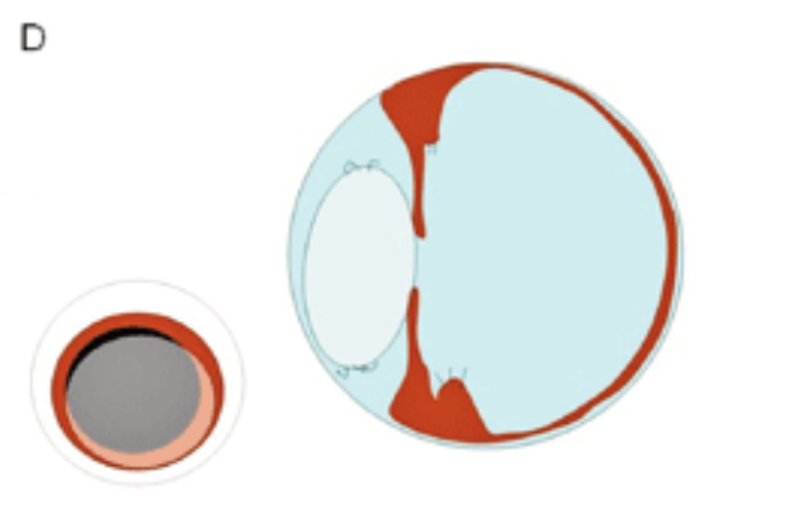
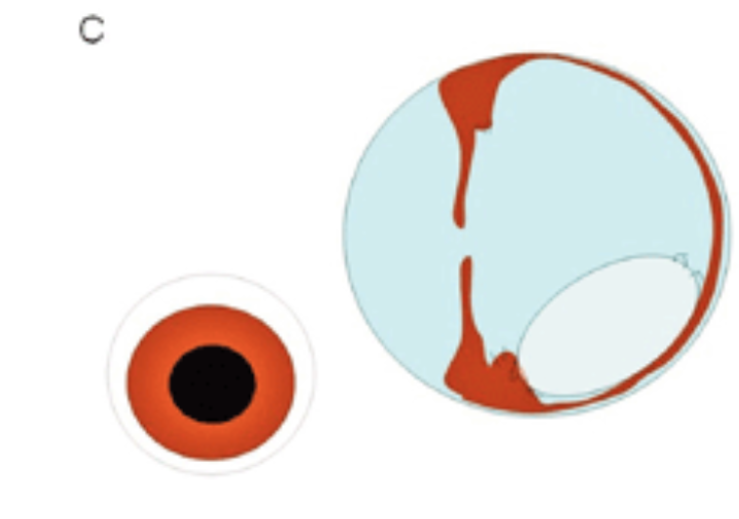
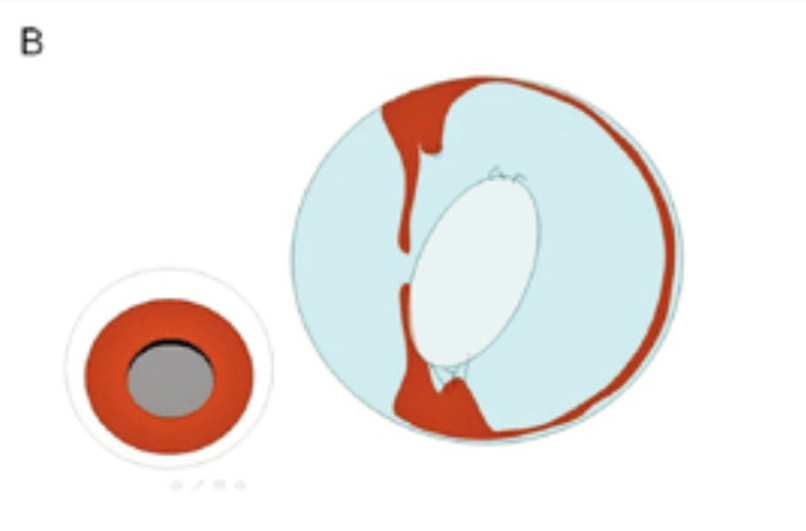
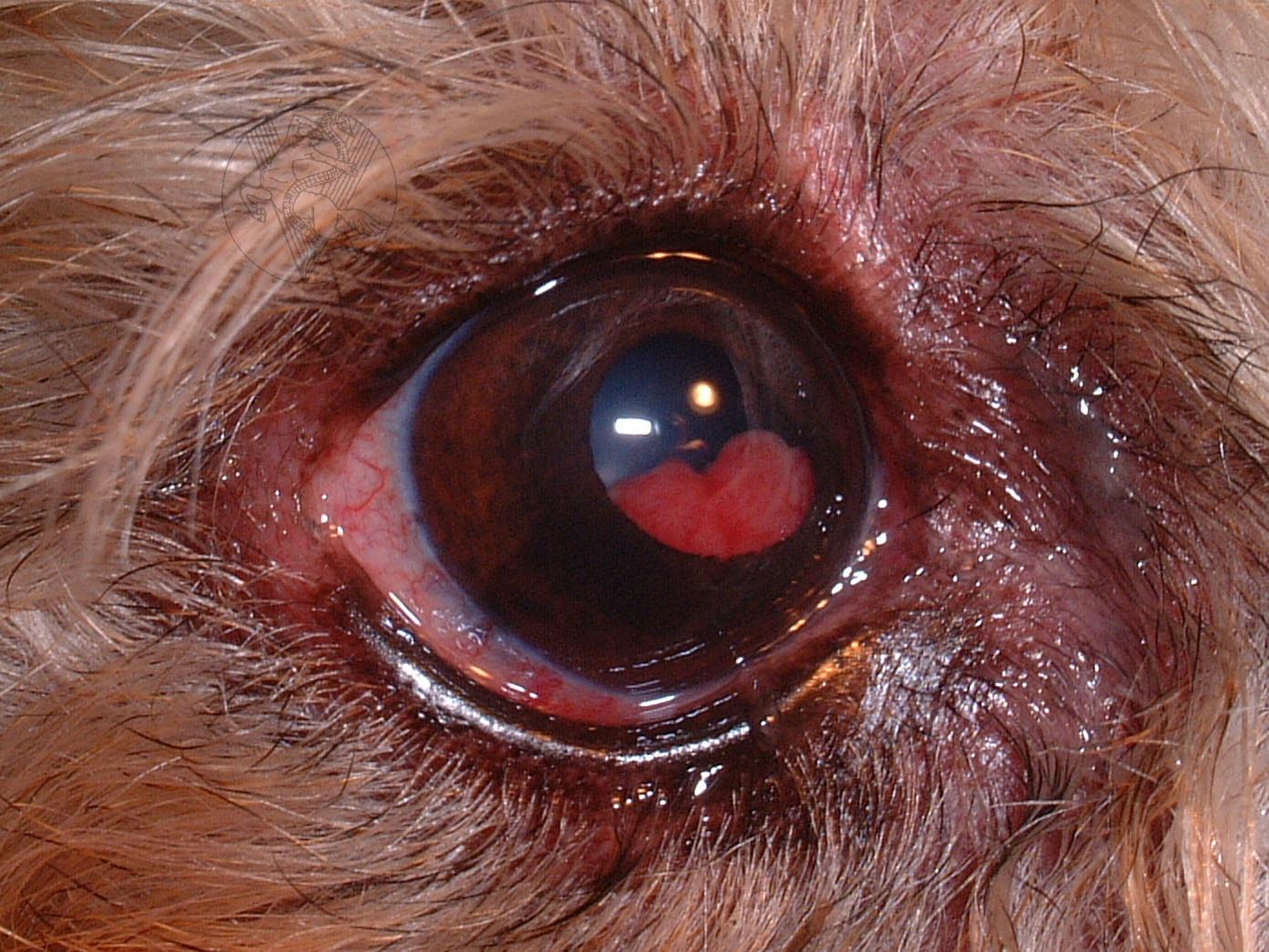
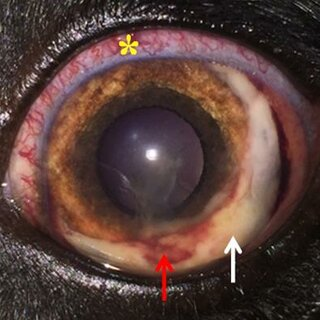
What are examples of neoplasia of the eye?
Iris melanoma
Ciliary body adenoma/adenocarcinoma
Uveal canine lymphoma
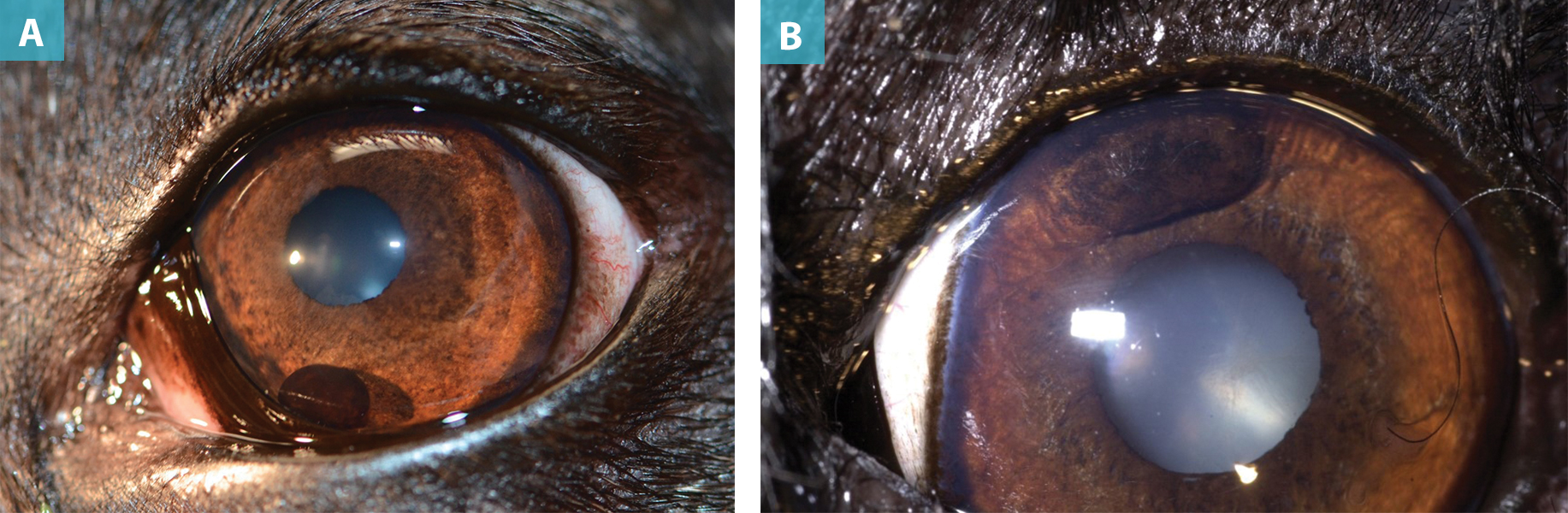
Pink-red mass in pupil, swollen conjunctiva, prominent third eyelid, mydriasis, detached retina, and potential glaucoma