Amines
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
what are amines?
nitrogen compounds in which one or more of the H atoms in NH3 has been replaced by an alkyl group
uses of amines?
Dyes, nylon, drugs, synthesis of new molecules; theyre very reactive
what are primary amines?
amines with one alkyl group attached to the N atom
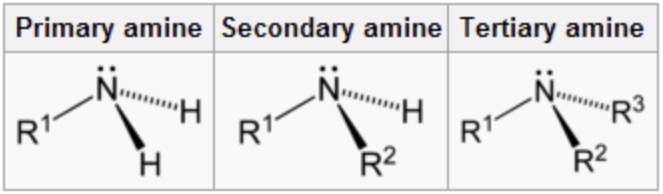
secondary amine?
amines with two alkyl groups attached to the N atom
tertiary amine?
amines with three alkyl groups attached to the N atom
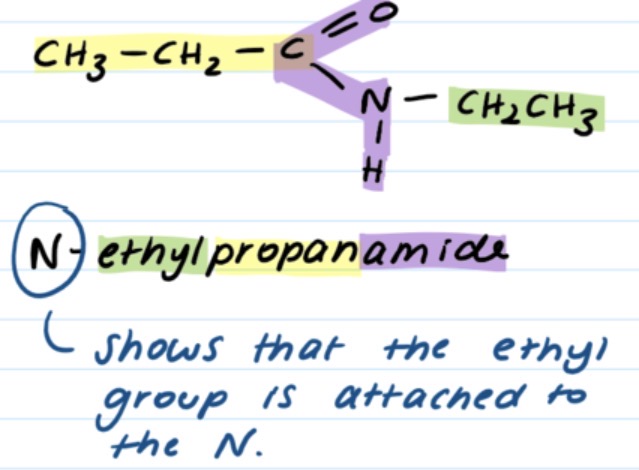
suffix for amines?
-amine
prefix for amines if other functional groups are present?
amino-
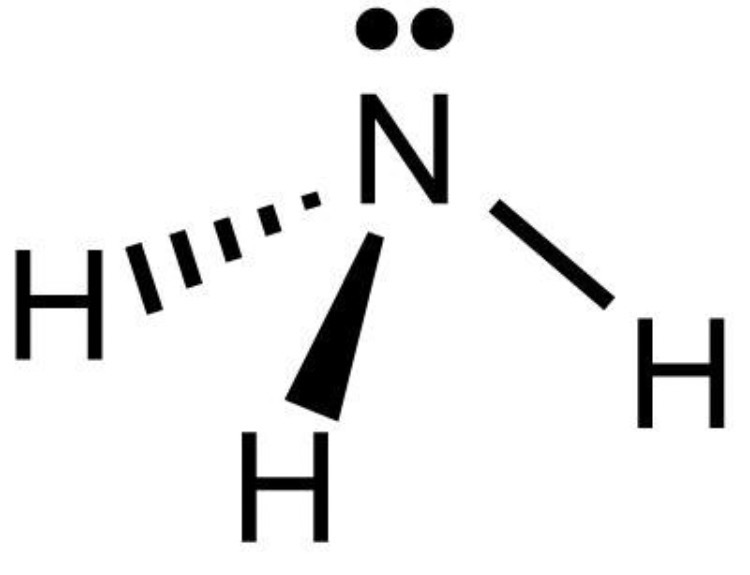
shape of amines? (such as ammonia)
pyramidal, 107° - due to presence of a lone pair
2 processes that produce amines?
nucleophilic substitution, reduction of nitriles
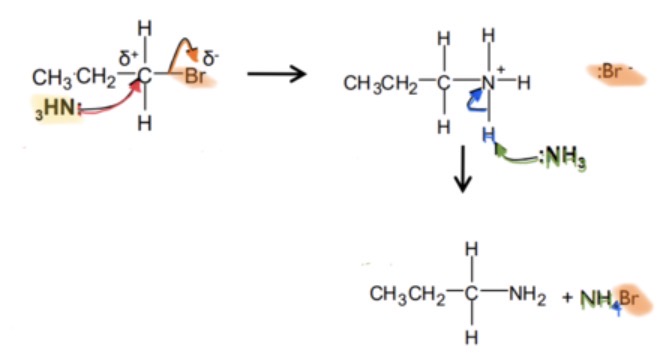
production of amines by nucleophilic substitution reaction?
primary/secondary amine + halogenoalkane -> alkyl-substituted amine + halogen acid
halogenoalkane + ammonia -> primary/secondary amine nucleophilic substitution mechanism?
if the substitution reaction continues until all the hydrogen atoms have been replaced with organic groups, what can be produced?
quaternary ammonium salt (quaternary ammonium cation and a halide ion)
reaction to produce a quaternary ammonium salt?
tertiary amine + halogenoalkane -> quaternary ammonium cation + halide anion
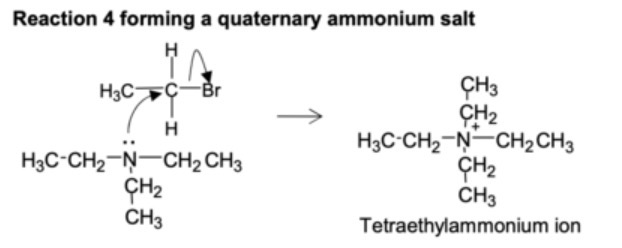
why are a mixture of products produced in the nucleophilic substitution reactions?
theres a number of possible substitutions
why does this reaction have low efficiency?
a mixture of products are produced, and reaction conditions have to be changed so only a single substitution occurs
how are reaction conditions changed to produce only a primary amine?
ammonia added in excess, or mixture of products can be separated using fractional distillation
how are nitriles reduced to produce amines?
hyrogenation
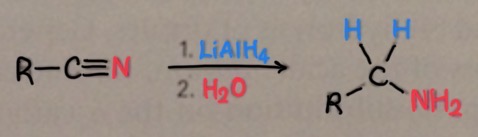
what does reduction of nitriles require?
LiAlH4 (reducing agent)
acidic conditions
or a conbination of hydrogen and nickel (catalytic hydrogenation)
how are aromatic amines produced? conditions?
reduction of nitrobenzene using concentrated HCl and a tin catalyst
what makes aromatic amines good conditioners?
theyre cationic surfacants, the two ends are attracted to different substances, preventing static from building ip on surfaces
what are cationic surfacants?
molecules with a positive and negative end
how are cationinc surfacants useful in industry?
static is prevented from building up on surfaces
what is a base?
proton acceptor
are amines bases? why?
yes because the lone pair on the nitrogen atom can accept protons
what does the base strength of amines depend on?
how available the electron pair is on the molecule;
more available electrons = more likely to accept a proton = stronger
why are amines weak bases?
Lone electron pair on nitrogen atom can accept protons, but its not always available
in organic molecules what affects how availale a lone electron pair is?
functional groups, by changing electron density around the bond
what is the inductive effect?
where different functional groups can affect how available a lone electron pair is by changing electron density around the bond
example of negative inductive effect?
benzene rings - draw electron density away from the nitrogen making it less available, so weaker base
example of positive inductive effect?
alkyl groups - push electron density towards the nitrogen making it 'more available', more alkyl groups means more pushing
are aliphatic amines or aromantic amines stronger bases?
aliphatic amines are stronger bases, aromantic amines are weaker
what are aliphatic amines?
amines without a benzene ring
how to amines act as nucleophiles?
the lone electron pair on nitrogen is attracted to delta positive regions
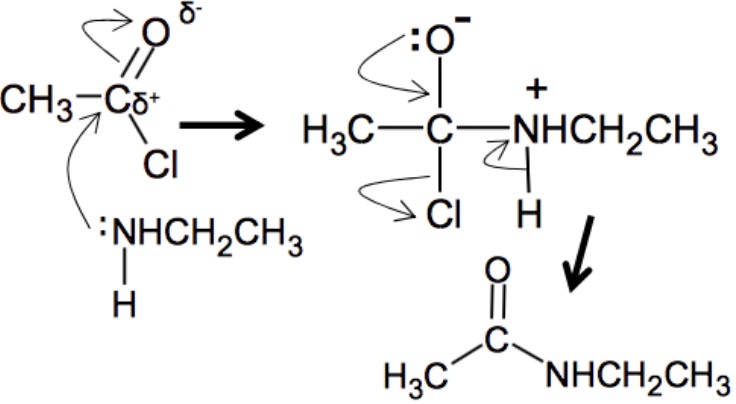
when amines undergo nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions with acyl chlorides, what is produced?
amides and N-substituted amides
acyl chloride + amine mechanism?
acid anhydride + amide -> ?
carboxylic acid (nucleophilic addition-elimination)
when naming n-substituted amides, what other functional group rules is it similar to?
esters