Overview of CNS: Cerebral Cortex, Brainstem, and Cerebellum
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Nervous System has 2 anatomically distinct divisions:
central nervous system (CNS)
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
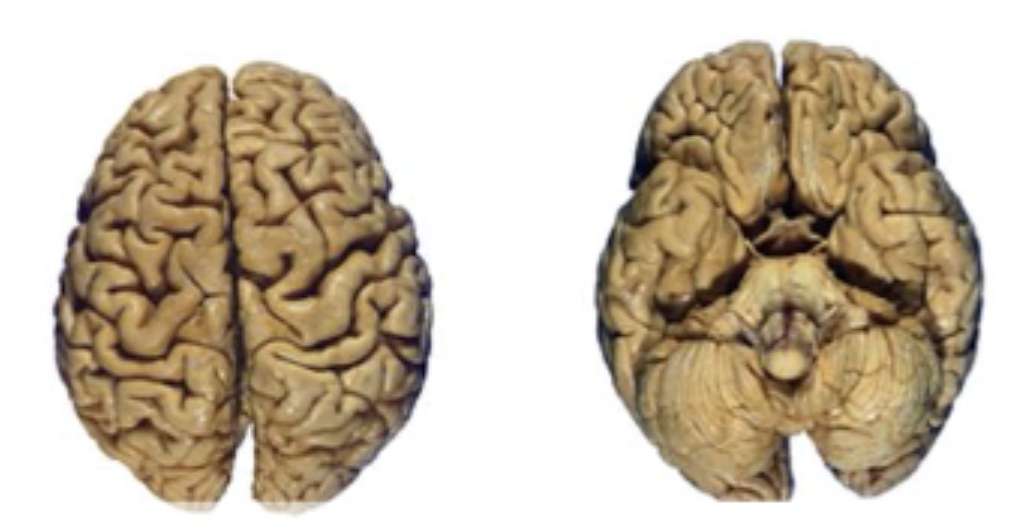
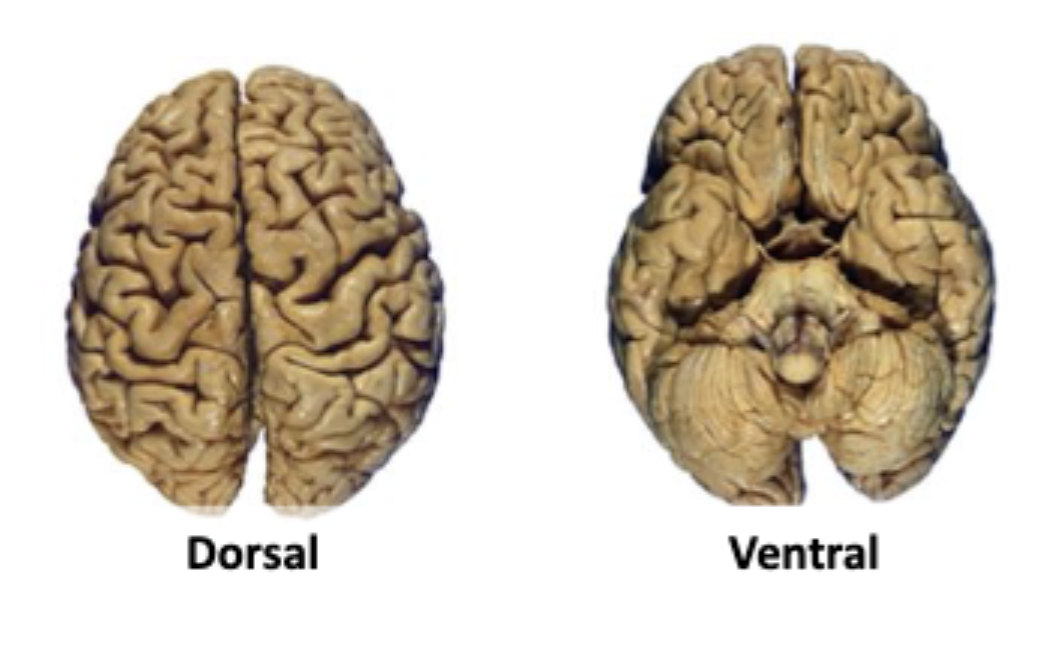
which side is dorsal vs ventral views?
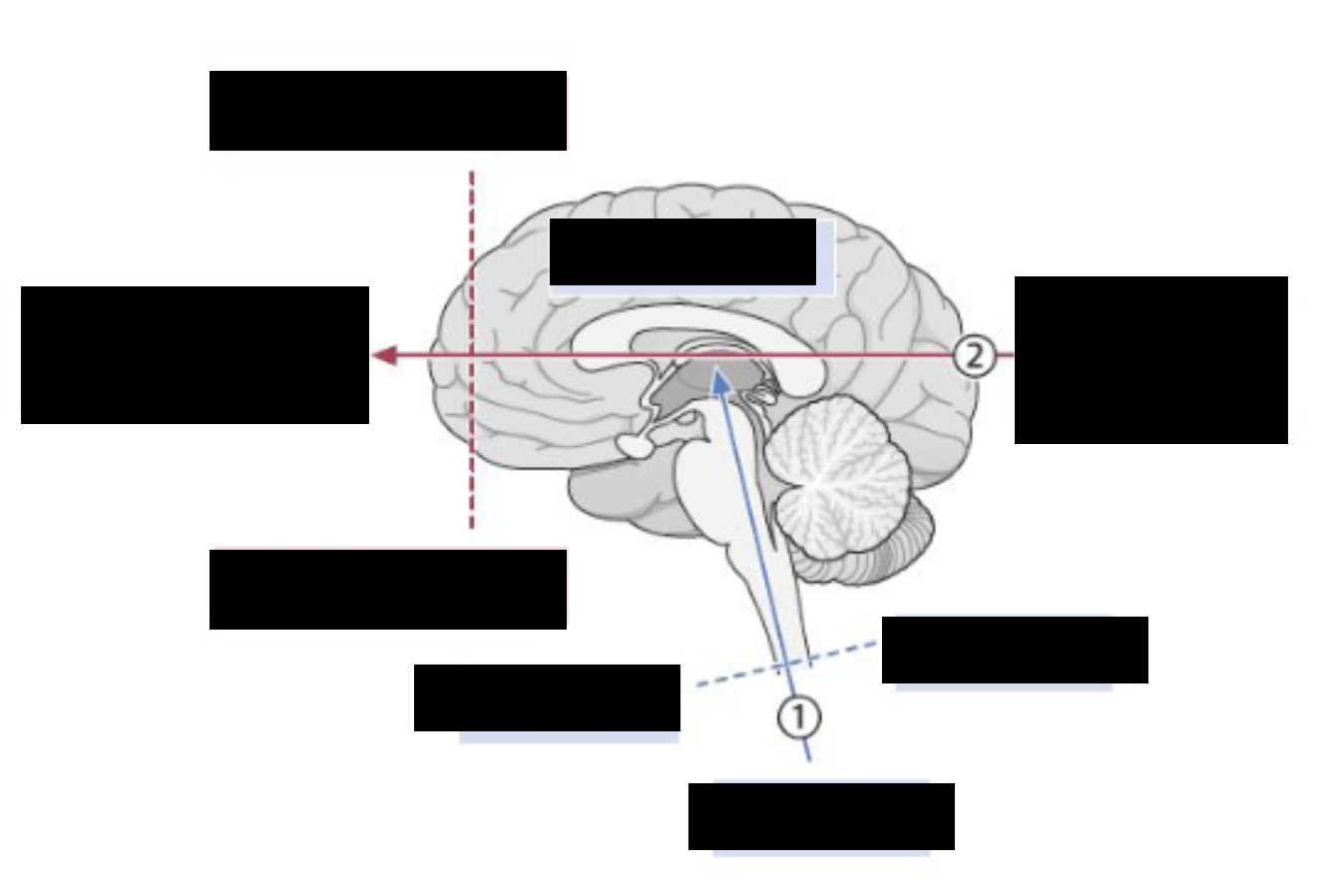
label the anatomical/directional
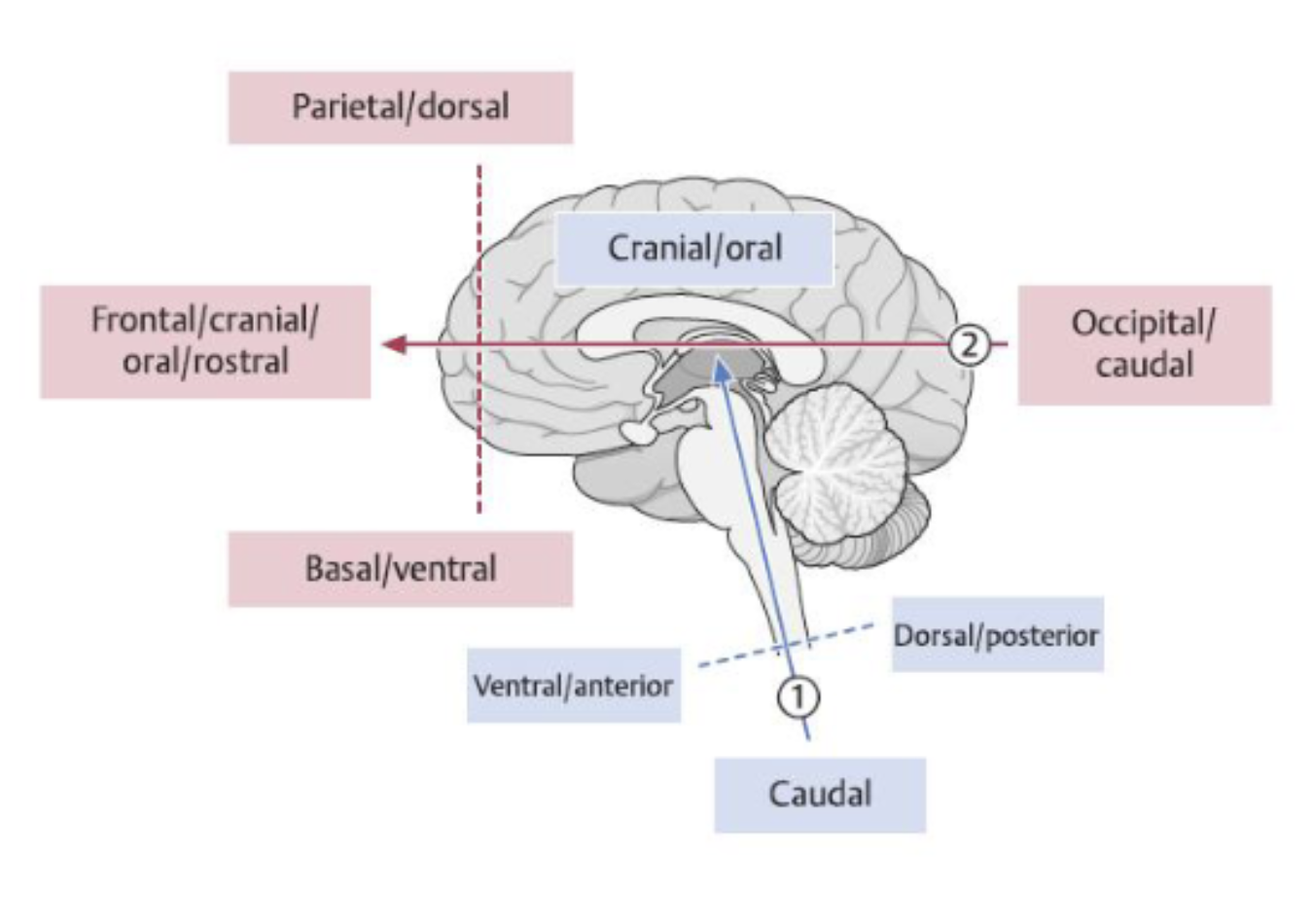
what does encephalon mean?
thing inside the head
what are the 3 primary brain vesicles during embryology?
prosencephalon (forebrain)
mesencephalon (midbrain)
rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
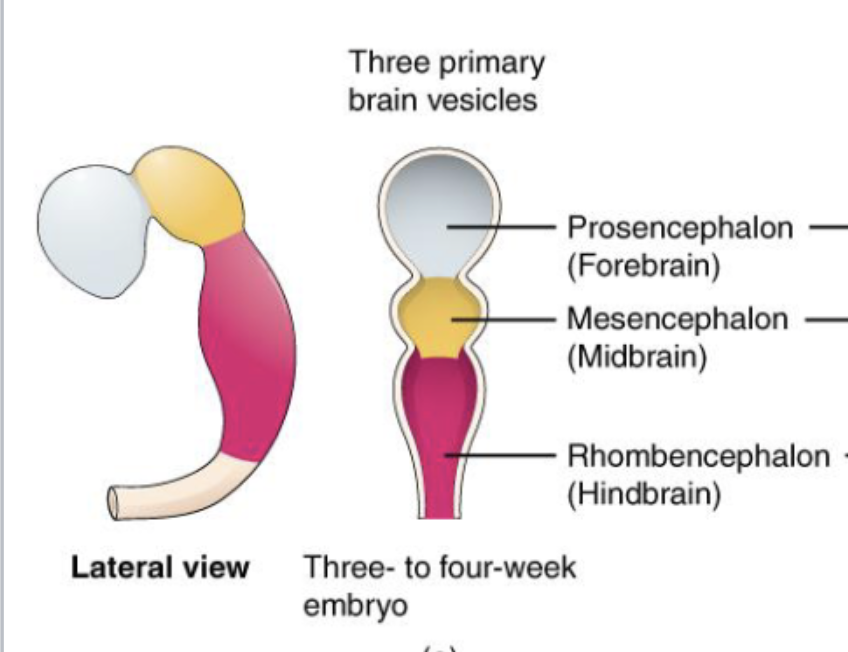
what secondary vesicles develop from each of the primary brain vesicles during embryology?
prosencephalon (forebrain)
telencephalon
diencephalon
mesencephalon (midbrain)
mesencephalon
rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
metencephalon
myelencephalon
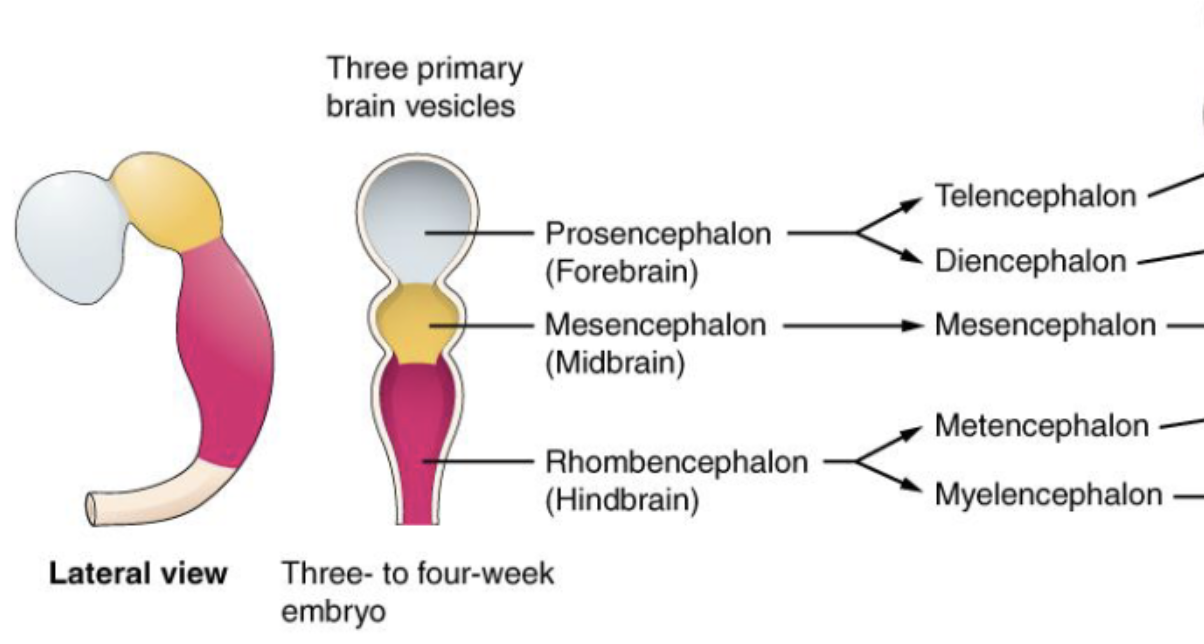
what adult brain structures are formed from each of the 5 secondary brain vesicles?
1. Telencephalon → Cerebrum (Cerebral Cortex,basal ganglia,hippocampus)
2. Diencephalon → Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus
3. Mesencephalon → Midbrain
4. Metencephalon → Pons and Cerebellum
5. Myencephalon → Medulla Oblongata
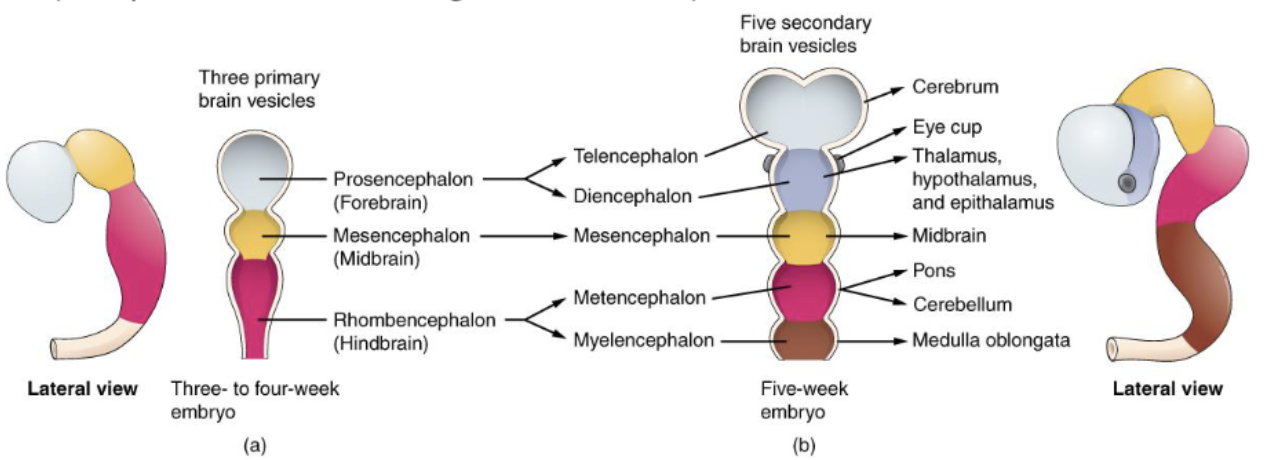
what secondary brain vesicle form does the cerebrum come from?
Telencephalon
what secondary brain vesicle form does the thalamus come from?
diencephalon
what secondary brain vesicle form does the midbrain come from?
mesencephalon
what secondary brain vesicle form does the pons and cerebellum come from?
metencephalon
what secondary brain vesicle form does the medulla oblongata come from?
myencephalon
what divides the brain into left and right hemispheres?
median longitudinal fissure
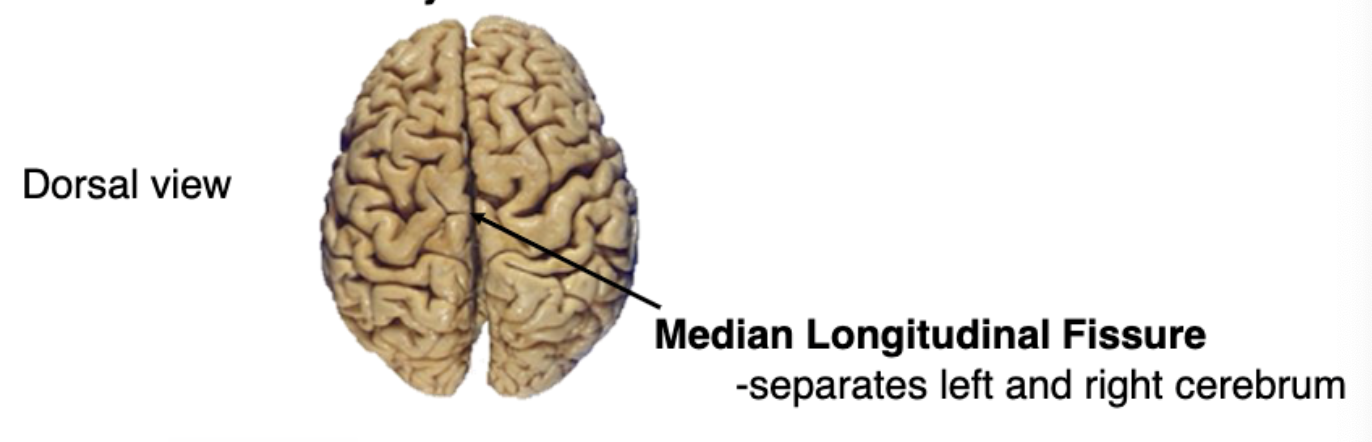
the convolutions observed on the surface of the brain are formed by
gyri and sulci
gyri increase the amount of 6-layered cortex. what does this help achieve?
increases the amount of information processing brain is capable of
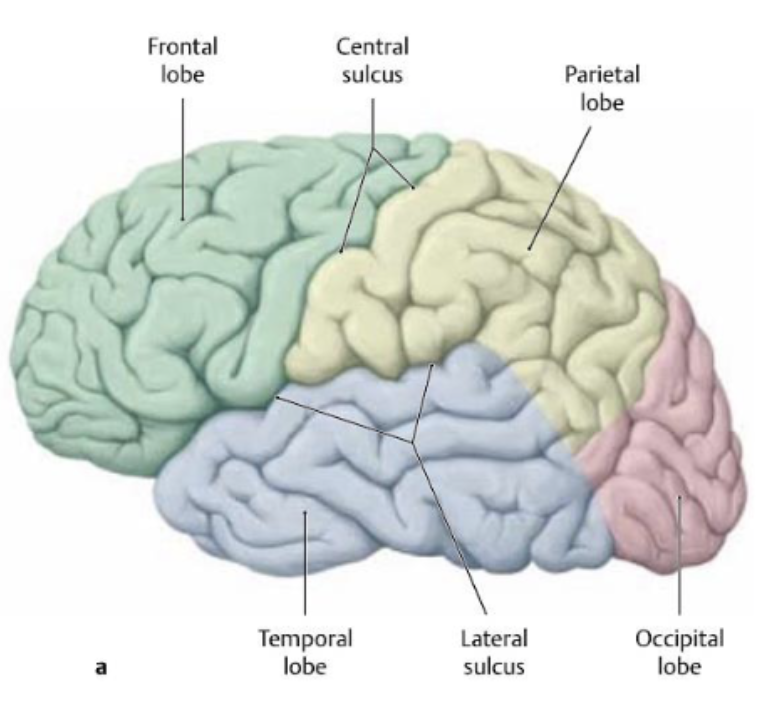
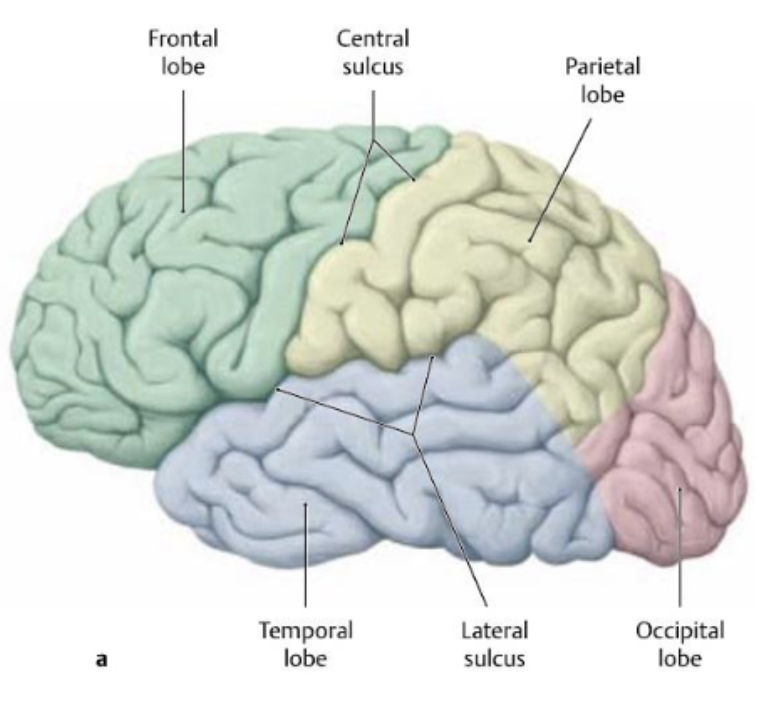
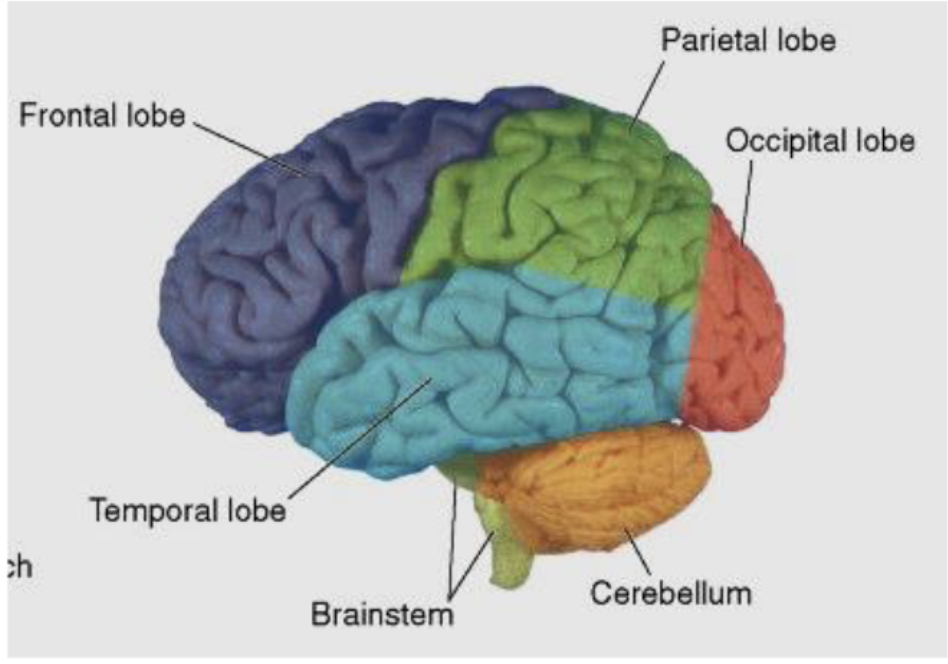
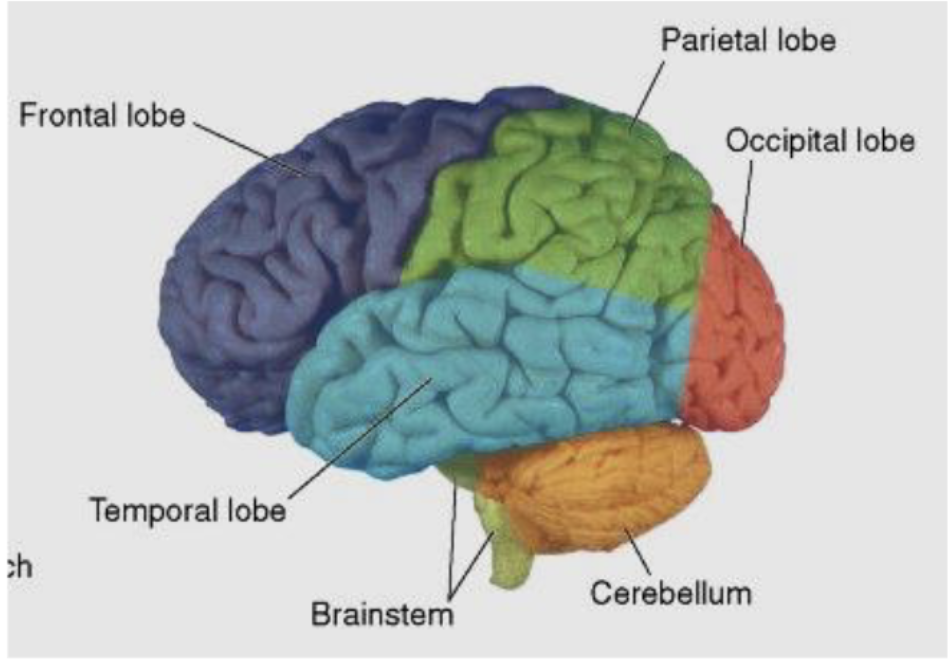
larger sulci divide the hemispheres into how many lobes? (named same as bones overlying them)
5 lobes
the cerebral hemispheres are joined together by the…?
corpus callosum (a white matter tract)
what lobes does the central sulcus separate?
frontal and parietal lobes
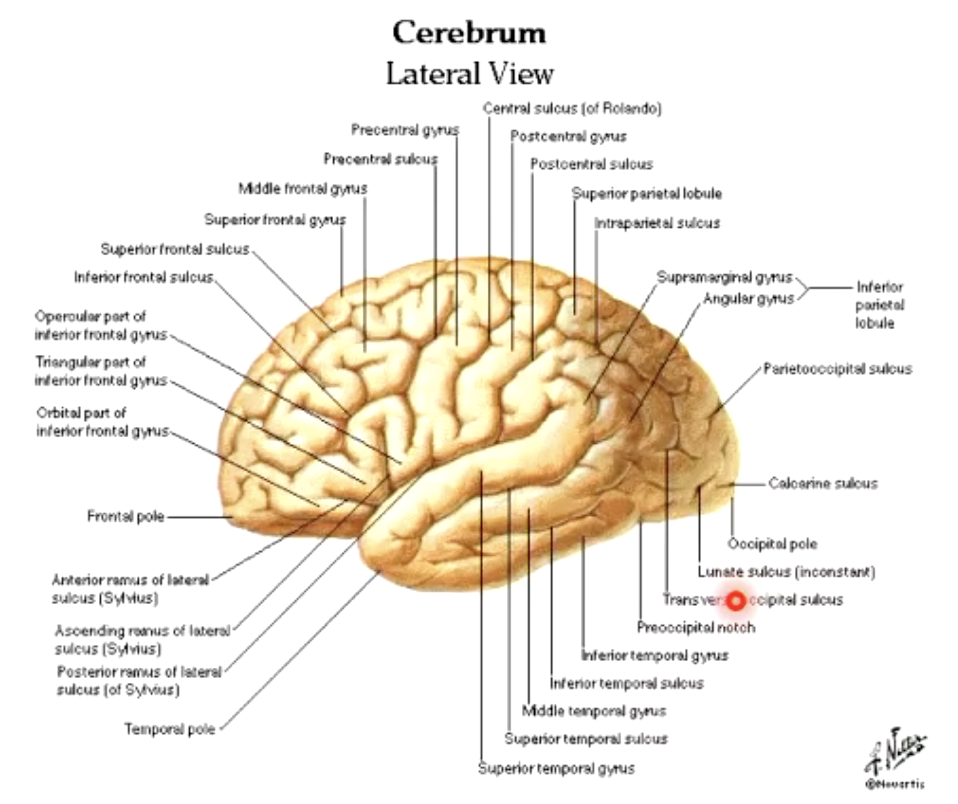
what lobes does the lateral sulcus separate?
frontal and parietal lobes from temporal lobe
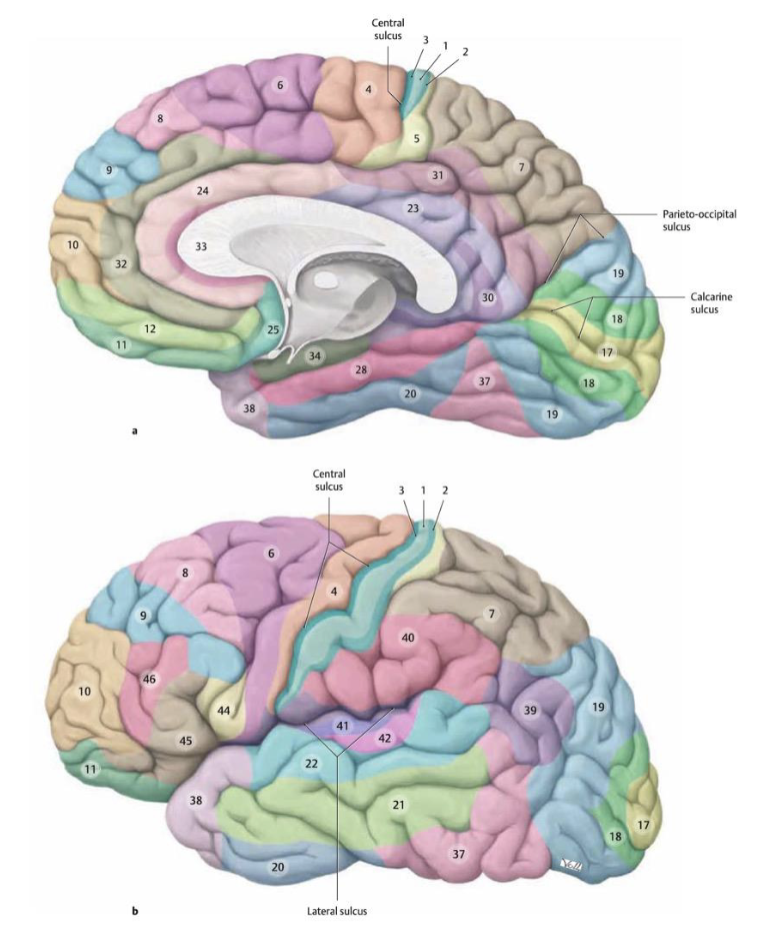
The cerebral cortex can be divided into regions defined by their histological structure and organization of cells (cytoarchitecture). These regions are collectively called
Brodmann areas
primary areas for motor control and sensory (that we’re consciously aware of)
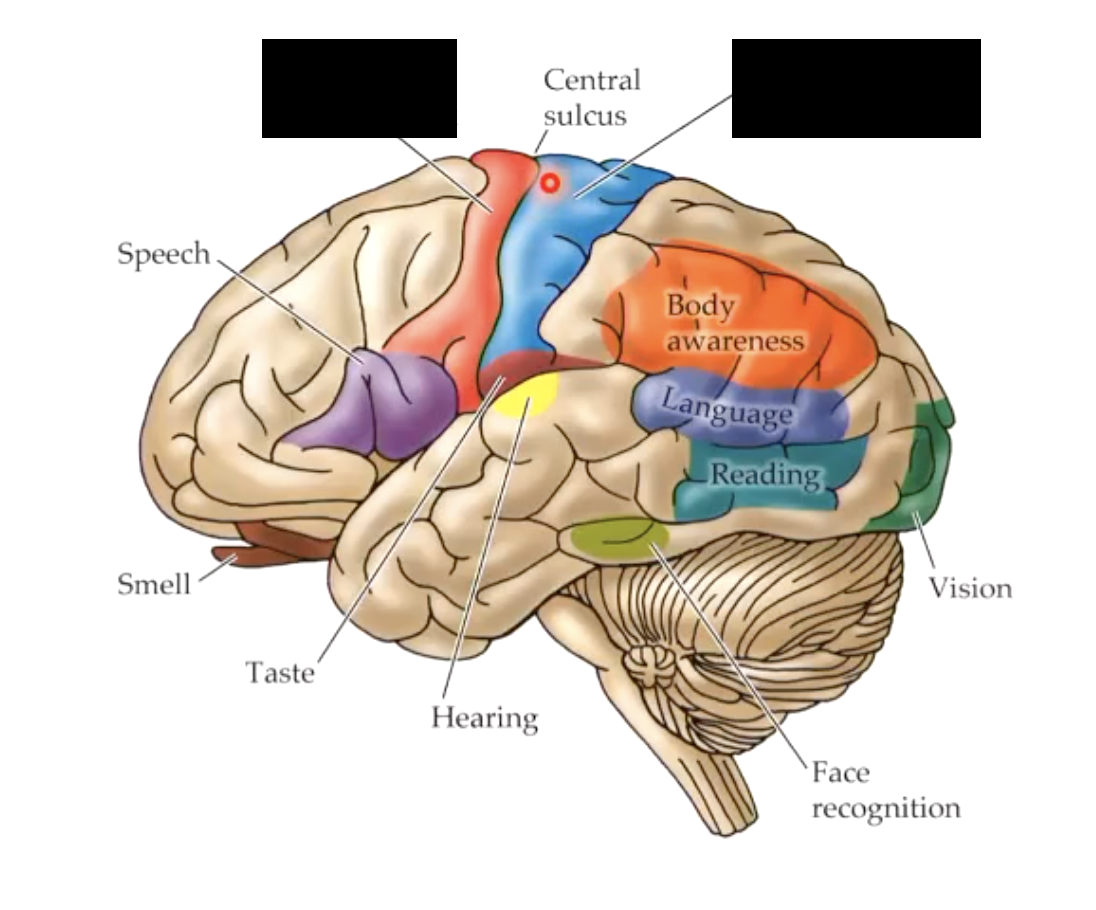
what does lateralization of the cerebral cortex mean?
Some neural processes and functions are specialized to one side (often misrepresented in popular culture)
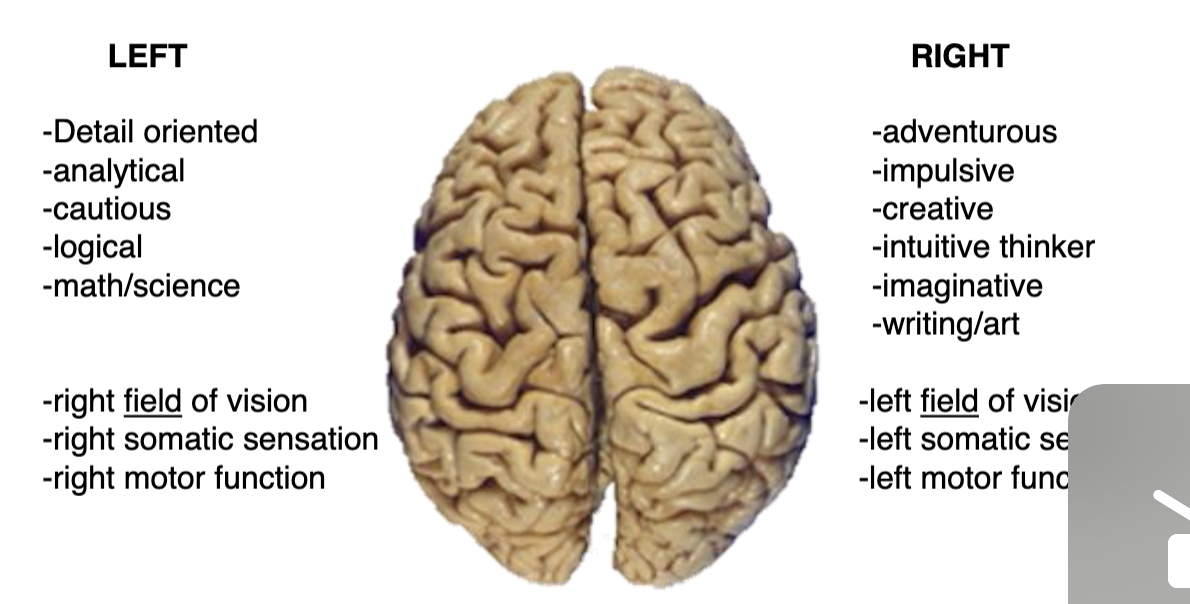
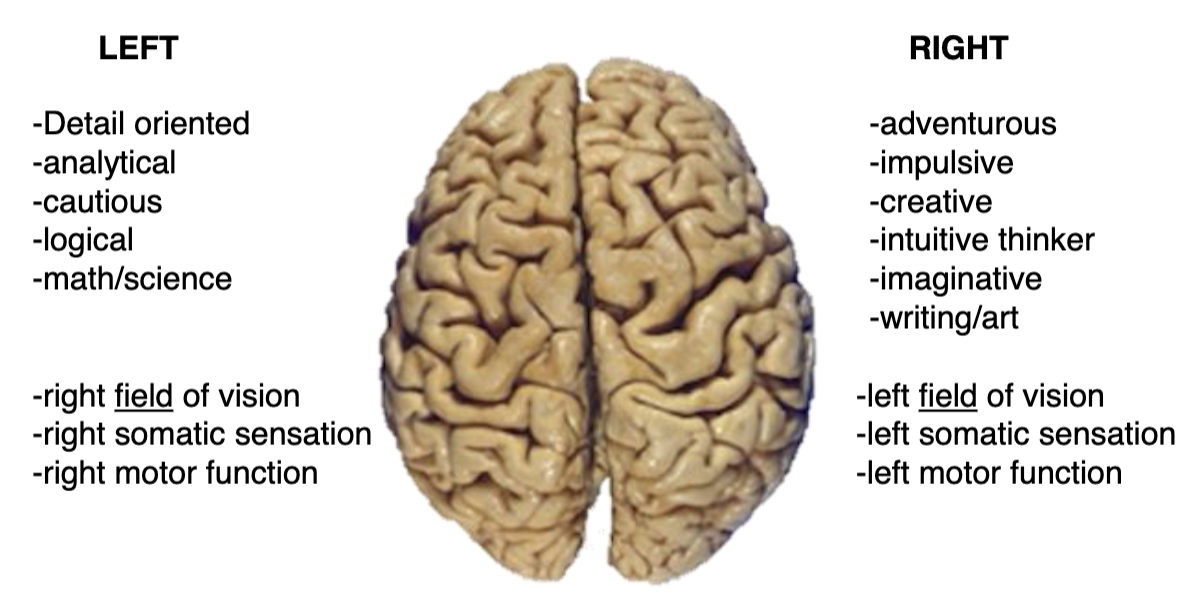
what are some processes/functions that are specialized to one side of the brain?
left side of brain
right field of vision
right somatic sensation
right motor function
right side of brain
left field of vision
left somatic sensation
left motor function
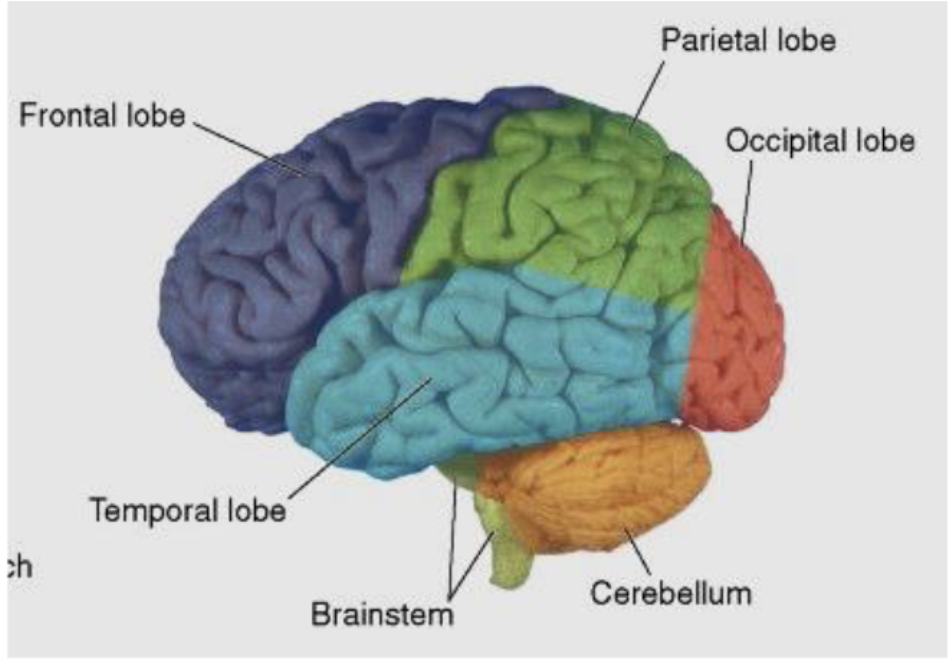
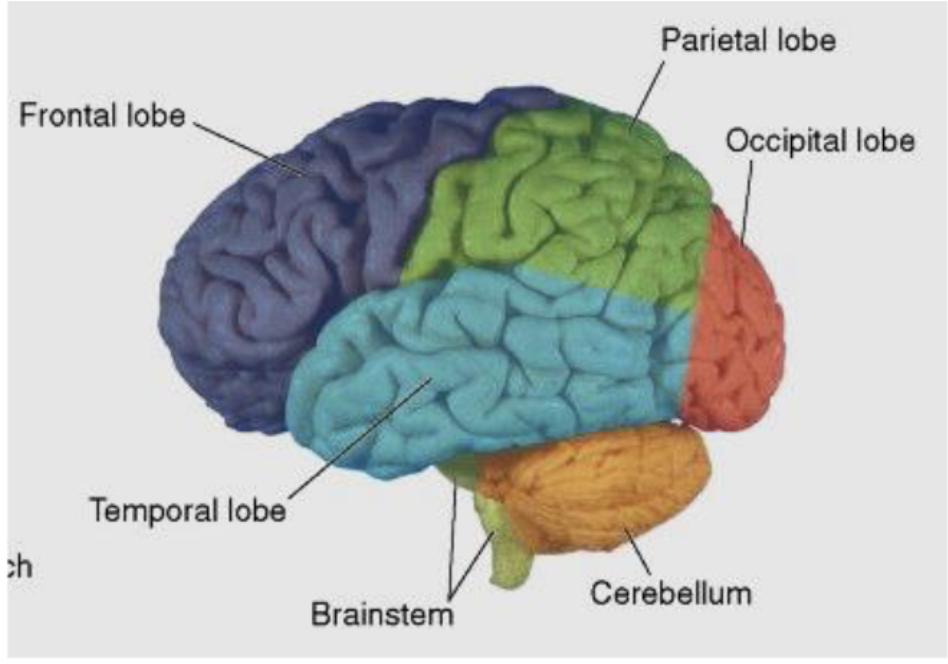
what is the frontal lobe primarily responsible for?
voluntary motor function (primary motor cortex)
higher intellectual function
executive planning
attention
cognition
what are some major areas within the frontal lobe?
prefrontal cortex
primary motor cortex
Broca’s area
what is the primary motor cortex (of frontal lobe) responsible for?
executes contralateral voluntary movement
what is the Broca’s area (of frontal lobe) responsible for? damage to this area is calle?
execution of language
damage = Broca’s expressive aphasia (patients know what they want to say, but can not get the words out)
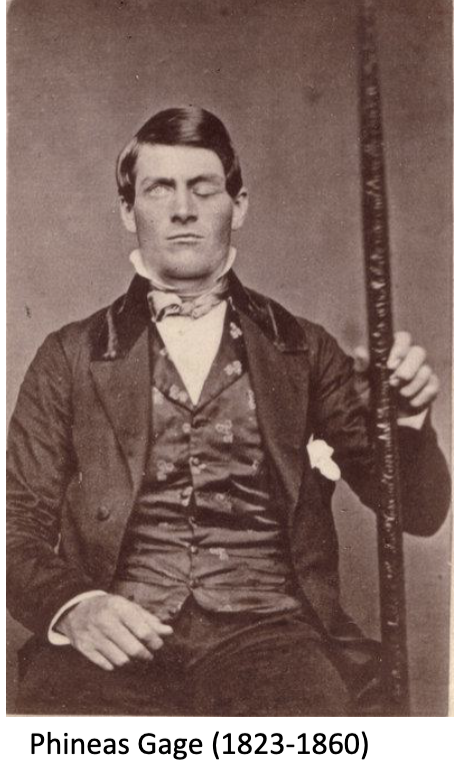

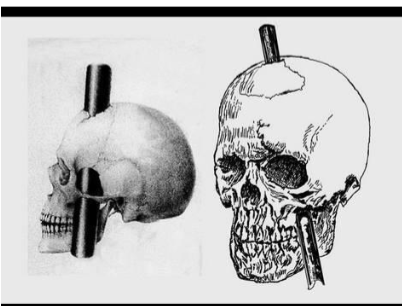
the case of phinease gage demonstrates what about the prefrontal cortex?
Within the frontal lobe, the prefrontal cortex is involved in personality expression, decision making, moderating social behavior and planning complex cognitive behavior
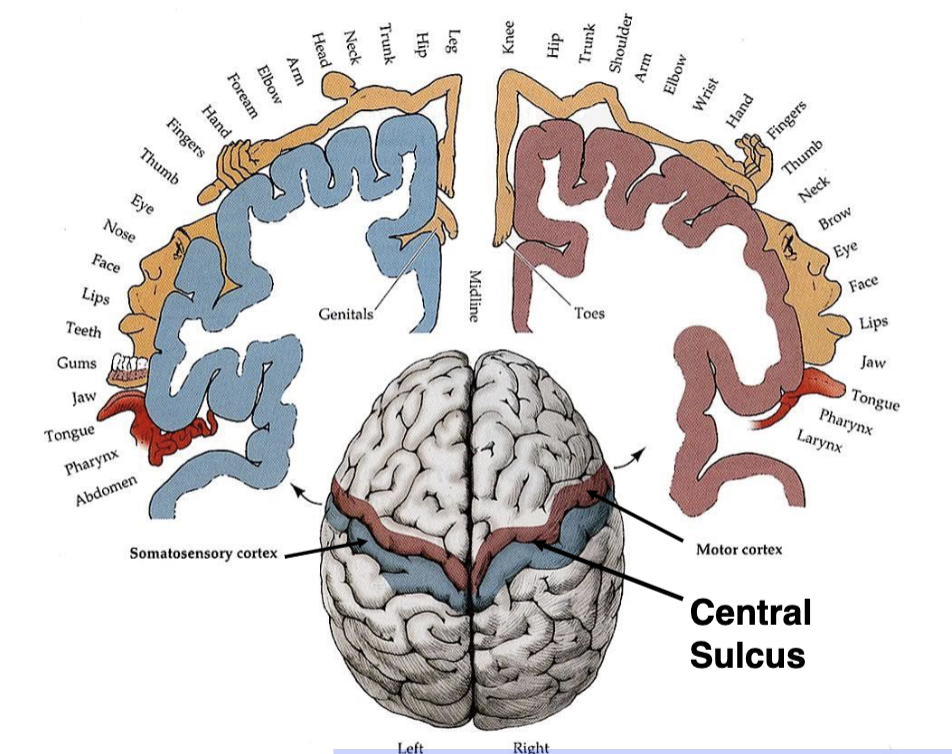
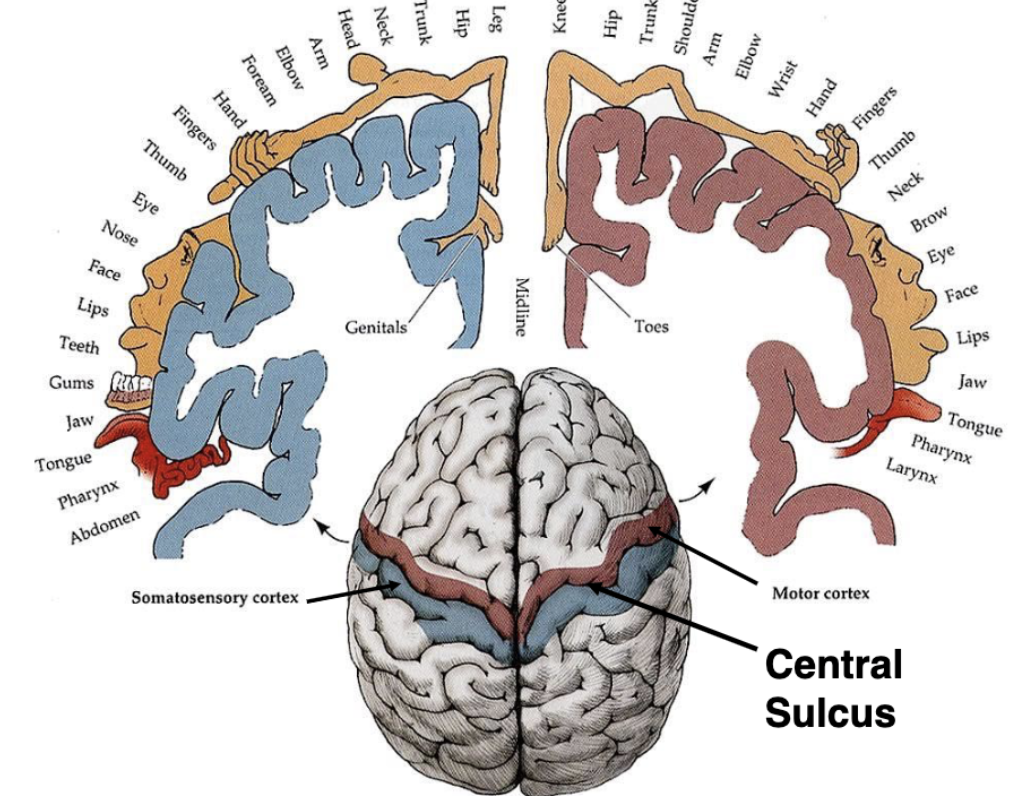
what is a cortical homunculus?
a somatotopic representation of the human body, based on the proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor or sensory functions for specific parts of the body
what is somatotopic representation?
different regions of brain are responsible for different functions
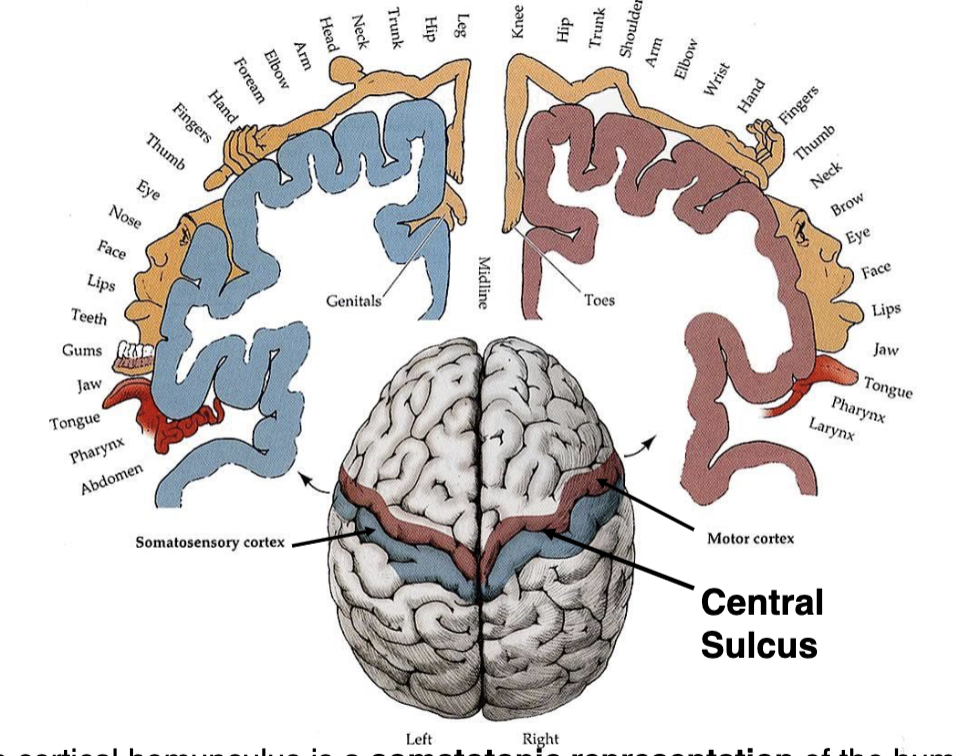
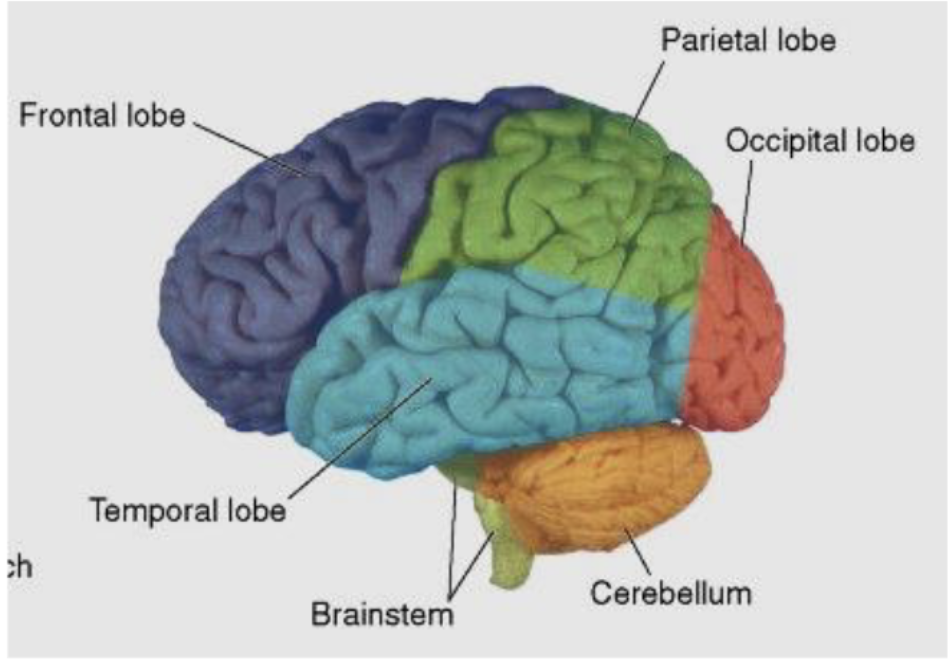
what is the parietal lobe primarily responsible for?
sensory processing
visuospatial integration
speech comprehension
what are the major areas of the parietal lobe?
primary sensory cortex
posterior parietal association cortex
the left and right hemispheres of the parietal lobe are responsible for slightly different functions. what are they?
right
awareness of external environment
spatial and proprioceptive skills
left
numbers, calculations
reading, writing, language
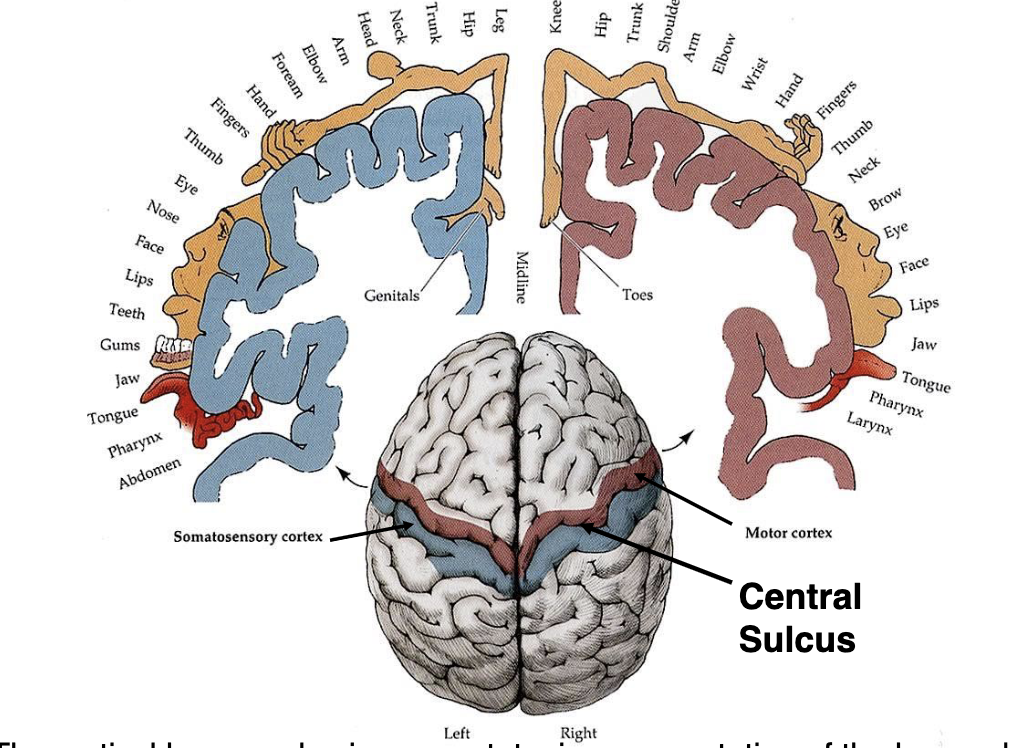
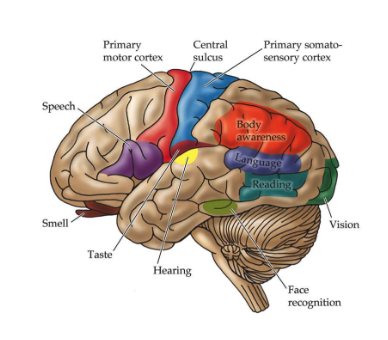
what are the blue and red specialized areas of the brain?
red = primary motor cortex (frontal)
blue = primary somatosensory cortex (parietal)
damage to the right side of the parietal lobe in the posterior parietal association cortex can lead to?
hemispatial neglect → contralesional visuospatial neglect defined by inability to process and perceive stimuli on the contralateral side
(damage to left side does not translate to same result)
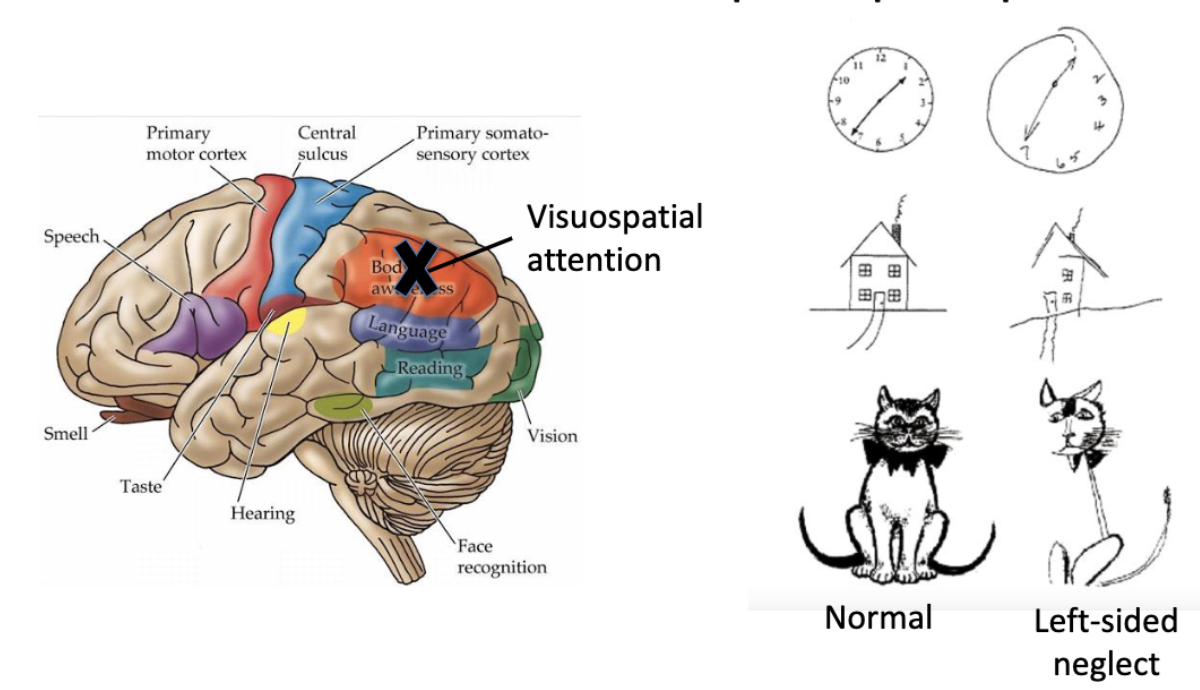
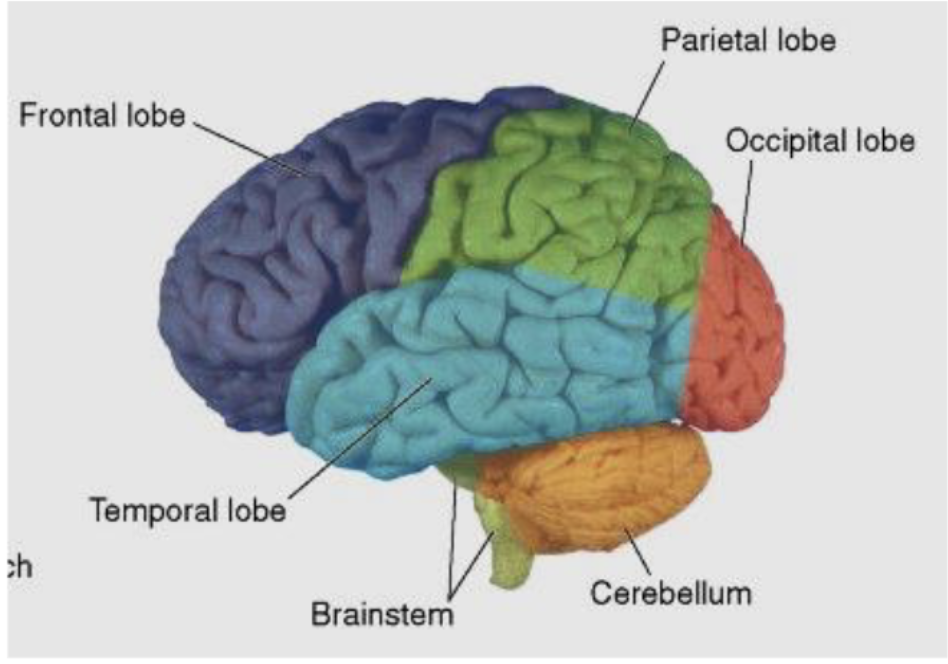
what is the temporal lobe primarily responsible for?
auditory function
language comprehension
facial recognition
memory and emotion
what are the major areas of the temporal lobe?
primary auditory cortex
hippocampus
amygdala
Wernicke’s area
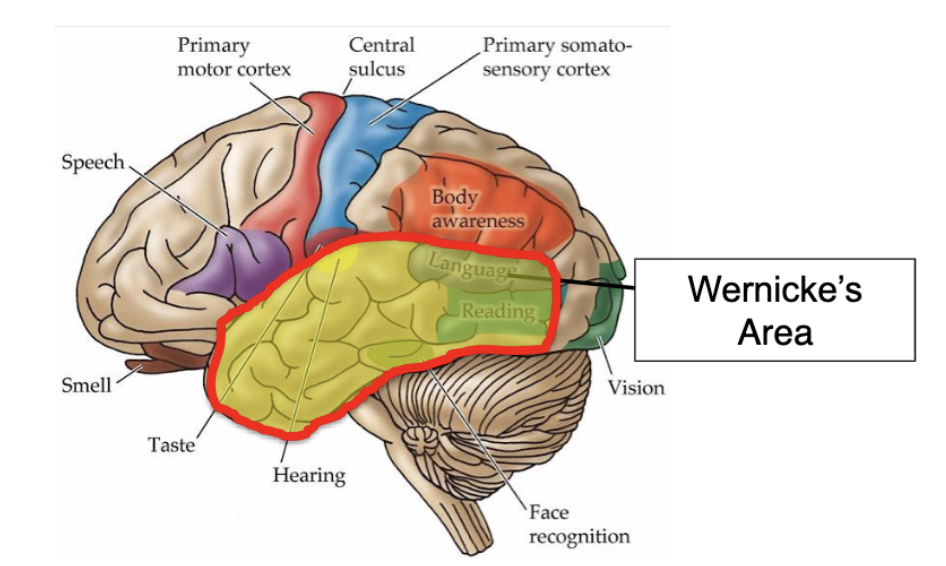
what is Wernicke’s aphasia?
(aka fluent aphasia) inability to comprehend language whether auditory or written
Wenicke’s aphasia is caused by damage to which part of the brain?
temporal lobe
what is the occipital lobe primarily responsible for?
visual processing
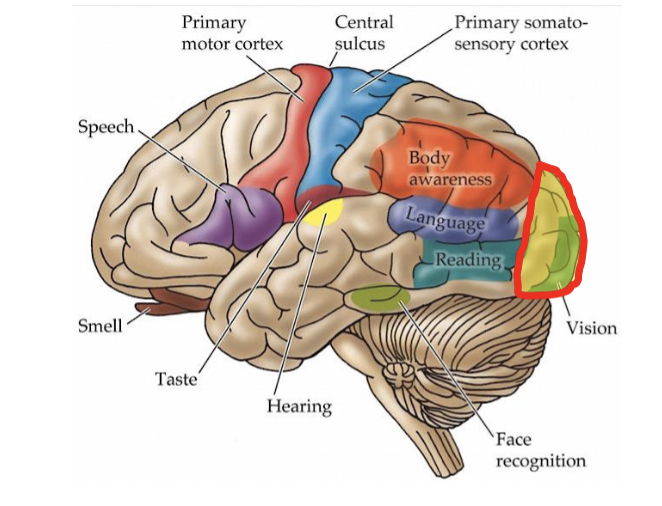
what are the major areas of the occipital lobe?
primary visual cortex
association visual cortex
what does the primary visual cortex do (of occipital lobe)? damage to this area can cause?
receives input from retina via lateral geniculate nucleus
lesions to PVC = cortical blindness
what are basal ganglia?
group of subcortical nuclei
what is the main component of the basal ganglia?
striatum with several subparts
what is the primary function of basal ganglia?
action selection (deciding which of several possible behaviors to execute at a given time and regulating them so that motor movements are performed smoothly)
specific areas of the basal ganglia are involved in _______ release and the brain’s ______ system
dopamine; reward
what structures make up the Limbic System? what is thsi system responsible for?
limbic lobe
hippocampus
amygdala
hypothalamus
associated with EMOTIONS (fear, aggression, drive for food/sex) and MEMORY
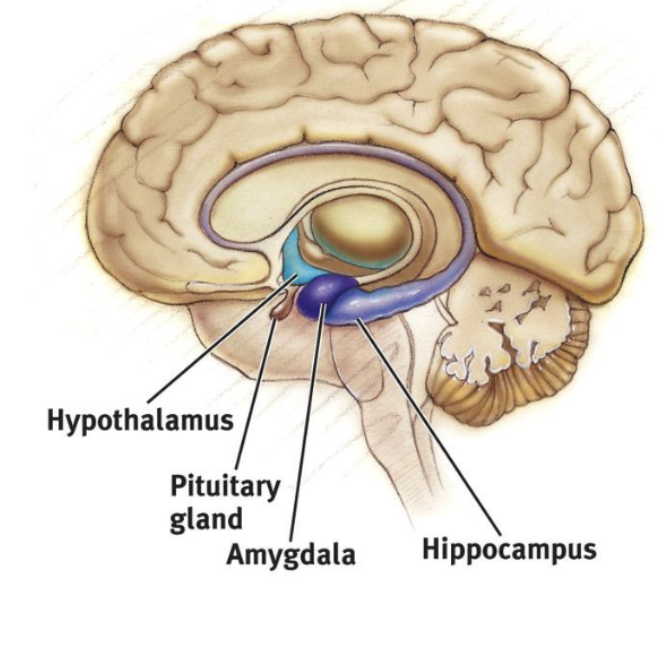
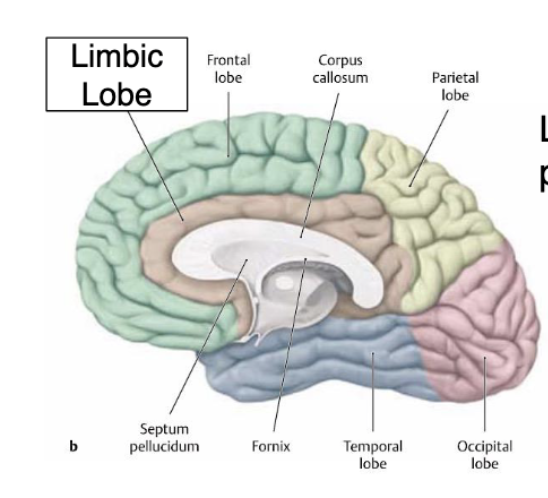
the limbic lobe is separated from the frontal and parietal lobes by…?
the cingulate sulcus
what is the ventricular system?
set of 4 interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles filled with CSF
CSF in the ventricular system acts as a …?
shock absorber
CSF in the ventricular system is produced by the…? (how much CSF is produced per day?)
choroid plexus (1/2 liter per day)
blockage of CSF channels in the ventricular system can lead to …??
hydrocephalus
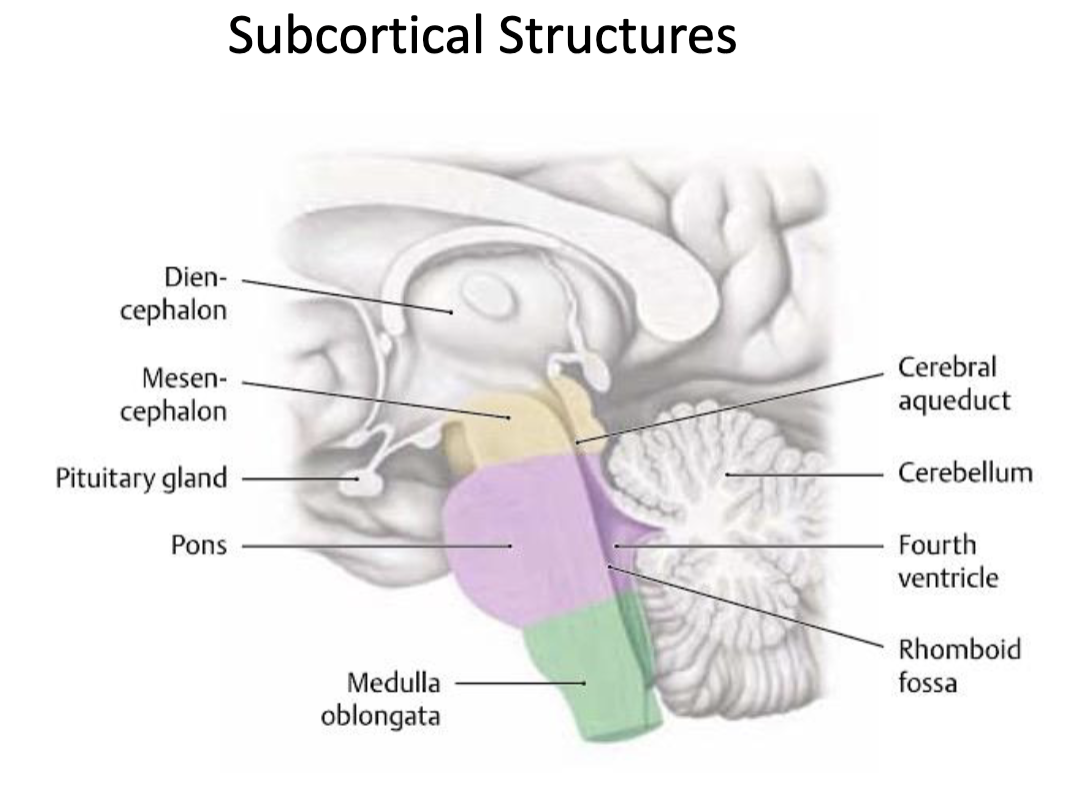
what are some key subcortical structures?
CSF from the ventricular system is absorbed into venous system through…?
arachnoid granulations
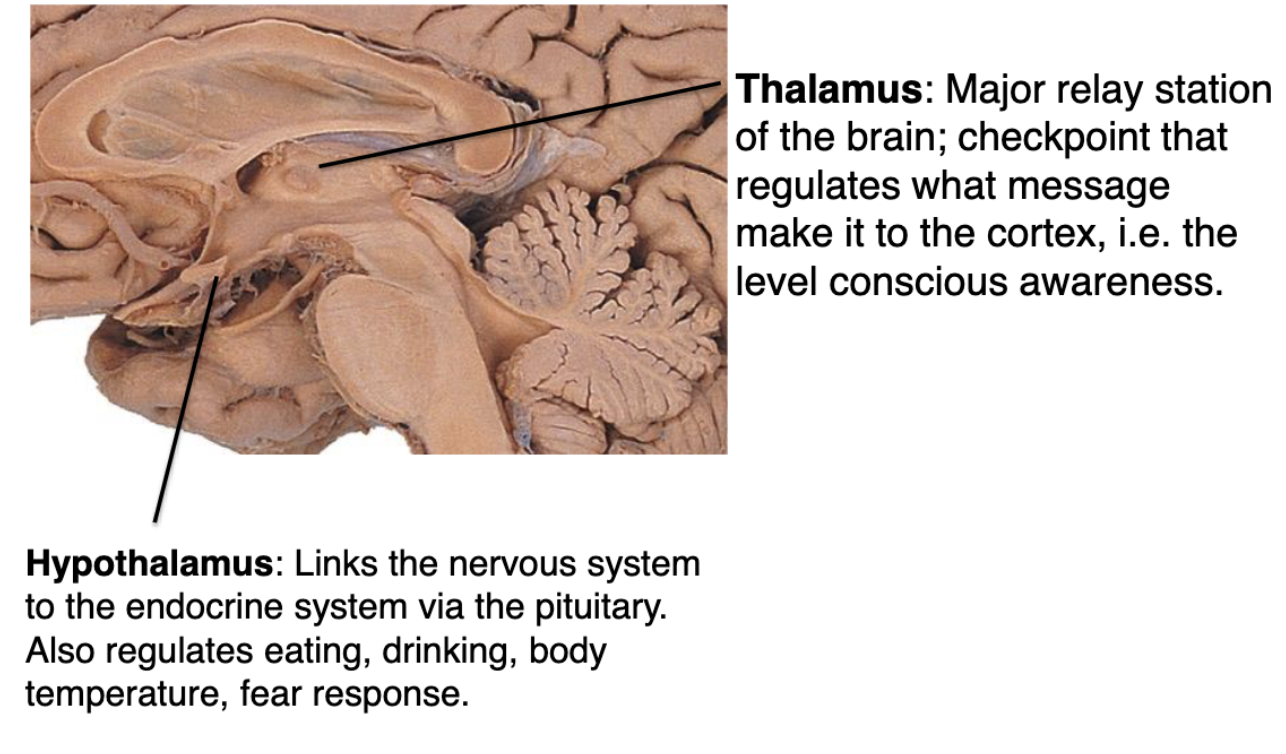
the diencephalon is comprised of what structures?
thalamus
hypothalamus
subthalamus
epithalamus
what is the function of the thalamus?
Major relay station of the brain; checkpoint that regulates what message make it to the cortex, i.e. the level conscious awareness
what is the function of the hypothalamus?
Links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary. Also regulates eating, drinking, body temperature, fear response
what structures make up the brainstem?
midbrain (mesencephalon)
pons
medulla
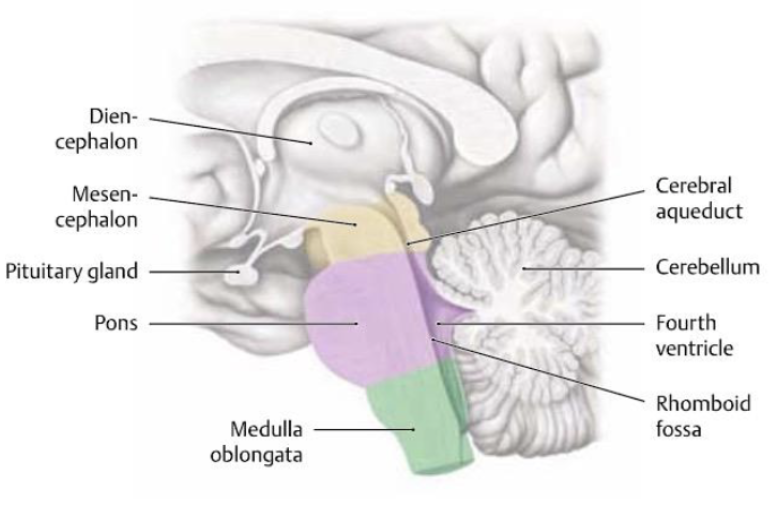
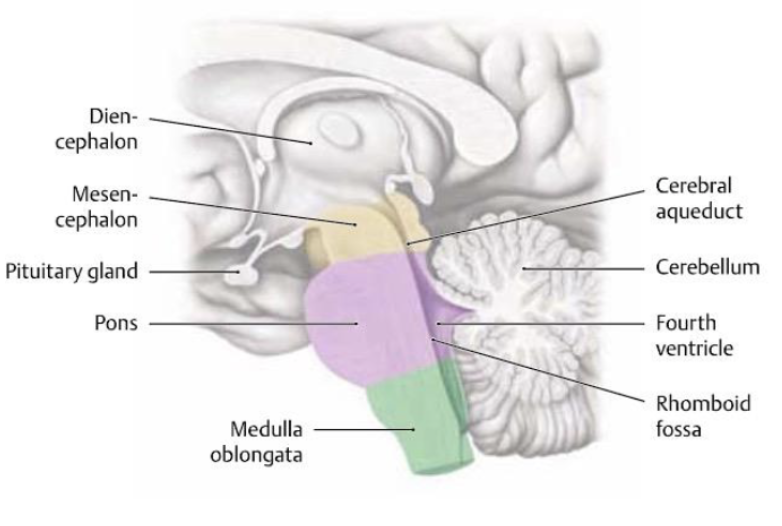
what is the function of the midbrain (brainstem)?
Contains relay nuclei involved in visual and auditory input. Responsible for arousal ”alertness”
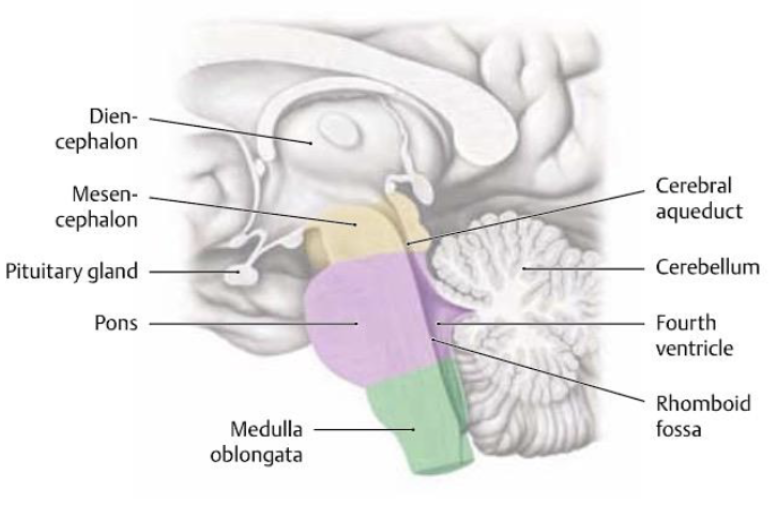
what is the function of the pons (brainstem)?
(latin for bridge) Relays fibers from cerebral cortex to the medulla and cerebellum
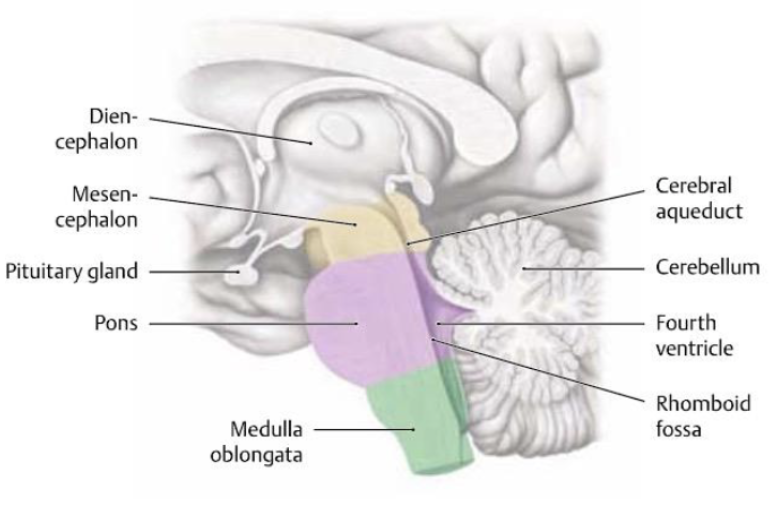
what is the function of the medulla (brainstem)?
Responsible for autonomic functions of breathing (CN IX/carotid body&sinus), heart rate and blood pressure (CN X & sympathetic), reflexes for vomiting, coughing, sneezing and swallowing.
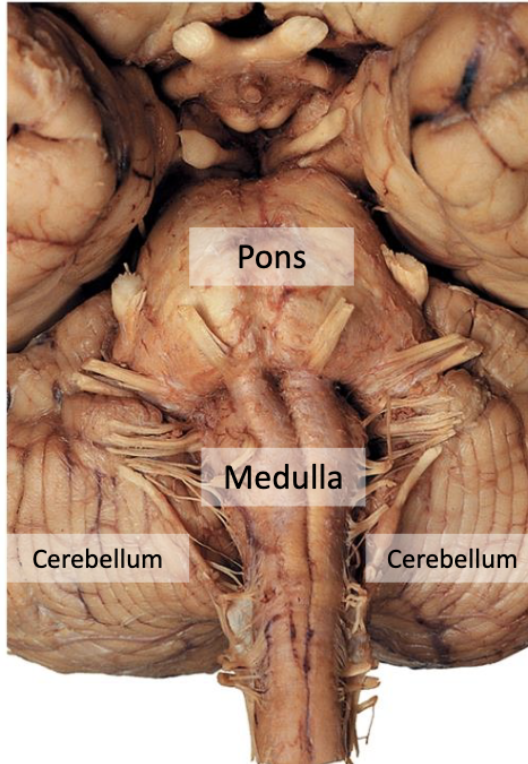
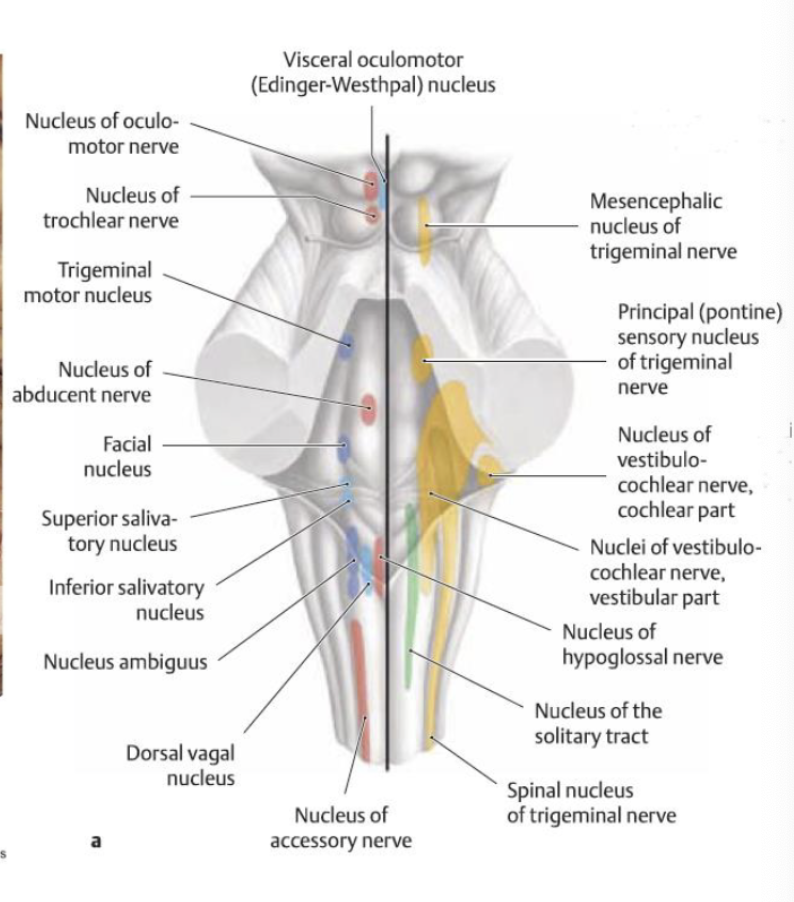
where are the cranial nerve nuclei located?
brainstem
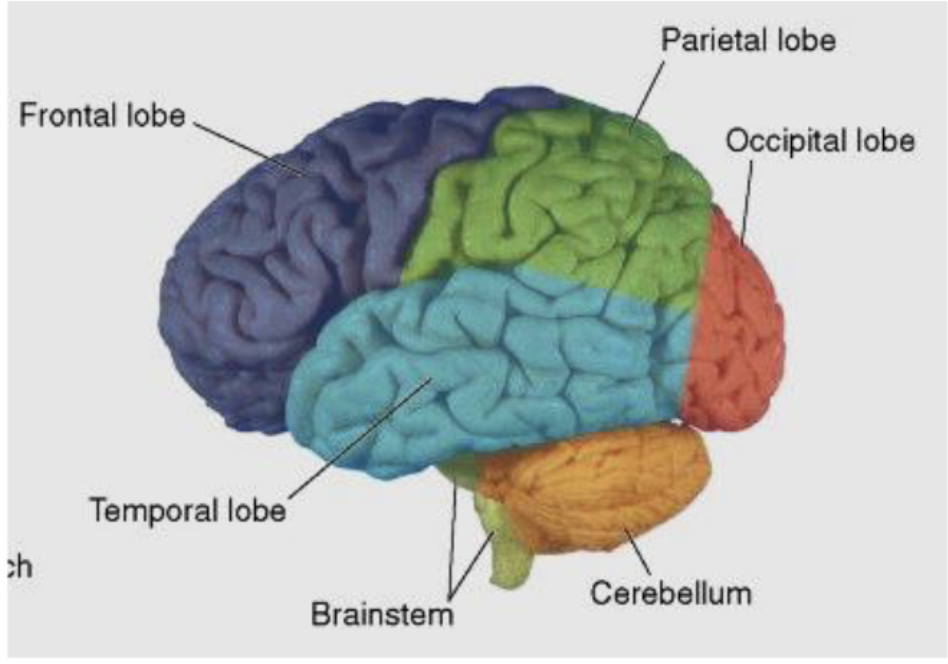
what is the function of the cerebellum (“little brain”)?
motor control (not conscious, more finetuning)
eye movements
postural tone
trunk/limb coordination
fine motor skills
balance and gait
paint avoidance
cerebellar damage can results in…?
disorders affecting fine movement, equilibrium, posture and motor learning
blood supply to the brain is called…?
circle of willis
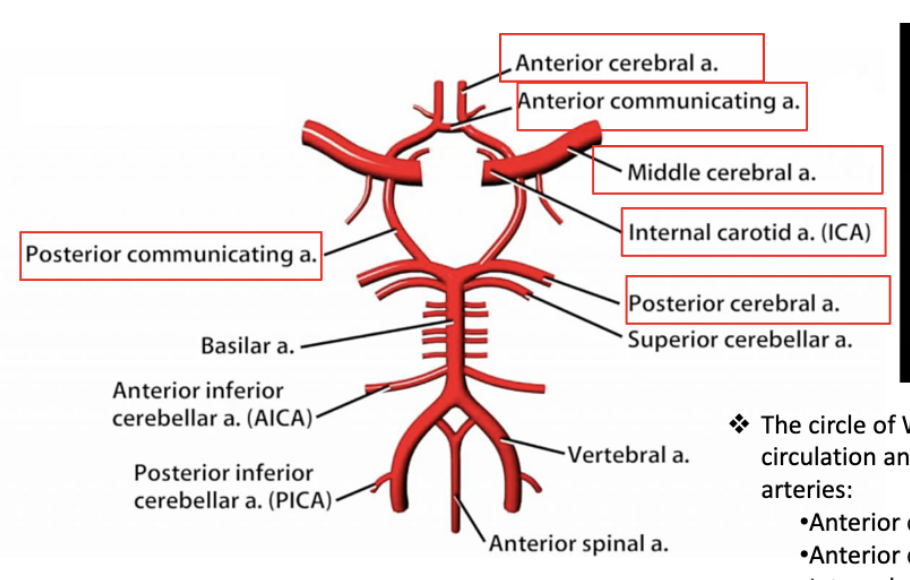
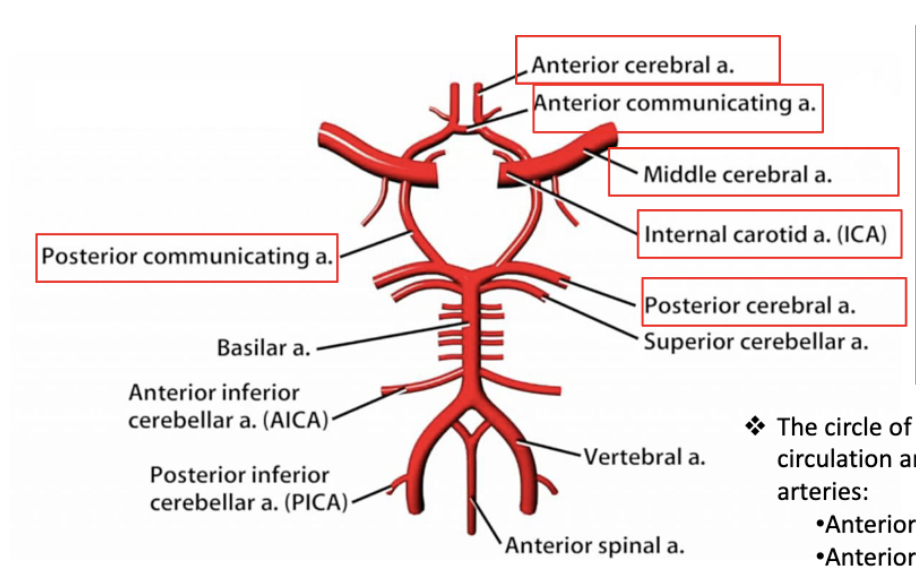
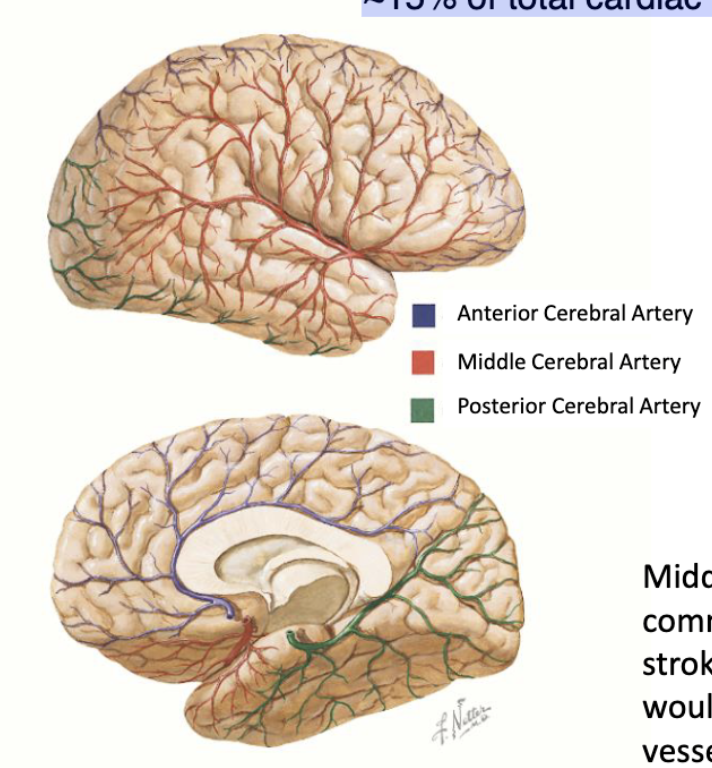
blood supply to the brain:
% from internal carotid
% from vertebral arteries
% of total cardiac output
~80% from internal carotid
~20% from vertebral arteries
~15% of total cardiac output
Middle Cerebral Artery is the most commonly occluded vessel in ischemic stroke. Can you predict which brain regions would be affected from occlusion of this vessel?
face
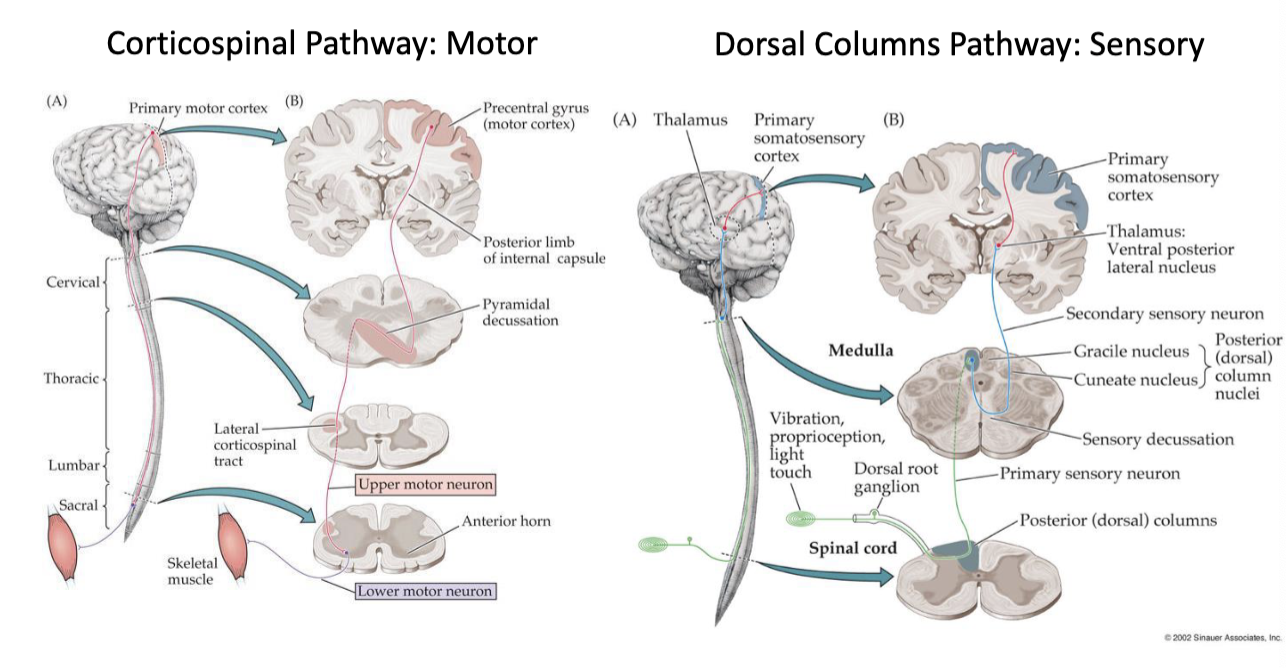
which neural pathway is motor? vs sensory?
motor → corticospinal pathway
sensory → dorsal columns pathway