Histology - Epithelia Tissue (Lab)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Histology
The study of tissues found in the body
Tissues
Groups of similar cells that perform a similar function
4 types of tissues in the body
Connective
Muscle
Epithelial
Nervous
Epithelial Tissue
Lines body cavities
Covers body surfaces
Forms glands in the body
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue
Multiple cells packed closely together with little extracellular material
Avascular
High rate of cellular division
Basal (bottom) cells rest on a basement membrane
Why is high rate of diffusion so important?
To regenerate abrased injury (lost cells restoring)
Avascular
(no blood vessels)
Receive their nutrients through diffusion from surrounding tissue
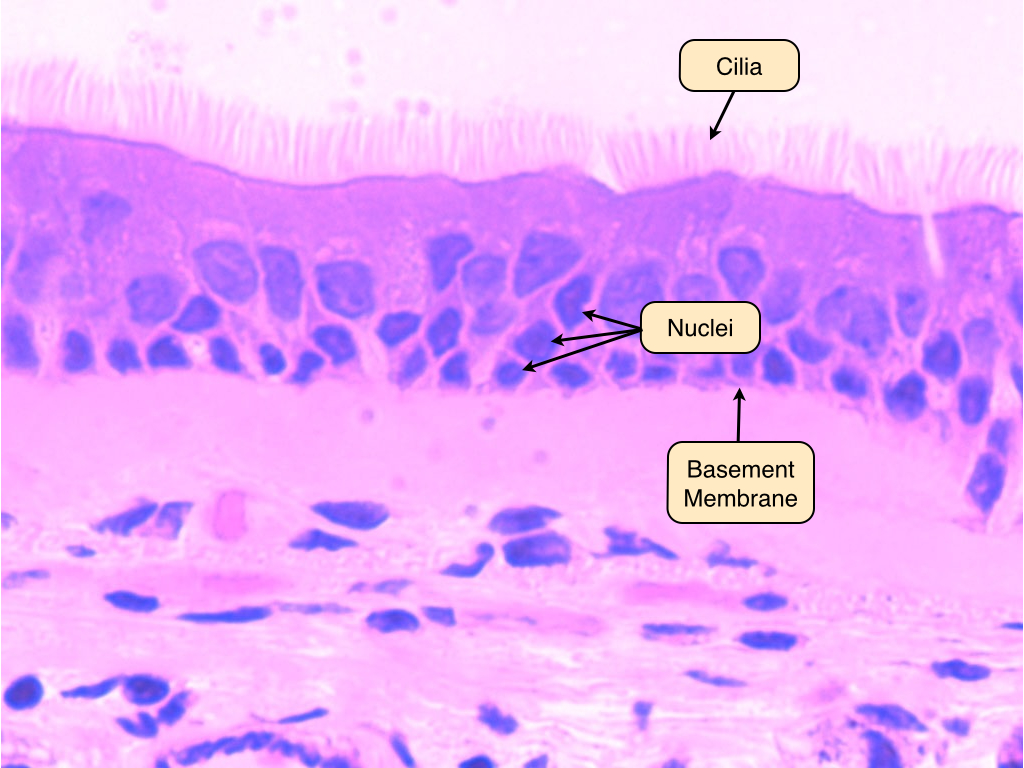
Basement membrane
What anchors the epithelia to the underlying (connective) tissue
Cell layers
Simple
Stratified
Pseudostratified
Simple
Single layer of cells
Stratified
2 or more layers
Pseudostratified
A single layer of cells that appears to be more than one layer – all cells do not reach the free surface
Cell Shape
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Transitional
Squamous
Flattened irregular shaped cell
Cuboidal
Cube-shaped cells
Columnar
Elongated rectangular shaped cells
Transitional
Cells change shape between squamous and cuboidal depending on needs of tissue (urinary bladder)
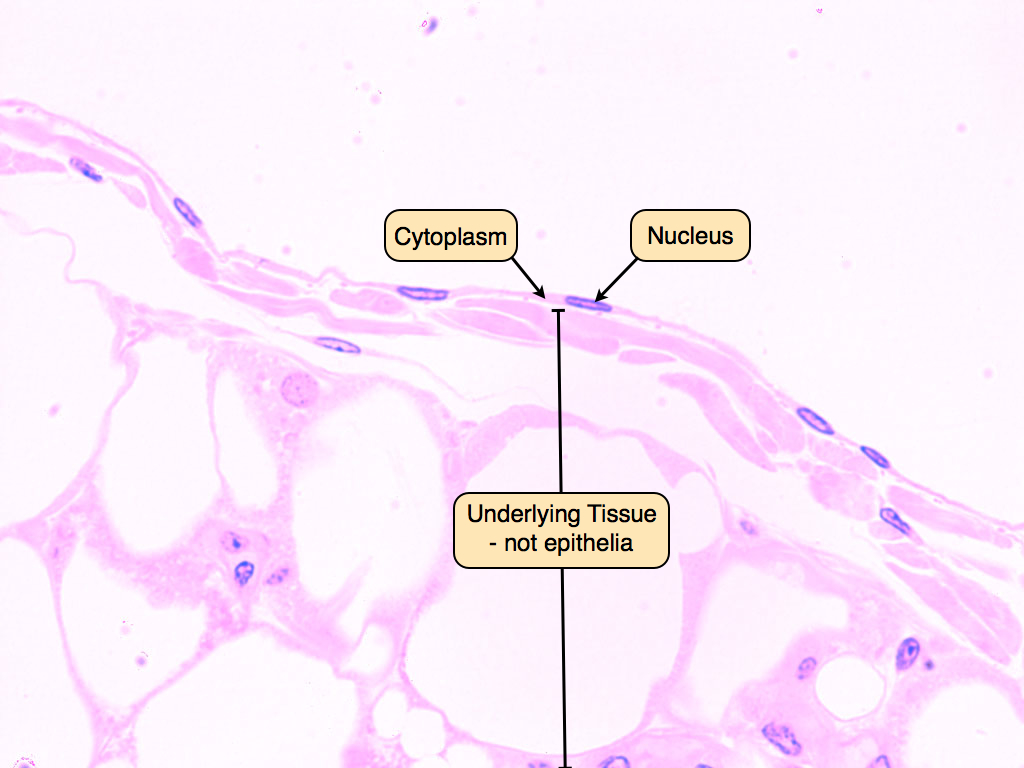
Simple Squamous
Single layer of flattened cells
Location: Lines heart, blood, and lymphatic vessels, alveoli of the lungs
We want a thin layer to be able to pass through (helps with diffusion)
Not rough and want to expand
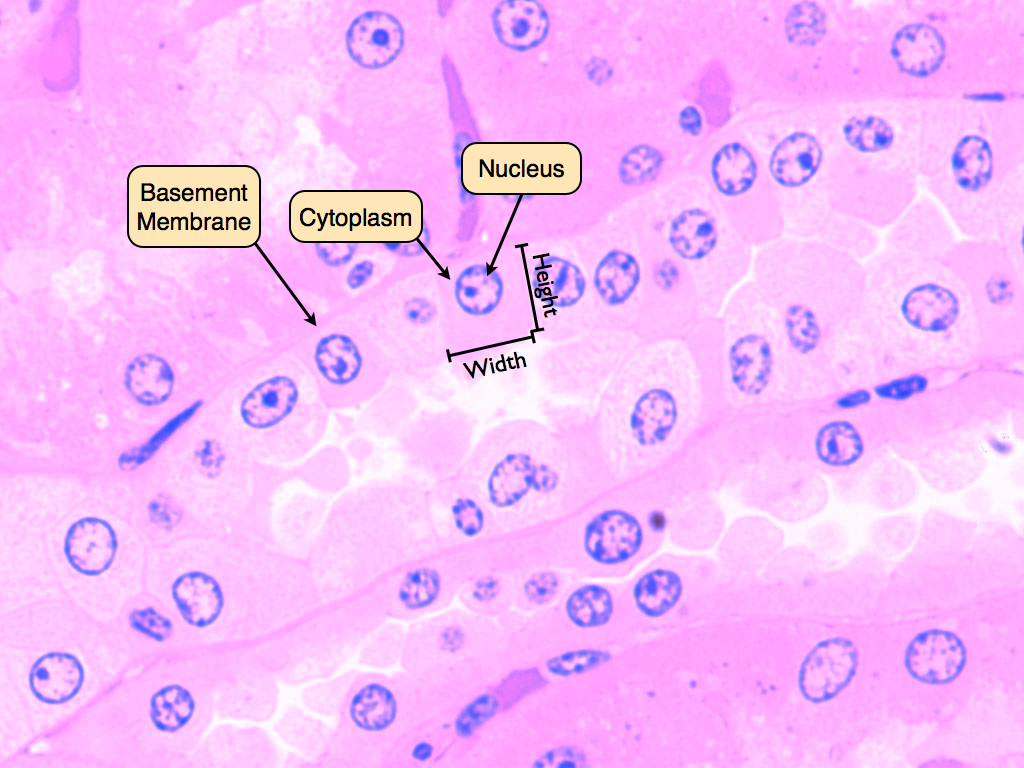
Simple Cuboidal
Single layer of cube-shaped cells
Line kidney tubules, ducts of many glands, surface of the ovary, capsule of the lens of eye
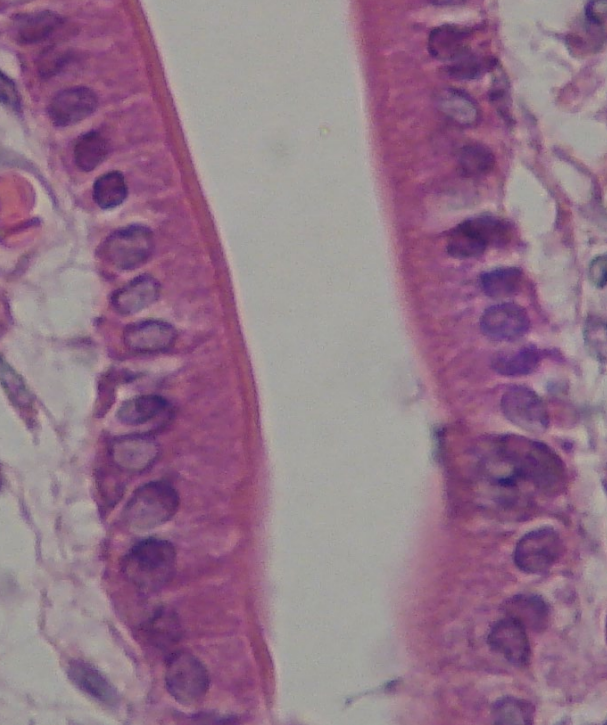
Ciliated Simple Columnar
Functions to move the cell using hair-like structures (cilia)
Location: Lines bronchioles of the respiratory tract, uterine tubes, and uterus
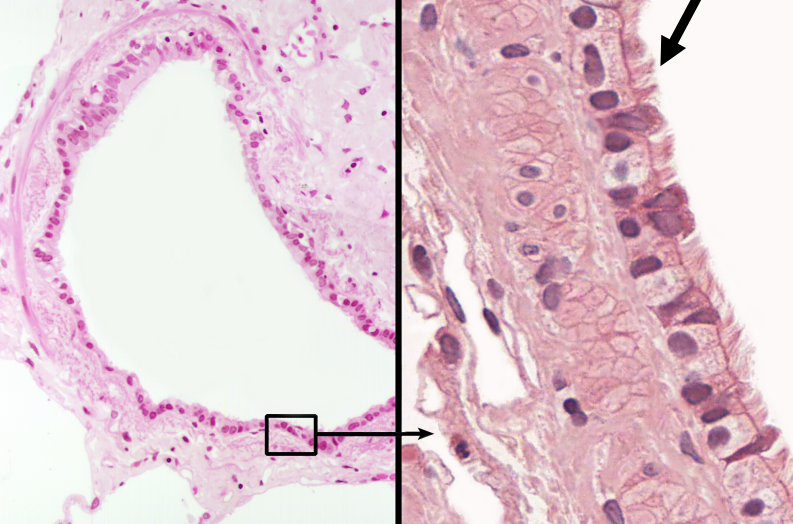
What function does cilia have?
Moving the cells through their surrounding fluid, for food uptake, and for sensing the environment
Non-ciliated Simple Columnar
Lines digestive tract, ducts, glands and gallbladder
Pseudostratified Columnar
A single layer of cells, but appears to be multiple layers
• All cells contact the basement membrane, but not all reach the free surface
Can be ciliated or non-ciliated
Lines airways of the respiratory tract, lines glands, and ducts
Stratified Squamous
Multiple layers of flattened cells → to protect lots of its cells
Deeper layers may be cuboidal or columnar
Location: Makes up the epidermis of the skin, lines oral cavity, esophagus, and vagina
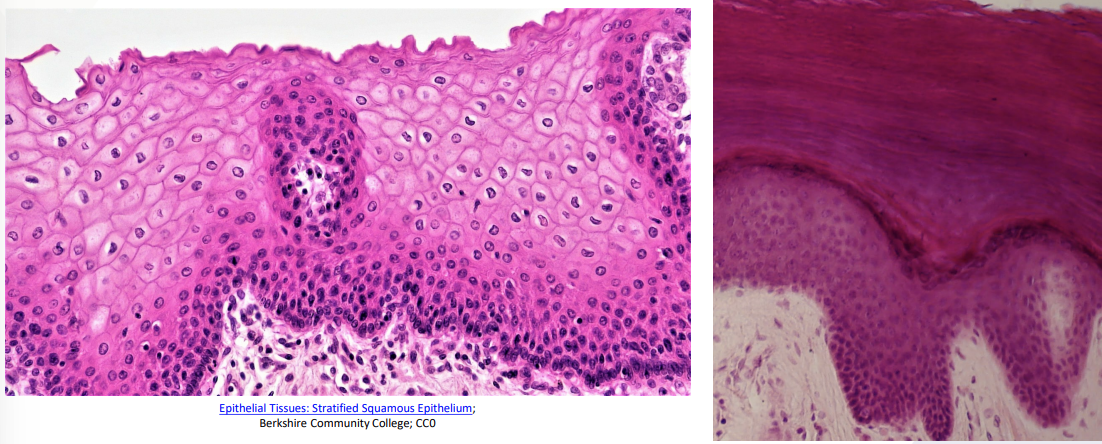
What purpose would having multiple layers serve?
Tissue is very thick (many layers) -> Safe penetration + protection
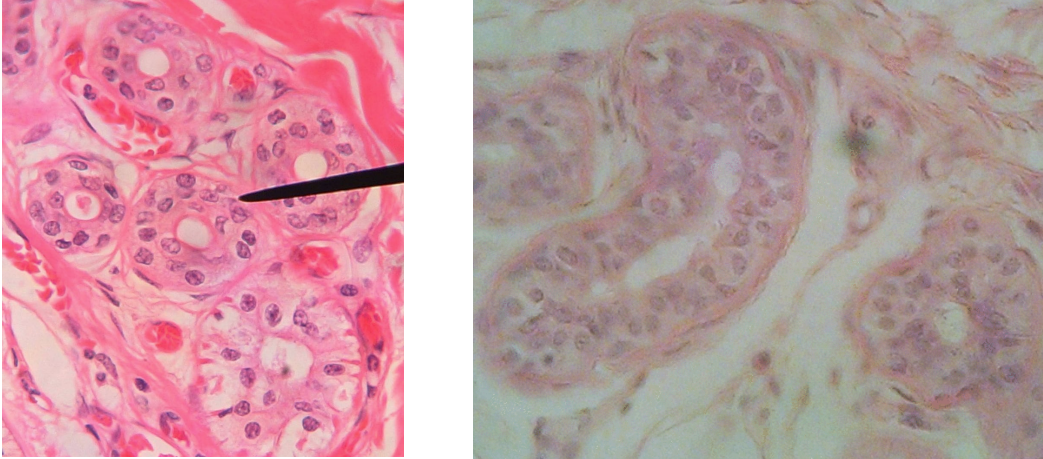
Stratified Cuboidal
Multiple layers of cube-shaped cells (apical layers or cuboidal)
A rare type of epithelium found in the ducts of adult sweat glands and the male urethra
Location: exocrine glands (sweat glands)
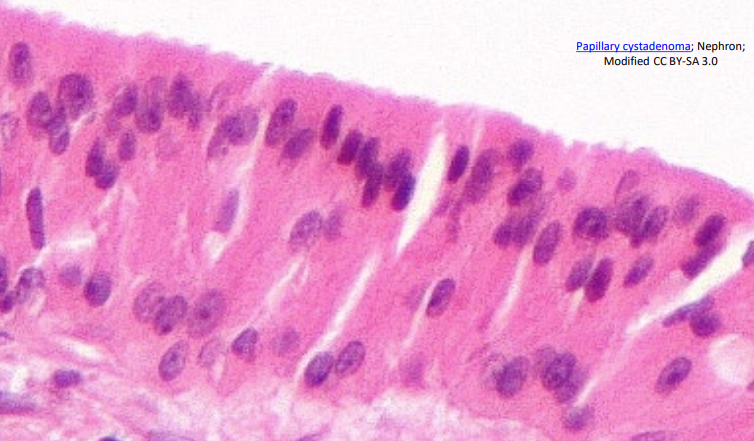
Stratified Columnar
Several layers of irregularly shaped cells; only the apical (top) layer is columnar
Location: Lines part of the urethra and the excretory ducts of some glands
Transitional Epithelial Tissue
Cells vary from flat (squamous) to cuboidal
Allows for change and shape of the tissue and to tighten or stretch
Lines the urinary bladder, parts of the ureters and urethra
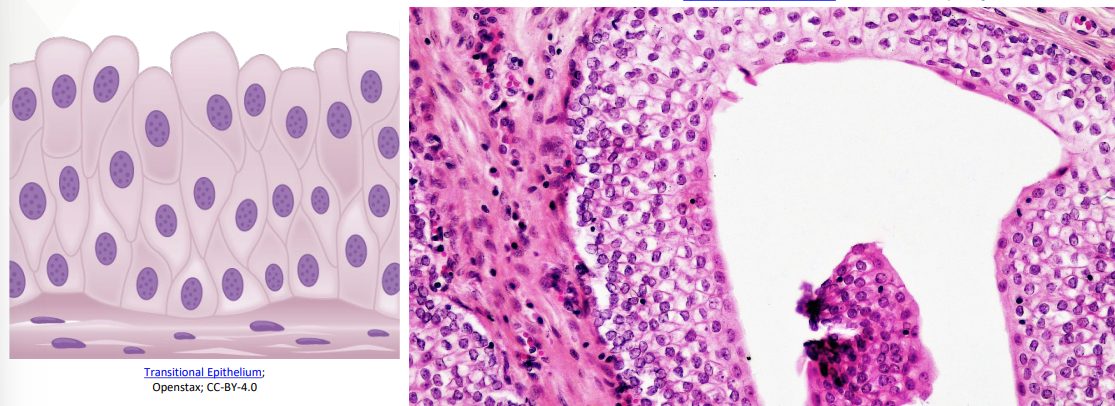
Why is it necessary for the cells in these locations to alter their shape?
The lining would expend to prepare for penetrations, therefore not ripping the skin when intercourse occurs