4.6.4 Logic Gates
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is a logic gate?
A device which applies logical operations to one or more Boolean inputs in order to produce a single output
What are the key logic gates?
- AND
- OR
- NOT
- XOR
- NAND
- NOR
What is a truth table?
A table showing every possible combination of inputs and the corresponding output
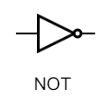
NOT Gate
Output will always be opposite to the input
→ Denoted with an overline
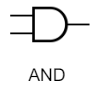
AND Gate
Only outputs true when both inputs are true
→ Denoted with a dot between the inputs
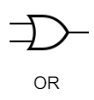
OR Gate
True if one or more inputs are true
→ Denoted with a (+) between inputs
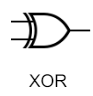
XOR Gate
Exclusive OR
→ Only true if strictly one input is true
→ Denoted with a circled (+) between inputs
NAND Gate
Not AND
→ Only true if both outputs are false
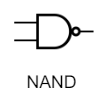
What are NAND gates also known as?
The universal gate
Why is the NAND gate considered universal?
Different combinations of NAND gates can act like NOT, OR and AND gates
What are the advantages of using NAND gates?
- Minimises the cost of production
- Using fewer gates can speed up processing
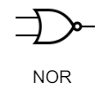
NOR Gate
Not OR
→ False if one or more inputs are false
What is an adder?
A logic circuit to add Boolean values together
What are the types of adders?
- Half
- Full
What is a half adder?
A logic circuit with two inputs, outputs and logic gates
→ Used to add two Boolean values
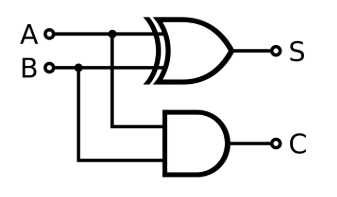
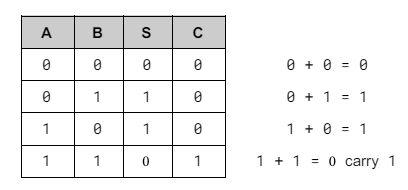
What is the truth table for a half adder?
S - Sum
C - Carry
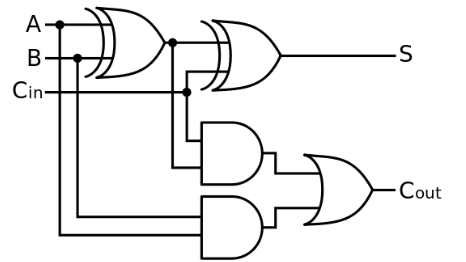
What is a full adder?
A logic circuit with three inputs and two outputs
→ Allows two boolean values and a carry bit from a previous operation
What is an edge-triggered D-type flip-flop?
A logic circuit which can be used as a memory unit for storing the value of a single bit
What are the inputs and outputs of a ETDTFF?
Inputs:
- Data
- Clock signal
Output:
- Value of the stored bit
How does the clock signal impact the ETDTFF?
- Clock signal alternates between 0 and 1 at a set frequency
- The value of the stored bit is set to the value of the data input with each change
- Can be used to synchronise numerous