MNGT 2000/50 - Foundations for Business Success (FINAL EXAM)
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
Why do people become entrepreneurs?
The desire to be one’s own boss
What is an entrepreneur?
Entrepreneurs typically are innovators who start companies to pursue their ideas for a new product or service.
What is a small-business owner?
Small-business owners are managers or people with technical expertise who started a business or bought an existing business and made a conscious decision to stay small.
What are the types of entrepreneurs
Classic Entrepreneurs
Multipreneurs
Intrapreneurs
What is a classic entrepreneur
Classic entrepreneurs are risk-takers who start their own companies based on innovative ideas
What is a micropreneurs
Entrepreneurs who start small and plan to stay small
What are growth-oriented entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs who want their business to grow into a major corporation
What are multipreneurs
Entrepreneurs who start a series of companies.
What are intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs who don’t own their own companies but apply their creativity, vision, and risk-taking within a large corporation.
What characteristics do successful entrepreneurs share?
Ambitious
Independent
Self-confident
Risk-takers
Visionary
Creative
Energetic
Passionate
Committed
What is Managerial Ability and Technical Knowledge
Skills on how to organize a company, develop operating strategies, obtain financing, and supervise day-to-day activities
What is a small business
Established for 5 years
Number of employees less that 50
How to start a new business
Finding the Idea
Choosing a Form of Business Organization
Developing the Business Plan
What are the Key Elements of a Business Plan
Executive summary
Vision and Mission Statement
Company Overview
Product and/or Service Plan
Marketing Plan
Management Plan
Operating Plan
Key Elements of a Business Plan
What is an Executive Summary
Overview of the business plan
Key Elements of a Business Plan
What is a Vision and Mission Statement
Business philosophy and company values
Key Elements of a Business Plan
What is a Company Overview
Type of company
Key Elements of a Business Plan
What is a Product and/or Service Plan
Explains why people will buy the product or service.
Key Elements of a Business Plan
What is a Marketing Plan
Who the firm’s customers will be and what type of competition it will face
Key Elements of a Business Plan
What is a Management Plan
Identifies the key players
Key Elements of a Business Plan
What is an Operating Plan
Explains the type of manufacturing or operating system
What are two ways to finance a business
Debt
Equity
What is bootstrapping
Funding the operation with your own resources
Who are Angel investors
High-net-worth individuals investing their own money
Who are venture capitalist
Firms that invest pooled capital from various sources
Components of a Business Model
Value Proposition
Profit Mechanism
Value Chain
Customer
Business Model
What is Value Proposition
What value do you offer the customer
Business Model
What is Profit Mechanism
Why does the business model generate profit
Business Model
What is Value Chain
How is the value proposition created
Business Model
Customer
Who is our target customer
What are the types of Business Models which seem relevant to new forms of organization
Affiliation
Crowdfunding
Crowdsourcing
Digitization
E-commerce
Flat-rate
Open Source
Peer-to-Peer
Types of Business Models
Affiliation
An affiliate (a third-party) earns a commission for promoting and selling another company's products or services.
Types of Business Models
Crowdfunding
Outsourcing the financing of a project to the general public.
Types of Business Models
Crowdsourcing
Outsourcing specific tasks to external actors
Types of Business Models
Digitalization
Transforming an existing product or service into a digital variant
Types of Business Models
E-Commerce
Traditional products or services are delivered via online channels
Types of Business Models
Flat Rate
Customers purchase a service or a product for a lump sum and then use it as much as they wish
Types of Business Models
Open Source
Company makes the source code of its software or hardware freely available to the public, encouraging community collaboration and innovation
Types of Business Models
Peer-to-Peer
Two individuals interact to buy sell goods and services directly with each other or produce goods and service together, without an intermediary third-party
What is strategic analysis
The process that firms use to study and understand the many different layers and aspects of their competitive environment.
The Competitive Environment
What are External factors
External factors are things in the global environment that may impact a firm’s operations or success, examples are a rise in interest rates, or a natural disaster.
Note: External factors cannot be controlled, but they must be managed effectively
Components of SWOT analysis
Strength
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
SWOT
What are Strengths
What the company is good at
SWOT
What are Weaknesses
What the company is not good at
SWOT
What are Opportunities
A potential situation that a firm is equipped to take advantage of
SWOT
What are Threats
Anything that would make it harder for the firm to be successful
Limitations of SWOT Analysis
It is more likely to overlook key issues because it is difficult to identify or imagine everything that could, for example, be a threat to the firm
What analysis can be used to assess a firm's external macro environment
PESTLE analysis
Components of PESTLE
Political
Economic
Sociocultural
Technological
Legal
Enviornmaental
What analysis can be used to assess a firm's micro environment
Porter’s Five Forces
What are Porter’s Five Forces
Industry Rivalry
Threat of New Entrants
Buyer Power
Threat of Substitutes
Supplier Power
Porter’s Five Forces
What is Industry Rivalry
How hard firms must fight against industry rivals (competitors) to gain customers and market share
Porter’s Five Forces
What is Threat of New Entrants
Barriers to Entry
Porter’s Five Forces
What is Buyer Power
Balance of power between a firm and its customers
Porter’s Five Forces
What is Threat of Subsitutes
Substitutes are completely different products or services that consumers would be willing to use instead of the product they currently use
Porter’s Five Forces
What is Supplier Power
Balance of power between firms and their suppliers
Why do managers conduct an internal analysis of their firms?
To understand the resources available to pursue new ideas, innovate and plan for the future
What are resources
Things a firm has to work with
What are capabilities
Things a firm can do
What is a firm’s value chain
Series of consecutive steps that go into the creation of a finished product
Two components of the Value chain
Primary Activities
Support Activities
Value Chain
What are Primary Activities
Actions a firm takes to directly provide a product or service to customers
Value Chain
What are Support Activities
Actions required to sustain the firm that are not directly part of product or service creation
What is the analytical tool used to assess resources and capabilities called
VRIO
Components of VRIO
Value
Rarity
Difficult to Imitate
Organized to capture value
What is Competitive Advantage
Factors that allow a company to produce goods or services better or more cheaply than its rivals
What is Cost Leadership
Firm’s ability to sell product or services cheaper than rivals
What is differentiation
The firm produces a good or service different to rivals to attract more customers
What is focus (Segmentation)
Focusing on marketing and selling to a smaller market/segment
The Strategy Cycle
What is the strategic management process?
Strategic Analysis
Develop Objectives
Create and Choose Strategies
Implement Strategies
Measure and Evaluate Performance
Vision and Mission
What is the vision statement (Broad)
Why do we exist?
What is the mission statement (Focused)
How will we accomplish our vision?
Analytical Tools to Formulate a Strategy
SWOT
PESTLE
Porter’s Five Forces
VRIO (Resources and Capabilities)
What are strategic objectives
They describe what the company will do to achive its mission
What is the Business Level Strategy
Means to achieve the specific goals of the organization
Cost Leadership
Differentiation
What is the Corporate Level Strategy
The highest level of strategy and is concerned with decisions about growing, maintaining, or shrinking very large companies long term.
What is the Grand Strategy
Does the firm want to grow, strive for stability, or take a defensive position in the marketplace?
The BCG Matrix
Question Mark
Star
Dog
Cash Cow
Characteristic of Question Mark
High Market Growth
Low Market Share
Characteristic of Star
High Market Growth
High Market Share
Characteristic of Dog
Low Market Growth
Low Market Share
Characteristic of Cash Cow
Low Market Growth
High Market Share
When would a company use a Defensive strategy
When its struggling in the market
What is an Operationalizing Grand strategy
Expanding a corporation to take a wider variety of forms
What is a Goal
Something that you are trying to accomplish
What framework to use when setting goals
SMART goals framework
Components of the SMART goals framework
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant
Time-Bound
How does the planning process cycle look like
Set Goals
Design a Plan
Implement Plan
Review Results
How long are short-term plans
Less than a year
How long are long-term plans
More than a year
Scale Levels of Planning
Strategic planning (Highest Level)
Tactical planning (Mid Level)
Operational planning (Low Level / Front-line Activities)
What is strategic planning
Performed by company executives to set the overall direction of the company
What is tactical planning
Planning that consists of broad ideas of what the company should do to pursue its mission
What is operational planning
Activities that each employee in the company will do to advance the tactical plans
What is Implementation of planned strategies
Refers to the execution of a strategy by assigning tasks for people to carry out to accomplish the company’s strategic goals.
How to measure Strategic performance
Financial reports or quality measures
What is leadership
The exercise of influence over those who depend on one another for attaining a mutual goal in a group setting.
What is management
A process consisting of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling
Differences between managers and leaders
Managers are assigned to be in the position
Leaders emerge from the situation
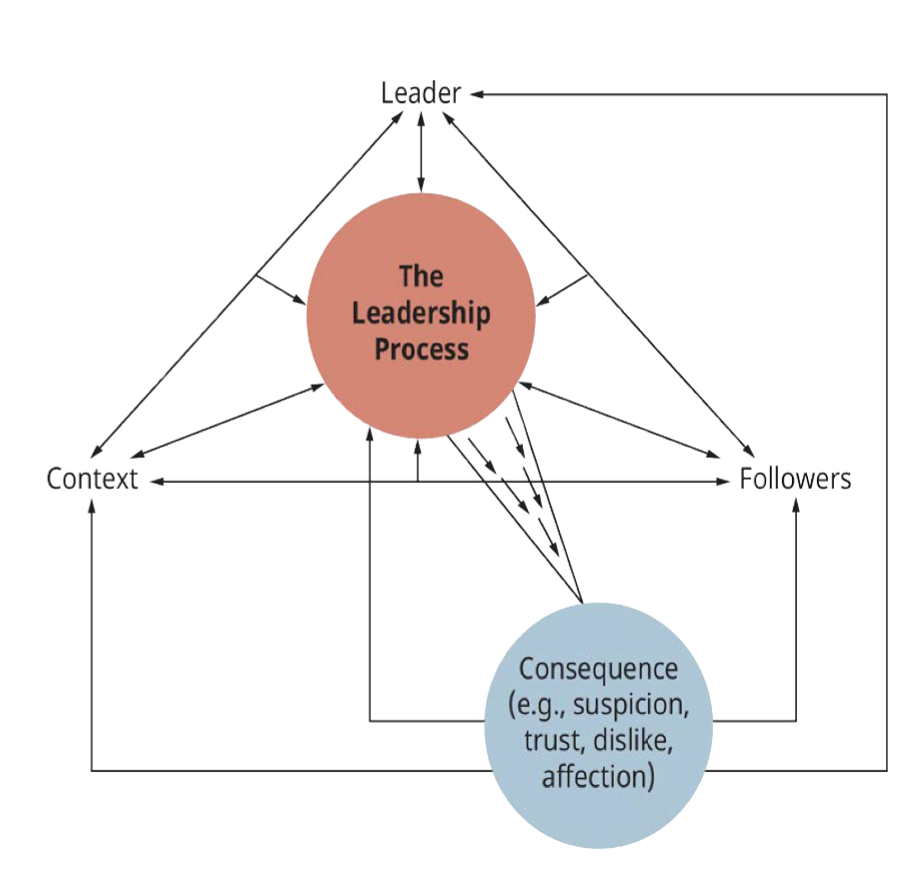
The Leadership Process Components
The leader
The context
The followers
The consequences
The Leadership Process