intermolecular forces (between)
the electrostatic interactions between molecules.
forces that exist between molecules.
(in strongest to weakest order)
HYDROGEN BONDING 🌊
H-FON
- When hydrogen bonds with fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen.
- These are very strong dipole-dipole interactions as FON are the most electronegative elements, creating the most strongly polarized bonds.
- The greater the difference in charge, the stronger the interaction (never stronger than formal charges ahem ions though.)
- More hydrogen bonds can not occur unless the compound was already in a hydrogen bond originally or in no bond.
DIPOLE-DIPOLE INTERACTIONS 😡❤️😊
What is a dipole?
A bond or molecule whose ends have opposite charges.
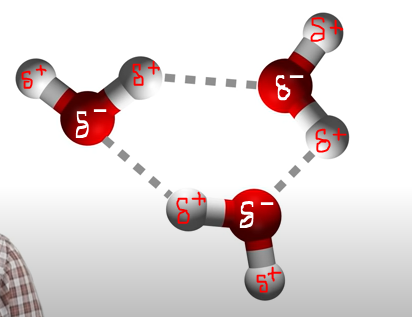
Attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.
Non-polar molecules/bonds cannot form dipole-dipole interactions as they have no charge.
Example of a dipole-dipole interaction
Water molecules are polar bc oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, thus, will pull the electrons in the bond towards itself. 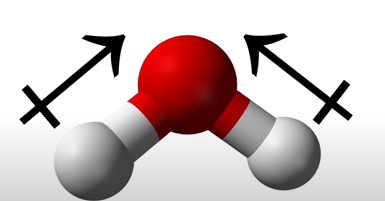
- oxygen will have a negative charge as it has electron excess (needs to get rid of some)
- hyrogens will have a positive charge as it has electron deficiency (lacking some)
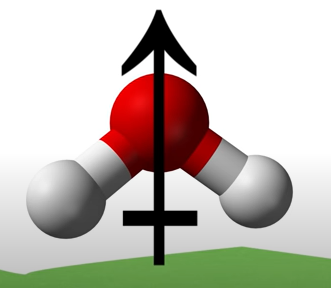
When the vectors (charges) are combined and one side has a stronger pull (electronegativity) than the other side, forming a dipole.
Ion-Dipole
When ions make interactions with atoms with the opposite charge.
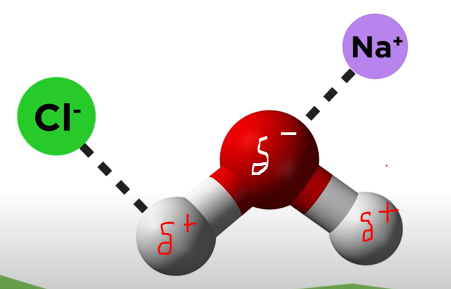
Dipole-dipole
molecules will move in such a way as to always be making electrostatic interactions between the negative end of one dipole and the positive end of another dipole.
DISPERSION FORCES 🁷🁷🁷🁷🁷🀷👈
DOMINOOOOOOS
- it is what monoatomic species & non-polar covalent compounds can do.
- a weak attraction occurs when a polar molecule induces a dipole in an atom or in a nonpolar molecule by disturbing the arrangement of electrons in the nonpolar species.
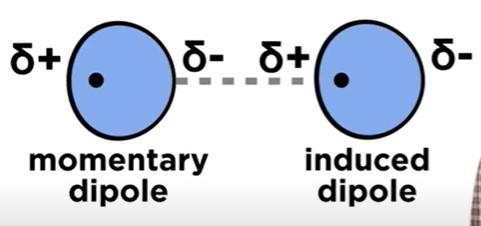
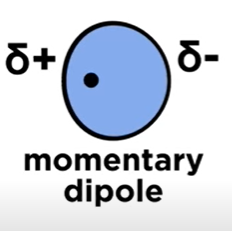
Momentary Dipole
When the electron cloud of an atom is SLIGHTLY lopsided, resulting in a small partial negative and positive charge.
Weaker than a formal dipole-dipole bond.
Induced Dipole
- When momentary Dipole approaches another atom, the partial negativity gets repeled, moving to the other side of the atom and resulting in a slight dipole.
Thus, there will be a momentary dipole + induced dipole interaction.