Week 2 - L2 : Purification, and Sequencing Techniques in Biochemistry
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is a protein domain?
Independently folding, stable structural units within a protein, usually about 50-250 amino acids long.
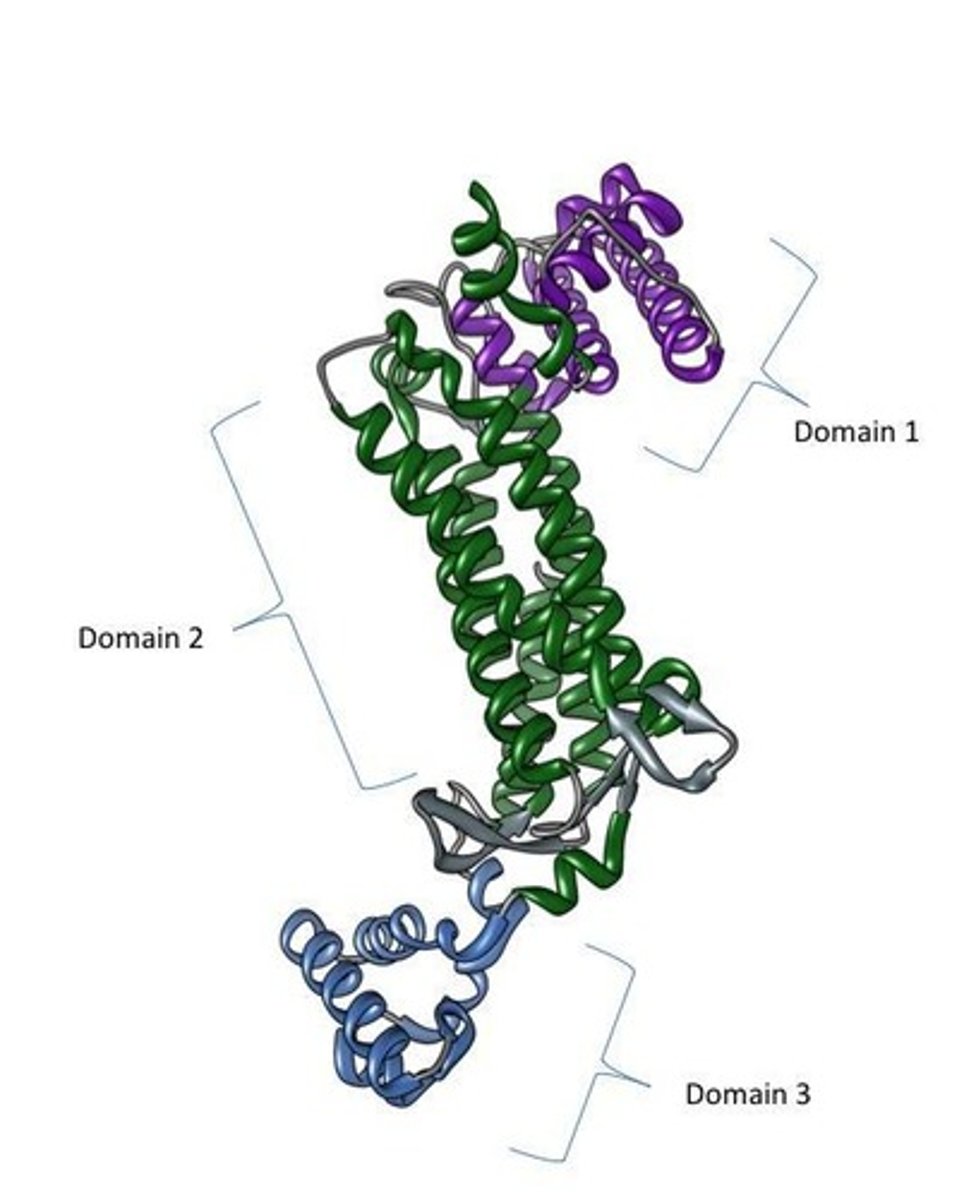
What is the significance of protein domains in terms of stability?
They can exist and retain structure/function even when separated from the rest of the protein.
How do protein domains contribute to protein assembly?
They serve as modular building blocks, allowing for the modular assembly of complex proteins.
What is a structural role of protein domains?
Provide a stable framework for a protein's overall architecture.
What is a functional role of protein domains?
Each domain can have a specific job, and domains can work together for complex functions.
How does bioinformatics utilize protein domains?
Domain identification helps predict protein function from sequence.
How are protein domains related to medicine?
Many diseases involve mutations in specific domains.
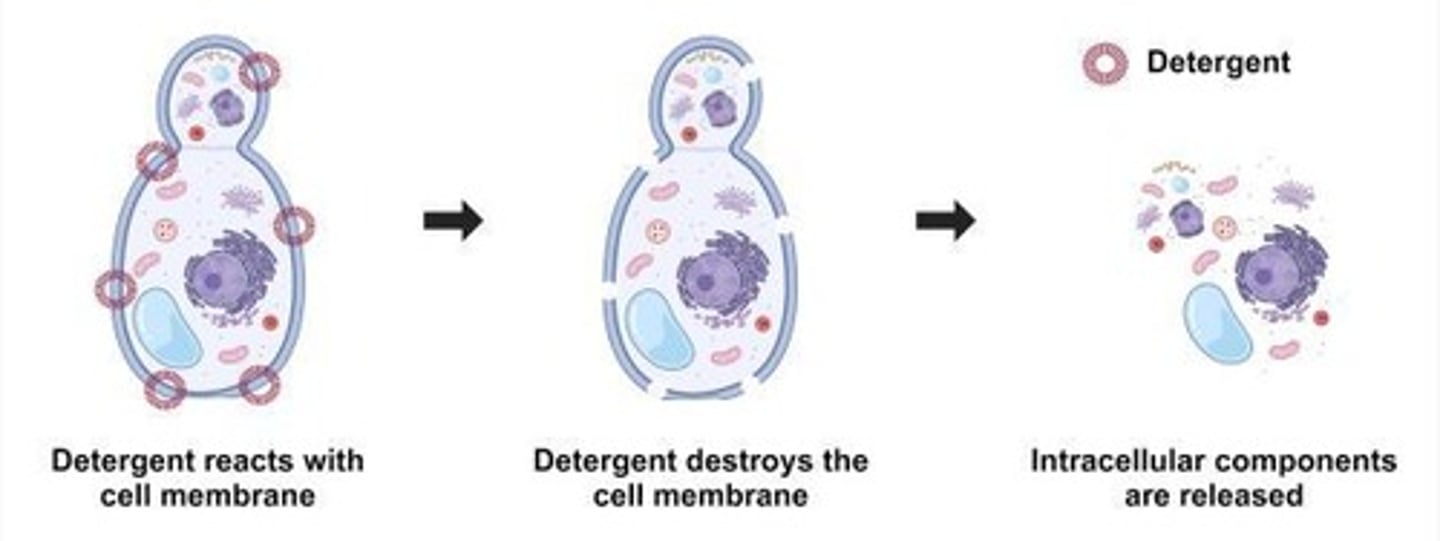
What is the first step in purifying proteins?
Prepare an extract by disrupting the cell membrane.
What is sonication in protein purification?
Using high frequency sound waves to create rapid pressure changes in liquid.
What is shearing in protein purification?
Using mechanical force to physically rip membranes apart.
What is the purpose of a lysis buffer?
Uses chemical detergents to solubilize membranes.
What does low-speed centrifugation remove?
Unbroken cells, nuclei, and large debris.

What is isolated during mid-speed centrifugation?
Mitochondria and lysosomes.
What does high-speed centrifugation isolate?
Microsomes and ribosomes.
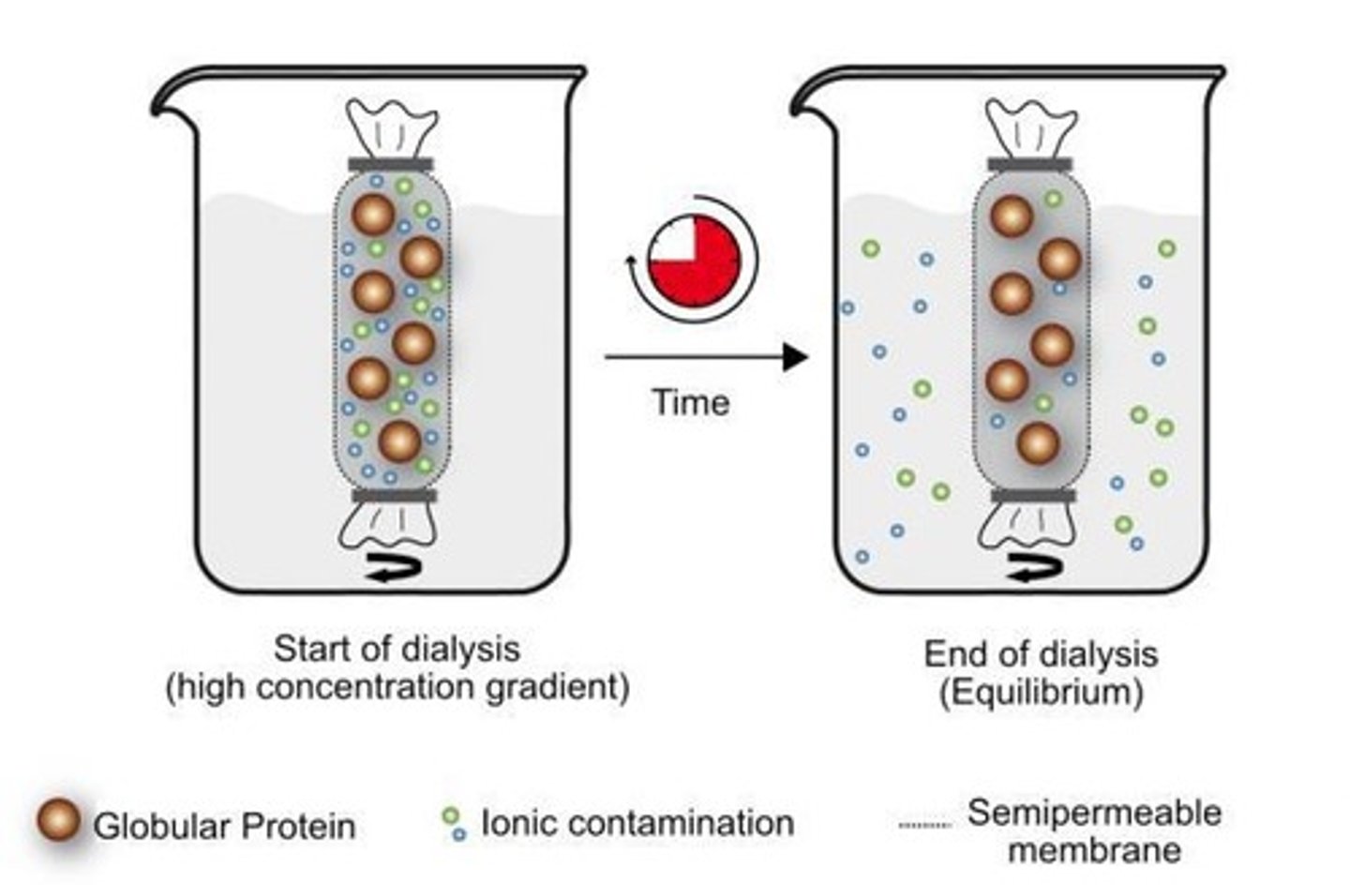
What is dialysis in protein purification?
Uses a semi-permeable membrane to separate small proteins from larger ones.
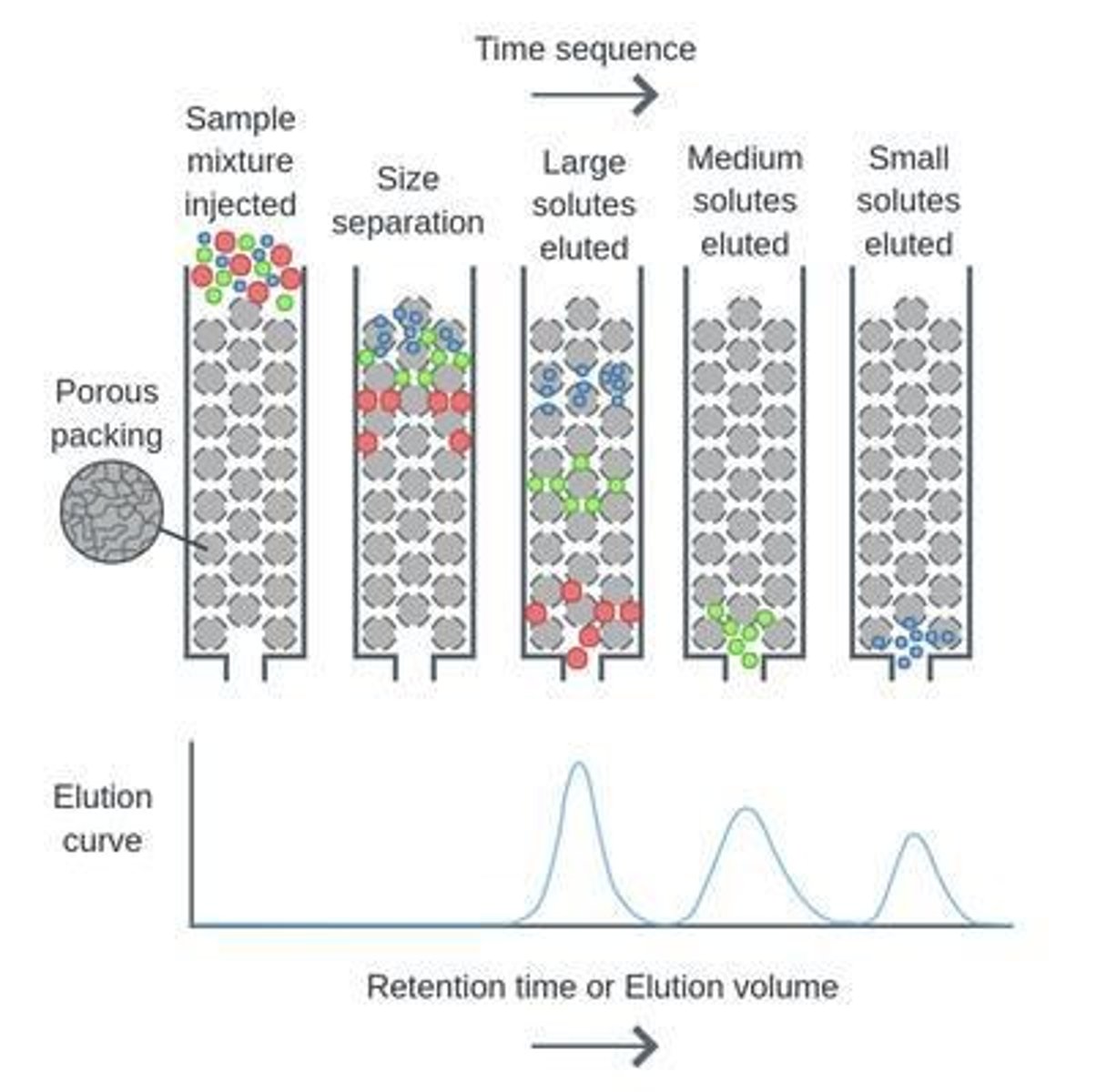
How does size exclusion chromatography work?
Separates molecules based on size using porous beads.
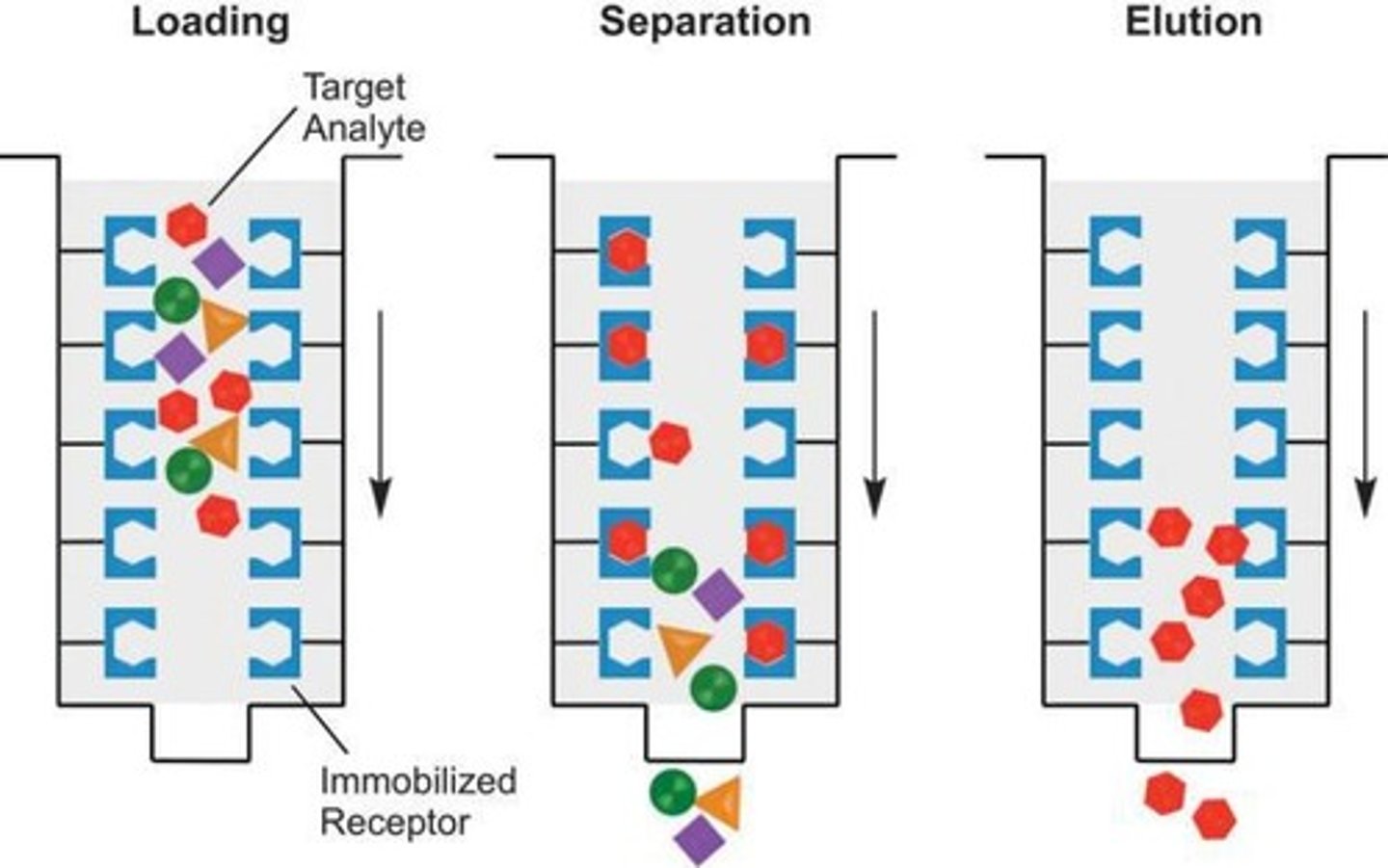
What is affinity chromatography?
Separates proteins based on specific binding interactions with a ligand on resin.
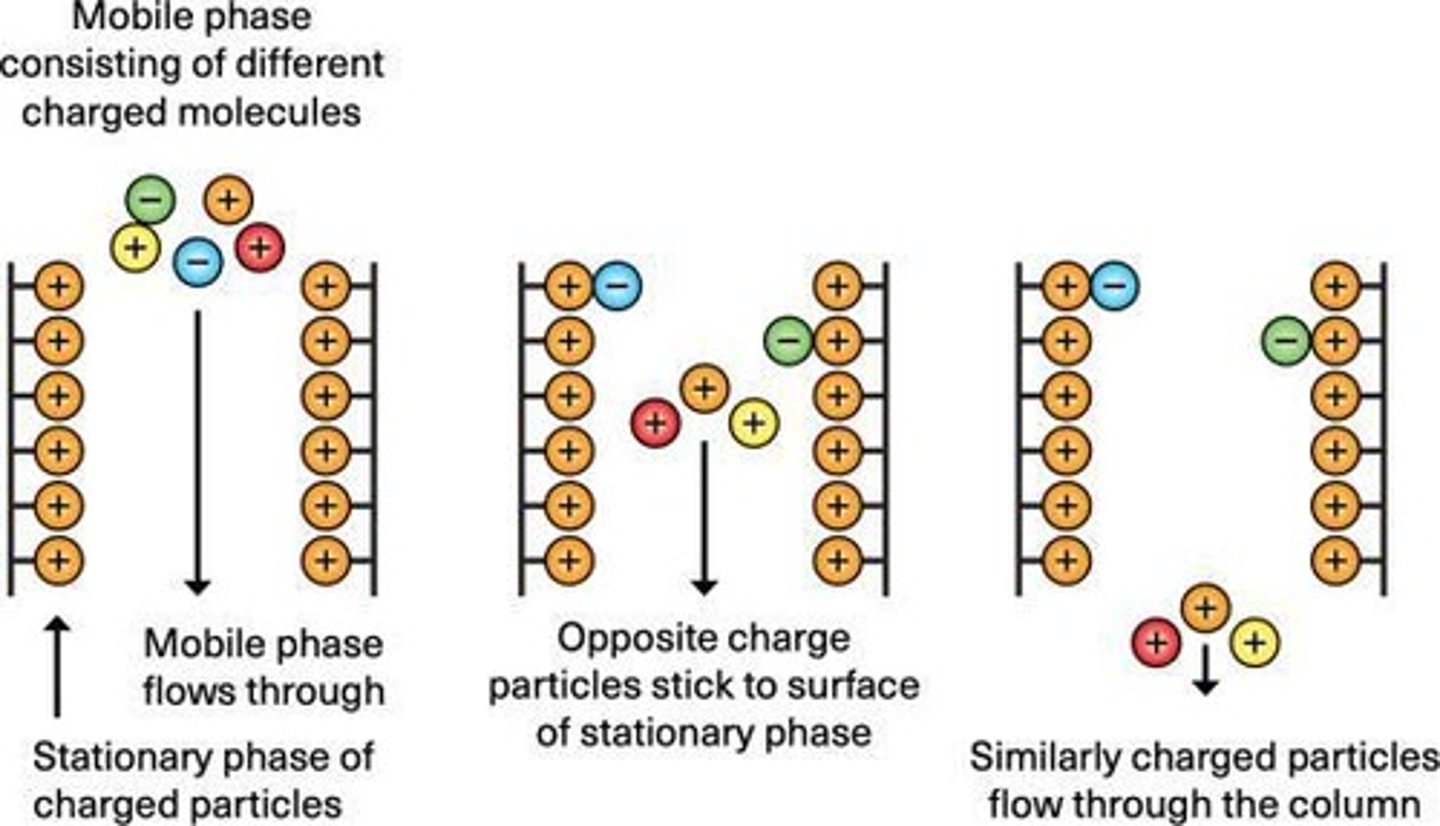
What is ion exchange chromatography?
Separates proteins based on their net surface charge at a given pH.
What are the steps in determining a protein's amino acid sequence?
1. Separate and purify the polypeptide chains.
2. Break the interchain disulfide linkages
3. Determine the amino acid concentration
4. Identify the terminal amino acid
5. Cleave the protein into small fragments
Why is it important to break interchain disulfide linkages?
To linearize the polypeptide for analysis.
What do amino acid analysers do?
Provide a report on the entire amino acid composition of a sample.
What is the purpose of identifying the terminal amino acid?
To determine the start and end of the polypeptide chain.
What method is commonly used for N-terminal sequencing and its limitations?
Edman degradation - Tag the N-terminal residue with Edmans reagent.
It can only sequence relatively short peptides, usually up to about 50 amino acids.
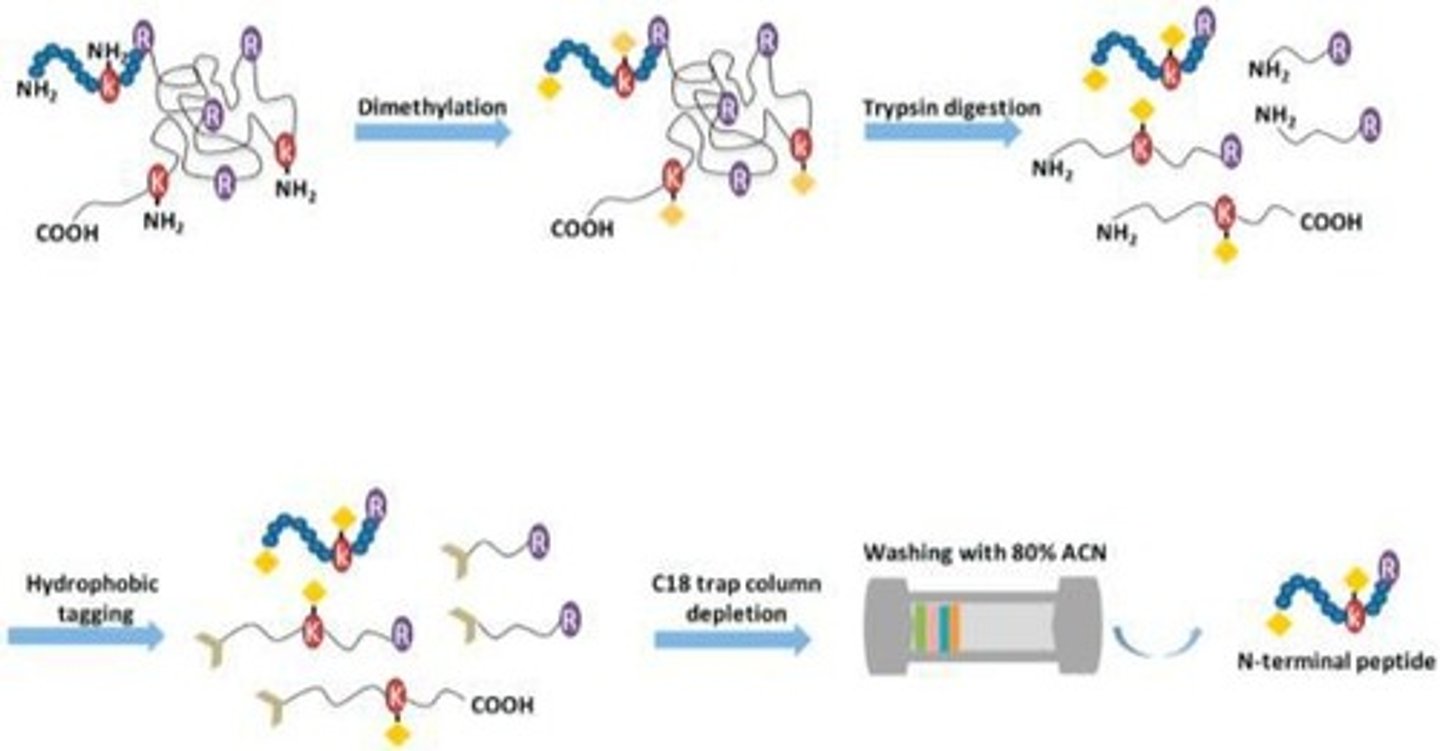
What is the akabori reaction used for?
To label the C-terminal residue of a polypeptide.
What is peptide mapping?
Reassembling polypeptide sequences from overlapping fragments.
What does mass spectrometry measure?
Mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of ionized molecules.
What is the difference between top-down and bottom-up mass spectrometry?
Top-down measures intact proteins, while bottom-up analyzes digested peptide fragments.