ANS 124: Sexual Dimorphism, Postnatal Growth
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is Witches Milk and what causes it?
Witches Milk is when the mom's hormone environment can induce the human baby's epithelial cells to make a tiny bit of milk.
Witches Milk can happen in what fraction of human babies?
1/3 of babies
In a study trying to see how testosterone restricts mammary development in males, what type of testosterone was used? Describe the process.
Radioactive testosterone was injected into mice to see where it binds to in the fetal mammary gland.
Where did the testosterone bind to in order to restrict mammary development in males?
Testosterone binds to receptors on the mesenchymal cells around the neck of the mammary sprout.
When testosterone binds to receptors on the mesenchymal cells, what does that activate?
activates the mesenchymal cells to divide and constrict the mammary sprout
Describe the structure of the mammary gland at birth. What is the MG sitting on?
At birth, the MG is a simple branched structure sitting at the edge of a "mammary fat pad".
After birth, what type of growth does the mammary gland first go through?
Isometric Growth
Describe the Isometric Growth of the mammary gland after birth.
the mammary ducts only grow at the same rate as the rest of the body (everything grows proportionally)
At what stage of life does the mammary gland STOP doing Isometric Growth?
At puberty
Once puberty approaches, what type of growth does the mammary gland go through?
Allometric Growth
Describe the Allometric Growth of the mammary gland at puberty.
Once puberty approaches, and the hormones kick in, the mammary ducts grow faster than the rest of the body.
Ultimately, what is the goal of the mammary gland during Allometric Growth?
To try to fill the mammary gland with as much epithelial cells as it can.
The number of epithelial cells in the mammary gland dictates what in lactation?
the amount of milk that can be produced
Around how many days old is a mouse weaned?
~21 days
Describe the mammary gland structure of a weanling mouse (21 days old).
A mammary fat pad, with a supramammary lymph node and a little bit of epithelial cell branching around the nipple.
Around how many weeks old does a mouse reach puberty?
~4 weeks old
Describe the mammary gland structure of a mouse at puberty (~4-5 weeks old).
The tree is a lot bigger and has filled a distance of 1/2 inch in just ~2 weeks.
What type of growth allows for the tree of the mouse mammary gland to grow so fast in just ~2 weeks during puberty?
Allometric Growth
The onset of allometric growth in the mouse mammary gland starts and continues when in relation to puberty?
starts BEFORE the beginning of puberty, and CONTINUES into puberty
By the end of puberty, what does the mouse mammary gland look like?
The tree of epithelial ducts has filled the mammary fat pad.
In the mouse and human mammary gland, what structures form at the end of epithelial branching during Allometric Growth?
Terminal End Buds
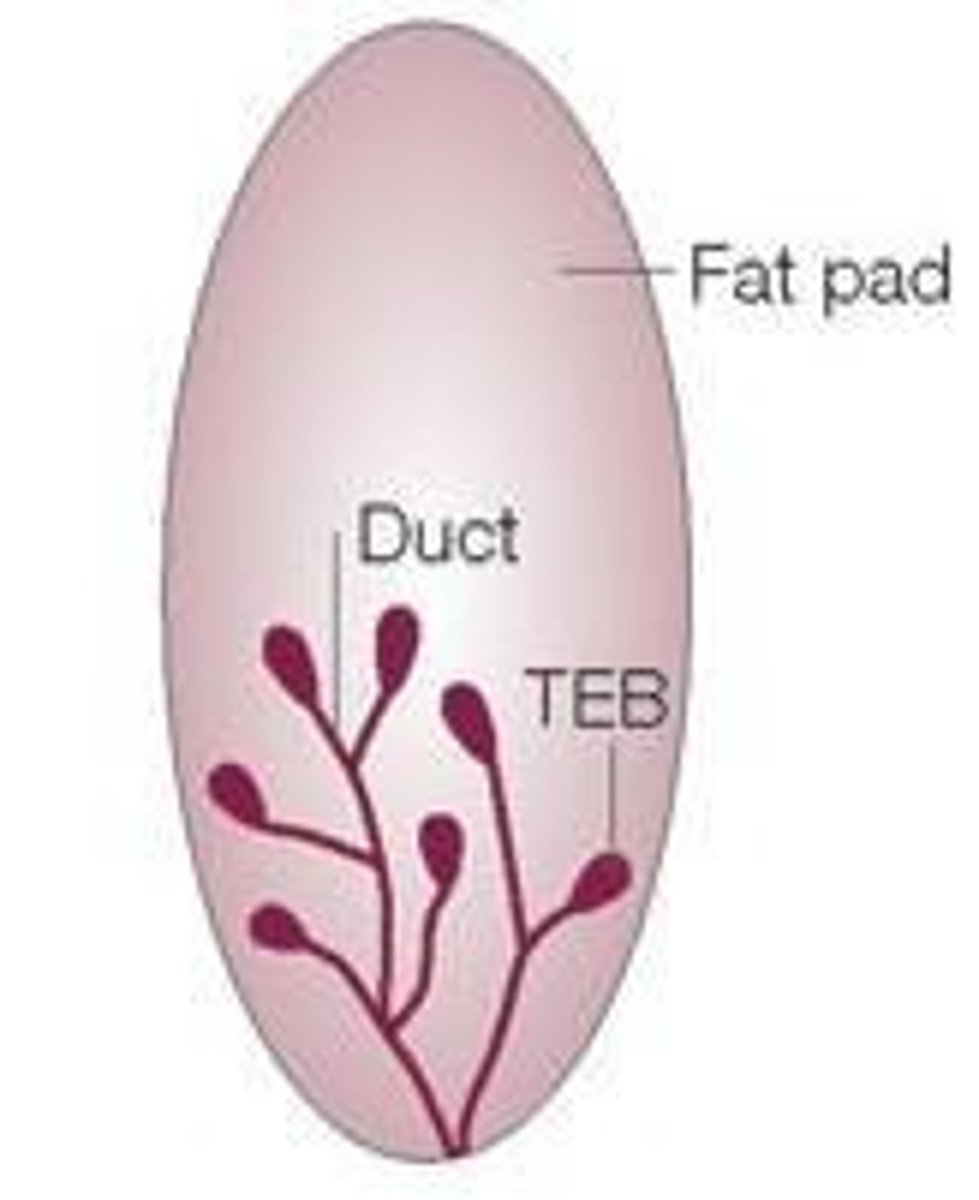
Describe the general structure of Terminal End Buds.
Epithelial cells around the outside edges of a hollow lumen.
The hollow lumen of the Terminal End Buds are for what purpose?
During lactation in the future, it is where the milk will flow through.
The Terminal End Buds are surrounded by what cells?
Adipose Tissue (adipocyte cells)
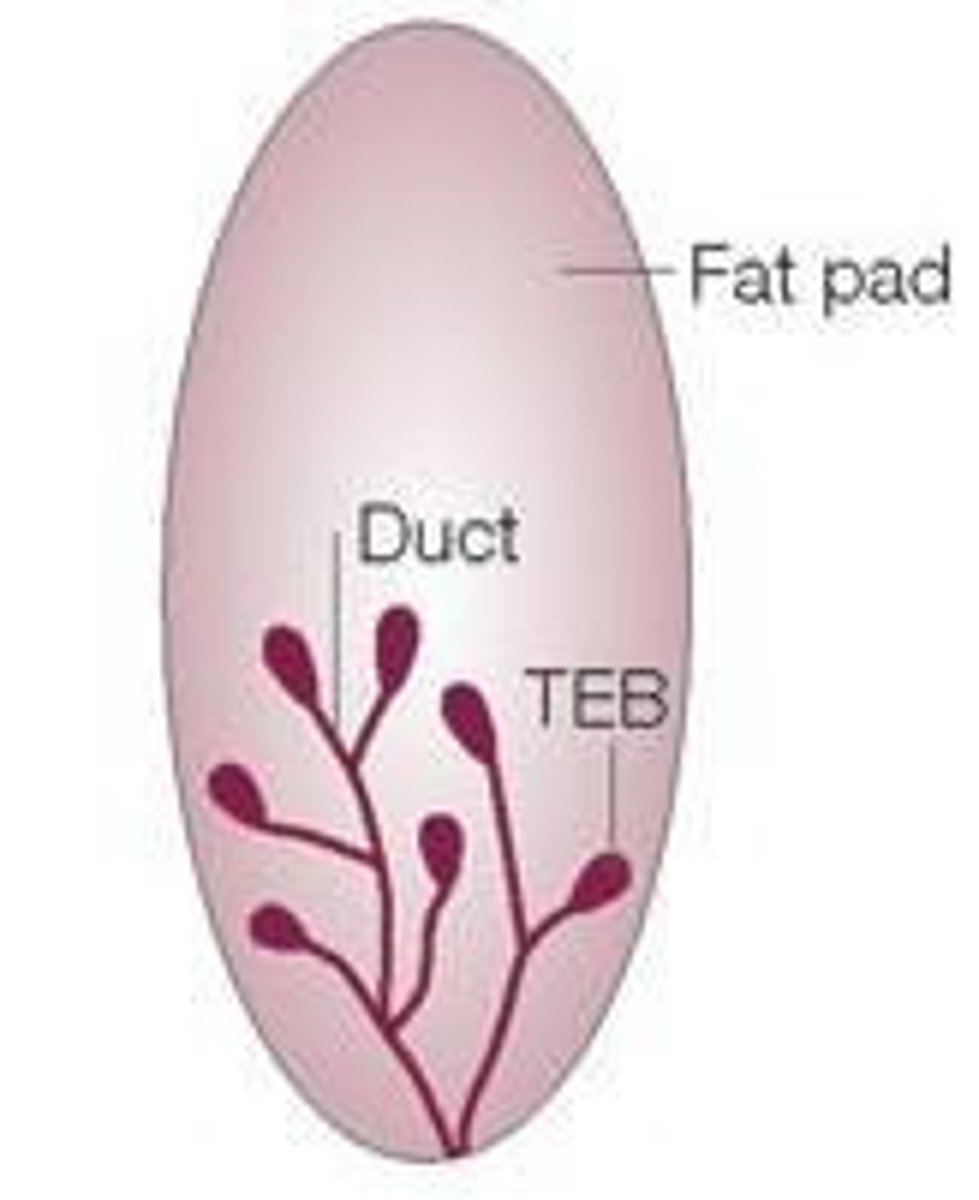
What do Adipocyte Cells store?
Stores fat as triglycerides
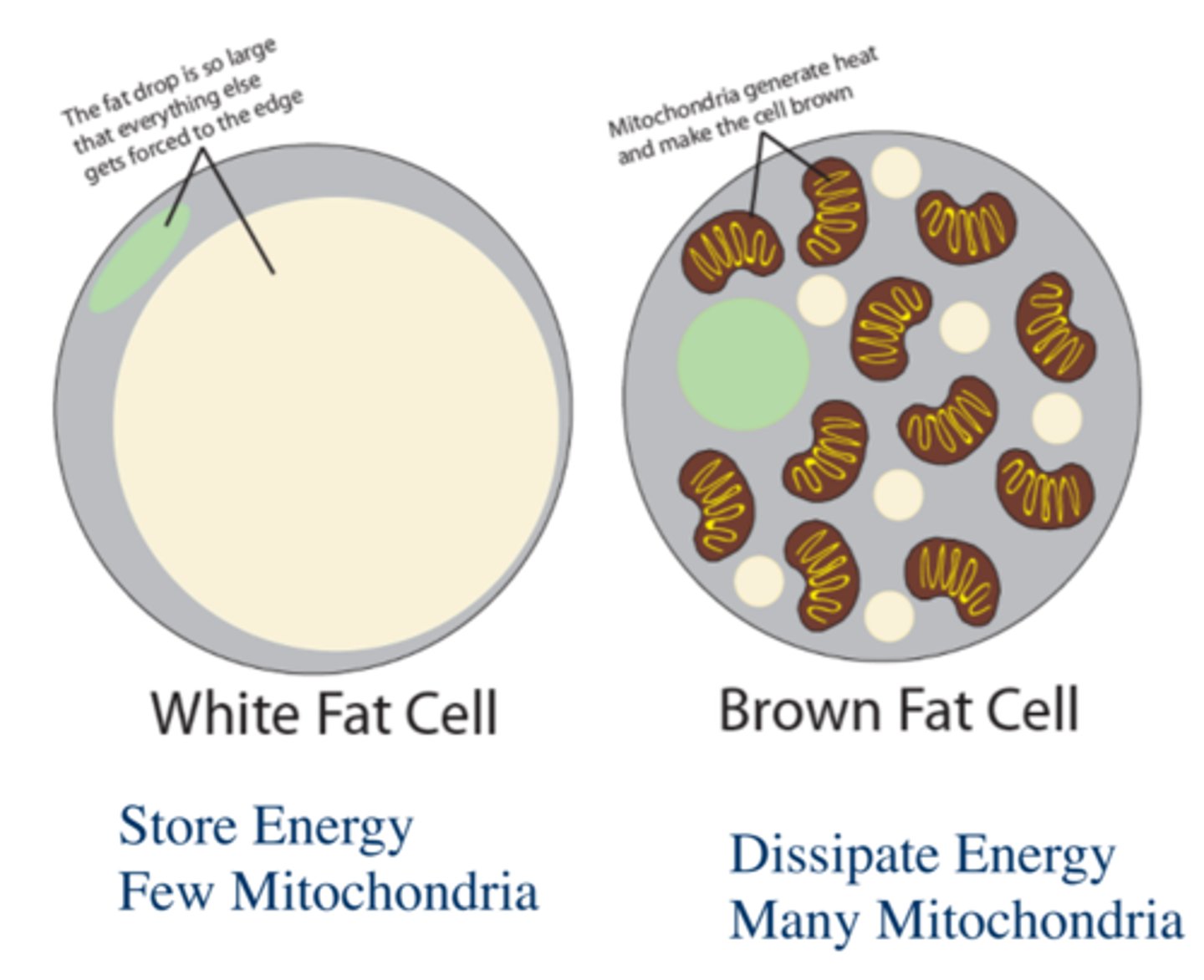
Describe how adipocyte cells look like under the microscope.
They appear transparent under the microscope because there is not a lot of things in there.
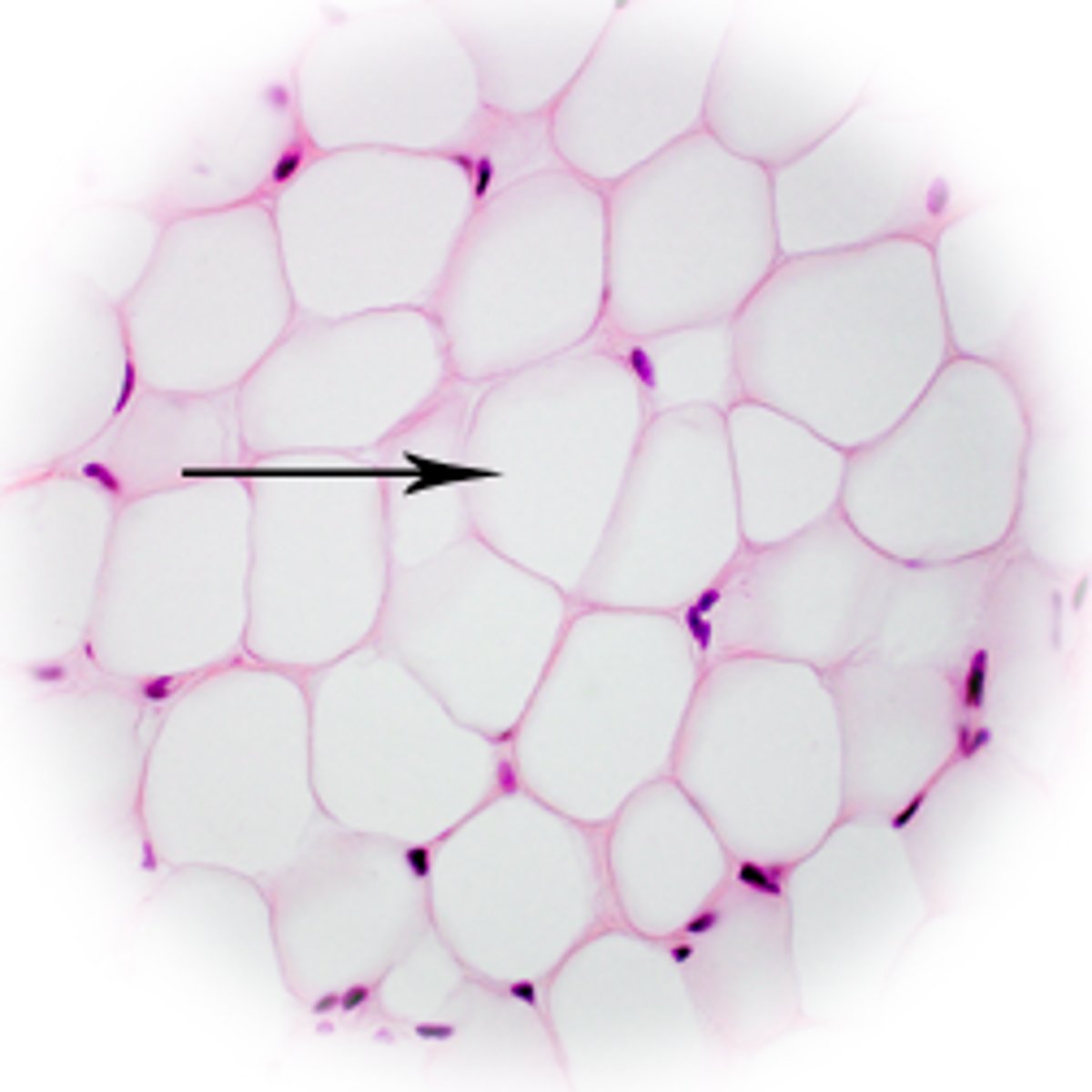
What process is happening to the epithelial cells that are surrounding the outside of the Terminal End Bud?
They are undergoing mitosis.
Specifically, where in the Terminal End Bud is a lot of mitosis happening in epithelial cells?
at the leading edge of the Terminal End Buds
What is the Parenchyma?
It is all the functional tissue of an organ.
What 2 cells make up the Parenchyma in the mammary gland?
Epithelial Cells
Myoepithelial Cells
The supporting cell types in the mammary gland are called what?
Stroma cell types
What 4 supporting cells make up the Stroma in the mammary gland?
Blood Vessels
Adipocytes
Immune Cells
Connective Tissue Cells
In the Mouse Mammary Parenchyma, are the epithelial cells directly in contact with the adipocytes of the fat pad?
Yes, epithelial cells contact adipocytes of fat pad.
In the Sheep Mammary Parenchyma, are the Terminal Ductal Lobular Unit (TDLU) directly in contact with the adipocytes of the fat pad?
No, between the TDLU and the adipocyte is connective tissue, so there is no contact.
What label/tag is used to study which epithelial cells in the Terminal End Bud are mitotic?
Bromodeoxyuridine (BRDU)
What is Bromodeoxyuridine (BRDU)?
a fake nucleotide with Bromine
Describe the process of how Bromodeoxyuridine (BRDU) is used to study which epithelial cells in the Terminal End Bud are mitotic.
Inject the animal with BRDU, put the mammary tissue under the microscope, and then do immunohistochemistry. The nuclei of epithelial cells with BRDU will be dark. These cells are mitotic because when cells divide, they will put BRDU in their DNA.
Most of the cells in the Terminal End Buds are dividing because of what type of growth?
Allometric Growth
During puberty, where in the body has the highest rate of cell division in the body?
Mammary Gland
Since the mammary gland has a high rate of cell division, that allows for what bad thing to happen?
Higher chances of cancer due to genetic mutations in cell division.
In the human body, around how many base pairs of ACTG are there in a cell?
~3 Billion base pairs
What happens to the ~3 Billion base pairs during cell division?
cell needs to be able to copy all of that in cell division
When does breast cancer usually start/initiate in humans? Why?
around 16, 18, 20-ish, when cell division is happening the most to make the mammary gland tree.
What process in the mammary gland allows for the tree to have hollowed out tubes?
Cells in the middle undergo apoptosis to create the hollow lumen in the ducts.
When a cell undergoes apoptosis, what happens to their DNA?
DNA breaks apart and becomes fragmented.
What can be used to study and track which cells are doing apoptosis in the mammary gland?
you can tag/label fragmented DNA to find which cells are undergoing apoptosis