Unit C: Light and Optics
1.0
Properties of Light
Light travels in straight lines
Light can be reflected
Light can be bent
Light is a form of Energy
microscopes- magnify minute things
telescope- magnify things that are far away
Two Types of Telescopes
Reflecting telescope
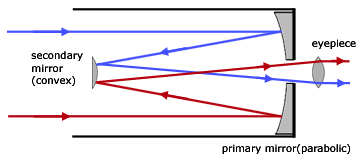 Refracting telescope
Refracting telescope
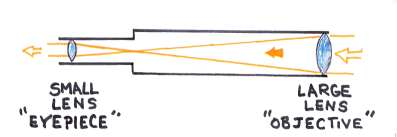 Binoculars
Binoculars
two fixed refracting (bending) telescopes
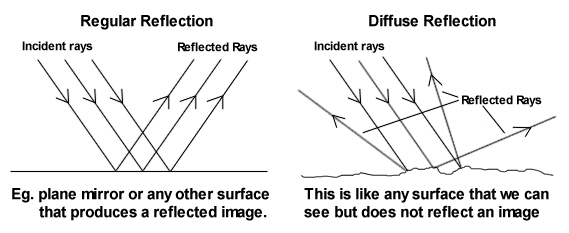
Two types of reflection
Regular reflection- a smooth, flat surface
Diffuse- rough, jagged surface
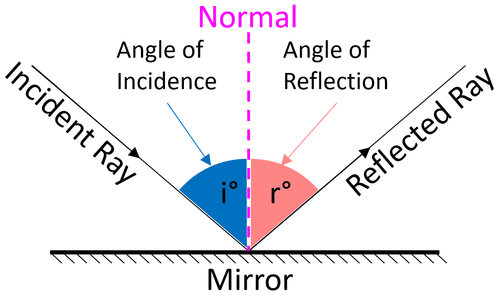
 The Law of Reflection
The Law of Reflection
The Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
 Curved Mirrors
Curved Mirrors
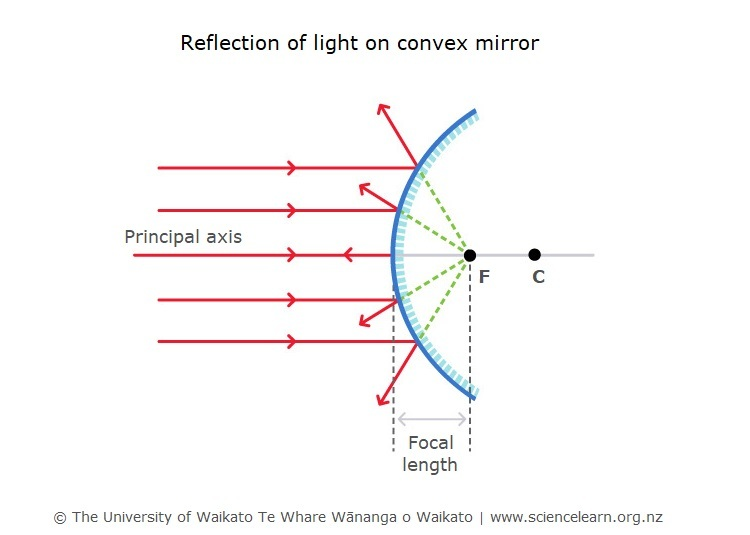
Concave mirrors- form an image that appears closer than it is and can be useful because it directs light everywhere. The focal point is in front of the mirror. ex. headlights, flashlights
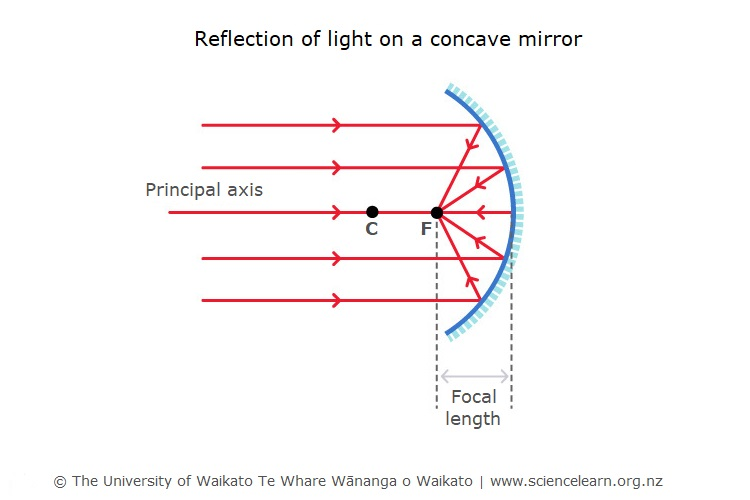
Convex mirror- forms images that appear much smaller and farther away. They can reflect light from a large area. ex passenger side mirror
 Refraction- the process in which light is bent as it transfers from one medium to another. Different media can alter the speed at which the light travels, causing it to bend
Refraction- the process in which light is bent as it transfers from one medium to another. Different media can alter the speed at which the light travels, causing it to bend
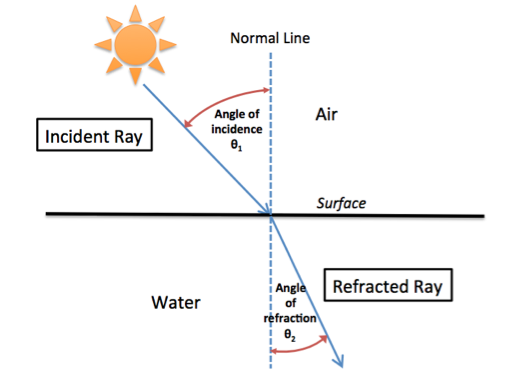
The Law of Refraction
The Law of Refraction states that when light travels from a less dense medium to a tender medium, it bends toward the normal. Similarly, when light travels from a more dense medium to a less dense medium, it bends away from the normal.
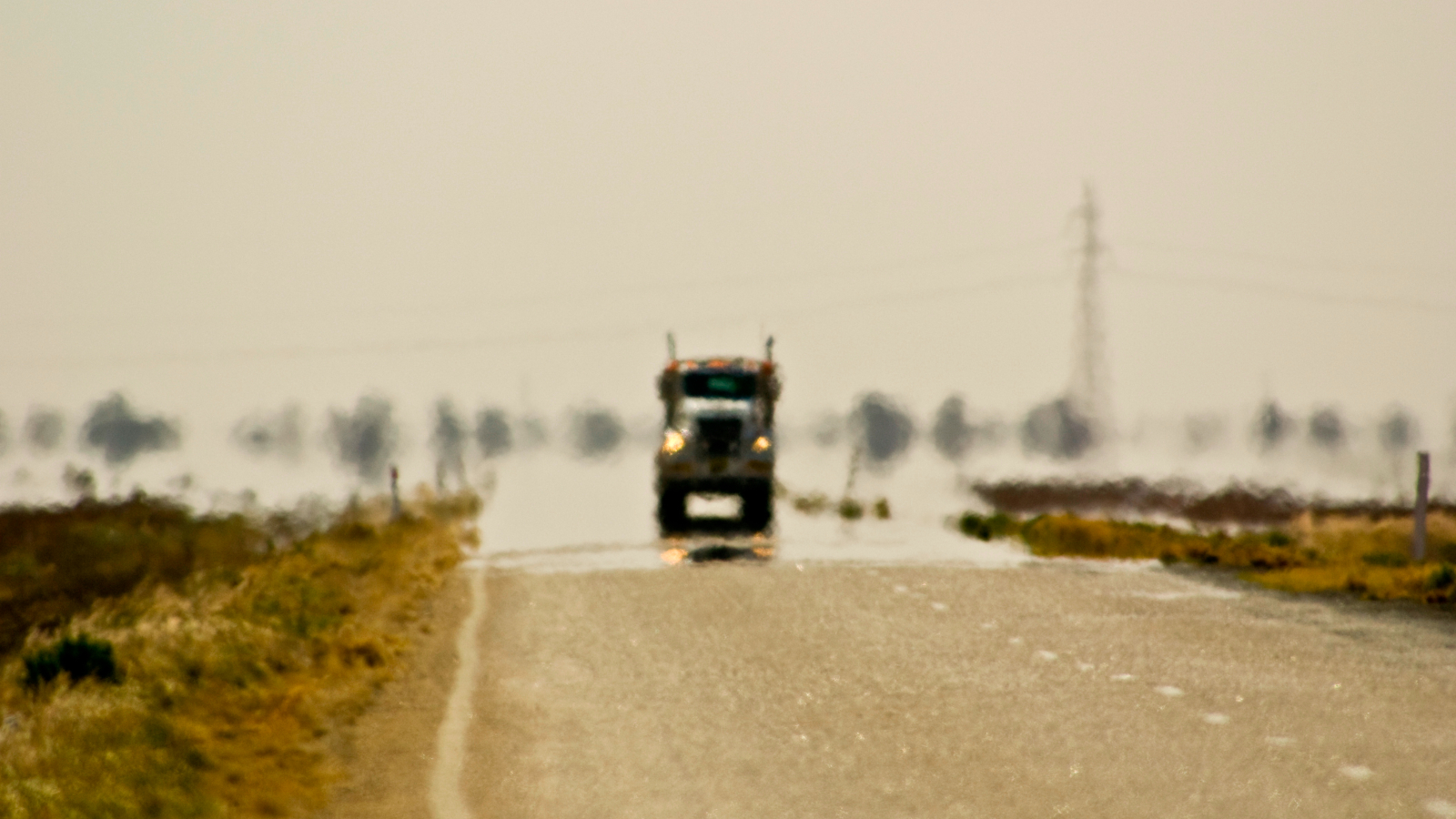
Mirage- is caused by refraction when light interacts with air with different temperature layers. Hotter air is less dense than cooler air

Lens- a curved piece of glass or transparent material
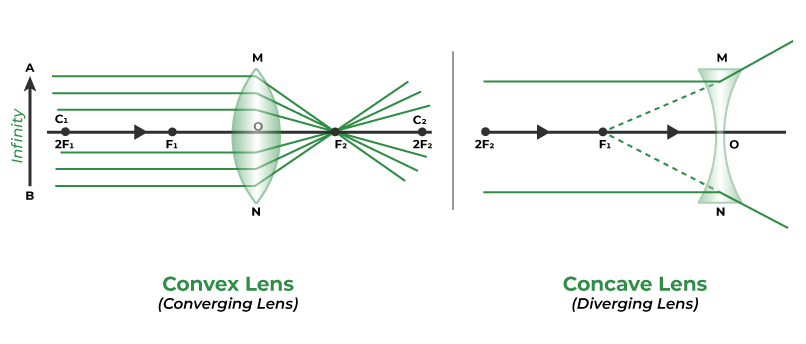
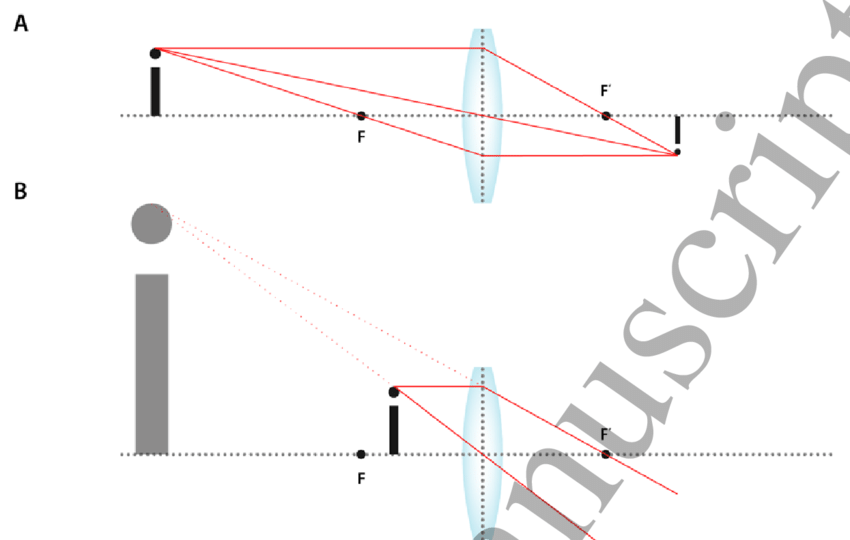
Image formation in a double convex lens
Three scenarios are possible based on where you place the object.
Beyond 2F (2 focal lengths away)- the image projected is real, reduced, and inverted
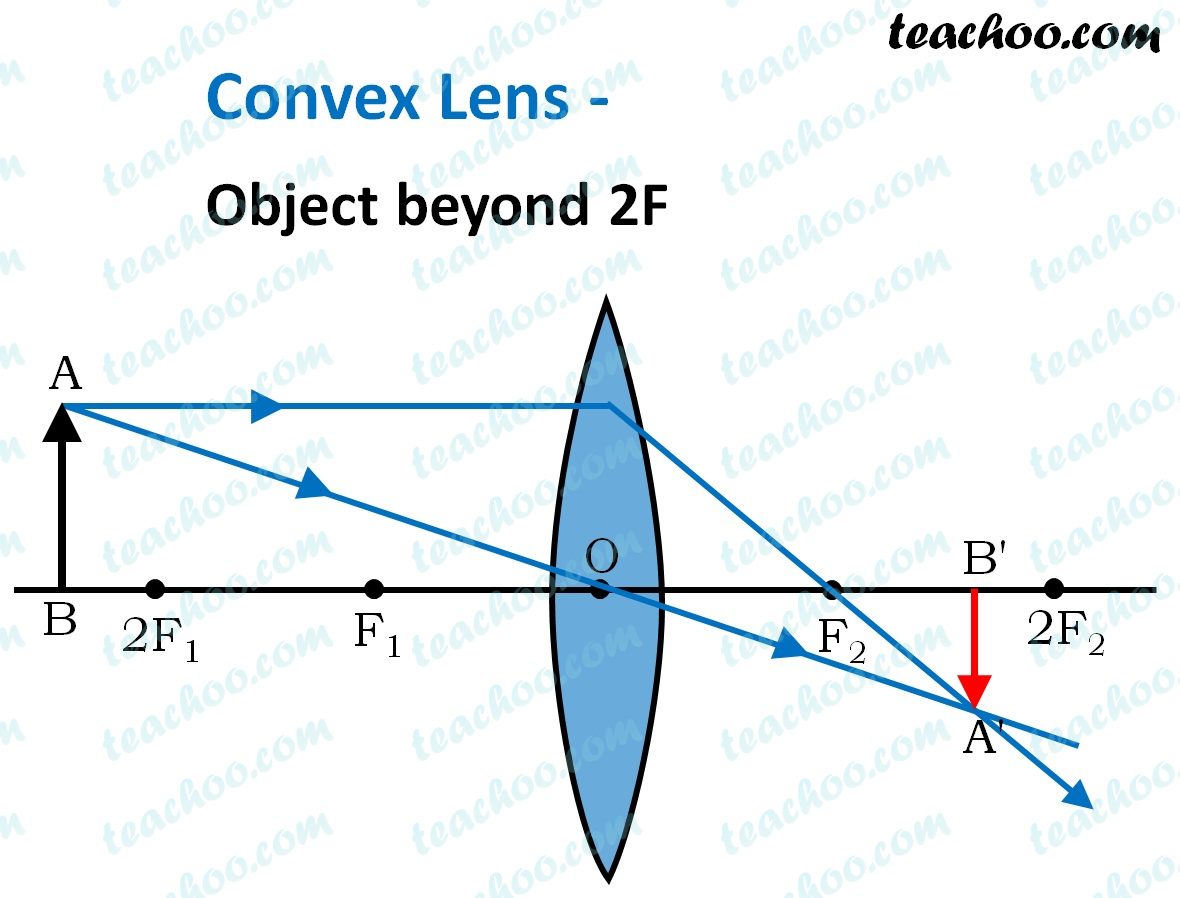 Between 2F and 1F- the image projected is real, inverted, and enlarged
Between 2F and 1F- the image projected is real, inverted, and enlarged
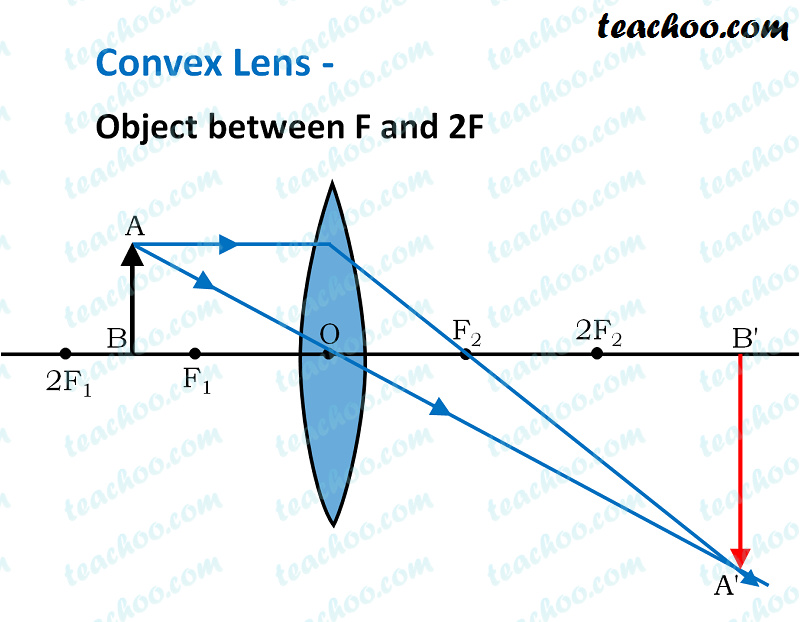 Between the lens and F- this is diagram B. The image is not real (virtual,) is upright, and enlarged
Between the lens and F- this is diagram B. The image is not real (virtual,) is upright, and enlarged
 The Wave Model of Light
The Wave Model of Light
Light behaves as a wave
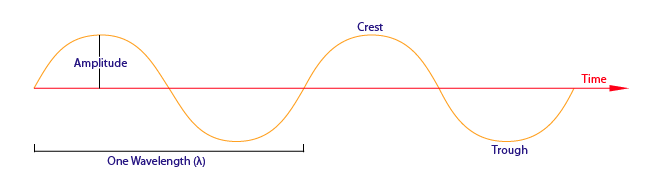 Rest position- when a wave passes through the line that represents time, it is called a rest position
Rest position- when a wave passes through the line that represents time, it is called a rest position
Crest- top of the wave
Trough- bottom of the wave
wavelength- the distance from crest to crest and trough to trough
Frequency
is the rate at which troughs and crests move up and down
frequency is measured in cycles per second
a cycle per second is a hertz (Hz)
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
EMR- electromagnetic radiation
and electrical field induces a magnetic field and that is how that wave continues
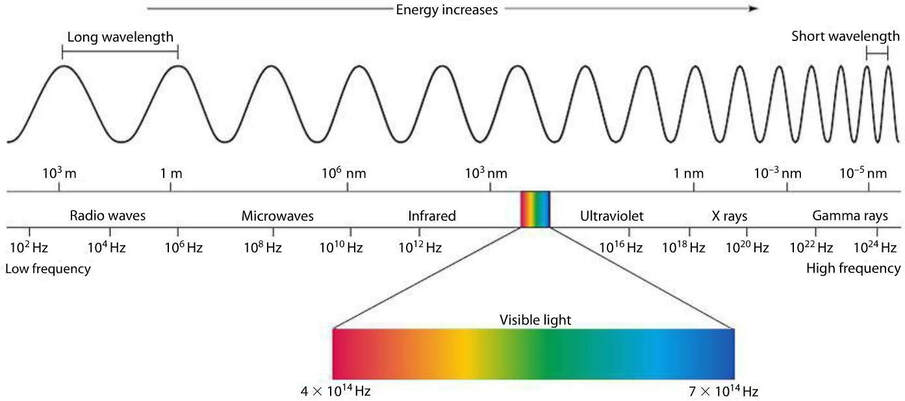
the longer the wavelength is, the slower the frequency and the lower the energy is
the shorter the wavelength is, the faster the frequency and the higher the energy is
Radiowaves
use for communication
searching for extraterrestrials
bounces off objects
used for communication
MRI (medical resonance imaging)
Microwaves
used for cooking- it excites the water particles, causing steam and cooking
RADAR- radio detection and ranging)
Infrared
cant be seen but is felt as heat
thermograms
Visible Light- ROY G BIV
UltraViolet (called ultraviolet because it comes after violet)
sunburns
retinal damage
skin cancer
X-rays
used in medical imaging
mutations
can’t pass through lead
Gamma Rays
cosmic radiation
the ozone layer blocks the rays
super high in energy
small
used for blasting cancer cells (radiation therapy)
Light energy
electrical
mechanical (kinetic)
chemical
thermal
Sources of Light
Natural
sun
candles, oil, wood (burning)
bioluminescence ( firefly, angler fish, plankton)
Artificial
incandescent (old-fashioned light bulbs, filament)
Fluorescent (paint, tube- uses phosphor powder)
Phosphorescent
glow in the dark (triggered by light)
Chemiluminescent
glowstick
triggered by chemical reactions
The Primary colors of light
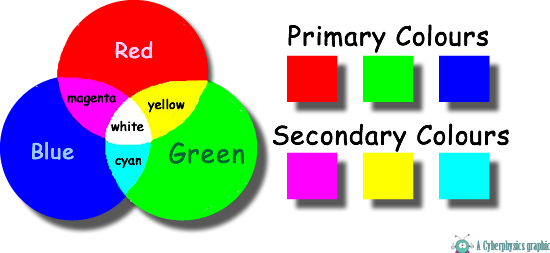
Theory of Colour Addition
The theory of color addition states that if you mix all three colors, you get white
The Eye
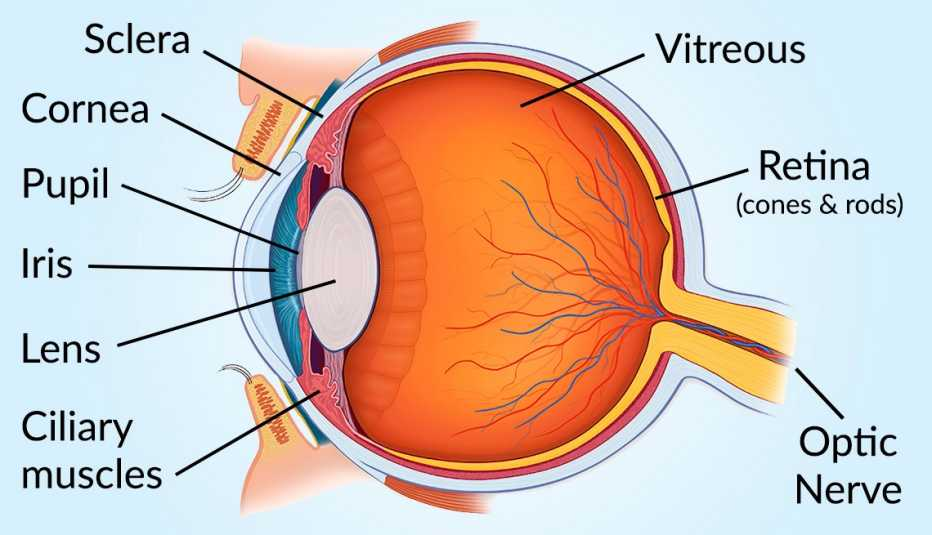
How the Human eye is compared to a Camera
pupil- aperture
iris- diaphragm
retina- film
lens-lens
How the Eye Works\
light enters the eye going through the cornea
the iris constricts or opens to control the amount of light
the ciliary muscles change the shape of the lens to help focus the light (this is called an accommodation reflex)
light is then focused on the retina
photoreceptors are stimulated by the light and send a chemical electrical signal, via the optic nerve
Photoreceptors are cells that detect light
Rods- light intensity
Cones- color
the brain interprets this signal as an image
Eyesight Difficulties
Astigmatism is caused by an irregularly shaped eyeball
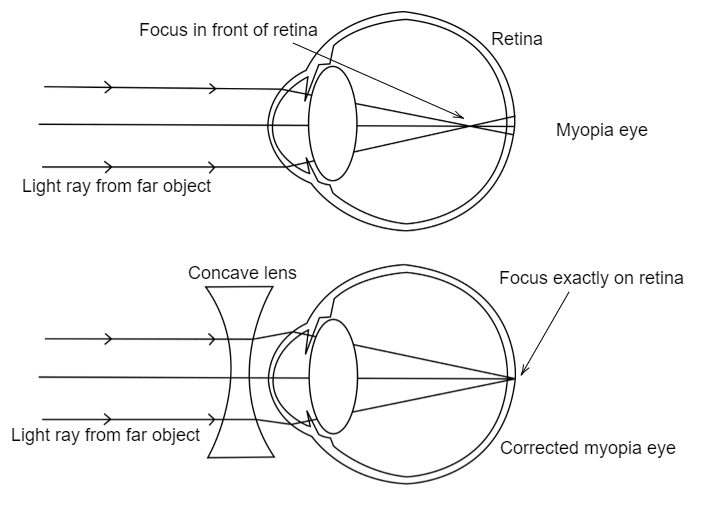
If your eye is too long, images form in front of the retina. This is called near-sightedness or myopic vision. Myopic individuals can see up close unaided.
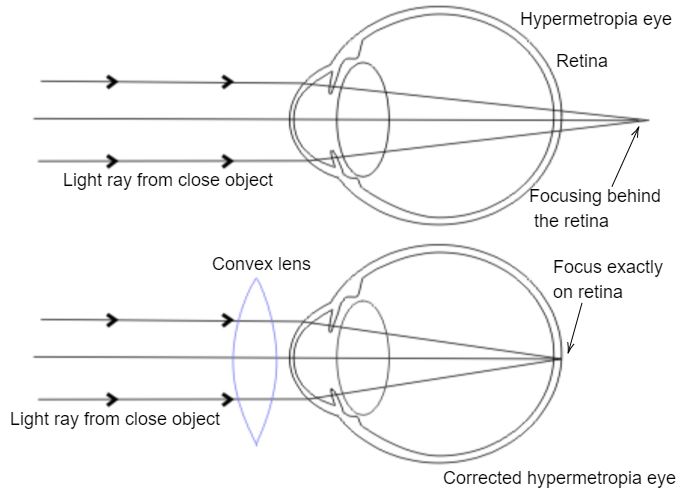
If your eye is too short, the image forms behind the retina. This is called far-sightedness or Hyperopic vision. Individuals with hyperopia can see far away unaided
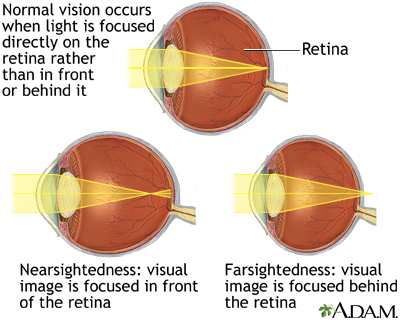
Near-sightedness is corrected with a concave lens
Far-sightedness is corrected with a convex lens
Laser eye surgery uses lasers to change the shape of the cornea
Eyes in the Animal Kingdom
Humans have what are known as “camera eyes” a retina, a cornea, and a lens
most vertebrates have camera eyes
Fish have perfectly round eyes therefore, they can see in almost all directions
nocturnal animals have a tapetum lucidium, a layer which acts as a mirror
Compound Eyes
Insects and crustaceans have compound eyes
each individual eyes are made up of smaller units called ommatidia (pl.) or a singular ommatidium that are great for tracking movement
but are lousy at forming coherent, or full, images
a mosaic image is formed
Stadium Images
are formed when cards are held up like an individual pixel

pixels (picture elements) are small units of color used in digital imagery
the greater the amount of pixels, the higher the resolution
resolution refers to the pixel density
THE END