Electromagnetic Induction
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Define magnetic flux
The measurement of total magnetic field that passes through a certain area
State Faraday’s Law
The magnitude of induced EMF in a circuit is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux
Magnitude of induced EMF → deflection size
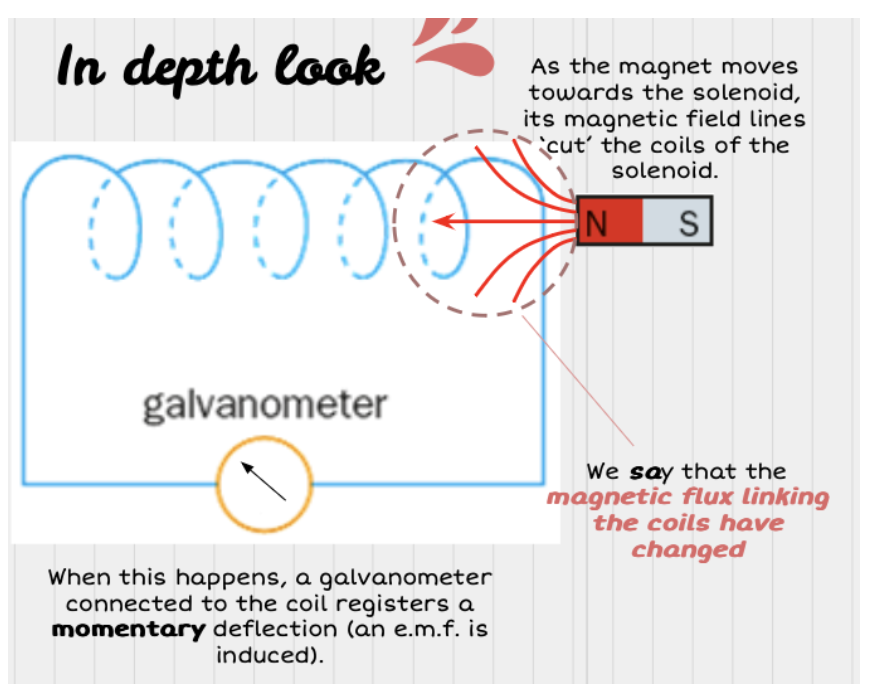
How can Faraday’s Law be observed?
Faster movement → greater deflection
When the magnet is not moving in the coil, there is no change in the magnetic flux linking the coils → no induced EMF
More turns in coil → more change in magnetic flux linkage → higher EMF induced
State Lenz’s Law
Direction of induced EMF is always such that its magnetic effect always opposes the motion or change producing it
What happens when the North pole of a magnet approaches a solenoid from the right?
To oppose the change, the solenoid needs to have a north pole on the right to repel the approaching magnet
The induced EMF is in a direction that will induce a North pole on the right of the solenoid
What happens when the North pole of a magnet leaves a solenoid from the right?
To oppose the change, the solenoid needs to have a south pole on the right to attract the magnet
The induced EMF is in a direction that will induce a south pole on the right of the solenoid
What is an AC generator?
An alternating current generator makes use of electromagnetic induction to convert mechanical energy into useful electrical energy *RHR
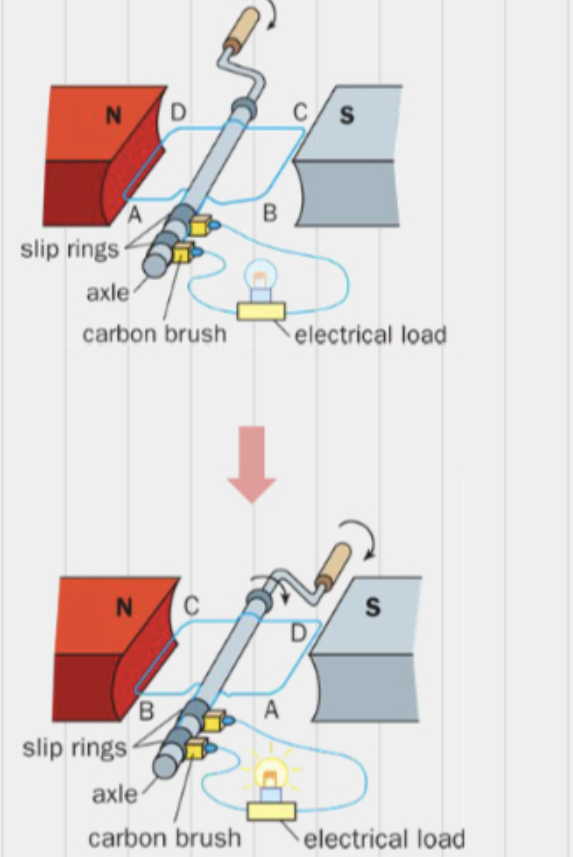
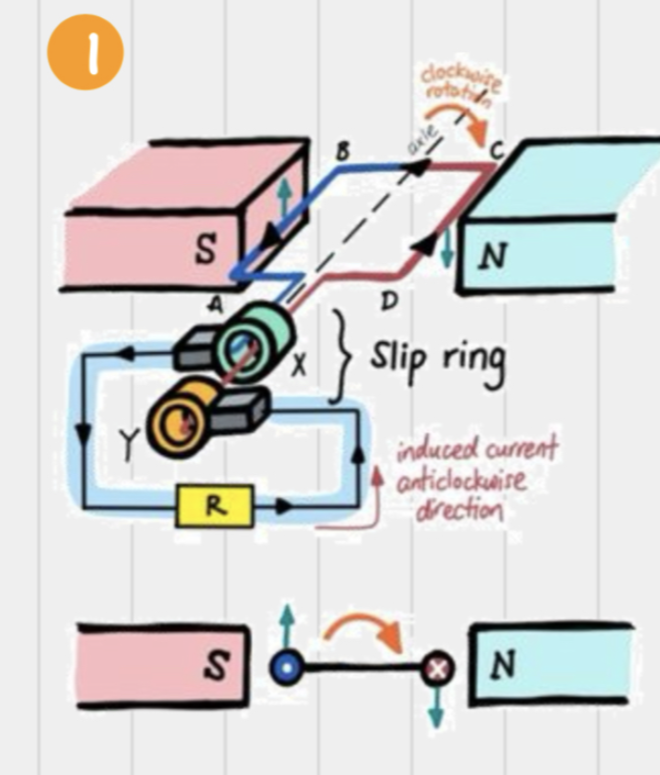
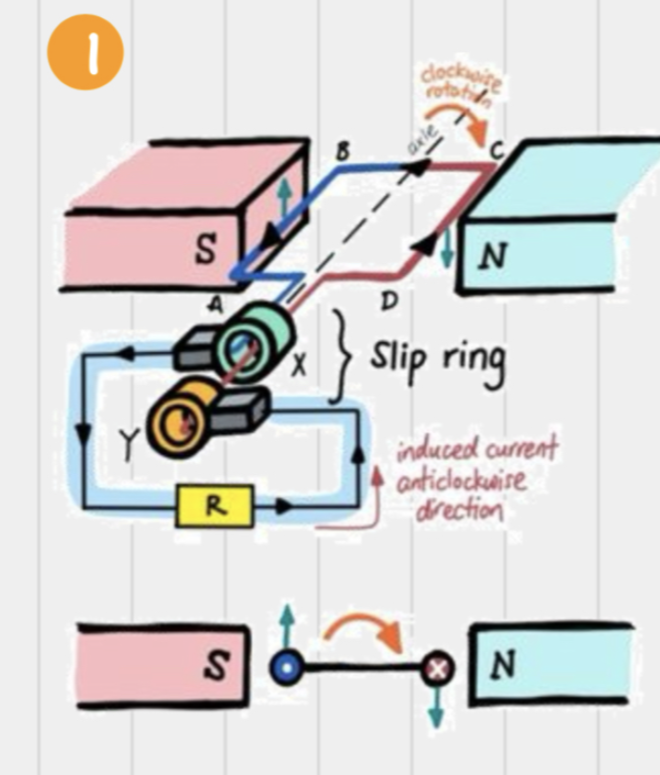
What happens in an AC generator when the coil is rotated clockwise?
Force on AB is up, force on CD is down
Induced current is anticlockwise
Magnetic field lines cut across by AB & CD at max. rate as the rate of change of magnetic flux is max.
Induced EMF is the greatest
What happens in an AC generator when the coil is vertical?
AB & CD are moving parallel to the magnetic field so they do not cut magnetic field lines
No rate of change of magnetic flux
No induced EMF
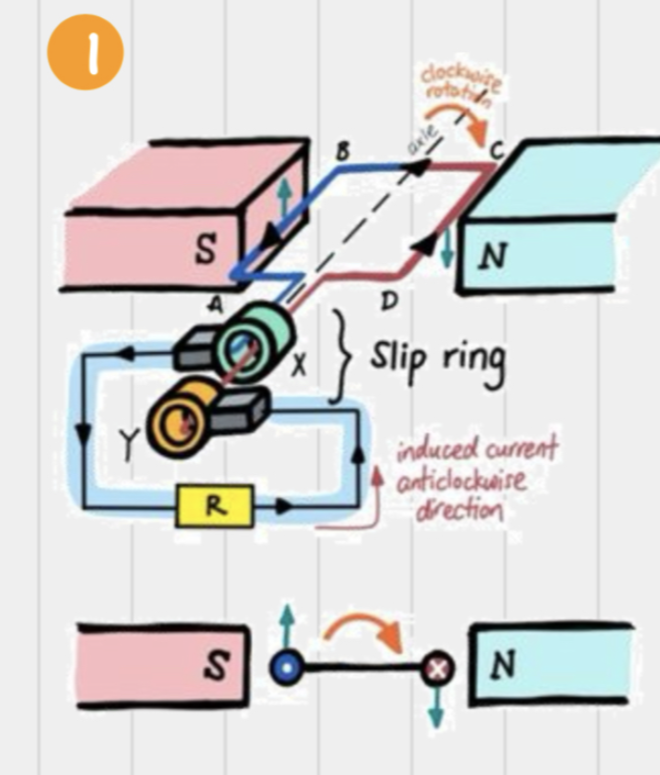
What happens in an AC generator after the coil comes down from a vertical position?
Force on AB is down, force on CD is up
Induced current reverses
Reverses every half cycle, hence current generated is alternating
Same thing as before the vertical position except for the reversal of directions
Graph representing induced EMF of an AC generator
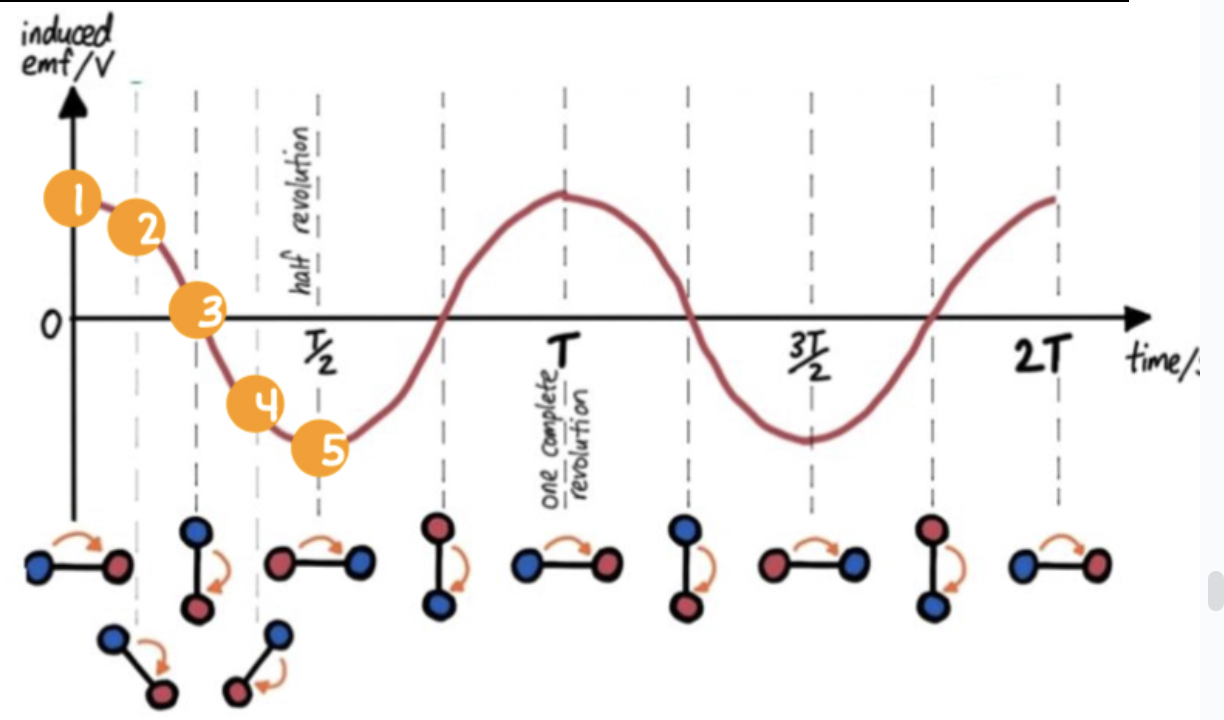
How can the magnitude of induced EMF be increased?
Increase the number of turns in the coil
Increasing the frequency of rotation
Winding the coil around a soft iron core to increase the magnetic flux linking the coil
Using stronger permanent magnets
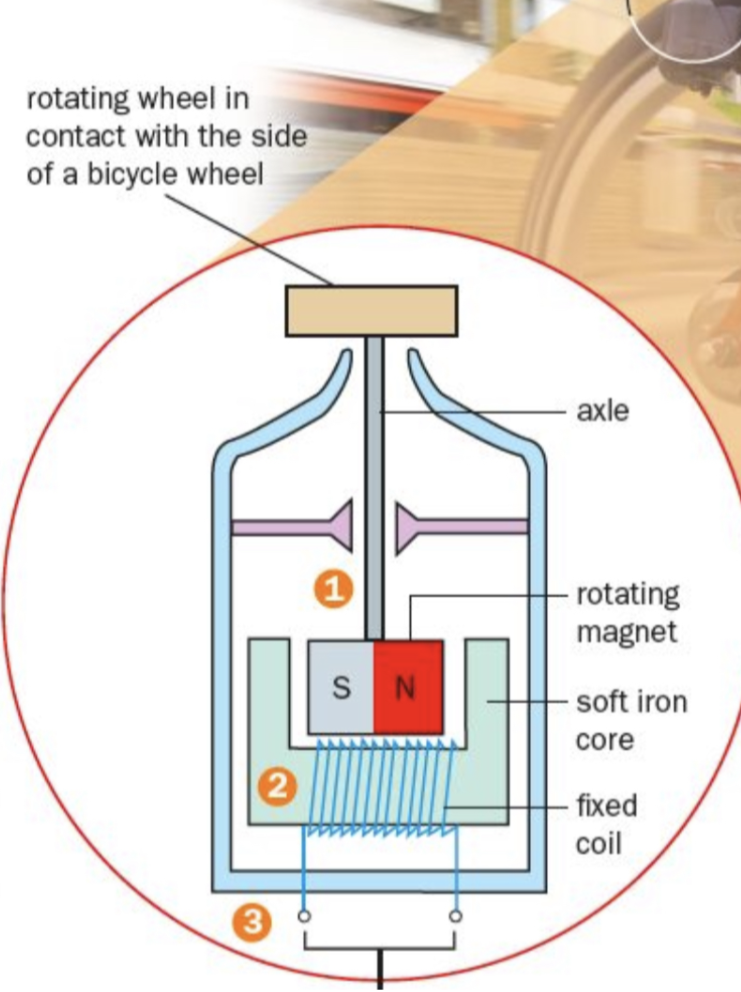
How does a fixed coil generator work?
A magnet connected to an axle and wheel rotates as the wheel rotates
Magnetic field lines linking the coil change as the magnet rotates, setting up and induced EMF in the coil
The induced EMF causes a current to flow through the output terminals to the load
What is a transformer?
A device that can change a high alternating voltage / current to a low alternating voltage / current or vice versa
What is the purpose of the laminated soft iron core in a transformer?
Concentrates the magnetic field lines of forces so that magnetic field is stronger
Soft iron is a soft magnetic material that allows the magnetic field to change direction easily in the core
Lamination reduces heat loss due to eddy currents
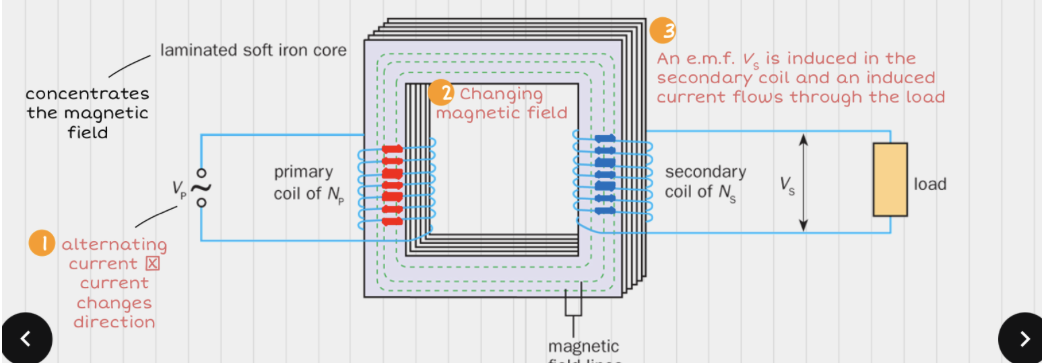
What are eddy currents?
Undesirable currents induced (in the soft iron core) that result in thermal energy loss
What is are the differences between a step-up and step-down transformer
Step-up → more turns in secondary coil, increases voltage
Step-down → fewer turns in secondary coil, decreases voltage
Equations relating the primary and secondary coil in a transformer
Vs / Vp = Ns / Np = Is / Ip
p = primary
s = secondary
N = no. of turns in coil
How do we calculate input and output power?
VpIp = VsIs
input power = output power
What is the power transmission problem?
Resistance in the metal cables used to transport electrical energy from power stations to households and factories results in heat loss
How can the power transmission problem be solved?
Stepping up the voltage using a transformer to increase voltage and reduce current to reduce power loss
Reduce I
Use thicker wires
Downsides are that they are heavy, require a stronger tower and expensive
Ploss = I²R