IGCSE Business Studies Unit 5 (Finance) - Definitions
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Capital expenditure
Investment spending on non-current (fixed assets) such as the purchase of land and buildings.
Revenue expenditure
Expenditure on the day-to-day running of a business, such as rent, wages, and utility bills.
Retained profit
The amount of net profit after tax that the business decides to keep within the business rather than paying out as dividends to its shareholders.
Owners funds
The money invested in an unincorporated business by their owners
Sale of Assets
An internal source of finance involving the sale of fixed assets that the business no longer needs
Share Capital
Share capital refers to the money raised from selling shares in a limited liability company
Bank Loans
Money borrowed from a bank, that is paid back in monthly payments over an agreed period of time plus interest
Overdraft
A short-term source of external finance, which involves a deficit in a bank account that is caused by drawing more money than the account holds.
Trade Credit
A short-term source of external finance involving an arrangement to buy goods and/or services on credit, without making immediate cash payments.
Grant
A sum of money given by a government or other organization for a particular purpose. An application must be made to prove that specific criterion has been met.
Subsidy
A sum of money granted by the government to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain affordable or competitive.
Debt-factoring
An external source of finance which involves a business raising cash by selling their outstanding trade receivables to a factoring company at a discount.
Leasing
An external source of finance that allows a business to use an asset over a fixed period, in return for regular payments. Ownership of the asset remains with the lessor.
Hire Purchase
An external source of finance used for buying certain fixed assets. An initial down payment is made and the balance (plus interest) is paid in monthly installments over an agreed period of time.
Venture Capital
A form of long-term external finance whereby investment banks and other financial institutions provide funds to small businesses that are believed to have long-term growth potential, in return for equity in the business.
Business Angels
Wealthy and entrepreneurial investors who risk their money by investing in small to medium-sized businesses that have high growth potential.
Expenses
Indirect costs of the business, which are not directly linked to the production or sale of a specific product/service e.g. management salaries, utility bills, business rates
Cost of Sales
Direct costs that can be specifically attributed to the production or sale of a particular good or service. eg. materials, packaging, commission, direct labour
Revenue
The income that a business receives from the selling its goods and services.
Profit
The financial surplus when total costs are deducted from revenue. It can be calculated by the formula: Revenue - Total costs
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Account)
A financial statement showing a businesses revenues, costs and profits over a period of time
Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet)
A financial statement that reports a company's assets, liabilities and shareholders' equity at a specific point in time
Net Current Assets (Working Capital)
The amount of available capital that a business can readily use for day-to-day operations. It can be calculated by the formula: Current Assets - Current Liabilities
Cash flow forecast
A document that shows a projection of an organisation's future cash inflows and outflows over a period of time
Cash inflow
Cash received by an organization in a particular period of time.
Cash outflow
Cash paid out by an organization in a particular period.
Working capital cycle
The period of time between spending cash on the materials needed for the production process and receiving cash payments from customers.
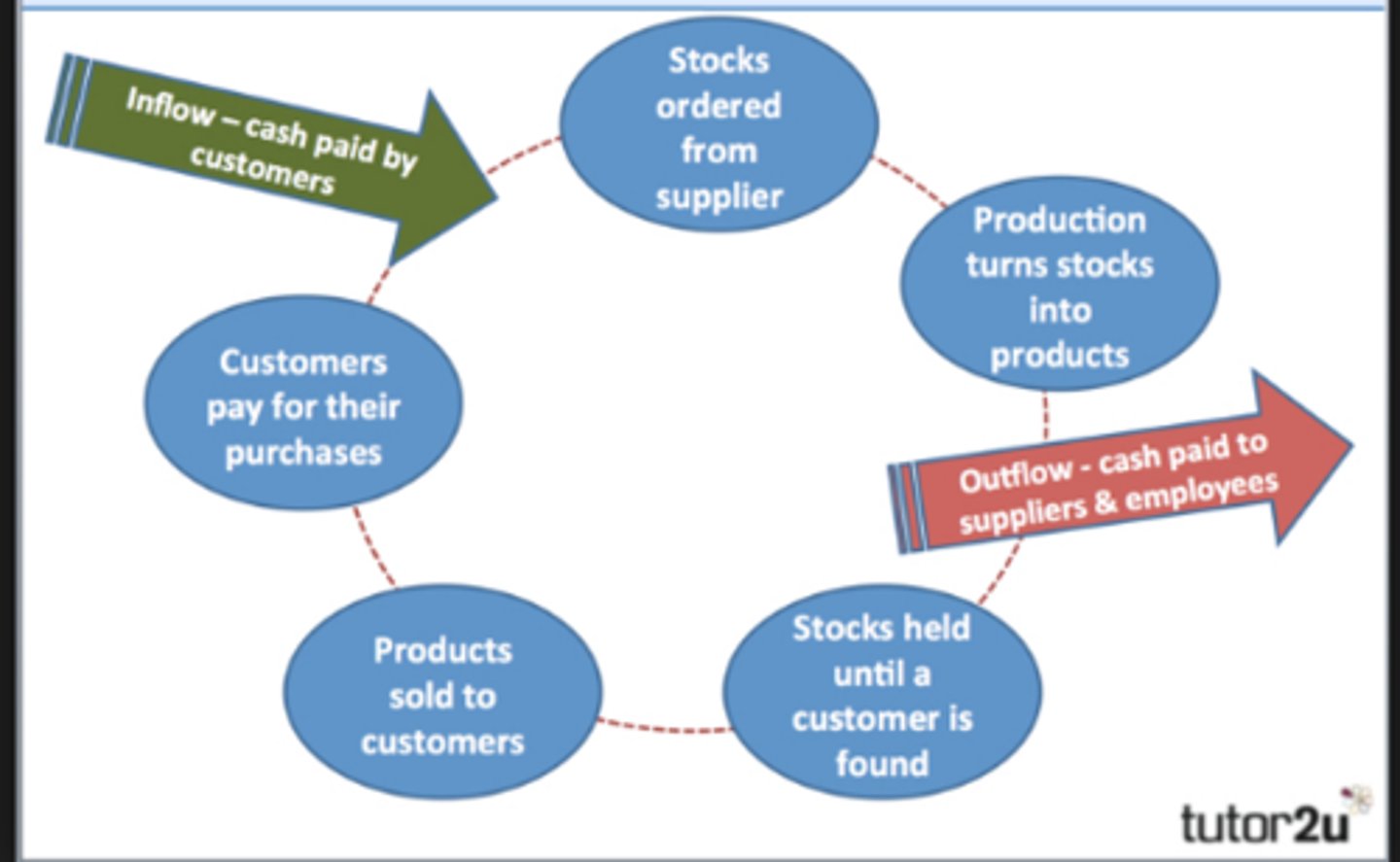
Ratio Analysis
The assessment of a firm's financial health using calculations and interpretations of financial ratios based on the firm's financial statements
Net Profit Margin
A profitability ratio which measures how much net profit is generated as a percentage of revenue. Calculated using the formula:
Net profit/sales revenue x 100
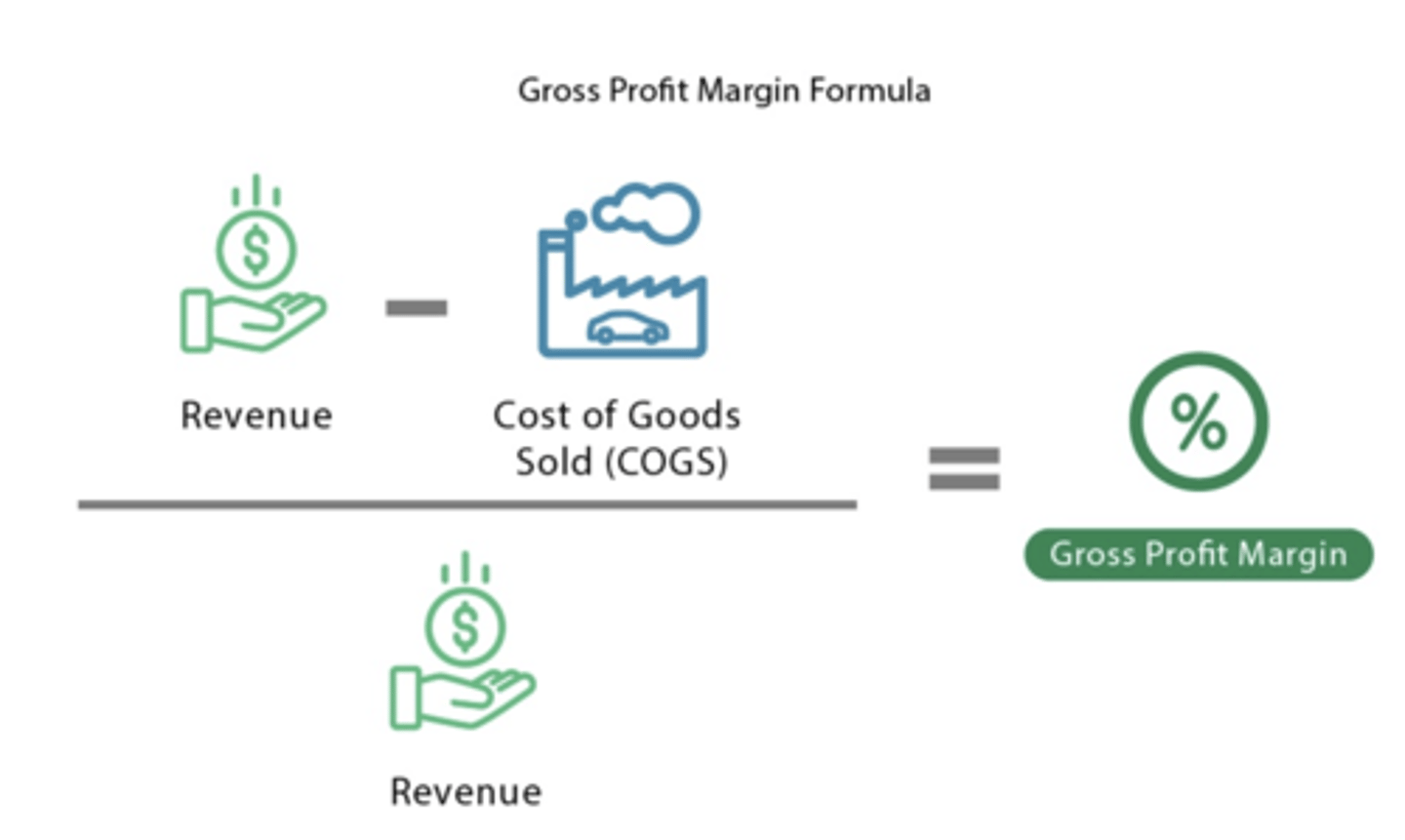
Gross Profit Margin
A profitability ratio that measures gross profit as a percentage of revenue, useful for tracking the direct cost of producing goods/services. Can be calculated by the formula:
Gross profit / revenue x 100
Current Ratio
A liquidity ratio that compares a business's current assets to its current liabilities. Can be calculated using the formula:
Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities
Acid-test (quick) ratio
A liquidity ratio that compares a business's current assets, not including inventory (stock), to its current liabilities. Can be calculated using the formula:
(Current Assets - Inventory) ÷ Current Liabilities
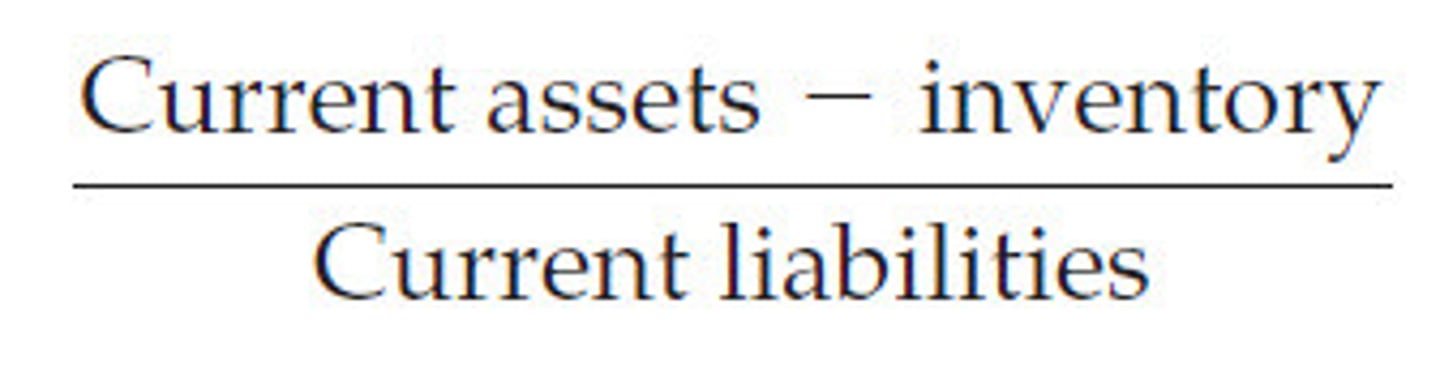
Return on capital employed (ROCE)
The (net) profit of a business as a percentage of the total amount of money used to generate it. Calculated by the formula:
Net Profit/Capital Employed * 100
Trade payables (Trade Creditors)
The total amount that the business owes to suppliers for goods purchased on credit but not yet paid for
Trade receivables (Debtors)
The total amount owed to the business by customers for goods/services sold on credit but not yet paid for
Inventory
The value of the stock of raw materials, components, partially completed and finished goods that is held by a business
Current assets
Assets the business owns that are used up within one year. Eg. Trade receivables, inventory, cash in the bank
Current Liabilities
The short-term debts of the business, due within a year. Eg. Trade payables, overdrafts, unpaid bills etc.
Capital employed
The total value of the finance invested in the business. Calculated by the formula:
Non-current assets + Share capital + Reserves
Non-current assets
Assets that the business owns that are used in the business for more than one year
Non-current liabilities
Debts owed by the business that are repayable in more than one year, sometimes called long-term liabilities. (eg. bank loans)
Gearing ratio
A measure of the percentage of capital employed that is financed by long term debt.
Calculated using the formula:
Non-current liabilities/Capital Employed *100
Annual Depreciation (Expense)
The portion of the cost of a non-current asset that is recorded as an expense each year of its useful life.
Gross Profit
The amount left after cost of sales are subtracted from the revenue.
Formula: Sales revenue - cost of sales
(net) profit
The amount left after expenses are subtracted from the gross profit.
Formula: Gross Profit - Expenses
Reserves
The accumulated retained profits that have been kept in the business
Dividends
The share of a company's after-tax profits that is paid out the shareholders
Net cash flow
Total inflows - total outflows over a given period of time
Opening balance
The amount of cash a business has at the start of the month (or other time period). It is the same as the closing balance from the previous month
Closing balance
The amount of cash a business has at the end of the month. Calculated by the formula:
Opening balance + net cash flow
Net Current Assets (Working Capital)
The ability of a business to repay short-term debts. Calculated by the formula: current assets - current liabilities
Shareholders equity
The amount invested into the business by its owners. Calculated by the formula: Share Capital + Reserves