Geology Exam 3
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Liquefaction
transformation of a granular material from a solid state into a liquid state; three requirements: loose granular sediment, saturation of the sediment from water, strong shaking
Lateral Spread
liquefaction of a subsurface layer; low slope 0.3-3 degrees; 10s of meters
Flow Failure
most catastrophic liquefaction; slope > 3 degrees; 10s of meters - 10s of miles
Ground Oscillation
liquefaction; slope is too gentle to permeate lateral movement; fissures open and close; sand boils up out of the grownd
Cause of Tsunamis
undersea disturbance, usually earthquakes on the seafloor
Character of Tsunami Waves
wavelengths up to 60 miles, can reach speeds of over 400mph, height changes as it approaches land, strip the beaches, cause flooding, destroy buildings, slow down as they reach land and commonly appear as a rapidly rising tide
Tsunami Safety Rules
earthquake is a natural tsunami warning, get to high ground; typically a series of waves not just one; they don’t issue false alarms; never go down the shore to watch
Tsunami Warning System
detects, locates, and sends out warnings to locations around Pacific Ocean, tide gauges and seismic stations, DART (deep ocean assessment and reporting of tsunamis) stations around Pacific and measures water pressure
Indonesian Tsunami and Earthquake
December 26, 2004; M9.0 earthquake off West Coast of Northern Sumatra; Java Trench (convergent plate boundary); over 230,000 killed across 14 countries; shaking lasted 10 minutes; waves began crashing within 15 minutes; two hours later hit India, 7 hours later hit Mauritius and Africa
Japanese Tsunami and Earthquake
2011, M9.03 earthquake; 70 km east of Oshika Peninsula; 15,882 deaths; 435mph up to 6 miles inland, lots of people lost power and fires started, destroyed the nuclear powerplant
Tectonic Setting of Western North America
Convergent off the coast of Alaska, Washington, and Oregon, Transform boundary in California
Origin of San Andreas Fault
a portion of the East Pacific rise was subducted under California creating a transform fault, some parts of the fault are locked with lots of friction, in the week or creeping parts, many earthquakes occur; majority of the fault is locked
1964 Great Alaskan Earthquake, plate tectonic setting
convergent boundary
64 Alaska cause
major subduction movement, Pacific plate moved under North American plate by about 30 feet
64 Alaska length of shaking and magnitude
M9.2 earthquake (2nd largest recorded); 4 minutes of shaking
64 Alaska types of damage
III - X on Mercalli scale, damage covered about 130,000 sq km, 131 killed, 122 of them killed by the tsunami, 16 killed in Oregon and California, large section of City of Seward slid into the ocean due to liquefaction
64 Alaska Aftershocks
thousands of aftershocks recorded in the months following, in the first day 11 smaller earthquakes were recorded
1906 San Francisco cause, length of shakings, magnitude, types of damage, foreshocks, aftershocks
265 miles of fault ruptured; M8.0; intensity from VII - IX; 60 seconds of shaking; 30 seconds before major shaking a small foreshock was felt; horizontal offset of about 20 feet; > 3,000 deaths, most damaged caused by the fire (80% of the city was burned down)
1989 San Francisco Earthquake cause, length of shakings, magnitude, types of damage, foreshocks, aftershocks
M7.0; 60 miles south of San Francisco; first major rupture since 1906; 25 miles of fault ruptured; intensity VI - IX; aftershocks M5.2 after 2.5 minutes and thousands of smaller quakes in the next couple of weeks; 11 seconds of shaking; 67 deaths; liquefaction around bay area; most people killed were on the double decker highway of I-880
Hydrologic Cycle
Evaporation, Precipitation, Return to Oceans
Porosity
the parts of rock or soil that are not occupied by solids, groundwater occupies porosity; Intergranular (space between sedimentary rocks); Fracture (cracks in the rocks)
Sink Holes
solution cavity that opens to the surface
Ground Water
all the water contained in spaces within rocks and soil; originates from precipitation
Surface Water
streams and lakes; originates from precipitation
Karst Topography
a landscape dominated by sink holes
Recharge and Discharge Zones
Recharge - where water enters the aquifer; Discharge - where water flows out of the aquifer
Water Table
the top of the saturated (phreatic) zone in an unconfined aquifer; line between saturated and unsaturated areas; shape changes mimicking the ground surface; moves up and down depending on rain
Groundwater Flow
moves through the porosity in rocks and soil; flows from high to low pressure; can flow uphill; flows down potential/pressure
Potential Surface
pressure surface created by differences in elevation of the water table
Cone of Depression
a conical depression in the potential surface
Springs
a place where groundwater discharges at the Earth’s surface
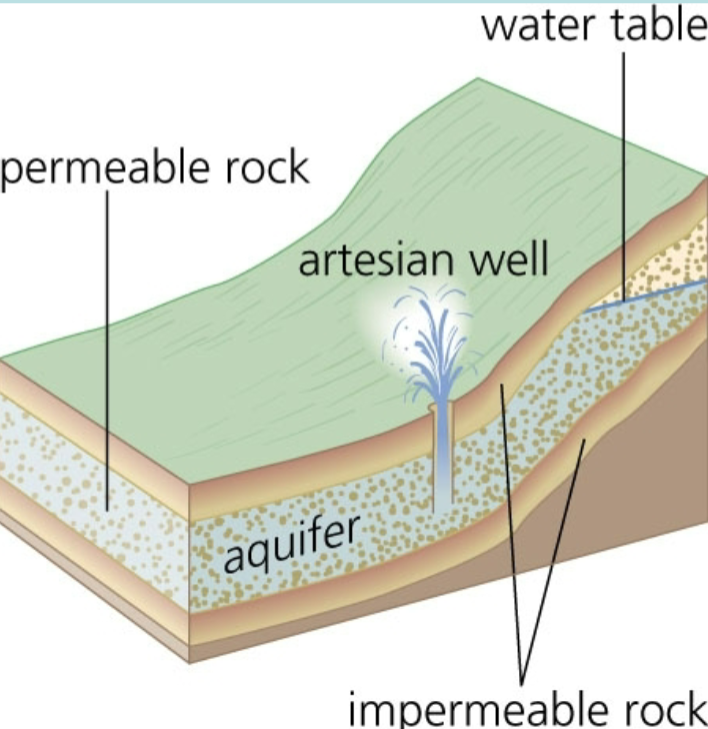
Confined Aquifer
an aquifer with an impermeable layer above it
Unconfined Aquifer
aquifer that is open to receive water from the surface
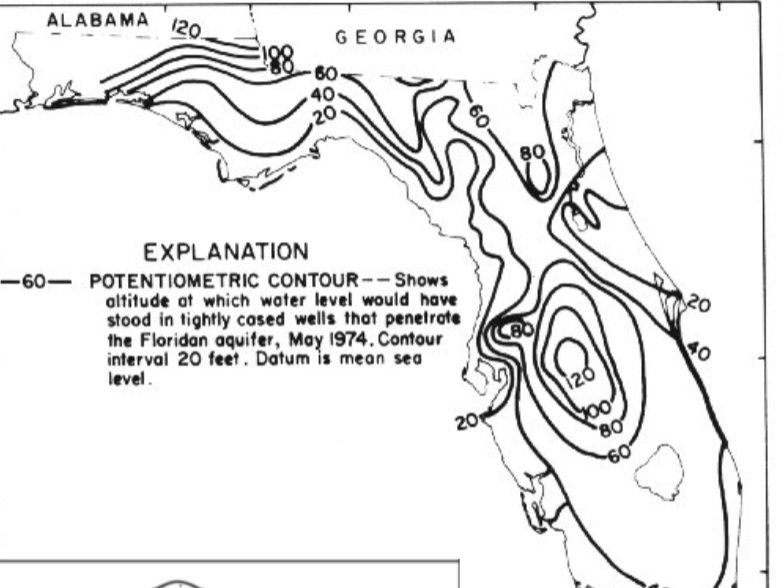
Potential Surface Map
lines connect points of equal potential, shows the shape of the pressure surface; ground water flows perpendicular to lines of equal potential
Streams
the part of the hydrologic cycle that returns water to the oceans on the land’s surface; made up of water and sediments
Tributaries
the collection system; a dendritic pattern of smaller streams that feed into the main trunk; number decreases downstream; “v” downstream
Main Trunk
transports the water, enormous drainage basins composed of many smaller sub-drainage basins
Delta
the dispersing system; where the water flows into a standing body of water
Longest Rivers
Nile - 4,132 miles Amazon - 4,000 miles Yangtze - 3,915 miles
Stream Gradient
decreases downstream (relief of the land/slope)
Velocity Patterns
decreases downstream
Stream Discharge
volume of water per time that passes through a stream; velocity x cross sectional area = discharge; velocity = feet/second; cross sectional area = width x depth
Hydrograph
a graph that shows discharge over time
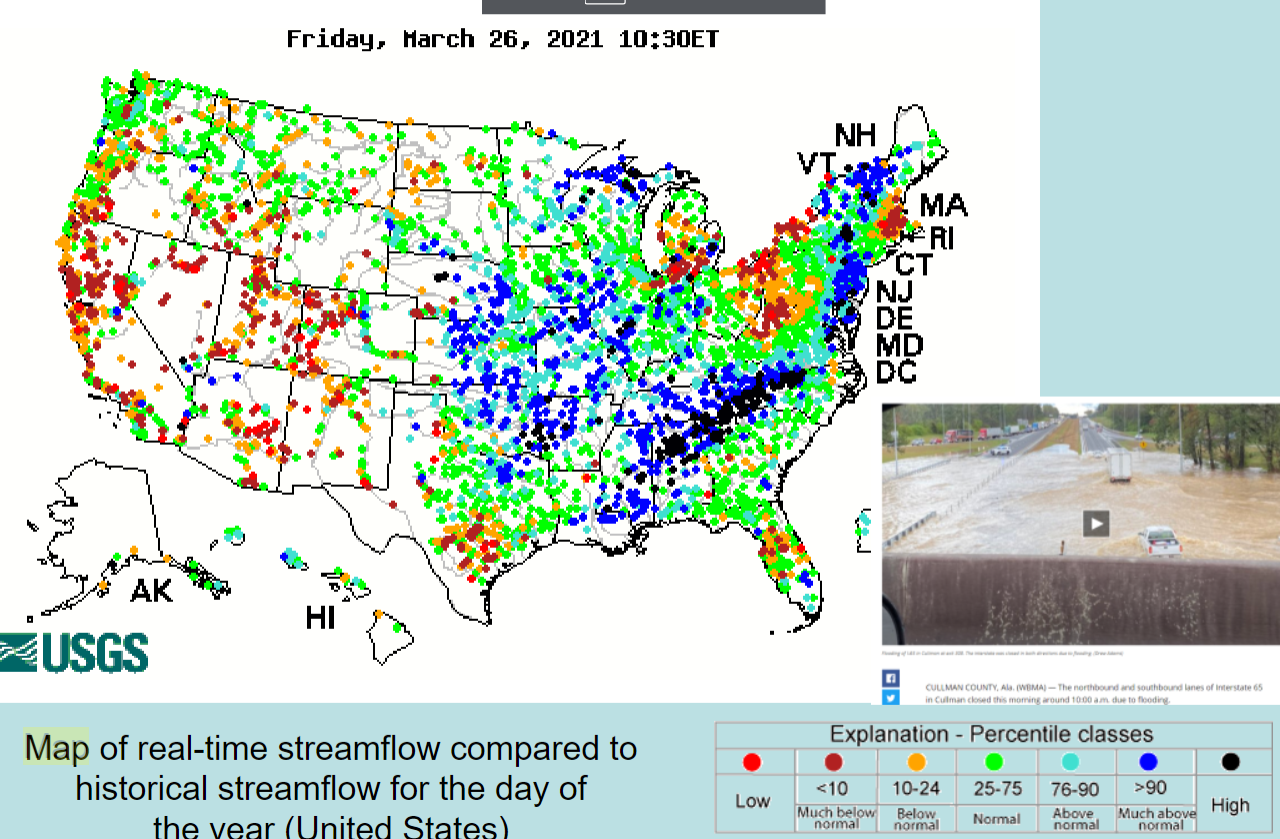
U.S. Rivers Discharge Map
map of real-time streamflow compared to historical streamflow for the day of the year
Drainage Basin
land area from which all precipitation flows to a single stream
Headward Erosion and Stream Piracy
erosion that expands drainage basins, stream piracy - when one stream intersects another and makes it one big one
Suspended Load
particles that are carried within the stream (fine grained - silt and clay)
Bed Load
particles that slide, roll, or bounce along the bottom of the stream (coarse grained)
Dissolved Load
atoms surrounded by water transported by the stream
Floodplain
the portion of a river system that is covered by water during flood stage
Meander
a winding course of stream bends; they migrate throughout the floodplain; erode and flatten out the continent; erode on outside of bend and deposit on inside
Entrenched Meander
rapid uplift of the land causing rapid down cutting
Point Bar
sand or gravel deposited on the inside of a meander bed (deposition)
Cut Bank
the steep walled part of the outside of the meander (erosion)
Oxbow Lake
isolated meander loops, form when a stream cuts through a meander neck
Natural Levee
a curvy-linear mound of sand and gravel that parallels the riverbank
Aquifer
a body of permeable rock saturated with water; water well target
Aquitard
an impermeable body; opposite of aquifer
Solution Cavity
large pores formed by the dissolution of rock; usually forms in limestone (caves)
Permeability
the ability of material to transmit water; grains size influences permeability
Spatial Distribution of Earthquakes
80% originate in circum-pacific belt (The Ring of Fire), 15% originate in Mediterranean-Asiatic belt, remaining earthquakes occur on ridges and scattered through the plates
River System
a network of connecting channels through which water is transmitted back to the oceans
Artesian Well
a well drilled into a confined aquifer with hydraulic pressure for the water to flow to the surface without pumping, the pressure surface is above the land surface
Alluvial Fan
semicircular deposit of coarse sediment formed where the stream gradient suddenly changes
Lake
large inland body of standing water that occurs in topographic depressions
Origins of topographic depressions
1 - melting blocks of glacier ice make kettle lakes 2 - volcanic eruptions 3 - in faults
Oligotrophic Lakes
poorly nourished, not many nutrients, few plants, abundant O2
Eutrophic
highly nourished, high nitrogen and phosphorus input, lots of algae/aquatic plants; algae die and decompose, animals die