Chemistry Chapter 17
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Last updated 3:24 PM on 2/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
Reaction rate
measurement of the change in moles of a reactant over time
2
New cards
Collision Theory
chemical reactions take place when molecules collide, provided that they
1. Have enough kinetic energy
2. Face the right way when they hit
1. Have enough kinetic energy
2. Face the right way when they hit
3
New cards
Reaction curve/potential energy curve
either endothermic or exothermic, show the energy needed to break bonds and form bonds
4
New cards
\+ΔH, more energy required to break bonds, less to from, feel cold, reactants have lower energy than products
Endothermic
5
New cards
\-ΔH, less energy to break bonds, more to form, feel warm, reactants have higher energy than products
Exothermic
6
New cards
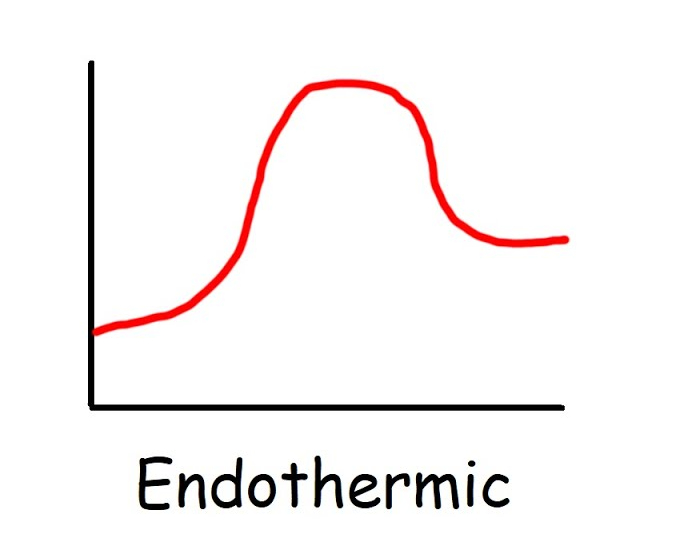
Endothermic graph
7
New cards
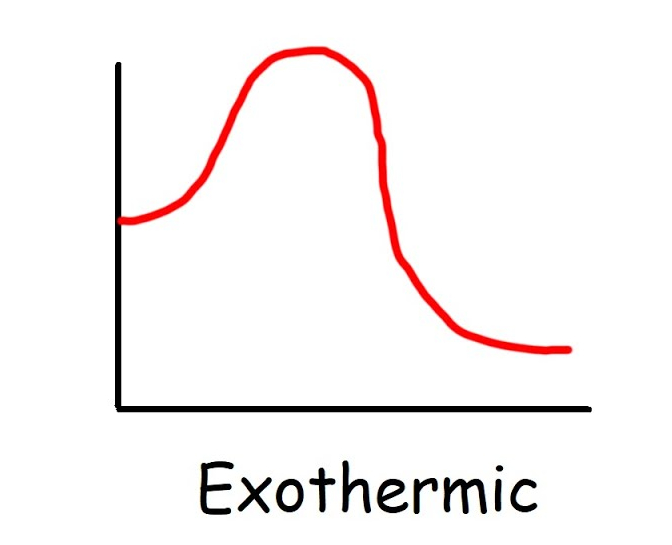
Exothermic graph
8
New cards
absorbs energy
breaks bonds
9
New cards
releases energy
forms bonds
10
New cards
final energy - initial energy
ΔH
11
New cards
Reversible
Reactions are ___________
12
New cards
Catalyst
speeds up a reaction by lowering activation barrier of a reaction
13
New cards
Inhibitor
slow down a reaction by raising the activation energy
14
New cards
Reversible reactions
reaction occurs both in the forward and reverse direction. As fast as products are being made, they are reverting back into reactants
15
New cards
Equilibrium
the concentration of the products and reactants do not change. The rate of the forward reactions is equal to the rate of the reverse reactions
16
New cards
Chemical equilibrium
as fast as reactants are being made, they are reverting back to reactants
17
New cards
Le Chatelier’s Principles
if stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the system changes to relieve stress
18
New cards
1. Temperature
2. Concentration
3. Pressure
Stresses that change equilibrium
19
New cards
More is added to reactants, the reaction shifts to the products
\
More is added to products, the reaction shifts to the reactants
\
Decrease reactants, reaction shifts toward reactants
\
Decrease products, reaction shifts toward products
\
More is added to products, the reaction shifts to the reactants
\
Decrease reactants, reaction shifts toward reactants
\
Decrease products, reaction shifts toward products
Effects of changing concentration
20
New cards
1. Adding heat shifts reaction to the reactants
2. Taking away hear shifts reaction to the products
Affect of Temperature
21
New cards
heat + AB + C ⇌ AC + B
Endothermic reaction and heat
22
New cards
AB + C ⇌ AC + B + heat
Exothermic reaction and heat
23
New cards
Only affects gases (reactants that have an unequal amount of gases in products and reactants). If pressure is increased, the reaction shifts to the reactants
Affects of pressure
24
New cards
Equilibrium constant
the ratio of the product concentrations to the reactant concentrations at equilibrium (\[ \]). Tells us the concentration of reactants and products
25
New cards
Spontaneous reaactions
exothermic, low activation energy, can occur quickly, slowly, occur naturally, favor products at equilibrium, release energy. Can occur by themselves and do not need outside energy put into a system
26
New cards
Free energy
amount of heat released from a reaction
27
New cards
entropy
disorder of a system
28
New cards
Law of disorder
states that all systems tend to move toward maximum disorder of randomness
29
New cards
Non spontaneous reactions
do not give a substantial amount of products at equilibrium. Need outside energy to begin
30
New cards
entropy; temperature
________ increases as _______ increases
Explore top notes
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1335d ago0.0(0)
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1335d ago0.0(0)