lecture 5 - T cell development & maturation
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
T-cell progenitors develop in the ____ ______ and migrate to the ______
T cell receptor ____ rearrange in the thymus
Immature T cells that recognise self ___ survive
Immature T cells that recognise self _____ undergo ________
Mature T cells migrate to the peripheral _______ organs and are activated by encountering _______ _______
Activated T cells migrate to sites of ________ and eliminate infection
bone marrow
thymus
genes
MHC
antigens
apoptosis
lymphoid
foreign antigens
infection
T cells (_____cytes) have two lineages : ___ and ____
this is facilitated by _____ signalling
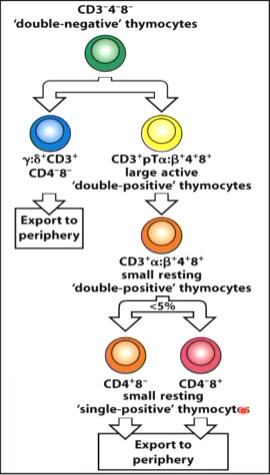
CD3-4-8- describes a _______-negative thymocyte
______ describes a CD4+ small resting single-positive thymocyte
thymocytes
CD4+
CD8+
Notch
double
CD4+8-
the thymus is composed of two parts: _____ and ______
cortical ______ cells express self-___.
double positive _______ that moderately bind to _____ commit to CD8+ lineage
those that bind to ______ commit to CD4+ lineage
the binding has to be perfect: ________ zone
this is called _____ selection
_______ epithelial cells present self-_______
binding too strongly commits the thymocyte to ________ to prevent _______
this is called ______ selection
this whole process is called thymic _________
cortex, medulla
epithelial, MHC
thymocytes, MHC I
MHC II
Goldilocks
positive
medullary, peptides/antigens
apoptosis, autoimmunity
negative
education
just
just