3 - Physical Thermodynamics and Fluids
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
heat (Q)
transfer of non-mechanical energy b/w a system and its environment
related to the total thermal nrg of an object (measured in joules)
temperature (T)
macroscopic measure of the average internal (thermal) nrg of a system
energy (E) is the TOTAL energy, but the temp (T) measures the energy (E) of the INDIVIDUAL molecule
how are energy and temperature different?
intensive property
property that does NOT depend on the amount of material
extensive property
property that depends on the mass of material
closed system
system that allows NO exchange of matter
molecules cannot go in and out of the system
BUT still allows work to be done
Q = mCΔT
m = mass
C = specific heat of molecule
ΔT = temp change
formula for heat (Q)
phase change
process where system changes phase (gas, liquid, solid)
naur <3
its phase can change (solid, liquid, gas)
does adding heat to the system always change its temperature?
T increases and/or gas expands (or both)
If Q > 0 for an ideal gas:
what happens to T (increase/decrease)?
gas (expands/constricts)?
zeroth law of thermodynamics
law that states when 2 substances are in contact, heat transfers b/w them until they achieve the same temperature (thermal EQ)
conduction
convection
radiation
what are the 3 modes of heat transfer?
conduction
heat transfer through solids in contact
conduction
when you place a metal spoon in a hot cup of tea or coffee. The heat from the hot liquid is conducted through the metal spoon and into your hand as you hold it, warming your hand.
which heat transfer method is this an example of?
convection
heat transfer through fluids circulation
convection
when you boil water in a pot on a stovetop. As the water is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, carrying heat energy with it. Cooler water then moves in to take its place, and the process repeats, creating a continuous cycle of heat transfer through the movement of the water.
which heat transfer method is this an example of?
radiation
heat transfer by emission of electromagnetic energy (EM nrg)
radiation
the warmth you feel from the sun on a sunny day.
which heat transfer method is this an example of?
ΔE = Q - W
Q = heat added to the system
Q > 0: heat ADDED to system
Q < 0: heat LEAVES the system
W = work done BY the system
W > 0: when system DOES work
W < 0: when work done ON system
what is the internal energy of a closed system? (ΔE)
heat gets added to the system
what happens to the internal energy when Q > 0?
system does the work
what happens when W > 0?
work is done ON the system
what happens when W < 0?
system DOING work
W > 0
is expansion an example of work done ON the system or the system DOING the work?
also does that mean W __ 0? (<,>)?
work done ON the system
W < 0
is contraction an example of work done ON the system or the system DOING the work?
also does that mean W __ 0? (<,>)?
PV = nRT
ideal gas law formula
work (W)
gas expands → V increases → W > 0
gas contracts → V decreases → W < 0
for ideal gas, volume (V) is related to ___________
V increases, W > 0 (system does work)
when gas expands, what happens to volume (V) and work (W)?
V decreases, W < 0 (work done ON system)
when gas contracts, what happens to volume (V) and work (W)?
energy (E)
for ideal gas, temperature (T) is related to ___________
Q ≠ 0, W ≠ 0, or both
but E = Q - W still though
if an ideal gas transitions from 1 state to another (gas, solids, liquids). what happens to Q and W?
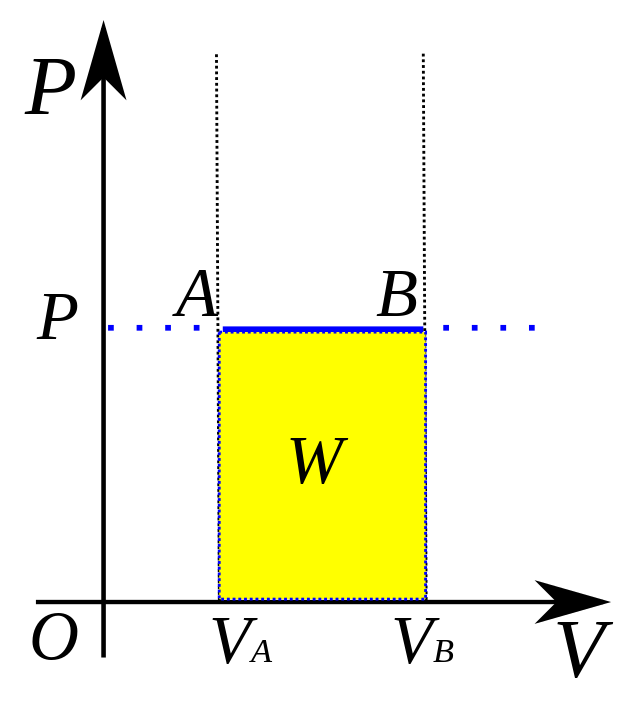
isobaric process
P = force / area
system has a constant pressure (ΔP = 0)
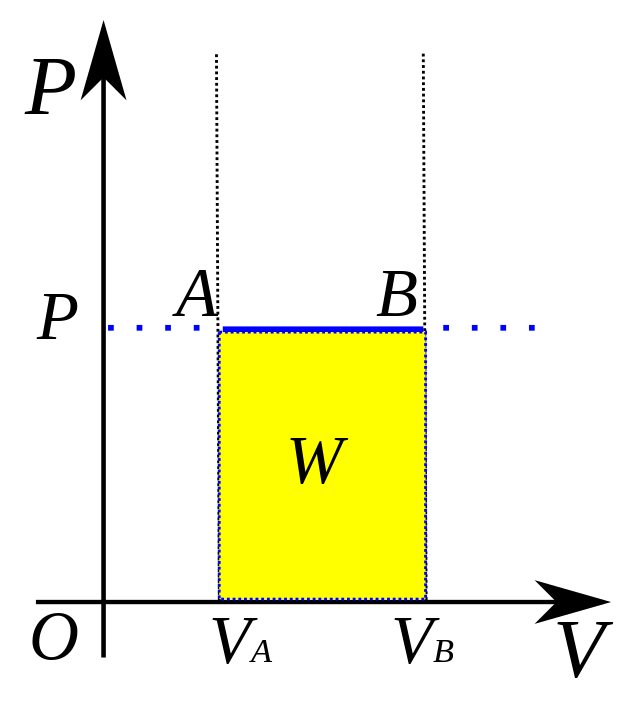
P = force / area
formula for isobaric processes to find pressure?
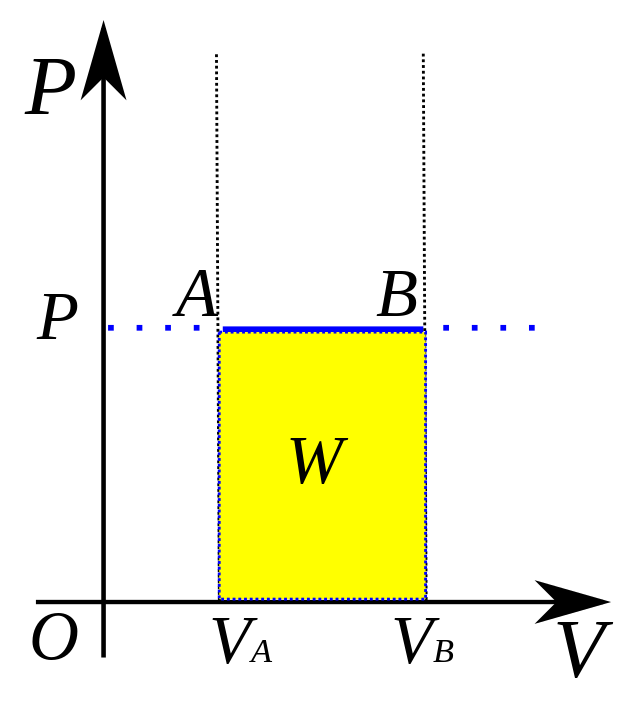
W = PΔV
SO… ΔE = Q - PΔV
formula to find work (W) and energy change (ΔE) in an isobaric system (ΔP constant)
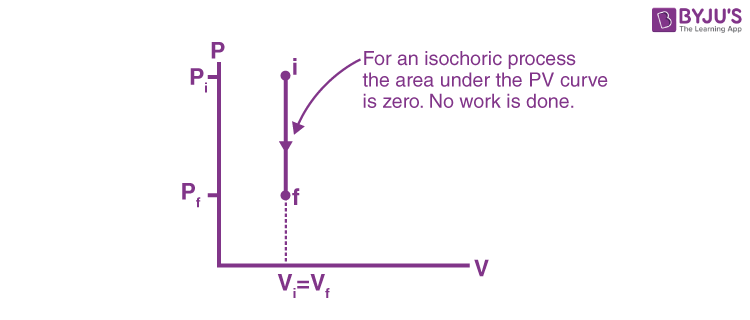
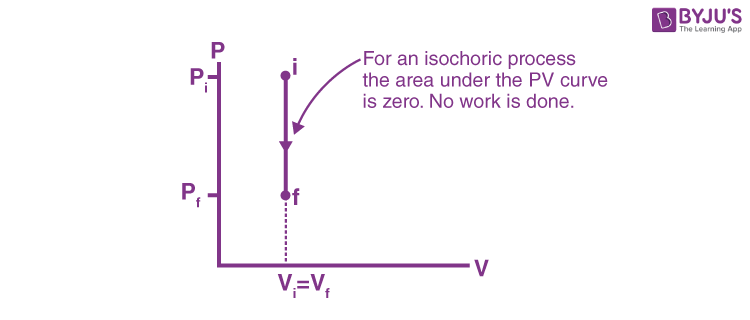
isochoric process
system has a constant volume (ΔV = 0)
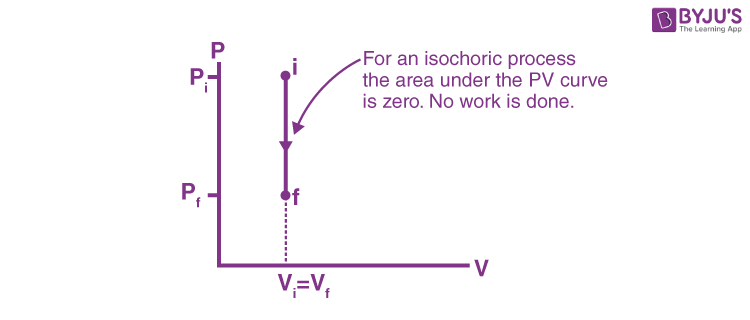
temperature rises… so pressure rises, and that’s it
for isochoric processes, what happens when heat is added? (Q > 0)
ΔE = Q (no W)
formula to find energy change (ΔE) in an isochoric process?
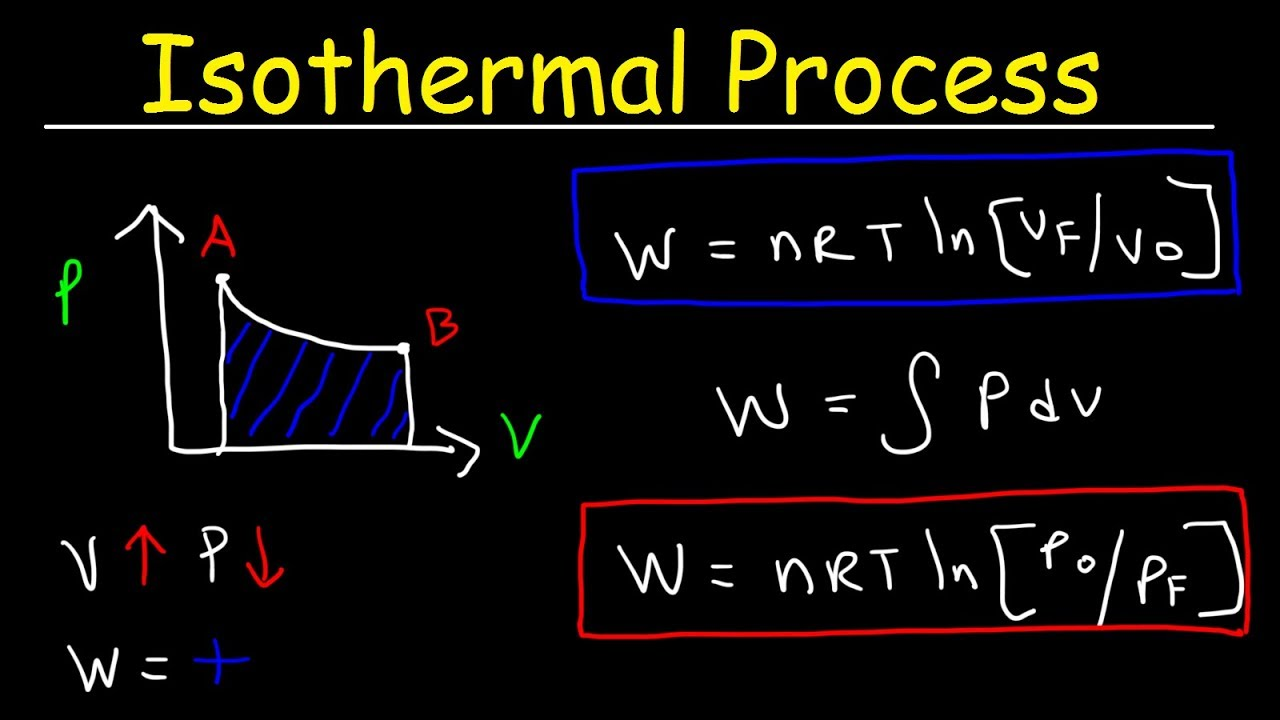
isothermal process
system in which temperature stays constant
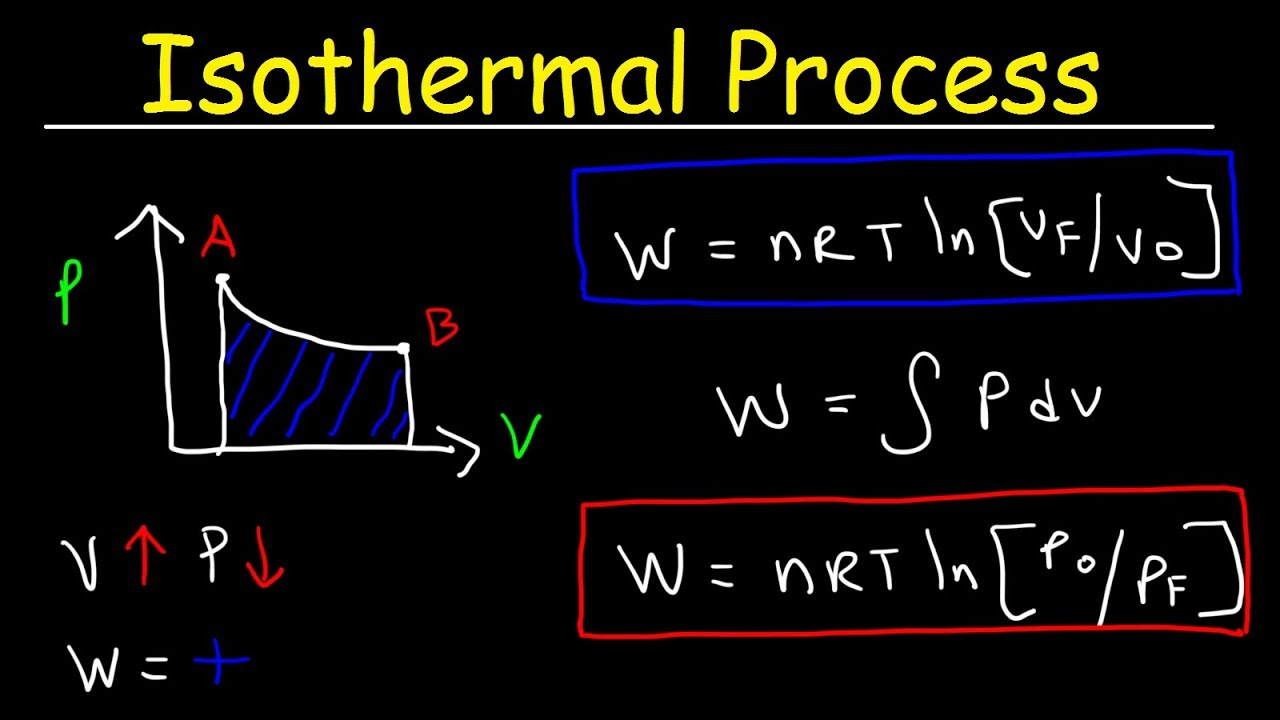
volume increase… so pressure decreases
what happens to isothermal process when heat is added? (Q > 0)
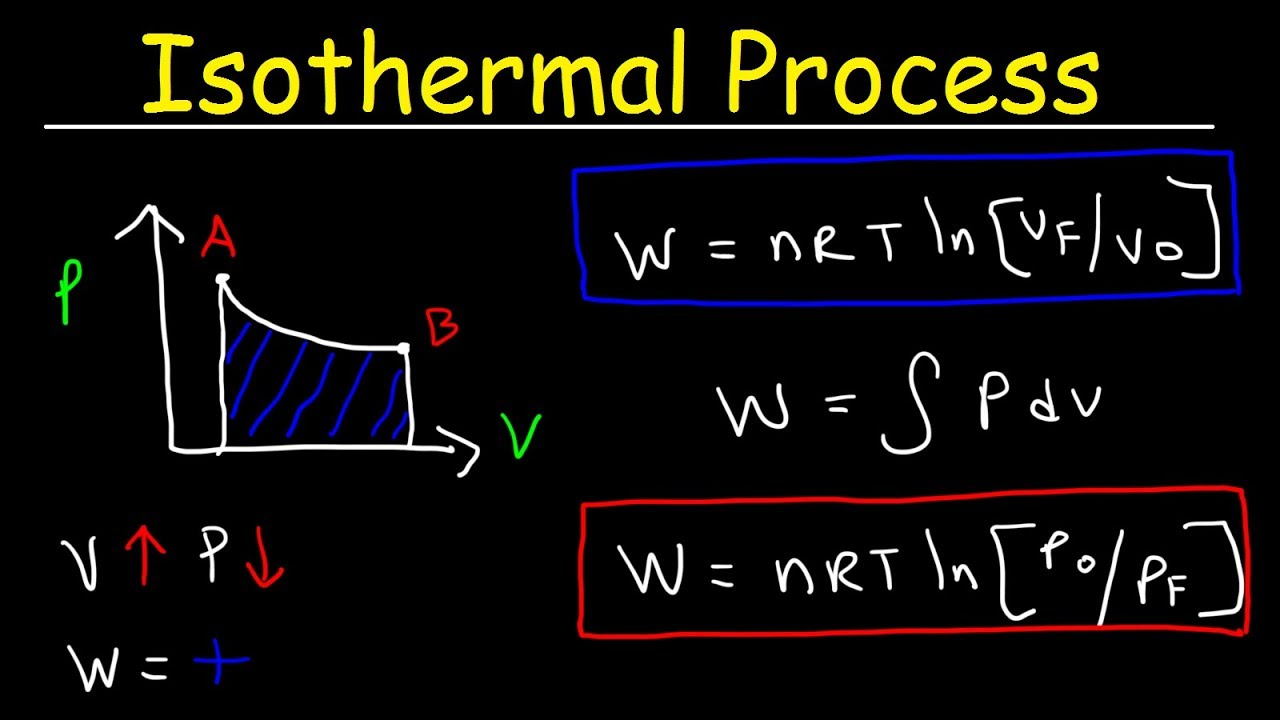
Q = W
since temp change is 0, ΔE is 0 bestie
formula to find energy change (ΔE) in an isothermal process
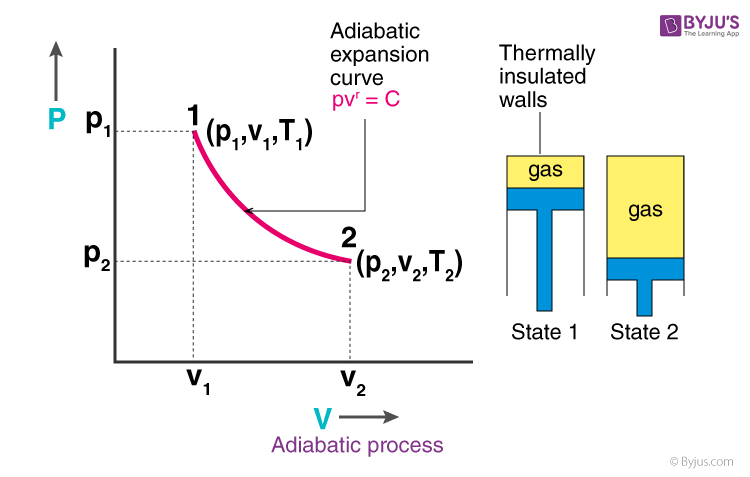
adiabatic process
system in which there is no heat transfer (ΔQ = 0)
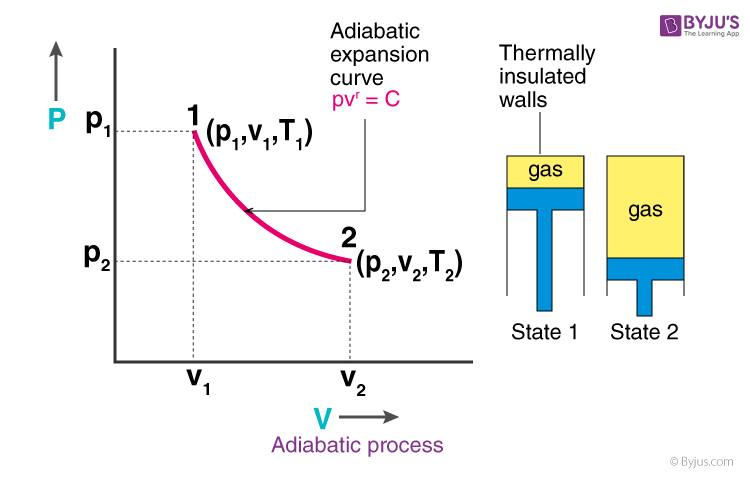
volume increases, pressure decreases, temperature decreases → nrg decreases
temp decrease bc gas molecules are doing work on the surroundings as they expand → reduction in kinetic energy
if volume increases in an adiabatic system, how does it affect V, P, T, and E?
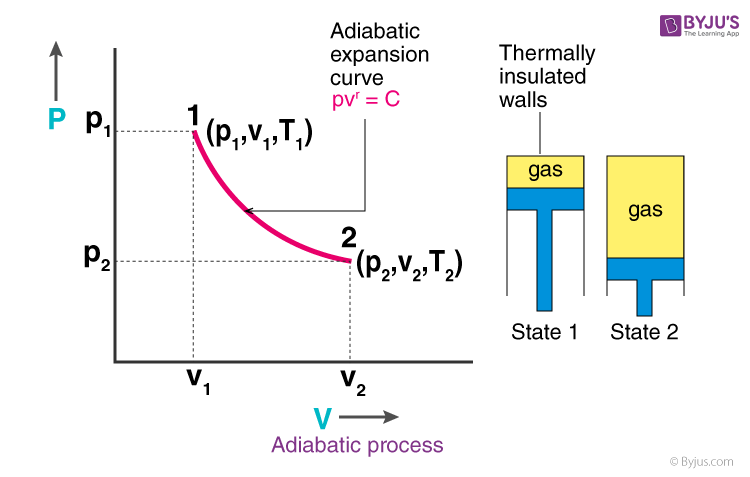
temp decrease bc gas molecules are doing work on the surroundings as they expand → reduction in kinetic energy
why does temp decrease and energy decrease in an adiabatic process when volume increases?
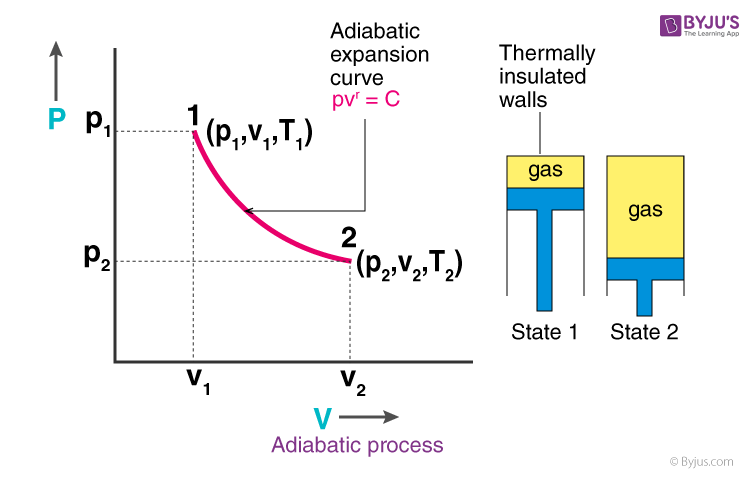
ΔE = -W
formula to find ΔE energy change in an adiabatic system
entropy
measure of disorder of the system
isolated system
system in which neither energy nor matter is exchanged with the outside
(ΔE = Q - W cannot be applied)
closed system
system in which matter is NOT exchanged with outside environment, but energy can come in and out (ΔE = Q - W)
either stays the same or increases during any thermodynamic processes
how is entropy in an isolated system look?
can decrease, but only if the entropy of its surrounding environment increased by a greater amount
can entropy of a closed system decrease?
density = mass / volume
density formula
specific gravity
density / density of water
density of water = 1000 kg/m3
ratio of density of fluid to density of water
density / density of water
density of water = 1000 kg/m3
specific gravity formula
Pbottom > Ptop
in terms of buoyancy, how does the pressure at the bottom compare to at the top? (<,>,=)
buoyant force
FB = (fluid density)(volume of obj. submerged)(g)
upward force exerted on object that’s partially/completely submerged in fluid d/t pressure difference between the top and bottom of object
FB = (fluid density)(volume of obj. submerged)(g)
formula of buoyant force
FB = (fluid density)(volume of obj. submerged)(g)
FB of iron: 1000 kg/m3(Vsub)(g)
FB of styrofoam: 1000 kg/m3(Vsub)(g)
FB the same in both!
if a piece of iron and a piece of styrofoam have the same volume submerged, which one has a greater FB?
Vsubmerged / Vfluid = ρobject / ρfluid
formula to show fraction submerged for buoyancy?
(3/4)Volume = ρobj / ρfluid
how to indicate that an object is ¾ submerged in buoyancy?
fluid is incompressible (ρ constant)
fluid has negligible viscosity (no intra-fluid friction)
laminar (streamline) flow (no added/removed fluid)
what are the 3 rules for ideal fluid flow
example of violations to the ideal fluid flow:
gas getting compressed/expanded
flow of viscous fluids (ex: molasses)
air turbulence (storms)
example of violations to the ideal fluid flow:
gas getting compressed/expanded
flow of viscous fluids (ex: molasses)
air turbulence (storms)