Lineage Commitment and Activation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Activation of a Naïve T-cell
TCR Signaling
Interaction of a mature T-cell receptor w/ antigen in the context of MHC.
Dependent on the expression of a co-receptor
2nd signal: co-stimulatory interaction
third signal: cytokine signaling
Cytokines signal through cytokine receptors
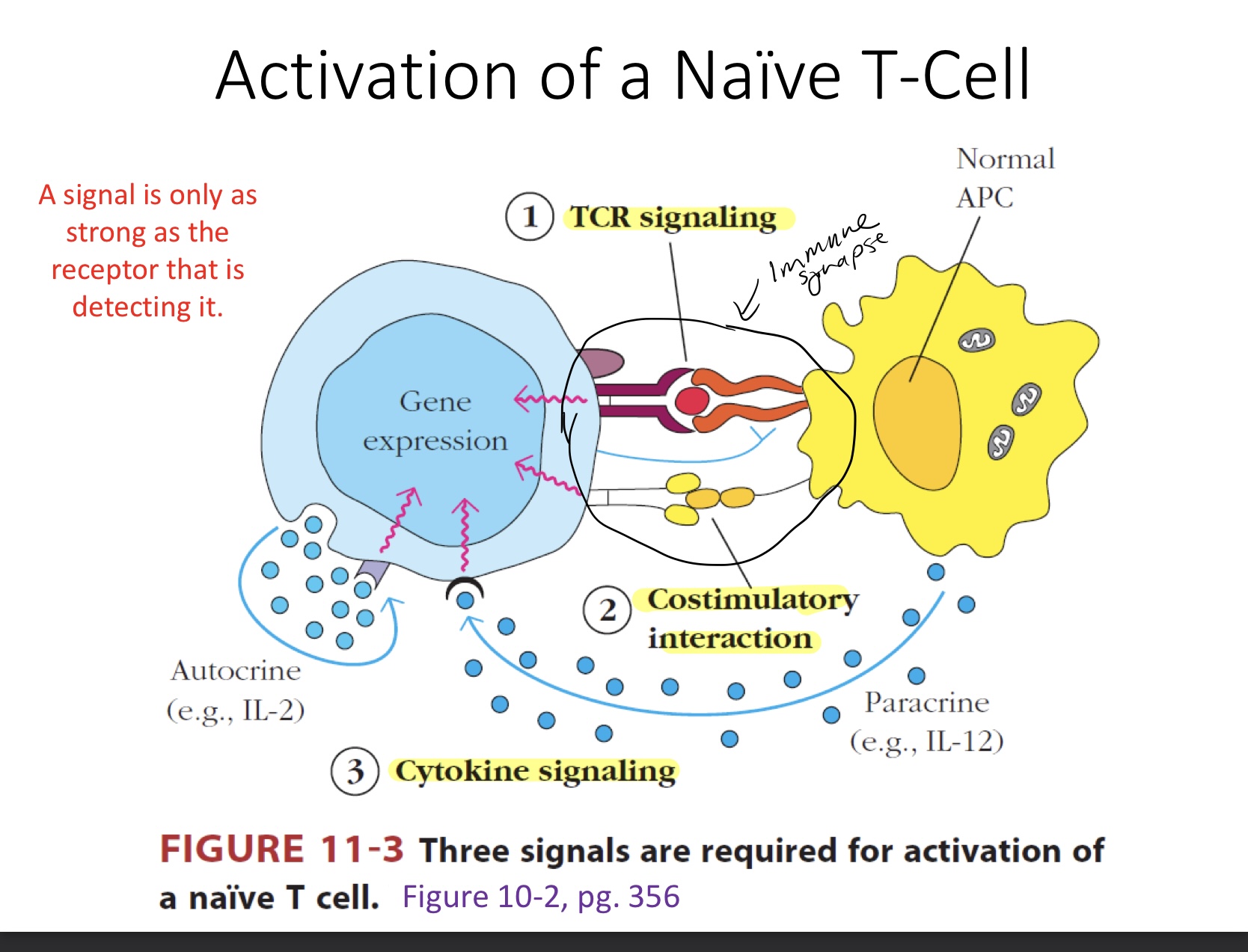
A signal is
Only as strong as the receptor that is detecting it
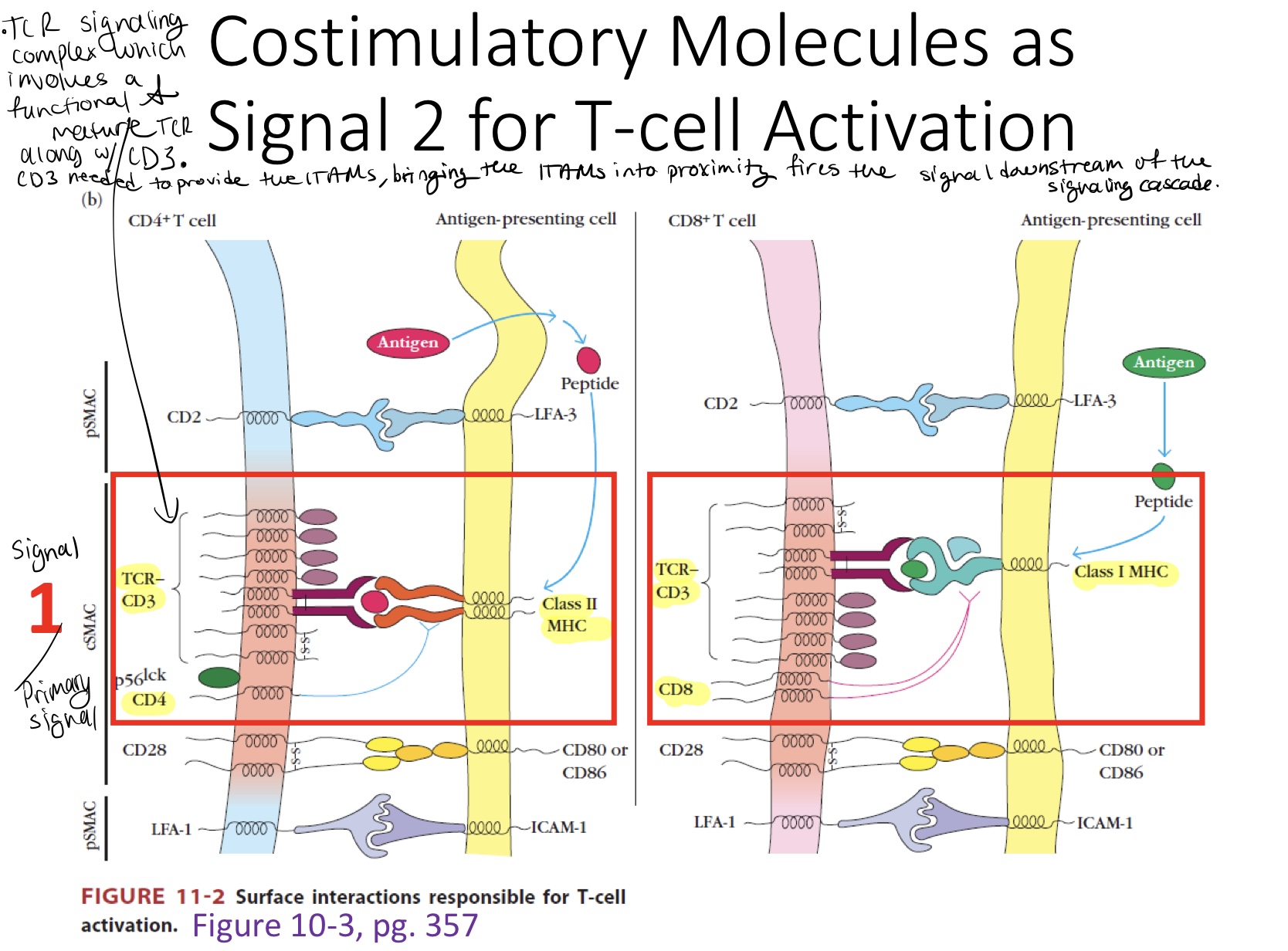
cSMAC
Central immune synapse
Central signal: signal 1
TCR/CD3
Co-receptors CD4 or CD8
Co-stim receptors (CD28)
pSMAC
Peripheral immune synapse
Peripheral signal: signal 2
Co-stim molecules.
There are some adhesion molecules which make the cells stick together.
Immune synapse
Space which the primary signal, the co-receptors & co-stim signal are all residing in the cell membrane.
Signal 1 aka primary signal
TLR signaling complex which involves a functional and mature TCR along with CD3. CD3 needed to provide the ITAMs. Bringing the ITAMs into proximity fires the signal downstream of the signaling cascade.
By the time you leave the thymus you have the ability to recognize antigen with a functional TCR (primary signal).
A naive T-cell
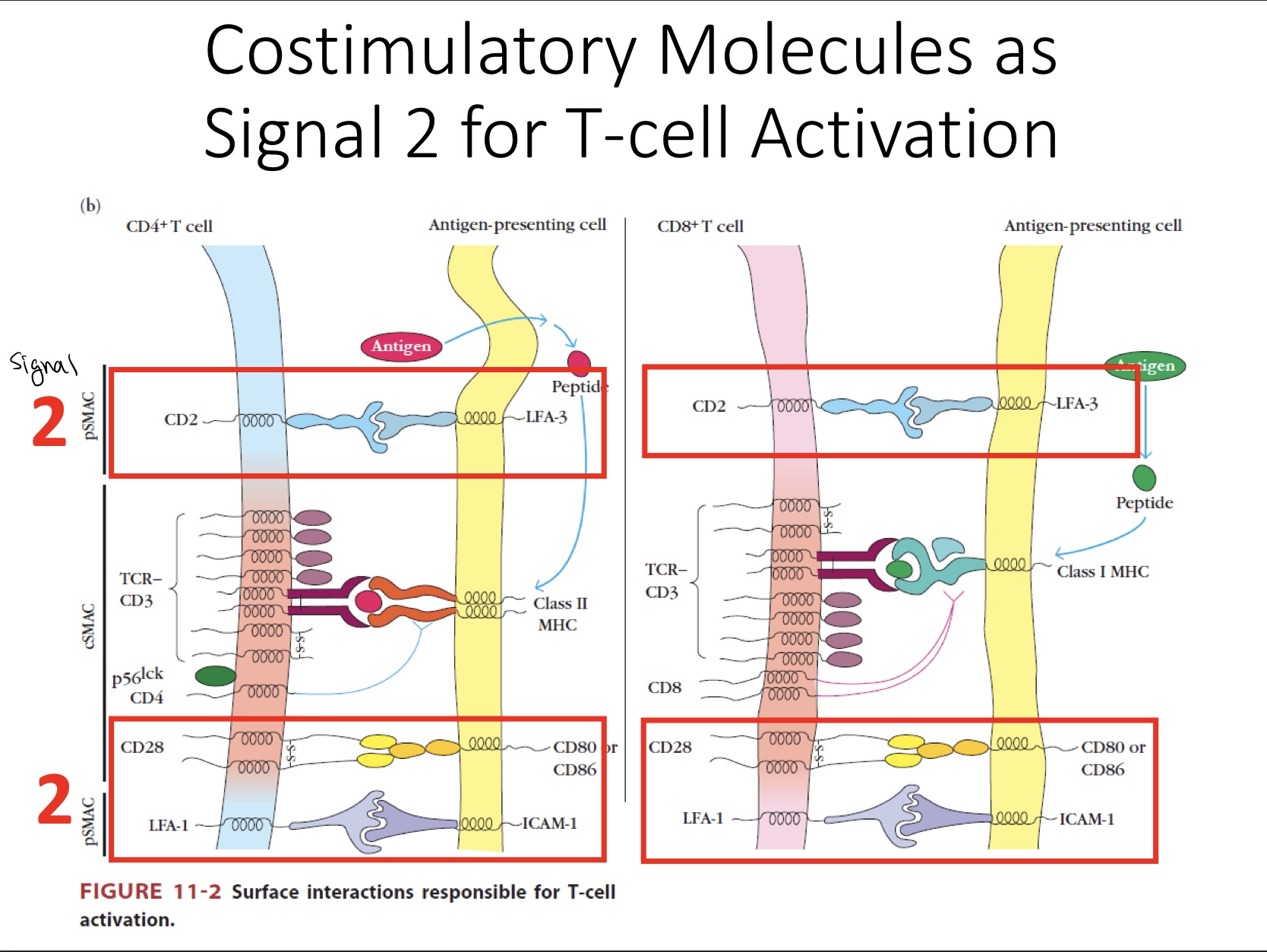
Signal 2
Recognized antigen & received a co-stim signal
Co-stim signal
is given by cells that are immunologically active.
Immunologically active: APC recognition through PRR, engulf antigen, puts on MHC
The co-stim receptor CD80/86 is part of APC activation
CD80/86
Ligands for CD28 co-stim receptor on T cell
Once the T cell expresses CD28 in the context of antigen then it becomes an activated T cell.
An activated CD4+
kicks out cytokines
An activated CD8+
It is now licensed to go out and make granules & start killing infected host cells
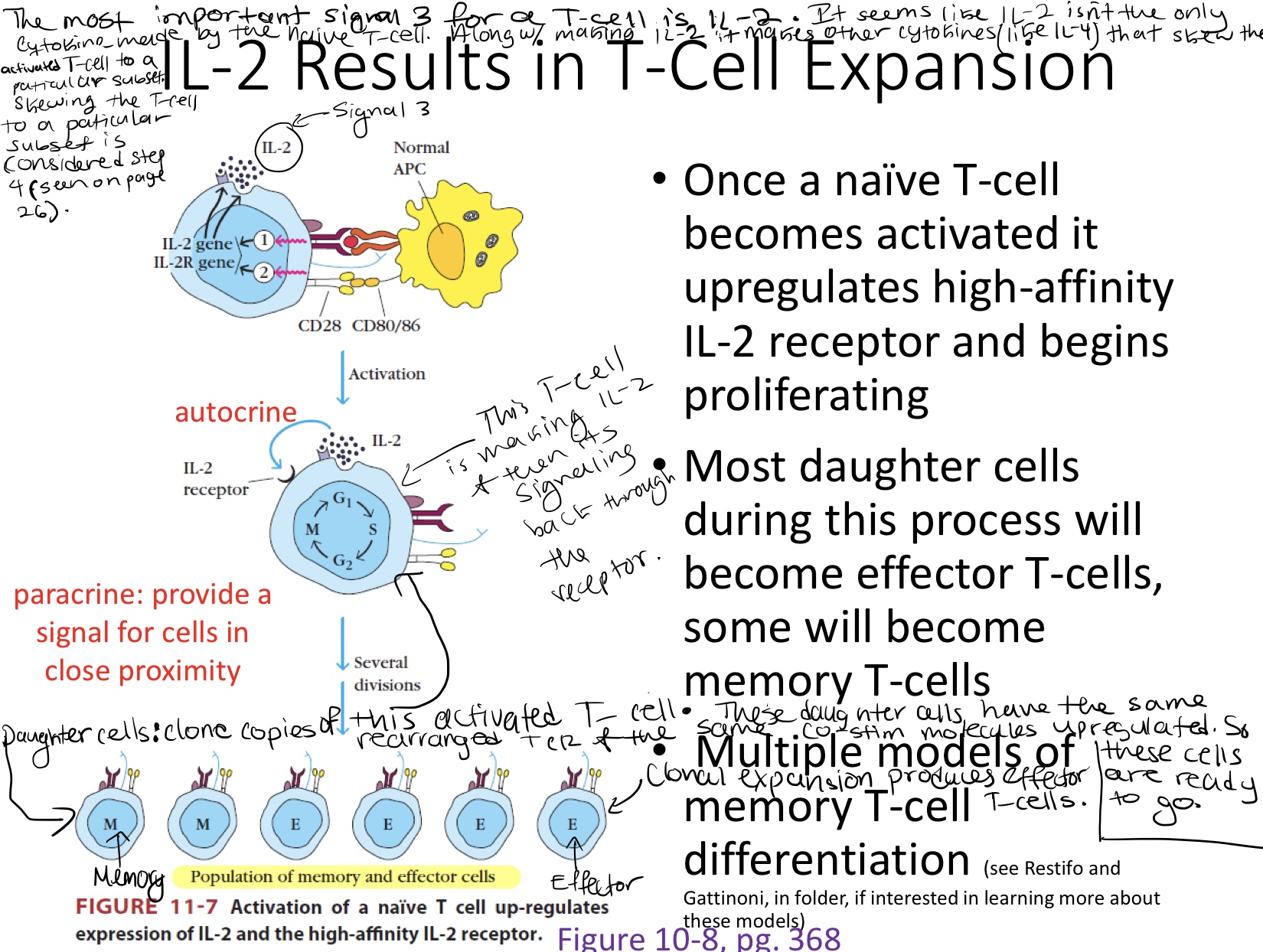
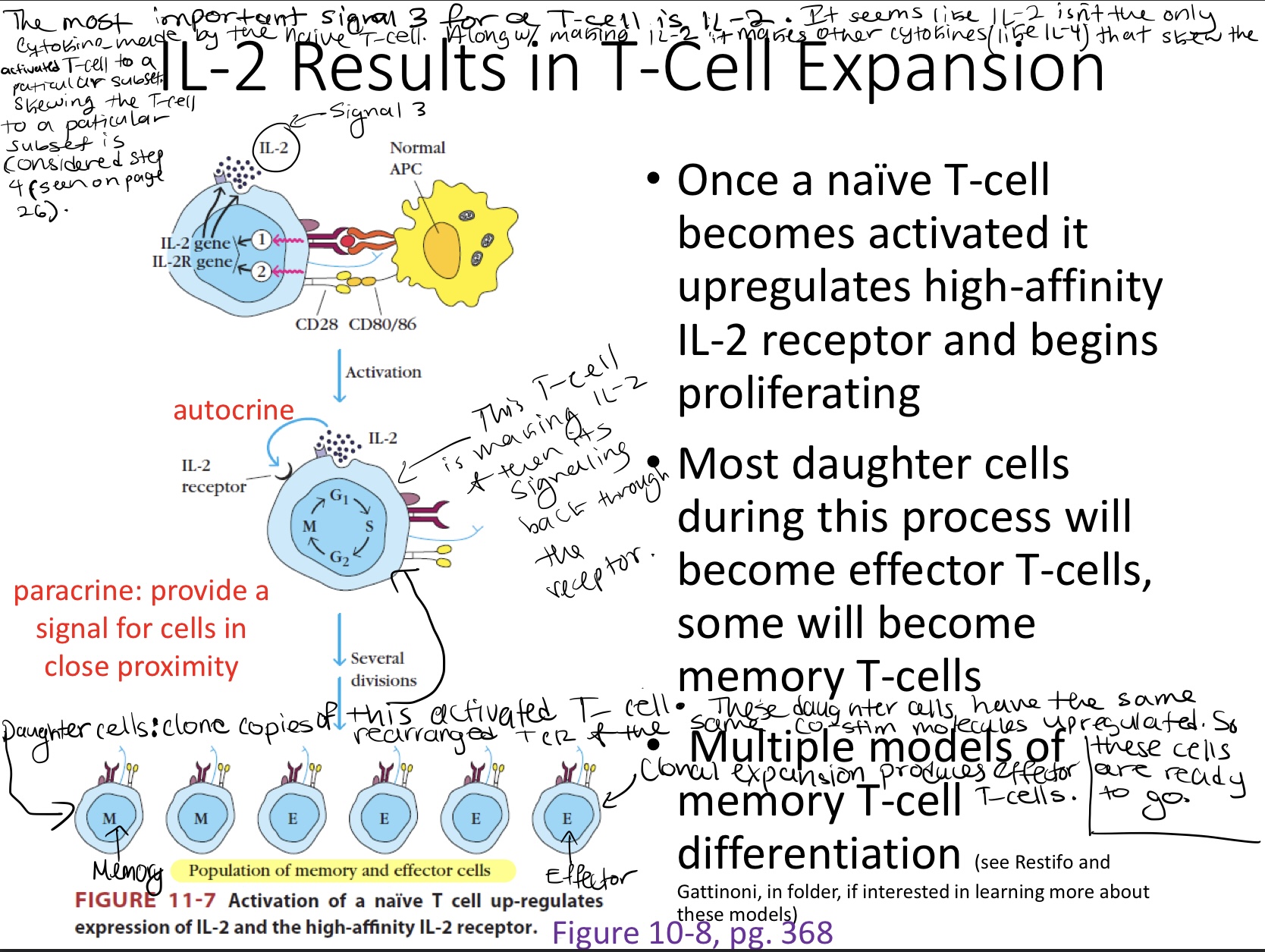
Signal 3
Cytokines signal back to the T-cell & they can drive the differentiation and the immune response that’s downstream of that activated T -cell
The most important signal 3 for a T-cell is IL-2.
IL-2 is a cytokine that causes clonal expansion of an activated T-cell
Once a naive T-cell becomes activated it up-regulates IL-2 & the high-affinity IL-2 receptor and begins proliferating.
Proliferating: the cell is being kicked into mitosis so it can divide
Clonal proliferation creates daughter cells that have the same rearranged TCR & co-stim up-regulated.
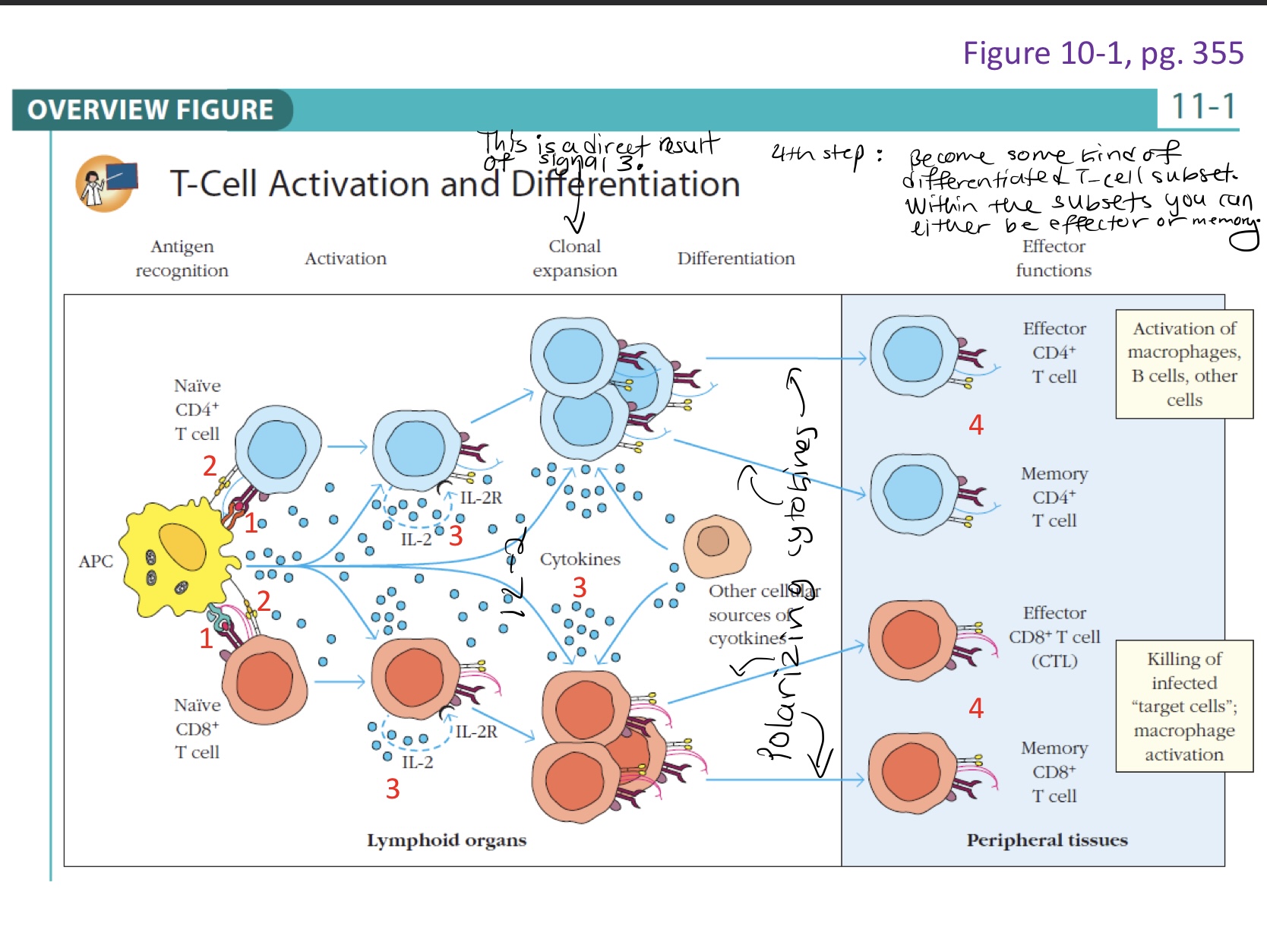
Most daughter cells will become effector T-cells, while some become memory T-cells.
Effector T-cells: cytokine factories that drive the immune response and lead to pathogen elimination
There are multiple models of memory T-cell differentiation.
Paracrine: providing cytokines that are signaling to cells in close proximity
Autocrine:
is when a cell makes cytokines and then it signals back on itself.
In the picture the T-cell is making IL-2 and then IL-2 signals back through the IL-2 receptor on the cell that made the IL-2.
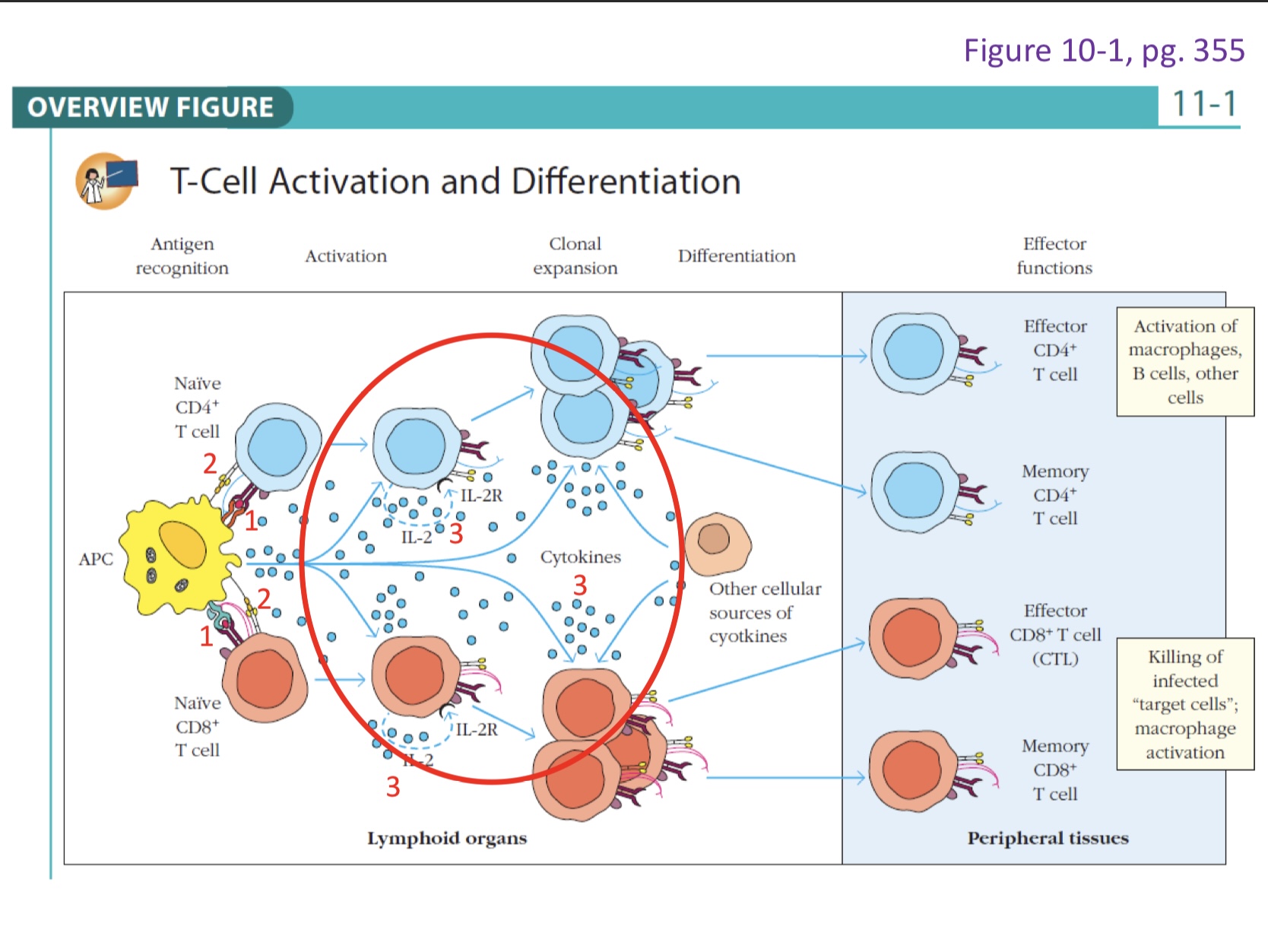
Signal 3 continued
APC can make IL-2 in the presence of primary and co-stim signals. This APC could be making signal 2 to feed the T- cell to get it to start proliferating. This is called paracrine signal.
Paracrine usually within the same physical location in the tissue.
Auto: self
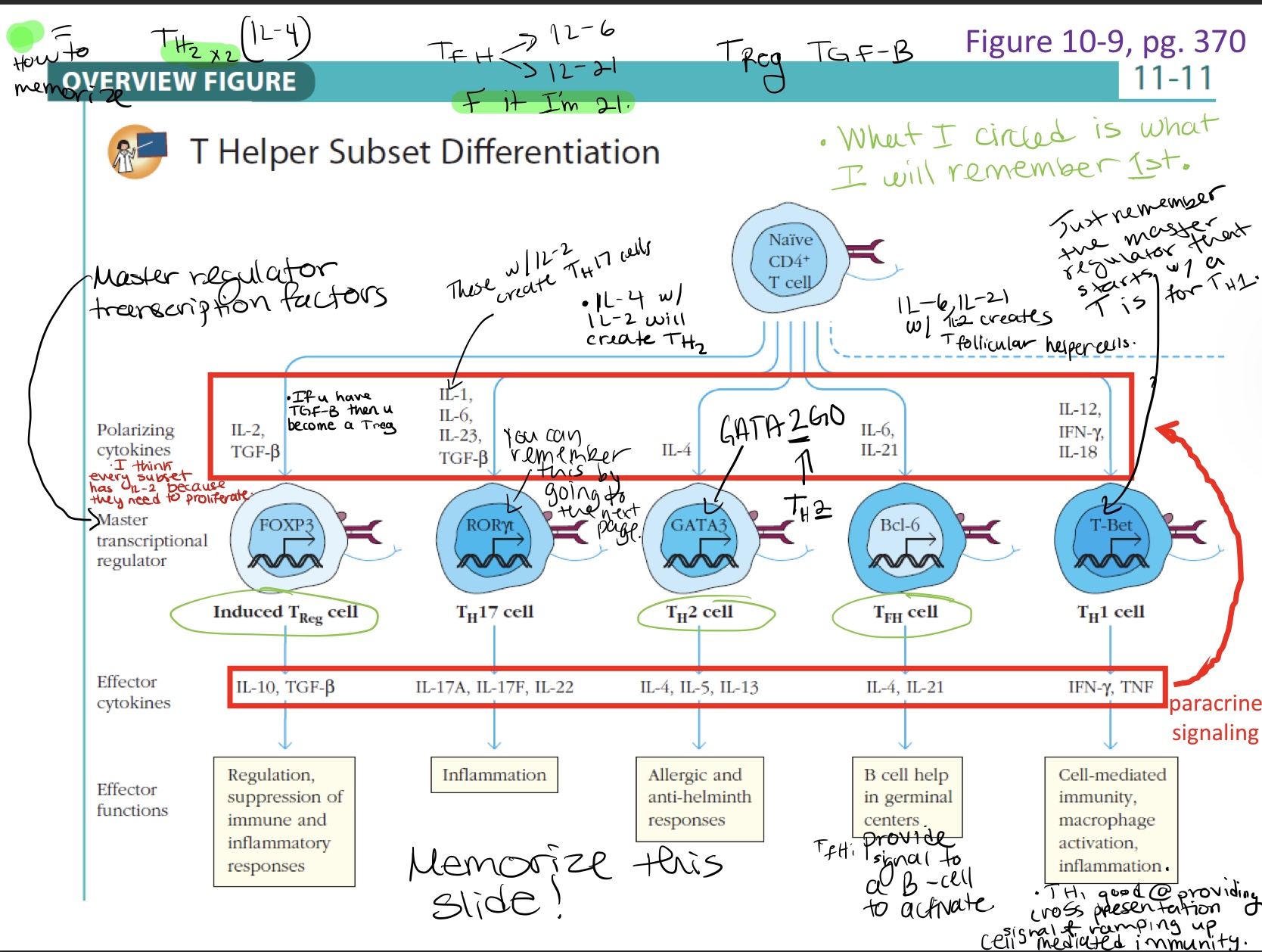
Polarizing & effector cytokines & paracrine signaling
The decision of a T cell to become one subset or another comes in the form of a polarizing cytokine signal.
Once you become one of these T cell subsets you create more effector cytokines.
These effector cytokines can signal back to create more of themselves. This signal is called a paracrine signal (refer to picture)
These effector cytokines can circle back to create more of its lineage, and you get amplification of the T cell signal
Steps to T-cell Activation
Activation signal
Co-stimulatory signal
Subset differentiation signal
Functional T-cell subset
Differentiated T-cell subset
Within the subsets you can either be an effector or memory T- cell.