The Science of Fingerprints
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential topics and historical milestones related to the science of fingerprints, including key figures, methods, and criminal cases.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the three main types of minutiae in fingerprint analysis?
Ending ridge, bifurcation, and dot.
What does IAFIS stand for?
Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System
After Electronic submission of fingerprints, agencies receive electronic responses to the submitted prints within what time frame?
Two hours, depending on time could be even faster.
Small Particle Reagent (SPR) is defined as what? and what do they do?
SPR is a suspension of fine molybdenum (also in magnetic powder) disulfide particles.
They adhere to fatty components of skin secretions to form a gray deposit.
Why must developed prints be photographed right away with regard to SPR?
The reaction product is very fragile with regard to the small particle reagent.
Silver Nitrate does what to skin secretions?
Reacts with chlorides in skin secretions to form silver chloride, a material which turns gray when exposed to light.
With Regard to Silver Nitrate, Why must prints be immediately photographed?
Prints developed with silver nitrate will eventually and permanently fill the background.
Iodine Fuming
What do Iodine fumes do in reaction with skin/fingerprints?
They react with oils and fatty deposits, producing a temporary yellow-brown reaction.
What type of fingerprinting is Iodine Fuming useful on?
Fresh prints, on porous and non-porous, non-metallic surfaces.
With regard to photographing fingerprints exposed to Iodine Fuming. Why is it important to photograph them immediately?
The reaction will rapidly fade, and the Iodine fuming cannot be redone.
1,8 Diazafluroren-9-one (DFO) is defined as:
a fluorescing ninhydrin analog found to produce up to 2.5 more prints than ninhydrin.
1,8 Diazafluroren-9-one (DFO) is useful on what types of surfaces?
Porous surfaces, especially paper.
1,8 Diazafluroren-9-one (DFO) can be developed more quickly using what technique?
Development can be accelerated through the application of controlled heat.
1,8 Diazafluroren-9-one (DFO); How does one view prints developed through this exposure?
Developed prints require the use of an alternate light source.
Fingerprinting powders
What are some of the characteristics and how are they used?
Powders adhere to water and fatty deposits. They are generally useful only on newer prints. They are useful on any dry, relatively smooth, non-adhesive surfaces. When using fingerprinting powders, it is best to use a pigment-based powder to contrast with the background.
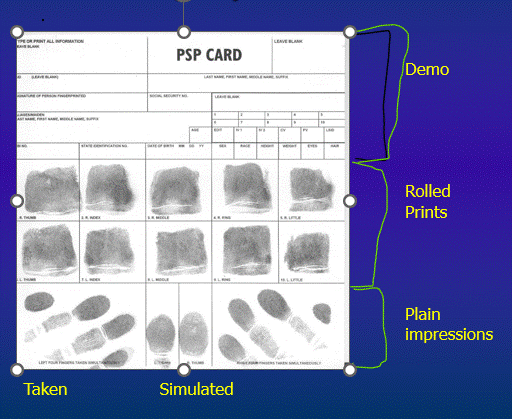
10-Print Fingerprint Card PSP card what needs to be filled out?
The demographics, Rolled Prints, Plain impressions, Taken and Simulated prints.
Fingerprints- Accidental is defined as:
There is no category to fit into. They contain two or more distinct types of patterns with the exception of the plain arch, with two or more deltas, or a pattern that has some of the requirements for two or more different types, or a pattern that conforms to none of the definitions.
These are seen in less than 1%.
Amido Black- is defined as:
Reacts with proteins in found in blood to form a black reaction.
It is useful only on blood-contaminated prints. It is highly sensitive.
Black Amido is useful on what type of surfaces? Can be developed in what type on what type of skin?
Useful on non-porous and some slightly porous surfaces. Sometimes can offer successful development of blood prints on dead human skin.

Twinned (Double) Loop
Consists of two separate loop formations with two deltas.
Chemical Processes used for Fingerprinting
Cyanoacrylate (superglue) Fuming is used mainly on what type of surfaces? It produces what type of finalized product, and how is it accelerated?
Mainly on non-porous surfaces, excellent on Styrofoam and plastic bags. It produces a white print and accelerates with heat or moisture.
Cyanoacrylate (superglue) Fuming prints must be dusted and enhanced with what?
Powders and/or treated with fluorescing dyes for enhancement to increase visibility and contrast.
Ninhydrin reacts with this to produce this result? What is ninhydrin useful for these types of surfaces specifically? How long is the development time for Ninhydrin?
Amino acids produce a purple reaction called “Ruhemann’s Purple”. It is useful on porous surfaces, especially paper. The development time is up to 10 days, but it can be accelerated by heat and humidity.
Physical Developer is defined as: is most useful on what types of surfaces and is successful on items exposed to what?
It is another silver-based developer that reacts to form a dark gray reaction. It is useful on paper, cardboard, and unvarnished, light-colored woods. It is very successful on items exposed to water.
Adhesive (Sticky) Side Powder Procedure and Definition:
It attaches itself to plastic print impressions on the adhesive side of tapes. Produces excellent results on light-colored or transparent tapes, including duct, masking, plastic surgical tape, foam tape and reinforced packing tapes and label. The process involves wetting tapes.
Fluorochromes Definition and Usage:
They are special dyes made to fluoresce and bond with developed print deposits. It must be used in conjunction with an ultraviolet or alternate light source.
Alternate Light Sources is useful in locating what finding what at the crime scene?
Fingerprints, bodily fluid stains, hairs and fibers, and narcotics
Alternate Light Sources defined:
Combines powerful illumination with optimum wavelengths, which allows fluorescence of different types of evidence.
Alternate Light Sources are especially useful in developing latent fingerprints on what types of surfaces?
Alternate light sources are useful in developing latent fingerprints on surfaces that do not yield prints when treated with conventional methods. When light is transmitted across an object, most of the light, and corresponding colors of the spectrum, are absorbed or reflected, allowing invisible prints to become visible.
Define RUVIS
Reflective Ultraviolet Imaging System.
How does RUVIS differ from visible light?
Ultraviolet light differs from visible light in that the UV wavelengths are too short to be seen by the unaided human eye.
What and how is the Krimesite Imaging Scope used?
The Krimesite Imaging scope is able to selectively amplify 254 nm shortwave ultraviolet light, and ignore all other wavelengths of light. The UV light is reflected from residue left behind in a fingerprint. The reflected UV light enter the Krimesite scope, is amplified several thousand times and is converted into visible light, providing a visible image of an untreated fingerprint.
Vacuum Fuming Chamber Vs Non- vacuum Fumed Items
Latent fingerprints are fumed with cyanoacrylate within a vacuum have been found to polymerize on ridge detail in a far more even manner than non-vacuum methods, leading to clearer and more defined prints.
Vacuum Fuming Chamber How is it done?
Fumes readily travel around corners and in and out of recesses of the item being processed.
Vacuum Metal Deposition- What is the process?
After an item is placed in the chamber, 4-5 mg of gold and several grams of zinc are placed into evaporation dishes, located under the item. A vacuum is drawn on the chamber. Gold is evaporated by passing a voltage through the dish. A very minute coating of gold is deposited over the entire item. Gold is absorbed into fingerprint residue. Zinc is then evaporated and deposited in the same manner. Zinc will only condense onto other metals. Therefore, it adheres to the gold-coated background and furrows between fingerprint ridge details.
LiveScan is defined as:
refers to the process of capturing fingerprints directly into a digitized format.
LiveScan- The digitized fingerprints can be transmitted where?
AFIS, the Pennsylvania State Police and FBI Criminal History Database.
Define CPIN:
Commonwealth, Photo, Imaging, Network
What is CPIN?
A computer network that extends throughout Pennsylvania and is used to record and store digital photographs of crime suspects. Photographs are taken of a suspect’s face, tattoos, birthmarks, or any other type of unique feature that may accurately identify him or her. CPIN is interfaced with LiveScan, AFIS and IAFIS.