1.3 Organizational objectives
Mission statements and vision statements
Mission statement: statement of the business’s core aims, phrased in a way to motivate employees and to stimulate interest by outside groups vision.
Statement: statement of what the organization would like to achieve or accomplish in the long term.

Aims, objectives, strategies and tactics
Corporate aims: long-term goals which a business hopes to achieve.
Divisional/operational objectives: short-term goals/targets or medium-term goals/targets usually specific in nature which must be achieved for an organization to attain its corporate aims.
Operational objectives should be “SMART”
- S - Specific
- Objectives should focus on what the business does and should apply directly to that business.
- Example: A hotel may set an objective of 75% bed occupancy over the winter period - the objective is specific to this business.
- M - Measurable
- Objectives that have a quantitative value are likely to prove to be more effective targets for directors and staff to work towards.
- Example: To increase sales in the south-east region by 15% this year.
- A - Achievable
- Setting objectives that are almost impossible to achieve in a given time will be pointless. They will demotivate staff who have the task of trying to reach these targets.
- R - Realistic and relevant
- Objectives should be realistic when compared with the resources of the company and should be expressed in terms relevant to the people who have to carry them out.
- Example: informing a factory cleaner about “increasing market share” is less relevant than target of reducing usage of cleaning materials by 20%.
- T - Time-specific
- A time limit should be set when an objective is established. Without a time limit it will be impossible to assess whether the objective has actually been met.
- Example: By when does the business expect to increase profits by 5%?
Interlinking aims, objectives and strategies
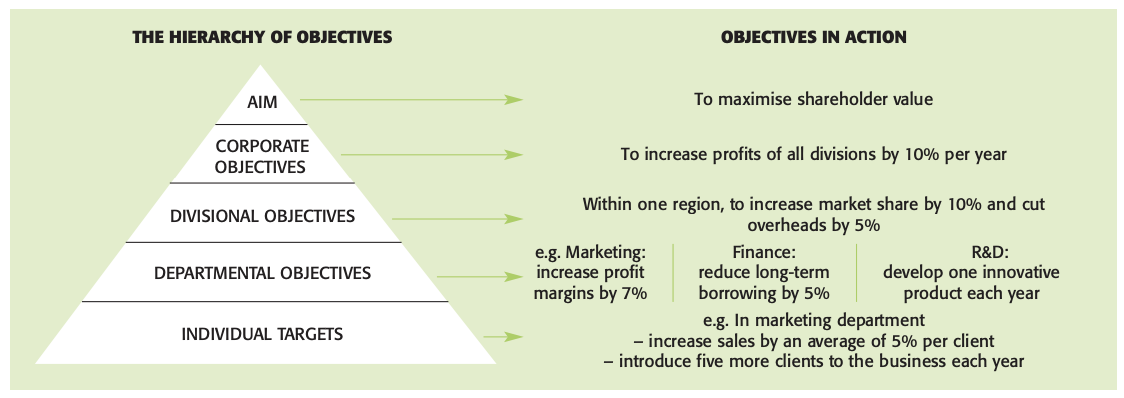
Links between objectives and strategies
- Corporate objectives:
- Grow revenues by 15% per annum in each of the next five years
- Marketing objectives:
- Increase UK market share to 17%
- Grow average customer spend by 5%
- Marketing strategies:
- Refocus product range on high margin items
- Introduce CRM systems into industrial division
- Marketing tactics:
- Improve agreements with key suppliers
- Conduct search engine advertising campaign
Difference between strategies and tactics
- Strategy: long-term plan of action for the whole organization, designed to achieve a particular goal.
- Tactic: short-term policy or decision aimed at resolving a particular problem or meeting a specific part of the overall strategy.
Common corporate aims
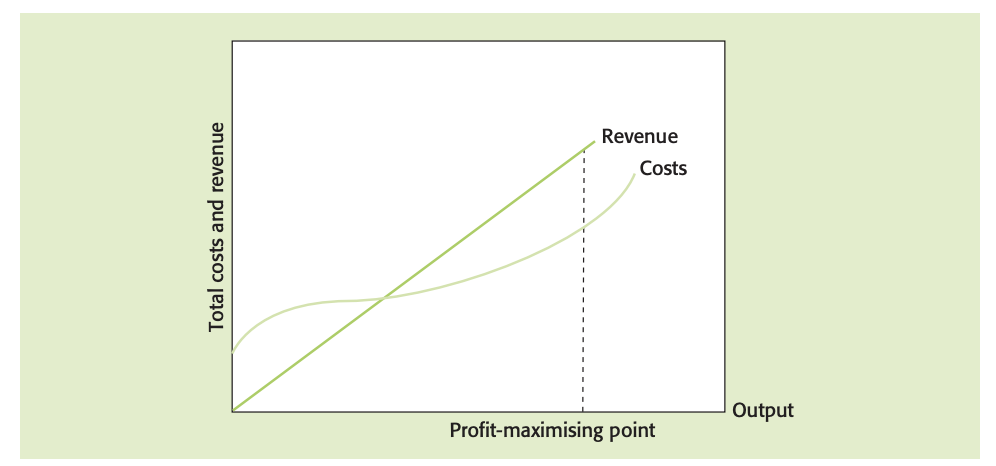
Profit maximization: producing at the level of output where the greatest positive difference between total revenue and total costs is achieved.
Profits are essential for rewarding investors in a business and for financing further growth and are necessary to persuade business owners and entrepreneurs to take risks.
Profit satisficing: aiming to achieve enough profit to keep the owners happy, but to work flat out to make as much profit as possible.
- Objective of owners of small businesses who wish to live comfortably but do not want to work very long hours in order to earn more profit.
The growth of a business (in terms of sales or value of output) has many potential benefits for the managers and owners:
- Larger firms will be less likely to be taken over and should be able to benefit from economies of scale.
- Managers may gain higher salaries and fringe benefits.
- Businesses that do not attempt to grow may cease to be competitive and eventually, will lose their appeal to new investors.
Increasing market share indicates that the marketing mix of the business is proving to be more successful than that of its competitors.
Survival
- The high failure rate of new businesses means that to survive for the first two years of trading is an important aim for entrepreneurs. Once the business has become firmly established, then other longer-term objectives can be established.
Maximizing short-term sales revenue could benefit managers and staff when salaries and bonuses are dependent on sales revenue levels. However, if increased sales are achieved by reducing prices, the actual profits of the business might fall.
Maximizing shareholder value
- Management (especially in public limited companies) take decisions that aim to increase the company share price and dividends paid to shareholders. These targets might be achieved by pursuing the goal of profit maximization. This shareholder value objective puts the interests of shareholders above those of other stakeholders.
Ethical objectives
Ethics: moral guidelines that determine decision making.
Ethical code (code of conduct): document detailing a company's rules and guidelines on staff behavior that must be followed by all employees.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Stakeholders: people or groups of people who can be affected by, and therefore have an interest in, any action by an organization.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR): this concept applies to those businesses that consider the interests of society by taking responsibility for the impact of their decisions and activities on customers, employees, communities and the environment.
Changes in corporate responsibility
Social audit: independent report on the impact a business has on society. This can cover pollution levels, health and safety record, sources of supplies, customer satisfaction and contribution to the community.
Factors determining corporate objectives
- Corporate culture
- Size and legal form of the business
- Public sector or private sector businesses
- Well-established businesses
Changing business objectives
- SWOT analysis: form of strategic analysis that identifies and analyses the main internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats that will influence the future direction and success of a business.
Ansoff’s matrix
- Ansoff’s matrix: model used to show the degree of risk associated with four growth strategies:
- Market penetration: achieving higher market shares in existing markets with existing products.
- Product development: development and sale of new products or new developments of existing products in existing markets.
- Market development: strategy of selling existing products in new markets.
- Diversification: process of selling different, unrelated goods or services in new markets.