Acute Kidney "Injury"
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
acute kidney injury (AKI) incidence
-common and consequential
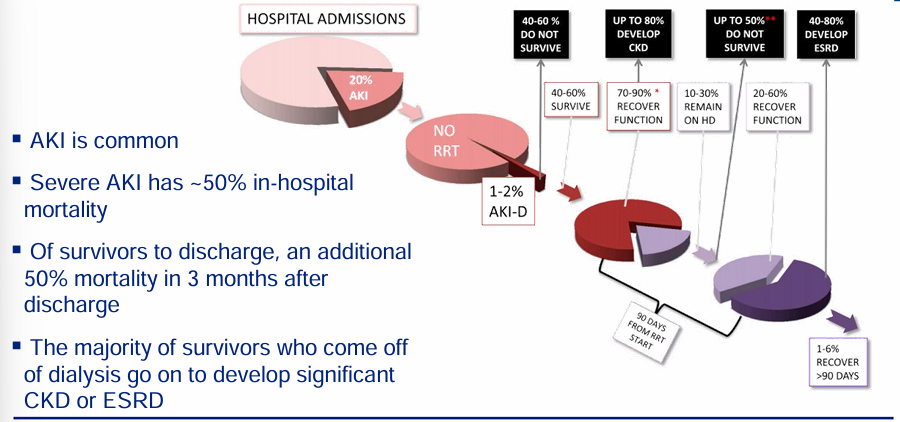
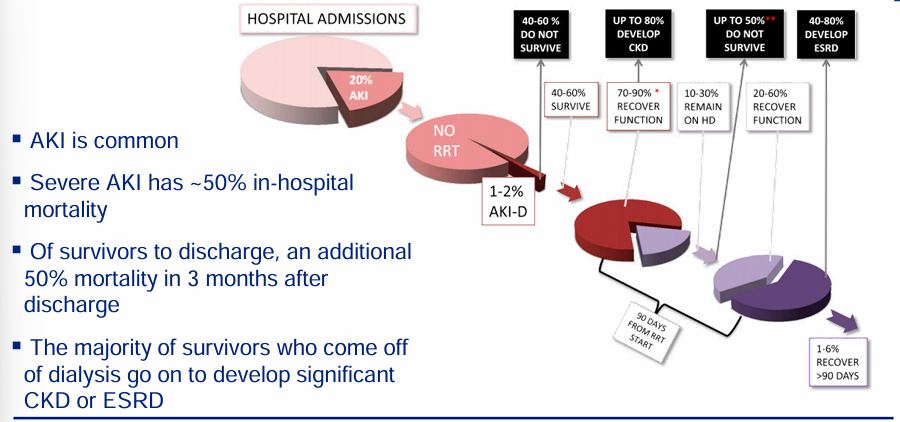
-severe AKI requiring dialysis in-hospital mortality = 50%
-AKI associated with increased risk of CKD and ESRD
-AKI associated with increased length of stay and healthcare costs (Cr >2.0 mg/dL = +8d LOS and + $33,161)
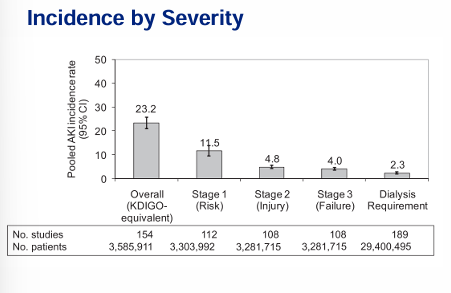
AKI definitions and staging
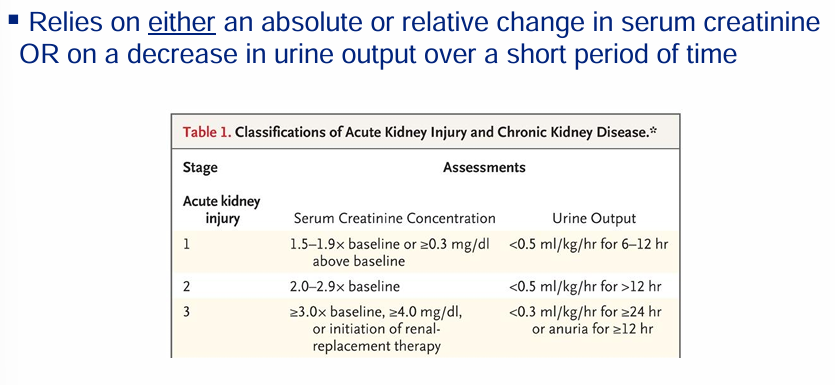
serum creatinine as a biomarker of filtration
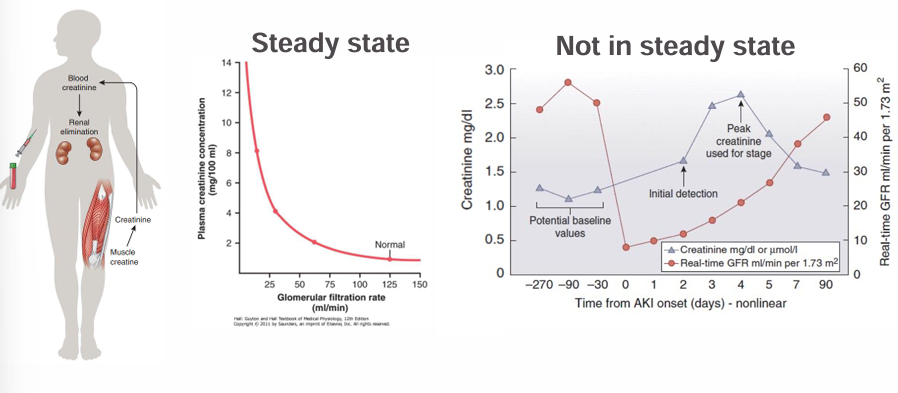
autoregulation of renal blood flow
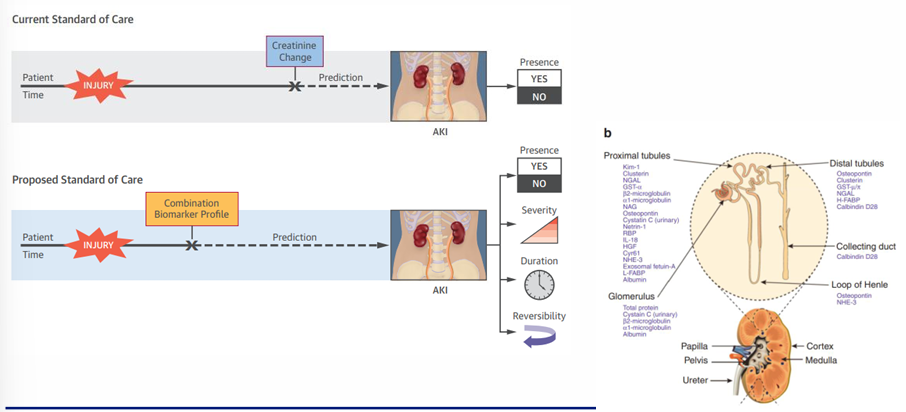
biomarkers of AKI
key points of AKI definitions

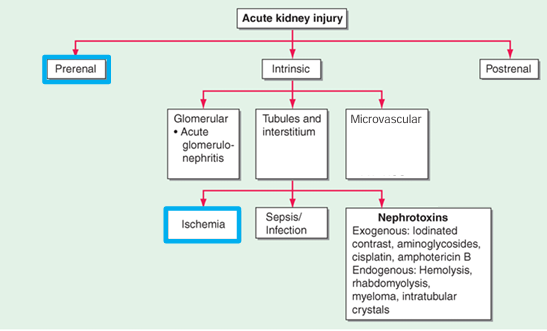
framework for approaching AKI
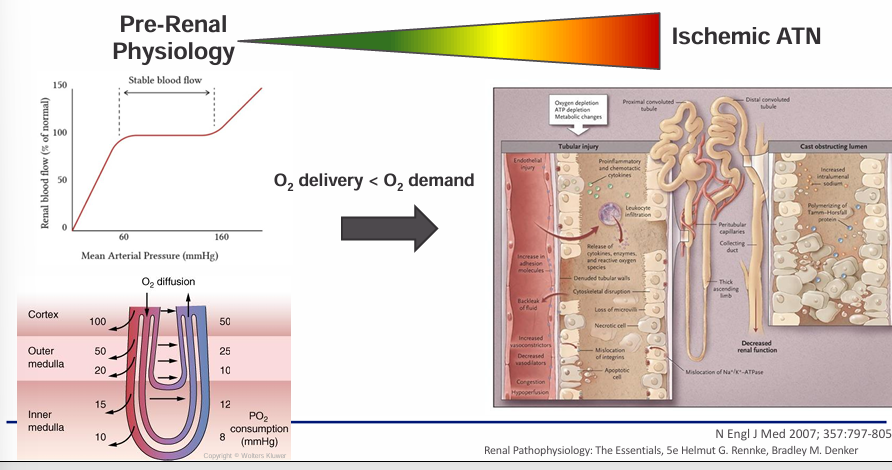
continuum of renal ischemia
-any insult that is severe enough or persists for long enough can overwhelm the kidney’s ability to autoregulate blood flow and consequently O2 delivery
-in other words, any insult can transform from simply pre-renal physiology into acute tubular necrosis (ATN)

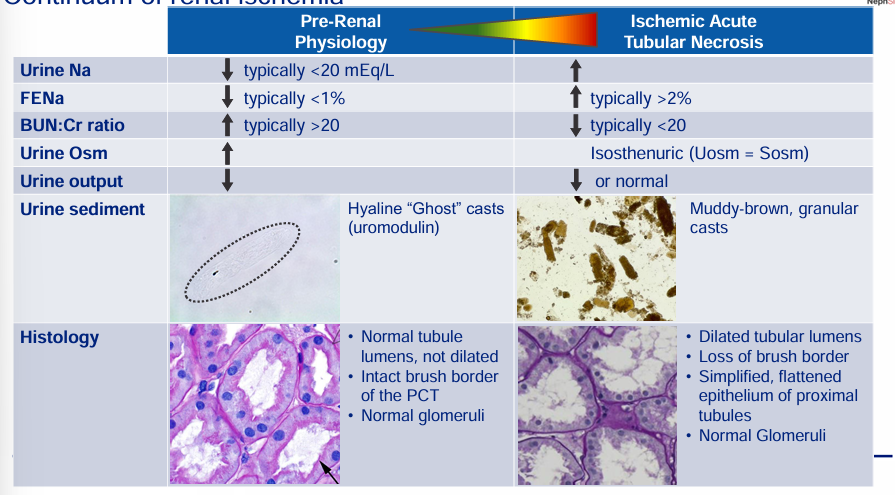
continuum of renal ischemia- pre-renal physiology and ischemic acute tubular necrosis
risk factors for renal hypoperfusion
adding 1L of normal saline (NS)
change in body compartments after 1L NS
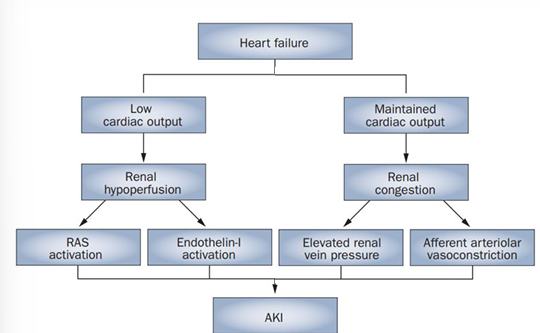
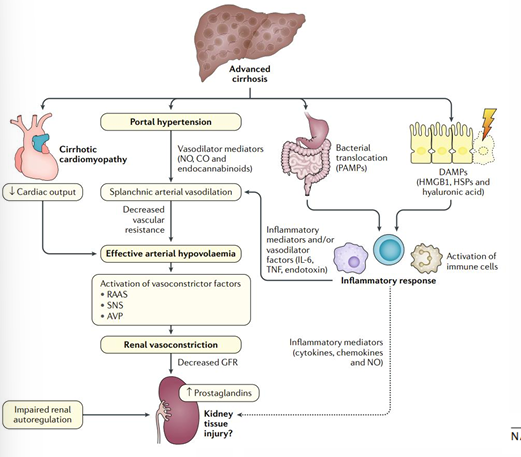
cardiorenal pathophysiology
-elevated Cr is even seen in heart failure with preserved CO
-increased renal venous congestion, local inflammation, and afferent vasoconstriction are hallmarks
-usually reversible
hepatorenal pathophysiology
-portal hypertension results in splanchnic vasodilation
-sensed arterial underfilling
-compensatory renal vasoconstriction and decreased GFR
-reversible (can even transplant the HRS kidneys)
key points of renal ischemia as a continuum
-pre-renal physiology and ischemic ATN lie on a continuum of renal ischemia
-any insult resulting in renal hypoperfusion can transform from pre-renal physiology to ATN
-differentiating renal hypoperfusion v. ATN relies on our ability to discern whether normal tubular function has been lost (UNa, Uosm, urine sediment)
-both cardiorenal and hepatorenal are multi-organ physiologic states resulting in extreme renal hypoperfusion which are purely functional changes in the short-term
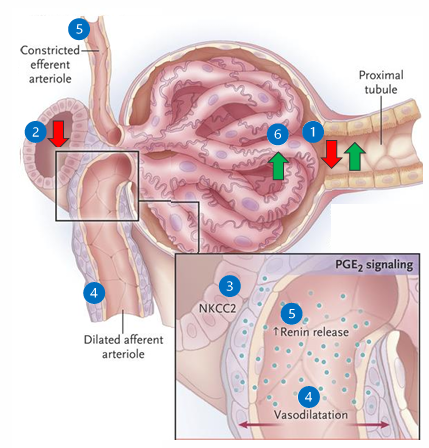
tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF)
1) renal perfusion drops and GFR decreases
2) filtrate NaCl flow reaching the macula densa decreases
3) sensed by the macula densa in the JGA
4) local mediators (PGE2) vasodilate the afferent arteriole
5) increased renin and increased angiotensin II results in efferent vasoconstriction
6) net effect is increased glomerular hydrostatic pressure and attempts to restore GFR (by increasing filtration fraction)
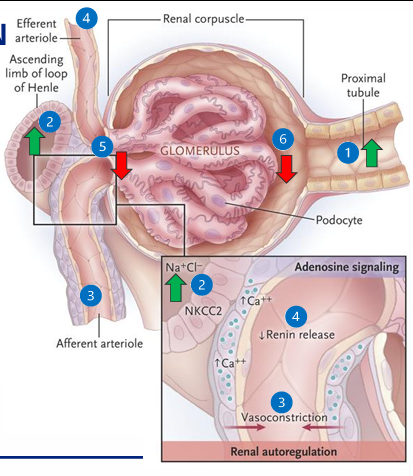
TGF in ATN
1) proximal tubule cells cannot reabsorb filtered NaCl
2) increased Cl flow sensed by the macula densa in the JGA
3) local mediators (adenosine) vasoconstrict the afferent arteriole
4) decreased renin and decreased angiotensin II results in efferent vasodilation
5) renal blood flow decreases, glomerular hydrostatic pressure decreases
6) GFR decreases to prevent ongoing NaCl loss
conversion to ATN
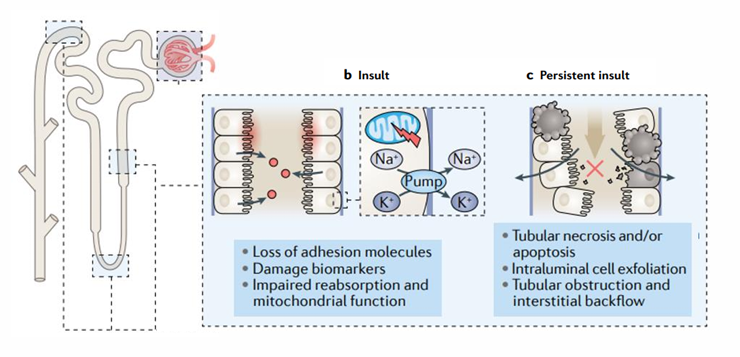
pathophysiology of sustained decreased GFR in ATN
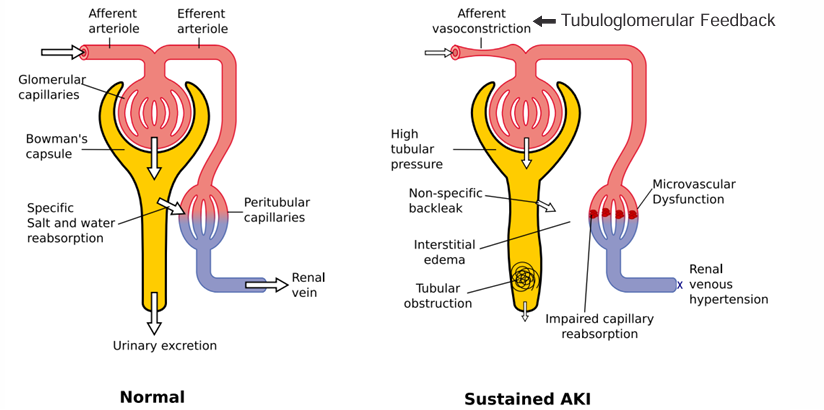
framework for approaching AKI
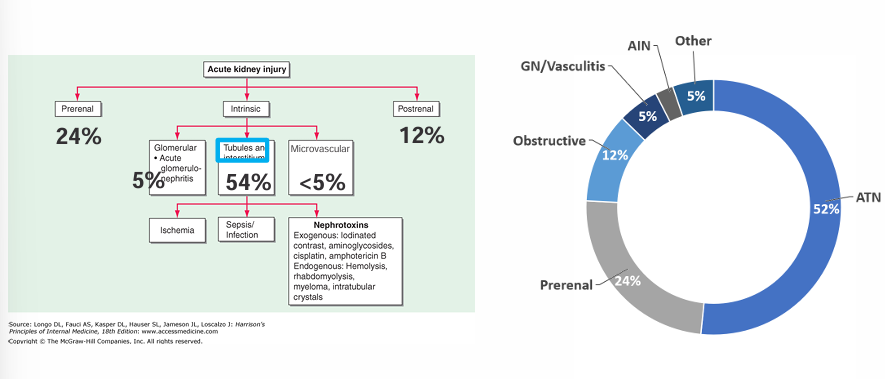
causes of ATN
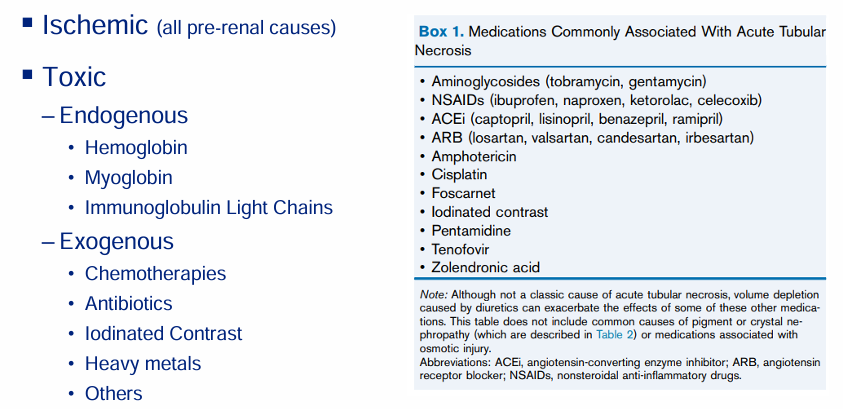
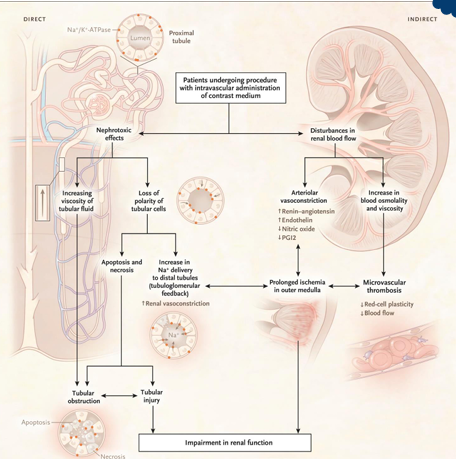
contrast nephropathy
-intravenous (CT scans) or intravenous (left-heart catheterization) administration of iodinated contrast
-intense arteriolar vasoconstriction
-hyperosmolality and hyperviscosity of vasa recta → thrombosis
-direct toxicity to proximal tubule cells
-usually reversible
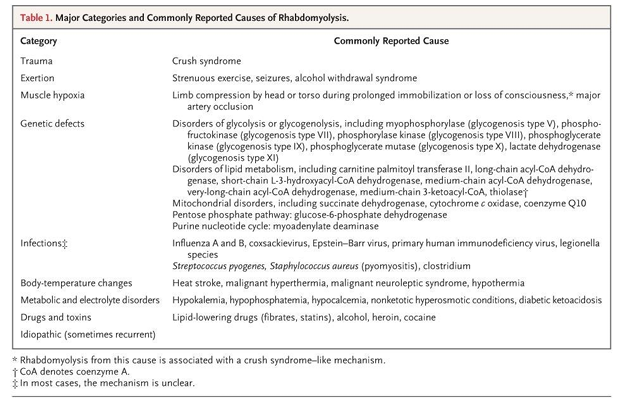
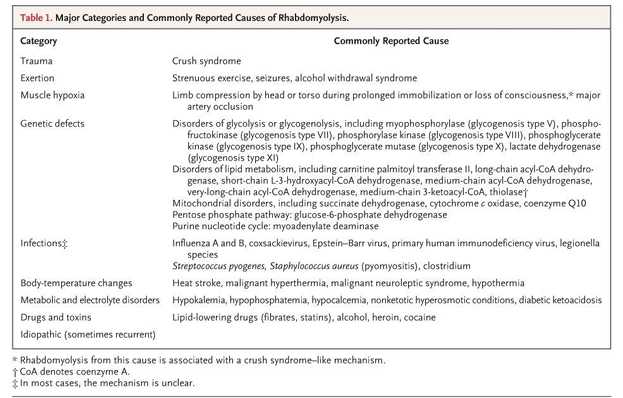
rhabdomyolysis
-breakdown of skeletal muscle
-intracellular myoglobin, K+ and P- released
-results in hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, volume depletion, and oxidative stress
-intense renal vasoconstriction, oxidative toxic ATN, and pigmented granular myoglobin casts with obstruction
-urinalysis +blood (myoglobin Fe) but few RBCs on microscopy
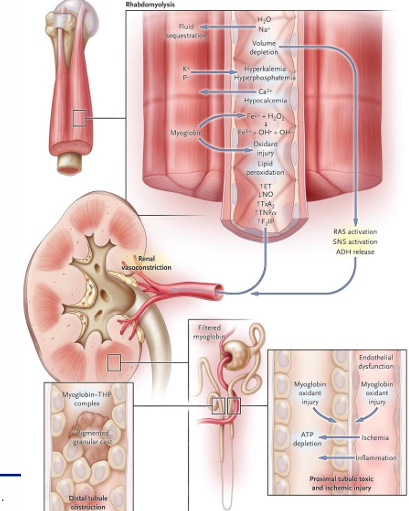
causes of rhabdomyolysis
key points of differential diagnosis in AKI
-history and urine sediment are key elements that determine the need for further workup
-serologic evaluation and renal biopsy are only indicated in select cases
-framework for AKI DDx includes pre-renal, post-renal, and intrinsic (glomerular, tubular, interstitial, and microvascular compartments)
-there are many non-ischemic causes of ATN, notably contrast nephropathy and rhabdomyolysis highlighted here
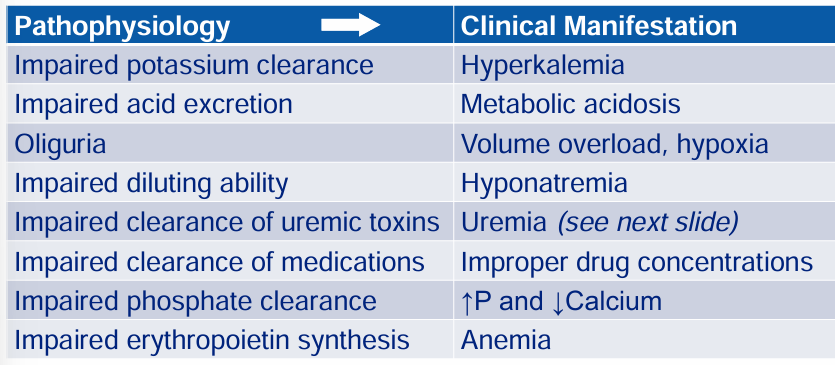
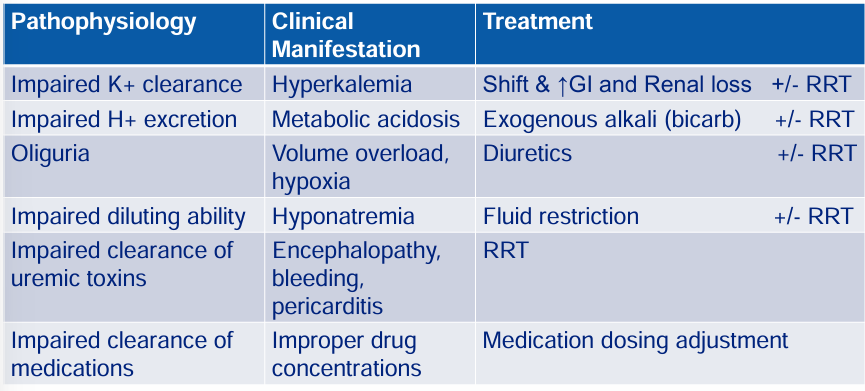
complications of severe AKI: pathophysiology → clinical manifestation
uremia
AKI as a multiorgan, systemic condition
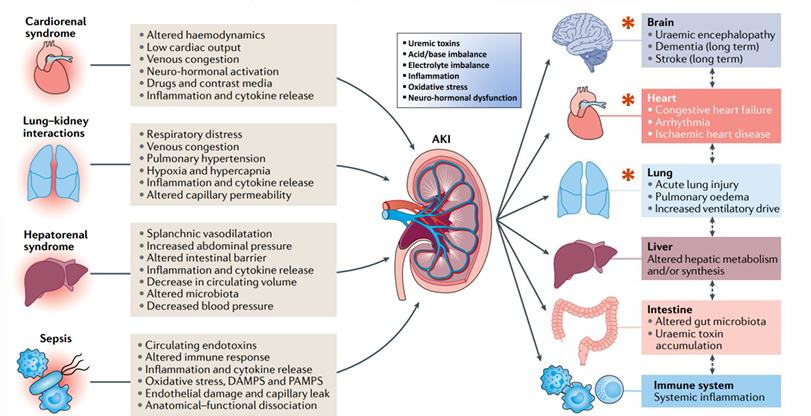
management of AKI
-primary and secondary prevention
-try to determine cause
-eliminate any ongoing toxic exposures or ischemic insults
-cause-specific treatment in select cases
-adjust medication dosing
-expectant management of ATN
-monitor for indications for renal replacement therapy (RRT)
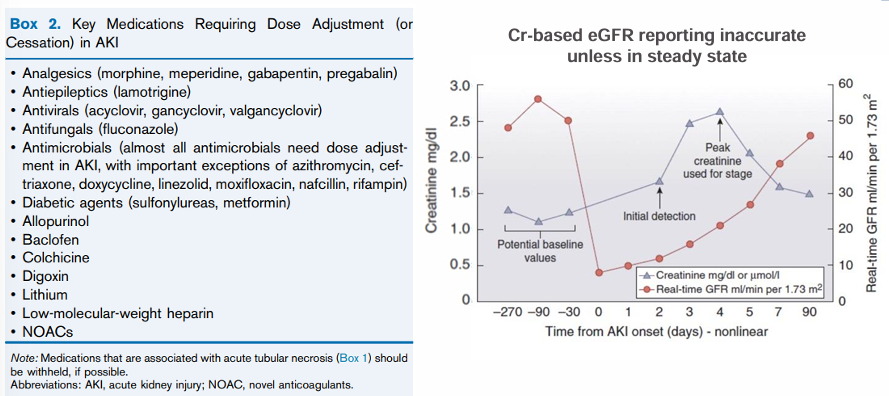
medication dosing in AKI
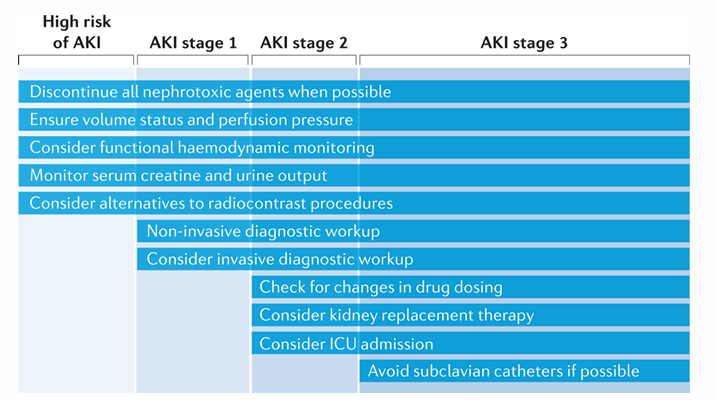
management of AKIO- high risk, stage I, stage II, stage III
treating complications of severe AKI- pathophysiology, clinical manifestation, treatment
natural history of AKI
future of AKI
key points- complications, treatment, outcomes
-determine etiology, eliminant ongoing insults, and implement cause-specific treatment if indicated
-primary and secondary prevention are paramount to decrease AKI incidence and the risk of CKD/ESRD (maladaptive fibrosis)
-adjust medication dosing to limit unintended supratherapeutic levels and toxicity
-monitor for indications for RRT
-high morbidity and mortality associated with AKI
-future of AKI management will rely on biomarkers of injury
summary
