M2: PLATELETS IN HEMOSTASIS
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
KABISADUHIN MO NA TO PLEASE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
Megakaryopoiesis
- translated as the development and maturation of megakaryocytes from the progenitor cell.
CFU-GEMM
- common myeloid progenitor where megakaryocytes arise from
GATA-1
- transcription gene that influences the rise of megakaryocytes from CFU-GEMM
FOG1
- cofactor that regulates GATA-1
MYB
- transcription gene product that suppresses megakaryocyte differentiation
GATA-1 and MYB
- act in opposition to balance megakaryopoiesis in one arm with differentiation to the red blood cell line in another arm.
1. burst-forming unit (BFU-MEG)
2. colony-forming unit (CFU-MEG)
3. light-density CFU (LD-CFU-Meg)
- three progenitor stages from least mature to more mature
Lymphocytes
- what do the three progenitor stages resemble making it not be distinguished by Wright-stain microscopy
BFU-Meg and CFU-Meg
- diploid and participate in normal mitosis, maintaining a viable pool of megakaryocyte progenitors.
LD-CFU-Meg
- does not have the capacity to divide but retains its DNA replication and cytoplasmic
maturation, endomitosis
Endomitosis
- partially characterized form of mitosis unique to megakaryocytes
Endomitosis
- a form of mitosis that lacks telophase and cytokinesis (separation into daughter cells).
RUNX1
- transcription factor that mediates mediates the switch from mitosis to endomitosis by suppressing the Rho/ROCK signaling pathway
- this is activated when GATA-1 and FOG1
Rho/ROCK signaling pathway
- suppresses the assembly of the actin cytoskeleton.
Actin and Myosin
- these are assembled inadequately in cytoplasmic constrictions, preventing cytokinesis
NF-E2
- transcription factor that influences production of ploidy in DNA replication
1. 8N
2. 16N
3. 32N
- ploidy with duplicate chromosome sets influenced by NF-E2
128N
- considered an unusual level of ploidy and may signal hematologic disease.
Terminal Differentiation
- As endomitosis proceeds, megakaryocyte progenitors leave the proliferative
phase and enter ________
MK-I stage or megakaryoblast
- least differentiated precursor of platelets
False
True
T or F
Megakaryoblasts resemble lymphocytes.
Megakaryoblasts resemble myeloblasts or
pronormoblasts.
plasma membrane blebs
- distinguishing feature of megakaryoblast from myeloblasts or pronormoblasts
plasma membrane blebs
- blunt projections from the margin that resemble platelets.
1. procoagulant-laden alpha granules
2. dense granules (dense bodies)
3. demarcation system (DMS)
- cytoplasmic ultrastructures of a developing megakaryoblast
DMS
- a series of membrane-lined channels that invade from the plasma membrane and grow inward to subdivide the entire cytoplasm.
DMS
- biologically identical to the megakaryocyte plasma membrane and ultimately delineates the individual platelets during thrombopoiesis.
Nuclear lobularity
- becomes apparent as an indentation at the 4N
replication stage, which makes the cell identifiable by light microscopy as the MK-II stage, or promegakaryocyte.
Promegakaryocyte
- features nuclear lobularity
- promegakaryocyte reaches its full ploidy level by the end of the MK-II stage.
MK-III stage
10x
30- to 50-um
- At the most abundant______, the megakaryocyte is easily recognized at ____ magnification because of its ______ diameter.
MK-I: 20
MK-II: 25
MK-III: 55
-% of precursors in MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
MK-I: 14-18 um
MK-II: 15-40 um
MK-III: 30-50 um
- diameter of MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
MK-I: round
MK-II: indented
MK-III: multilobed
-nucleus of MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
MK-I: 2-6
MK-II: variable
MK-III: not visible
- nucleoli of MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
MK-I: homogenous
MK-II: mod condensed
MK-III: deeply and variably condensed
- chromatin of MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
MK-I: 3:1
MK-II: 1:2
MK-III: 1:4
- nucleus to cytoplasm ratio of MK-I, MK-II, MK-IIIq
MK-I: absent
MK-II: absent
MK-III: absent
- mitosis in MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
MK-I: present
MK-II: ends
MK-III: absent
- endomitosis in MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
MK-I: basophilic
MK-II: basophilic and granular
MK-III: azurophilic and granular
- cytoplasm of MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
MK-I: present
MK-II: present
MK-III: present
- alpha granules, dense granules, and demarcation system of MK-I, MK-II, MK-III
Thrombopoiesis
- platelet shedding at full maturation
naked megakaryocyte nuclei
- what does thrombopoiesis leave behind that is consumed by marrow macrophages
2000-4000
- number of platelets a megakaryocyte can produce through thrombopoiesis
10^8 megakaryocytes
10^11 platelets
- number of megakaryocytes, platelets produced on an average
8-9 days
- total turnover rate of megakaryocytes to platelets
abluminal
sinusoid-lining endothelial cell
proplatelet
- Megakayocyte is adjacent to the _____ membrane of the ____ and extends a ______ process through or between the endothelial cells into the vascular sinus.
1. TPO
2. IL-3
3. IL-6
4. IL-11
- cytokine/hormone involved in platelet production (megakaryopoiesis and thrombopoiesis)
1. Differentiation to Progenitors
2. Differentiation to Megakaryocytes
3. Late Maturation
- function of TPO in platelet production
1. Differentiation to Progenitors
2. Differentiation to Megakaryocytes
- function of IL-3 in platelet production
1. Late Maturation
2. Thrombopoiesis
- function of IL-6 in platelet production
1. Differentiation to Megakaryocytes
2. Late Maturation
3. Thrombopoiesis
- function of IL-11 in platelet production
Proplatelet Process
- sheds the platelets which are cells consisting of
granular cytoplasm with a membrane but no nuclear material, into the venous sinus of the bone marrow.
2.5 um
- average diameter of a platelet
8-10 fL
- MPV of platelets
1. Circular to Irregular
2. Lavender
3. Granular
- appearance of platelets on a Wright-stained wedge preparation blood film
150-450x10^9/L
- normal platelet count in peripheral blood
Spleen
- sequesters the additional 1/3 of platelets
Relative Thrombocytopenia
- what is the possible condition if there is hypersplenism or splenomegaly
Platelets become irregular and sticky, extending pseudopods, and adhering to neighboring structures or aggregating with one another.
- how do platelets respond to conditions of hemostatic need through cellular and humoral immunity
Reticulated Platelets (stress platelets)
- appear in compensation for thrombocytopenia
- markedly larger than ordinary mature circulating platelets
6 um
- diameter of reticulated platelets
12-14 fL
- MPV of reticulated platelets
False (baliktad)
T or F
Stress platelets round up in citrated whole blood.
Stress platelets become cylindrical and beaded in EDTA.
True
True
T or F
Stress platelets resemble the fragments of megakaryocyte proplatelet processes.
This is observed in citrated whole blood.
True
T or F
Under healthy steady-state conditions, the rate of platelet release from the
megakaryocytes is equivalent to the rate of platelet removal from the circulation.
35,000 +/- 4300 platelets/mL/day
- net rate of production is expressed as platelet turnover
2-9 days
- lifespan of a platelet
Electron Microscopy
- where is the detailed anatomy of a platelet best elaborated
1. plasma membrane
2. submembrane
3. cytoskeleton
4. organelles
- four major areas of the platelet structure
plasma membrane
- part of platelet which consists of the platelet's outer membrane and related structures
submembrane
- part of platelet which links the membrane and the inner cell body
cytoskeleton (sol-gel zone)
- part of platelet which constitutes the matrix or muscle and skeletal portion of the platelet
1. granules
2. dense bodies
3. lysosomes
4. mitochondria
- platelet organelles consists of ___
7.5 nm
- thickness of the platelet plasma membrane
trilaminar
- unit structure of platelet plasma membrane
Glycocalyx
- thicker and denser than that of most blood cells, ranging in thickness from 10 to 50 nm.
Ia
Ib
Ic
IIa
IIb
III
IV
V
IX
- glycoproteins in the glycocalyx of platelets
Glycocalyx
- provides a surface to which some coagulation factors may adhere during
secondary hemostasis.
Plasma membrane
- underlying the glycocalyx which serves as the physical and chemical barrier between the intracellular and extracellular constituents of the platelet.
Sodium/Potassium ATPase Pump
- maintains a transmembrane ionic gradient
1. phosphatidylserine
2. phosphatidylcholine
3. phosphatidylinositol
- phospholipid constituents in the plasma membrane of platelets
platelet factor VIII (von Willebrand factor)
- an important constituent for the acceleration of blood coagulation and for platelet adhesion, is also located in the lipoprotein-rich plasma membrane of platelets
submembrane
- this area lies beneath the plasma membrane.
submembrane
- separates the organelles within the inner matrix of unaltered platelets and the cell wall.
submembrane
- contains an organized system of filaments which are physiologically comparable to the
microfilaments and submicrofilaments of the microtubule system.
submembrane filaments
- contribute to the regulation of the normal platelet discoid shape, act as a base for pseudopod formation, and interact with other contractile proteins to
modulate platelet adhesion and clot retraction after activation.
cytoskeleton
- underlies the submembrane area.
cytoskeleton
- represents the matrix of the platelet cytoplasm and consists of a circumferential microtubule system and randomly arranged microfilaments that form an intraplatelet matrix that support the discoid shape of the platelet.
Microfilaments in cytoskeleton
- provide the contractile force after activation that directs the organelles toward the center of the cell with control and direction from the microtubules.
Cytoskeleton
- serves as stabilizing component to regulate the arrangement of the internal organelles and microtubular system within the resting platelet body.
Cytoskeleton
- facilitates communication between the organelles and the platelet's external surroundings.
Microtubule System in Cytoskeleton
plays an important role in
the contractile response of platelets to stimulus.
Microtubule System in Cytoskeleton
- It acts to mediate and influence the extent of the platelet contractile response.
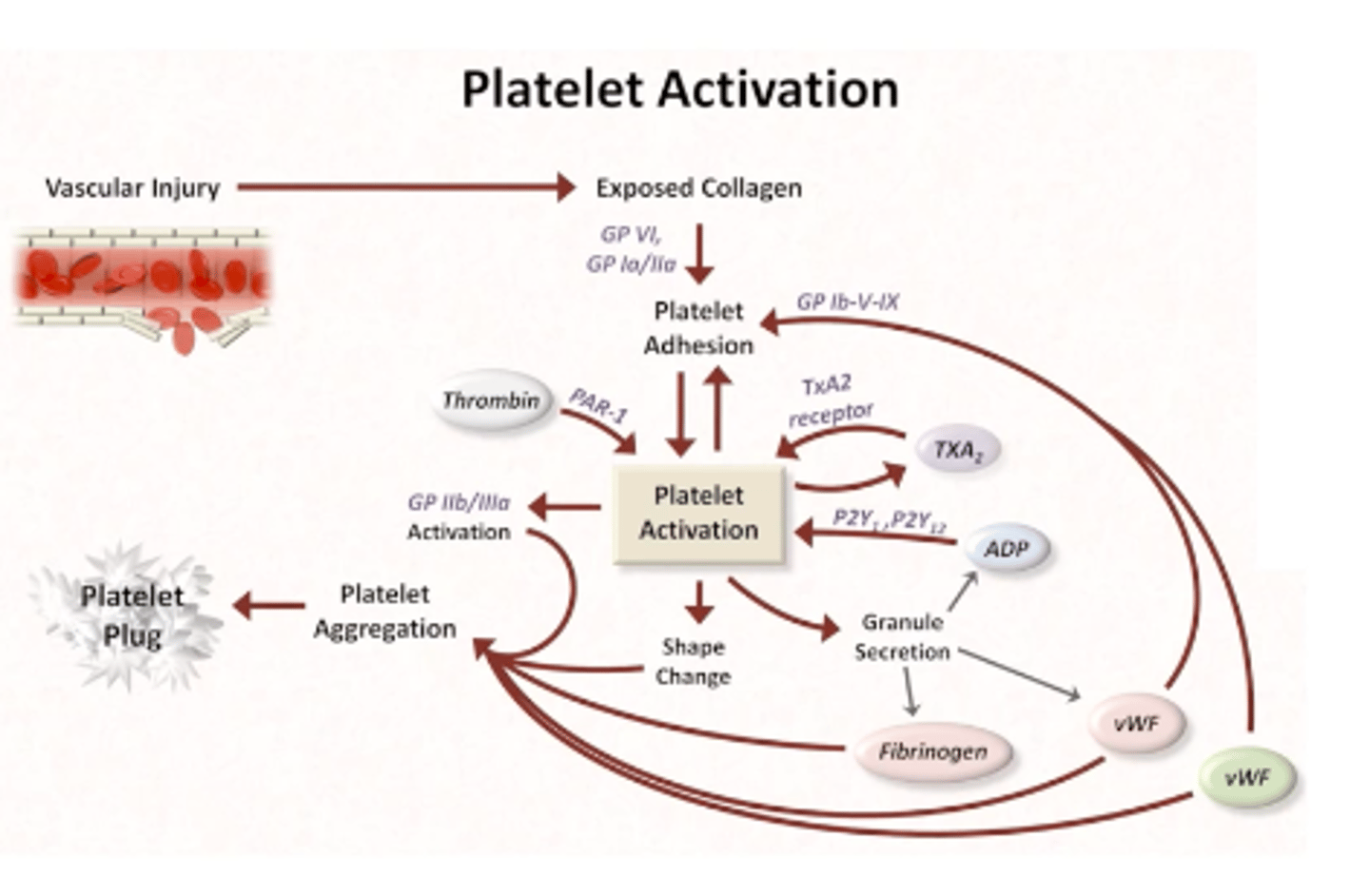
platelet activation
1. ADP, ATP
2. GDP, GTP
3. Calcium
4. Magnesium
5. Serotonin
- granule content of dense bodies of platelets
1. Platelet Specific Proteins
2. Multimerin
3. Adhesive glycoproteins
4. Coagulation Factors
5. Mitogenic Factors
6. Fibrinolytic Inhibitors
7. Membrane-associated proteins
- granule content of alpha-granules
1. Platelet Factor 4 (PF4)
2. Beta-Thromboglobulin family
- platelet specific proteins
Fibrinogen
Von Willebrand Factor
Fibronectin
Thrombospondin
Vitronectin
- adhesive glycoproteins
Factor V
Factor XI
Protein S
- coagulation factors
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Transforming growth factor-B
Endothelial cell growth factor
- mitogenic factors
Alpha2-Plasmin Inhibitor
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- fibrinolytic inhibitors