Nate. L - AP Psychology All Terms 2024
1/649
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
650 Terms
Psychology
A derivation of physiology (biology) and philosophy
Structuralism
Part of the Early Approaches: used INTROSPECTION (act of looking inward to examine mental experience) to determine the underlying STRUCTURES of the mind
Functionalism
Part of the Early Approaches: need to analyze the PURPOSE of behavior
Psychoanalytic/dynamic
A psychological approach that emphasizes the role of unconscious conflicts and early childhood experiences in shaping personality and behavior.
Behavioral
Refers to actions or reactions of organisms in response to internal and external stimuli, often studied in psychology and biology.
Humanistic
Emphasizes individual potential for growth, self-actualization, and personal fulfillment. It focuses on subjective experiences and the importance of the present moment.
Cognitive
Refers to mental processes such as thinking, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making. It involves perception, attention, memory, and language.
Evolutionary
Relating to or based on the process of gradual development and change over time, particularly in the context of biological organisms adapting to their environment.
Biological
Brain, NTs
Sociocultural
Pertaining to the influence of social and cultural factors on an individual's thoughts, behaviors, and development.
Biopsychosocial
A model that considers biological, psychological, and social factors in understanding health and illness. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of these aspects.
Mary Calkins:
First Female President of American Psychological Association (APA).
Margaret Floy Washburn
Psychologist known for her experimental work in animal behavior and motor theory development; first woman to receive a psychology Ph.D. in the U.S.
Charles Darwin
Natural Selection and Evolution
Dorothea Dix
Advocate for mental health reform, improved conditions for mentally ill, and founder of mental asylums in the 19th century.
Stanley Hall
American psychologist who founded the first U.S. psychology lab and the American Psychological Association. Known for his work in child development.
William James
Who was a pioneering American psychologist and philosopher, known for his work in functionalism and pragmatism.
Wilhelm Wundt
German psychologist who established the first psychology laboratory in 1879, marking the birth of experimental psychology.
Basic Research
Investigating fundamental principles and theories to expand knowledge without immediate practical application.
Applied Research
A type of research that aims to solve practical problems and produce solutions relevant to real-world issues and situations.
Psychologist
A professional who studies behavior and mental processes, applies scientific methods to understand and help individuals, groups, or organizations.
Psychiatrist
Specialized medical doctor who diagnoses and treats mental illnesses through therapy, medication, and other interventions.
Advantages of Experiments
Control over variables
Establish cause-effect relationships
Replicable and generalizable results
Disadvantages of Experiments
Potential biases, ethical concerns, limited generalizability, artificial settings, and cost constraints are disadvantages of experiments.
Independent Variable
The variable manipulated by the researcher to observe its effect on the dependent variable. It is the presumed cause in an experiment.
Experimental Group
The group in an experiment that receives the treatment or intervention being tested by researchers. There can be multiple.
Control Group
A group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment being studied, used as a comparison to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. There can only be 1
Placebo Effect
Where a fake treatment leads to real improvement in a patient's condition due to their belief in the treatment's efficacy.
Dependent Variable
Variable that is measured and affected by the independent variable in an experiment. It is the outcome or response that is being studied.
Double-Blind
Research method where both participants and researchers are unaware of who is receiving the treatment or the placebo to prevent bias.
Single-Blind
A research design where participants are unaware of which treatment they receive, reducing bias. Researchers know who receives what.
Quasi-experimental design
Random assignment to conditions is impossible (can’t randomly assign gender)
Operational Definition
A precise description of how a variable will be measured or manipulated in a research study. It translates abstract concepts into concrete terms for consistency and clarity. Allows for an experiment to be repeated.
Confound
error/ flaw in study
Random Assignment
Randomly assigning participants to different groups in an experiment helps ensure that each group is similar at the start, increasing the validity of the results.
Random Sample (selection)
A subset of individuals chosen from a larger set in a way that each member has an equal chance of being selected, ensuring representativeness. (Assignment and sampling can be done via names in a hat, computer generation, etc))
Representative Sample
A subset of a population that accurately reflects the demographics and characteristics of the entire group, enabling generalizations to be made.
Stratified Sampling
Where the population is divided into subgroups, or strata, and a random sample is taken from each subgroup to ensure representation.
Advantages of Correlation
Helps identify relationships between variables, measures the strength and direction of relationships, aids in making predictions based on patterns in data.
Disadvantages of Correlation
It does not imply causation, can be affected by outliers, and may not account for confounding variables."
Correlation doese’t equal…
Causation
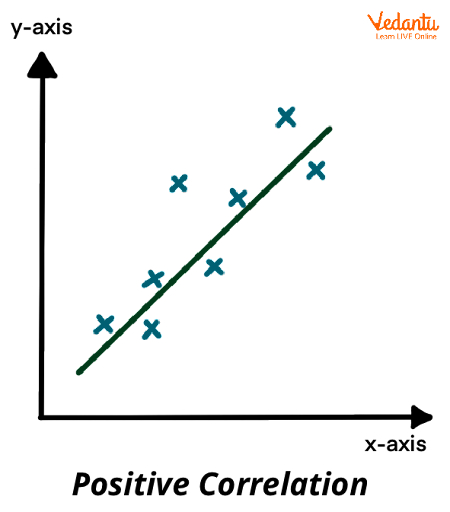

Positive Correlation
variables increase & decrease together
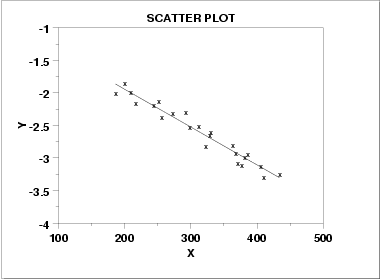
Negative Correlation
as one variable increases the other decreases
The stronger the number…
The stronger the relationship REGARDLESS of the pos/neg sign.
Stronger Relationships
= points closer together on graph
3rd variable problem (lurking variable)
Occurs when a third variable influences both the independent and dependent variables, leading to a false association between them.
Illusory correlation
Perceiving a relationship between variables that doesn't exist or is weaker than assumed.
Survey
Research method to collect data from a population to analyze trends or gather information on opinions, behaviors, or characteristics. Often done through questionnaires or interviews.
Social Desirability
Tendency to respond in a way that is viewed favorably by others, rather than truthfully, to avoid negative judgment or gain approval.
Wording Effects
The impact of phrasing on responses in surveys or questionnaires, influencing how individuals interpret and answer questions.
Advantages for Naturalistic Observation
Real-world behavior, high external validity, allows for studying complex behaviors in natural settings, minimal researcher interference.
Disadvantages for Naturalistic Observation
Limited control over variables, potential for observer bias, difficulty in replicating findings.
Advantages of Case Study
In-depth analysis, unique situations, detailed data collection, and rich insights for rare phenomena or complex issues.
Disadvantages of Case Study
Limited generalizability
Potential bias in data collection
Time-consuming
Subject to researcher interpretation
Descriptive Statistics
Summarize and describe data using measures like mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. It helps to understand patterns and trends in a dataset.
Measures of Central Tendency
Statistical values used to summarize the center of a data set, including mean, median, and mode. They provide insight into the typical or average value in a distribution.
Mean
The Average (use in normal distribution)
Median
Middle number (use in skewed distribution)
Mode
Most occurring number
Skews
Skews are a measure of the asymmetry of a distribution. Positive skew means a longer right tail, negative skew means a longer left tail.
Inferential Statistics
Techniques used to analyze data and make predictions or inferences about a population based on a sample.
Statistical Significance
The likelihood that a result or relationship is not due to chance, but rather a real effect in the population.
Ethical Guidelines
Principles that ensure research participants are treated with respect, confidentiality, and informed consent, promoting ethical behavior in research.
Confidentiality
Identities kept secret
Debriefing
A structured conversation post-experiment to inform participants of the study's purpose, address concerns, and ensure their well-being.
Neurotransmitter
Chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another, influencing various functions like mood, muscle movement, and memory.
Action Potential
Brief electrical impulse that carries information along a neuron, resulting from the movement of ions across the neuron membrane. Movement of Na and K ions across membrane sends an electrical charge.
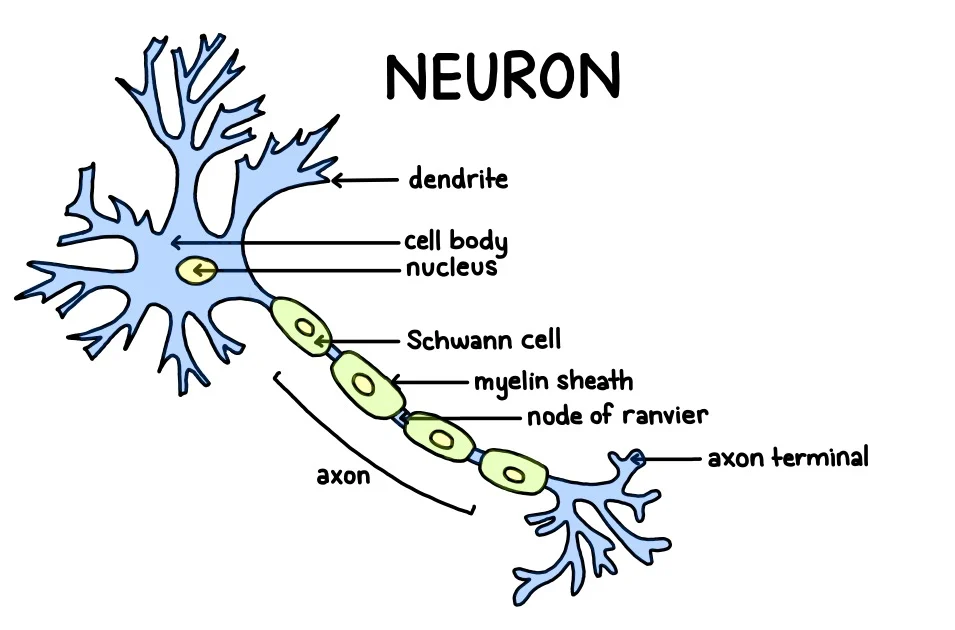
Neuron
Basic unit of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals.
Dendrites
Branch-like extensions of a neuron that receive messages from other neurons. They play a crucial role in transmitting electrical signals within the brain.
Soma
The body as distinct from the mind; in neuroscience, refers to the cell body of a neuron that contains the nucleus and maintains the cell's functions.
Axon
Part of a neuron that transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles. It is covered by the myelin sheath to speed up signal transmission.
Myelin Sheath
Insulating layer around nerve fibers that speeds up electrical impulses. It protects and helps transmit nerve signals efficiently.
Terminals
release neurotransmitters – send signal onto next neuron
Vesicles
Small membrane-bound sacs that transport cellular materials. They play a crucial role in intracellular transport and communication within cells. (Sac — rhymes with testicles)
Synapse
Location where nerve impulses are transmitted from one neuron to another or to an effector cell.
Key site for communication in the nervous system.
Gap between neurons
All or none law
Principle stating that once a neuron reaches its threshold, it fires at full strength, not varying in intensity.R
Refractory Period
Refers to the time post-response when a neuron cannot generate another action potential. It is crucial for understanding neural communication.
Sensory Neurons
Nerve cells that transmit sensory information (such as touch or pain) from the body to the central nervous system for processing.
Afferent Neurons
brain Accepts signals
Motor Neurons
Neurons that carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles, enabling voluntary movements like walking and talking.
Efferent Neurons
Neurons that carry signals away from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, enabling motor functions and responses.
Interneurons
Nerve cells that transmit signals between sensory neurons and motor neurons. They play a crucial role in processing information in the central nervous system.
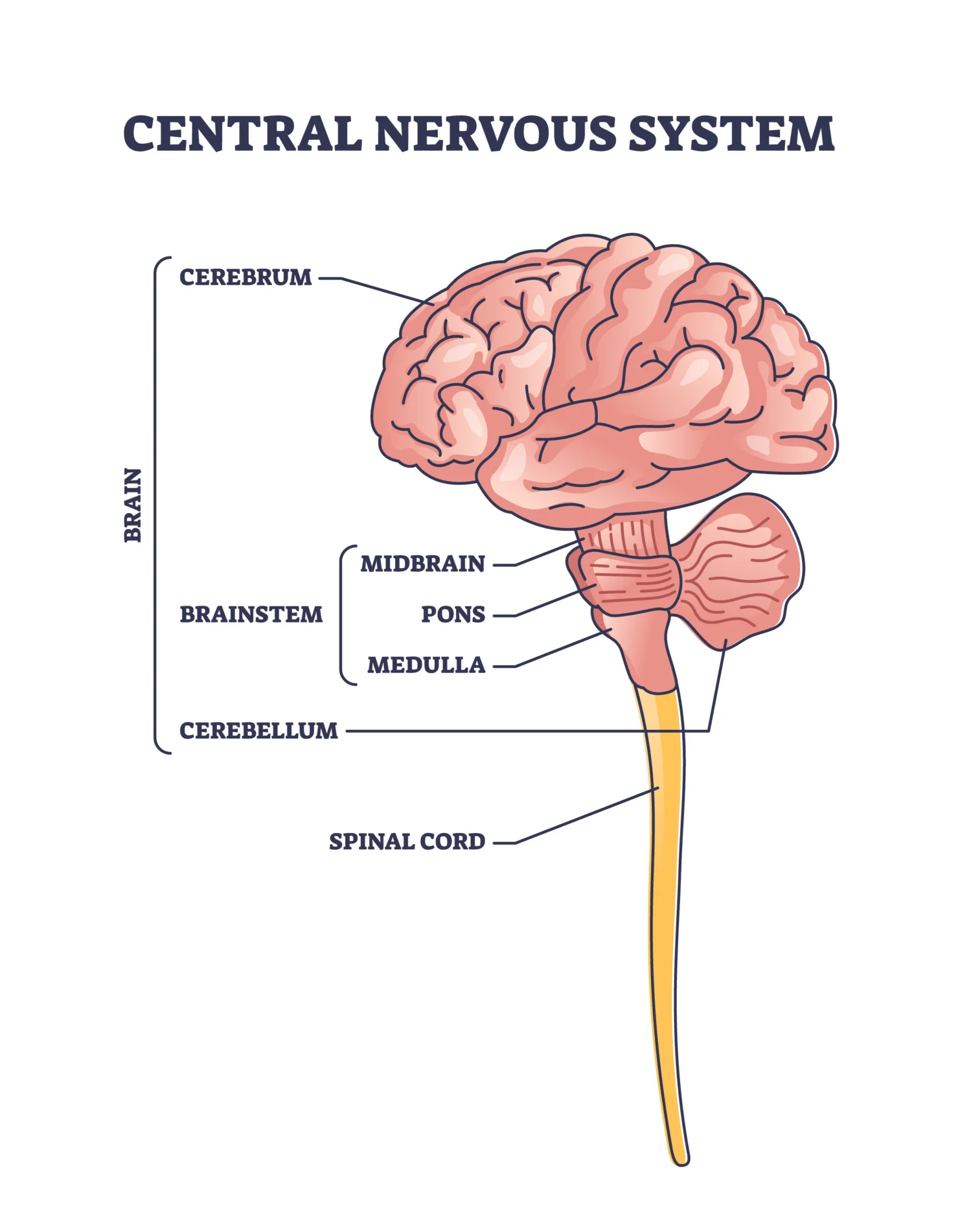
Central Nervous System
Consists of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and transmitting information throughout the body.
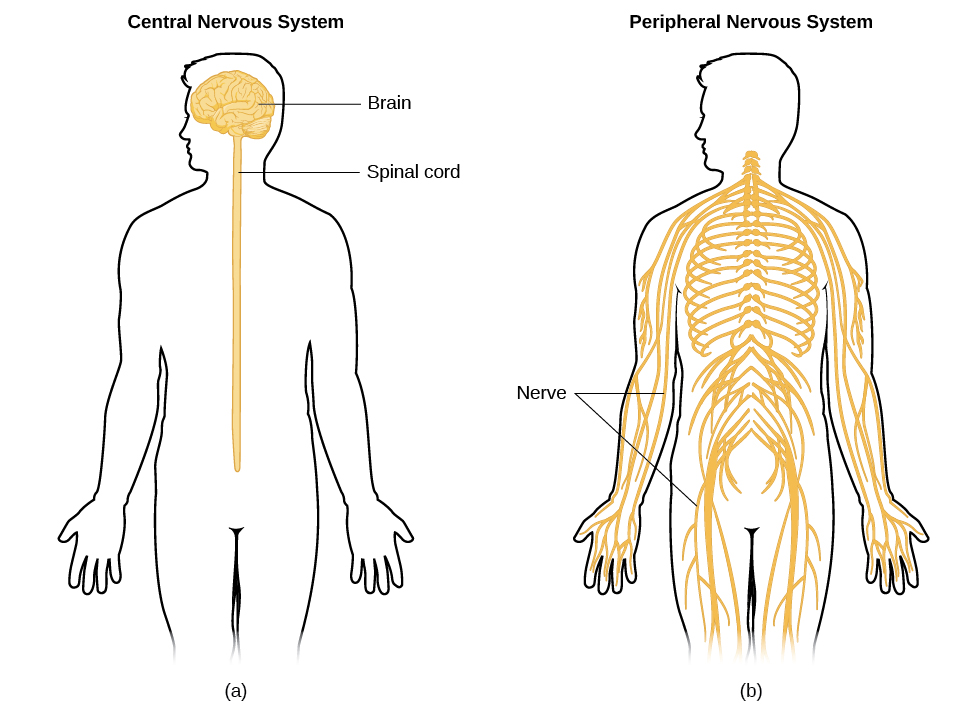
Peripheral Nervous System
The part of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord, connecting the central nervous system to the rest of the body through nerves.
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary movements by sending signals from the brain to muscles. Includes sensory neurons responsible for touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception.
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions like heartbeat and digestion. Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Part of the autonomic nervous system that activates the body's fight-or-flight response, preparing it for stressful situations by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and releasing adrenaline.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Part of autonomic nervous system that conserves energy, slows heart rate, increases digestion, and promotes relaxation.
GABA
Inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps reduce neuronal excitability in the brain, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety.
glutamatE
A neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in brain function, including learning and memory. It is an Excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
dopamine
A neurotransmitter that plays a key role in pleasure, reward, and motivation pathways in the brain. It is associated with feelings of happiness and satisfaction.
serotonin
a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. It plays a crucial role in maintaining emotional well-being and is often linked to feelings of happiness and relaxation.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contraction, memory, and learning. Plays a role in the parasympathetic nervous system.
Epinephrine & Norepinephrine
Sympathetic NS arousal
Hormones released by the adrenal glands in response to stress
Increase heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels
Fight-or-flight response activation
Endorphins
Chemicals produced by the body that act as natural painkillers and can induce feelings of pleasure or euphoria.
Oxytocin
a hormone released by the pituitary gland that plays a role in social bonding, childbirth, and breastfeeding.
agonist
A molecule that binds to a receptor and activates it to produce a biological response.
antagonist
a drug that blocks a neurotransmitter
reuptake
Reuptake is the process where neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron after signaling, regulating neurotransmitter levels in the synapse.
Used for depression treatment
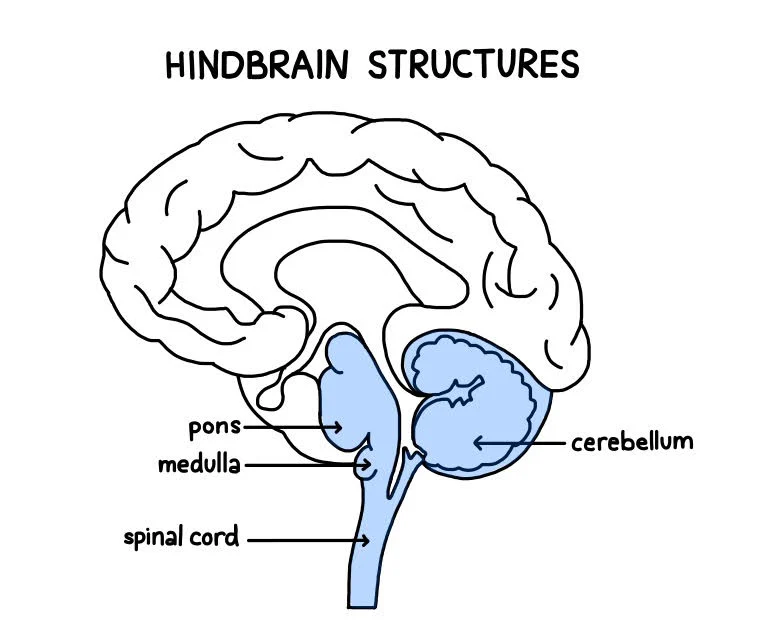
hindbrain
the region of the brainstem that includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. It controls basic life functions like breathing, heart rate, and coordination.