Trigonometry
Section 8.1- Vocab Section
What type of triangle
if the c2 value is less than a+b, it is an acute triangle. If the c squared is more than a+b, it is obtuse.
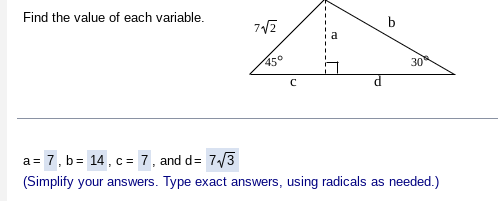
45-45-90 Triangle- Side lengths
if x2 +x2 = c2 then it follows that c = x√2, where x is the length of each leg of the triangle. so, X times the square root of 2, giving the hypotenuse. In some situations, it is better to just round the square root instead of simplifying the radical, especially in real- world problems/ situations.
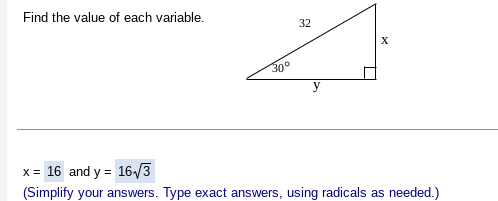
30-60-90 Triangle- Angles
In a 30-60-90 triangle, the side lengths are in the ratio X: x√3: 2x. This means that if the length of the shorter leg (opposite the 30-degree angle) is x, then the longer leg (opposite the 60-degree angle) will be x√3, and the hypotenuse will be 2x.
So, the smallest side is X, the hypotenuse is 2x, and the long leg is x√3, which correspond to angles of 30 degrees and 60 degrees, respectively.
Section 8.2- Trigonometric Ratios
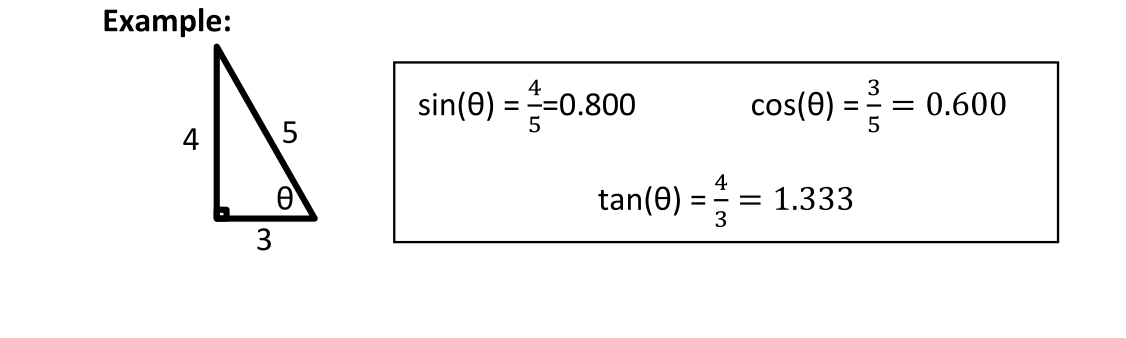
There are SIX different trig. Ratios; but focus on 3. Cosine, Sine, and Tangent. All the trig. funcs. Can be written as ratios comparing side lengths.
Vocab
“ Theta” (θ) is used to represent a missing angle measure.
“ Ajacent” is the leg that touches θ
“ Opposite” is the leg not touching θ
Using Trig. Functions
sine(θ) = sin(θ) = opposite/ hypotenuse
cosine(θ) = cos(θ) = ajacent/ hypotnuse
tangent(θ) = tan(θ) = opposite/ajacent
Example Of Trig Function
Missing Side Measure
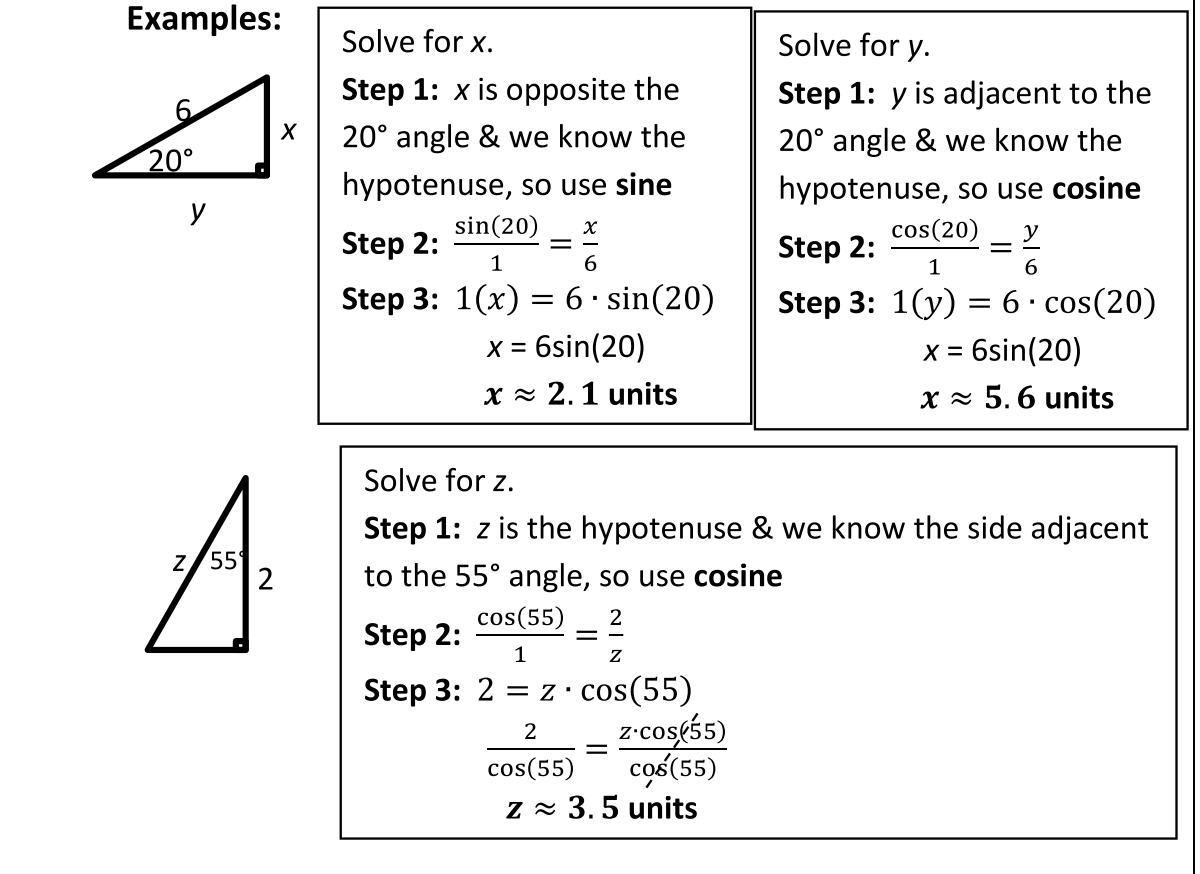
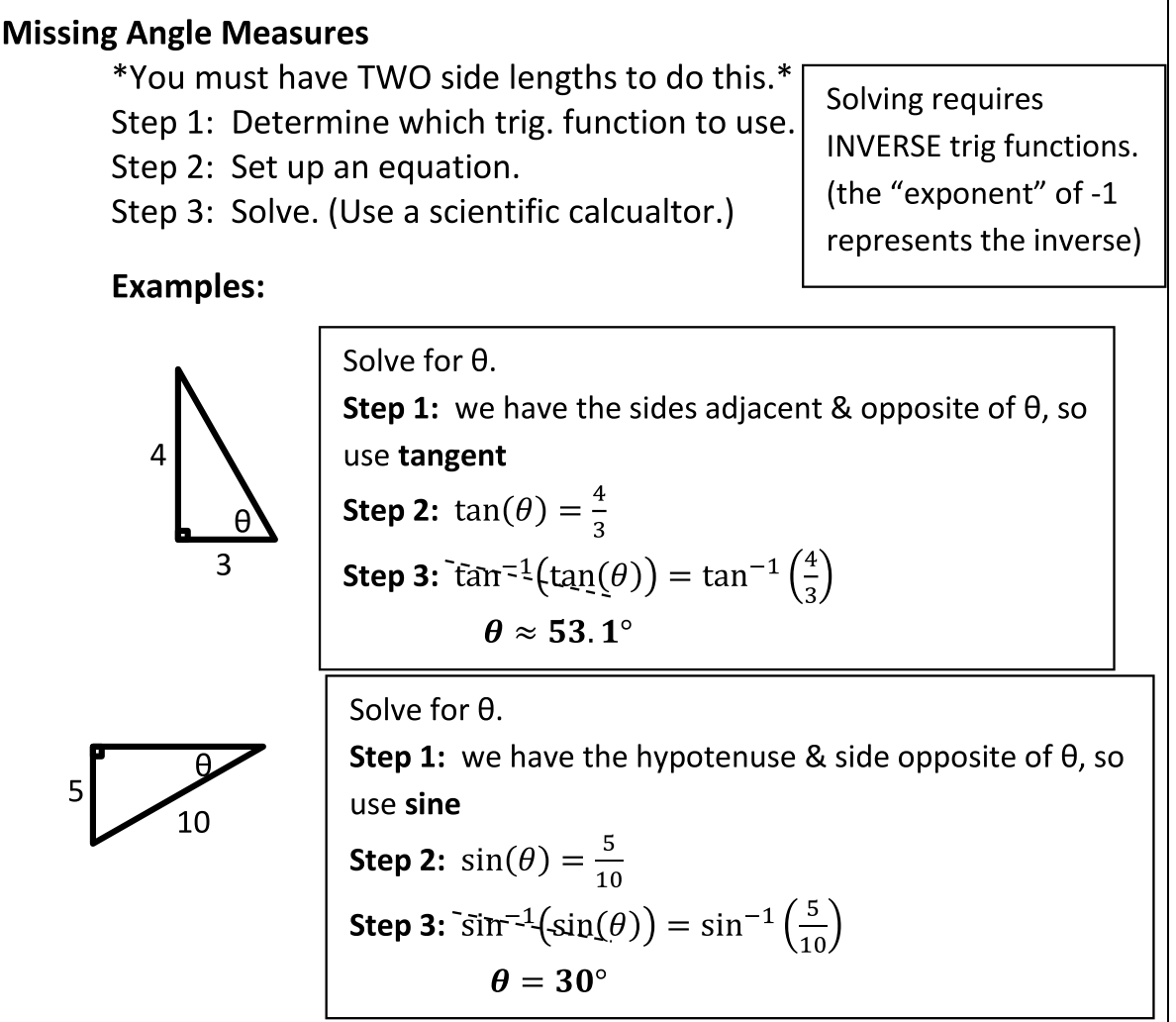
Missing Angle Measure
SOLVING REQUIRES INVERSE TRIG. FUNCTIONS (EXPONENT OF -1)
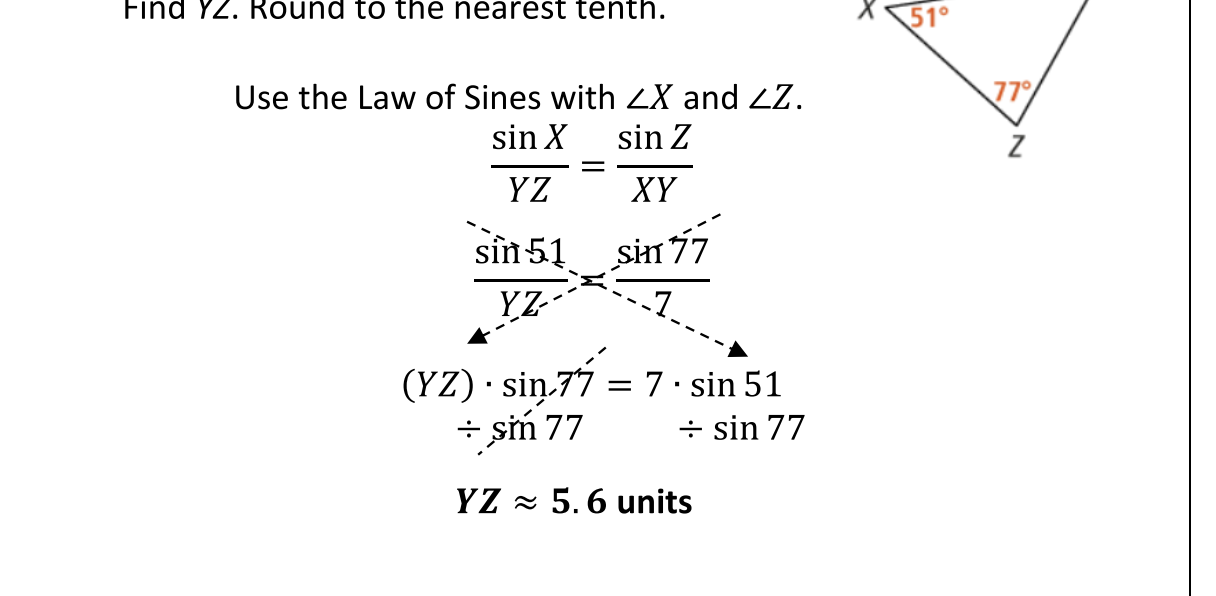
Section 8.3- The Law of Sines
Notes 8.3
sinA/a = sinB/b = sinC/c
Section 8.4- The Law of Cosines
Notes
c2 = a2 + b2 − 2ab cos(C)
to remember: Pythagorean formula but add -2ab cos(C).
It’s only supposed to be used when you have SSS or SAS TO FIND THE 3RD SIDE/ANGLE— TO BE ABLE TO USE LAW OF SINES.
To find a missing angle, you solve it geometrically, when you get to cos(s); you use arcsin to find the result.
Section 8.5- Problem-Solving with Trigonometry
Vocab
Angle of elevation
The angle is created by two rays, one parallel to the ground, and the second one above it, at the angle you're looking at.
Angle of depression
The angle created by two rays is the opposite of the angle of elevation.
use tangent for solving the problems most of the time
New area formula
1/2(b,c)sin(A)
Review
Important Formulas
Pythagorean fromula = a2 +b2 = c2
Triangle Type = if c2>a2+b2 then it’s acute. if c2<a2+b2 then its obtuse
454590 Triangle = x2+x2= c2 then the hypotenuse is x√2
306090 Triangle = (1)x, √3(x), 2(x)
sin(θ)=opposite/hypotenuse, cos(θ) =adjacent -hypotenuse, tan(θ) = opposite/adjacent
Area formula: 1/2(b,c)sin(A)
Law of Sines: this second
Law of Cosines- this first
a2 + b2 − 2ab cos(C) = c2