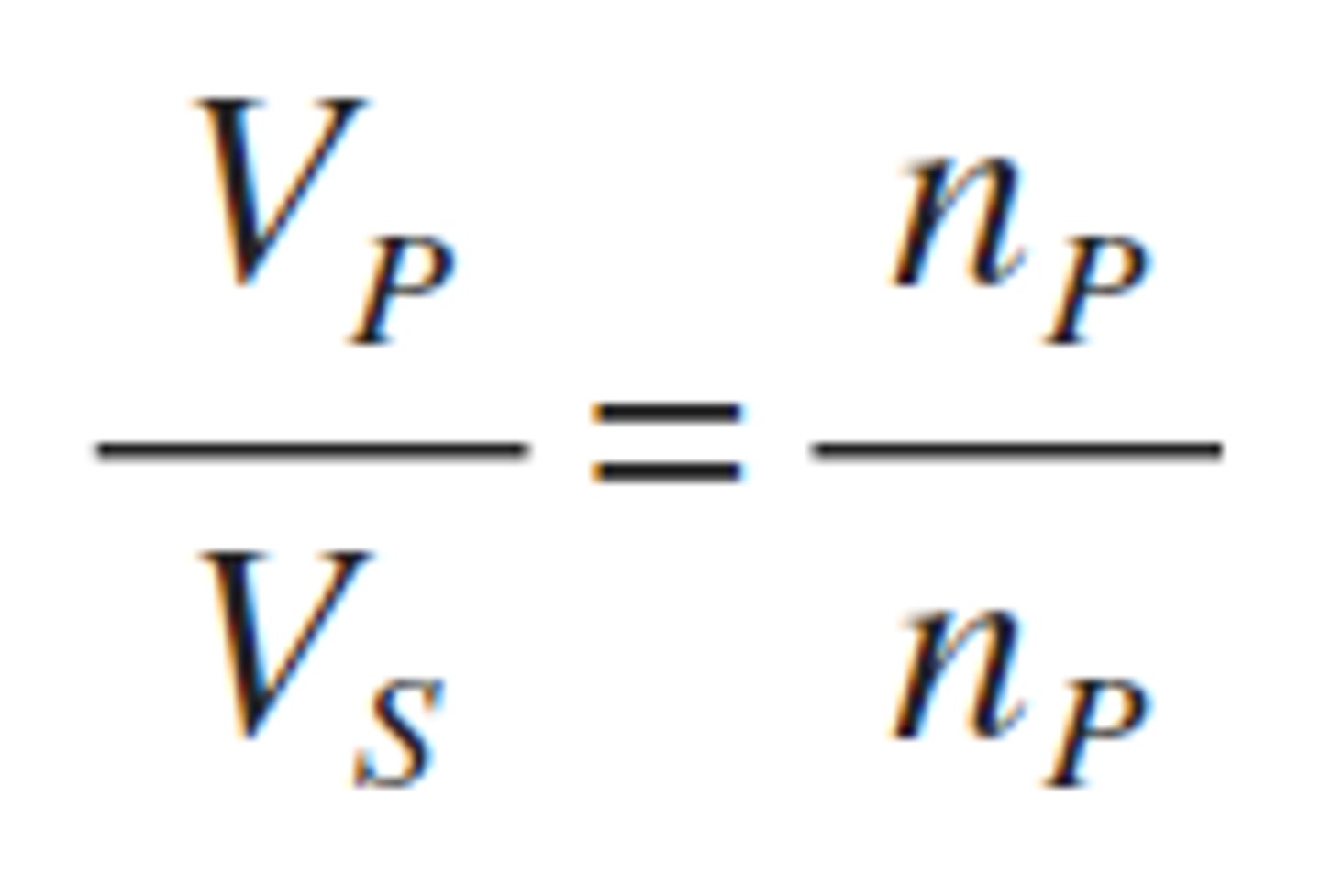QCAA Physics unit 3 and 4
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
234 Terms
What is a vector?
Something with magnitude and direction
What is a scalar quantity?
A quantity that has only magnitude and no direction
True or False: Vectors can be resolved into horizontal and vertical components.
True
True or False: Horizonal and vertical components of velocity are dependent on each other
False. Horizonal and vertical components of velocity are INDEPENDENT of each other
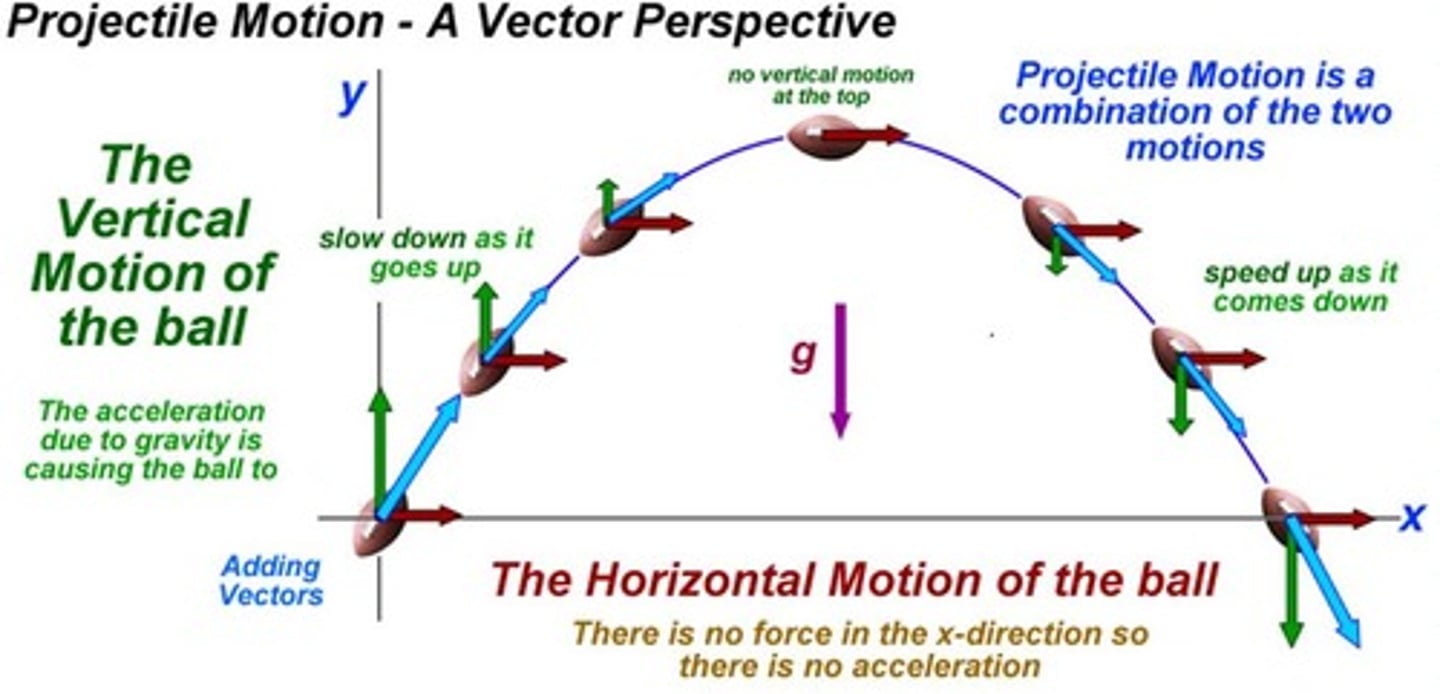
what sort of path does an object experiencing projectile motion follow?
Parabolic
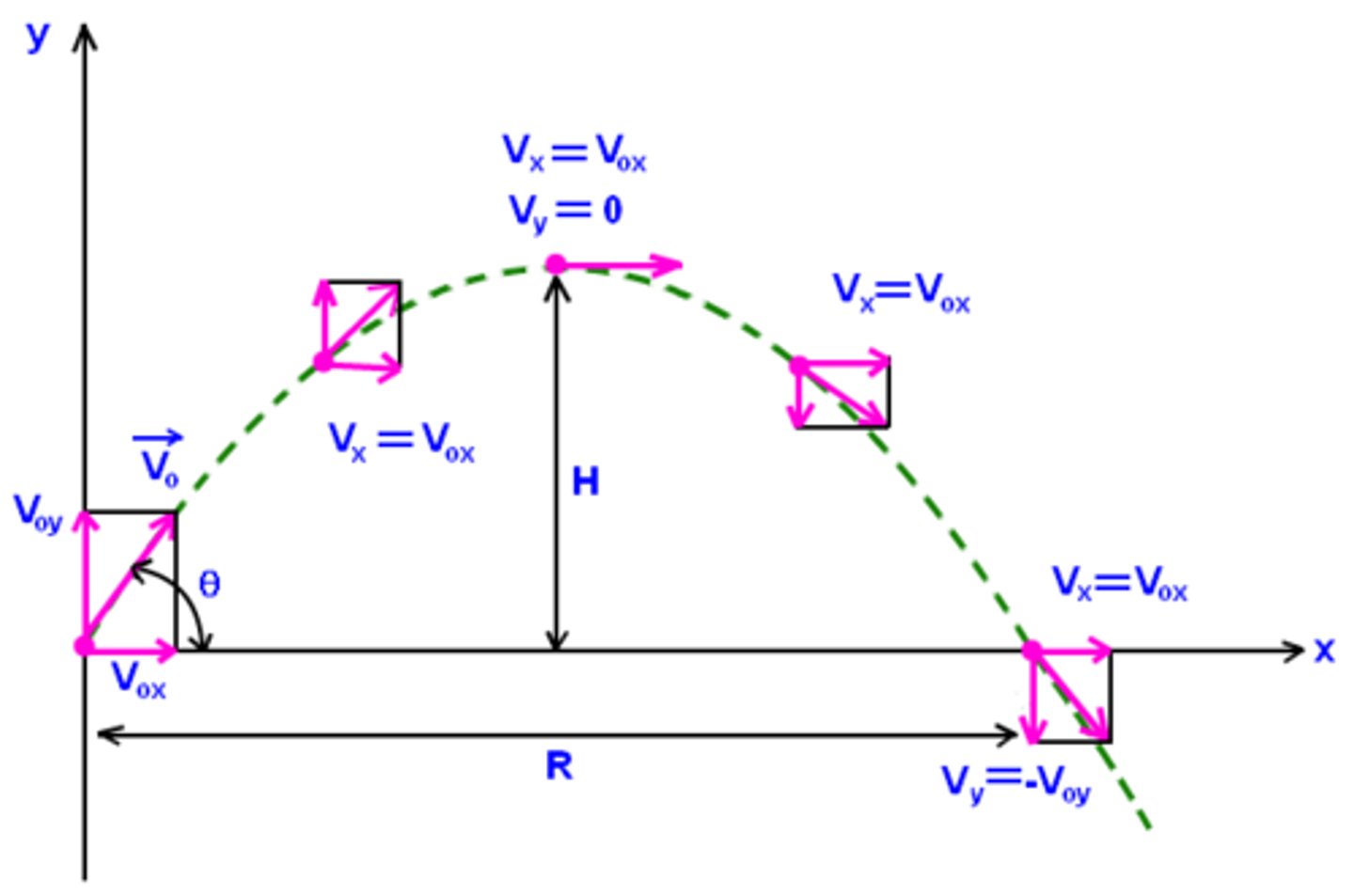
Why does vertical velocity = 0 at the max of its path?
At max the gravity starts to pull the object down. on the way up the speed is slowing down however on the way down the object is speeding up because of Gravity.
What force impacts projectile motion?
Gravity. It is the only acceleration experienced by an object in projectile motion
When is the Vertical displacement= 0 in projectile motion?
When an object completes a parabolic path. However, if there is a 1/2 parabolic path there will be a vertical displacement.
True or False: Time is always the same in both horizontal and vertical directions.
True. time is independent of all variables it carries on as usual
Will there be a displacement in x when the angle is 90*?
No. there is no displacement as 90* is straight up and down
What is the value of ay?
ay= -9.8m/s^2 as gravity always acts vertically downwards.
calculate Ux of a projectile with an initial velocity of 38m/s at an angle of 42*. Round your answer to the nearest whole integer.
Ux=(38)(Cos(42*)
=28.23m/s
= 28m/s (rounded)
Calculate the max height reached by a projectile with an initial velocity of 15m/s at an angle of 30 degrees. Answer to the nearest 2 decimal places.
max height = 2.87m
how to calculate Fnet on an inclined plane?
Fnet= ma
Draw a generic free body diagram of an object on an inclined plane.
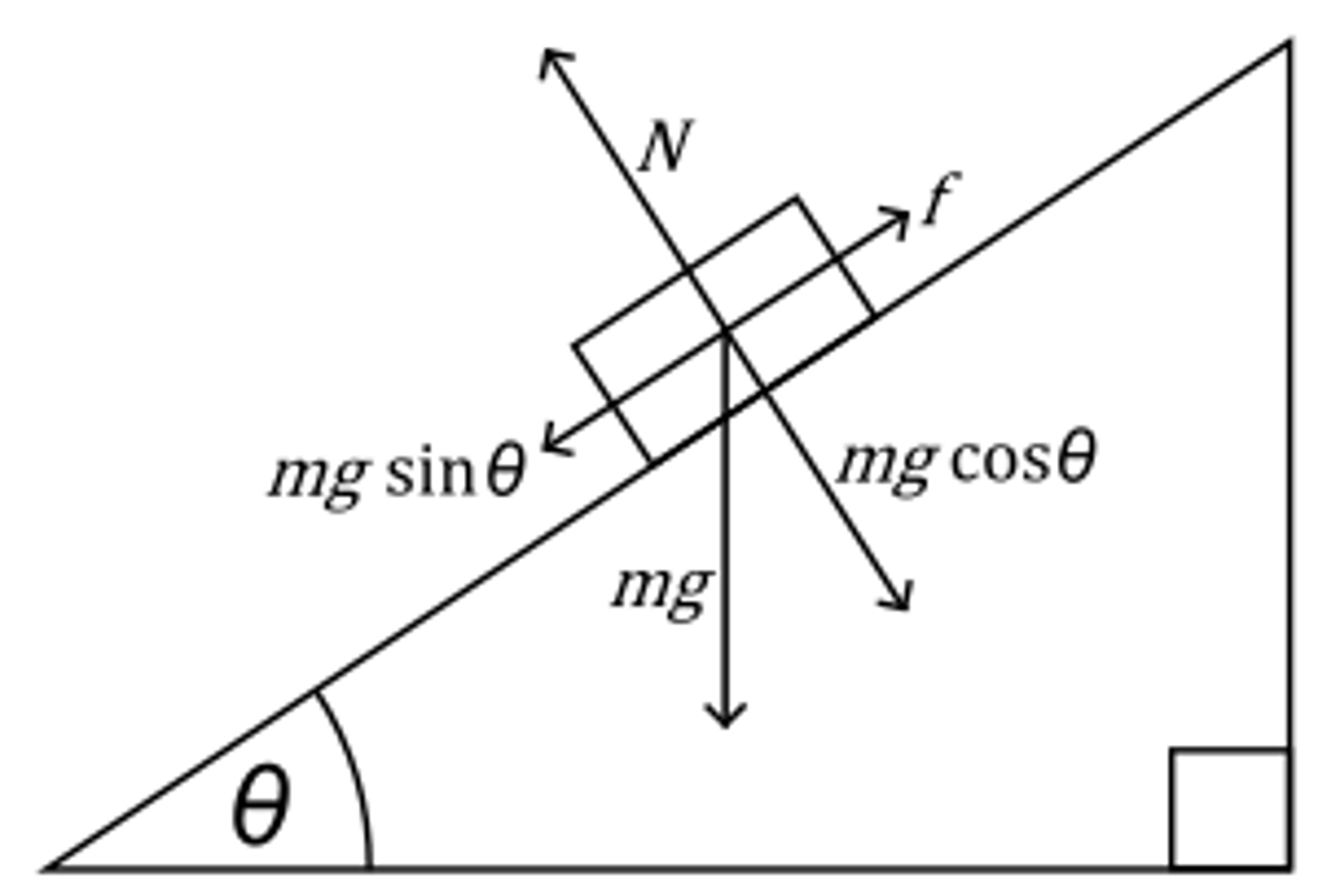
Calculate the acceleration of a 10kg object down a plane inclined at 30 degrees.
a=(g)(Sin(angle))
a= (9.8)(Sin(30))
a-4.9m/s^2
Define Uniform circular motion
an object moving in a circular path at a constant speed-NOT velocity
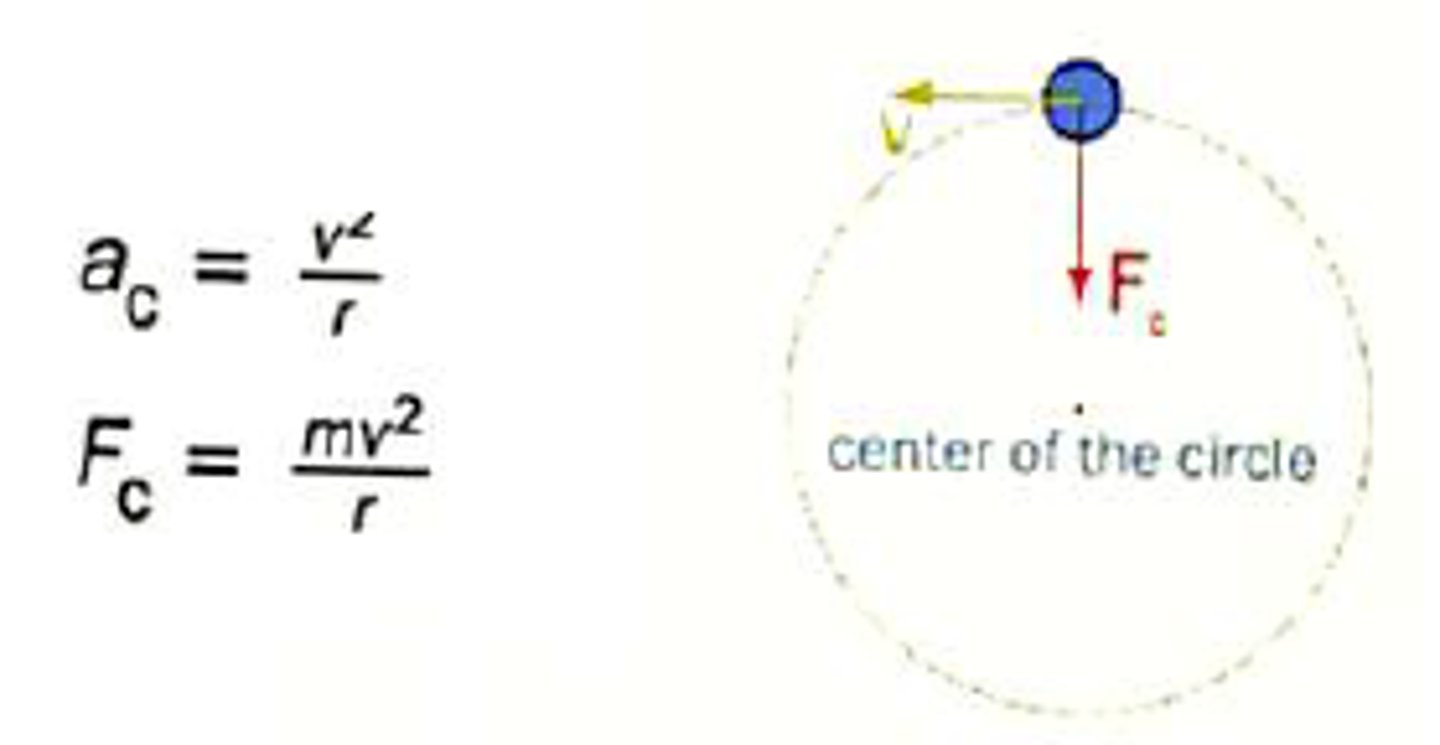
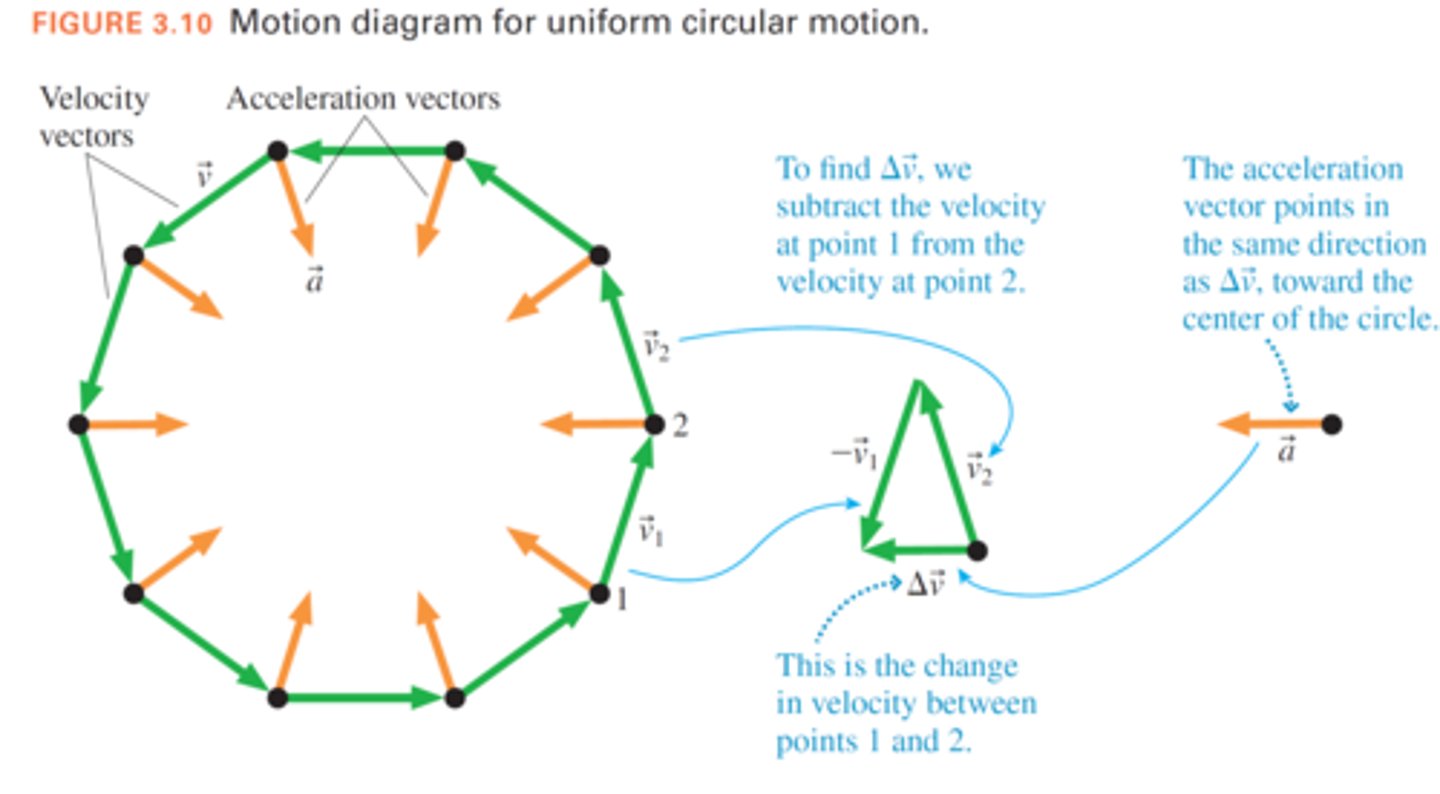
True or False: Velocity is always perpendicular to the acceleration in the direction of motion.
True.
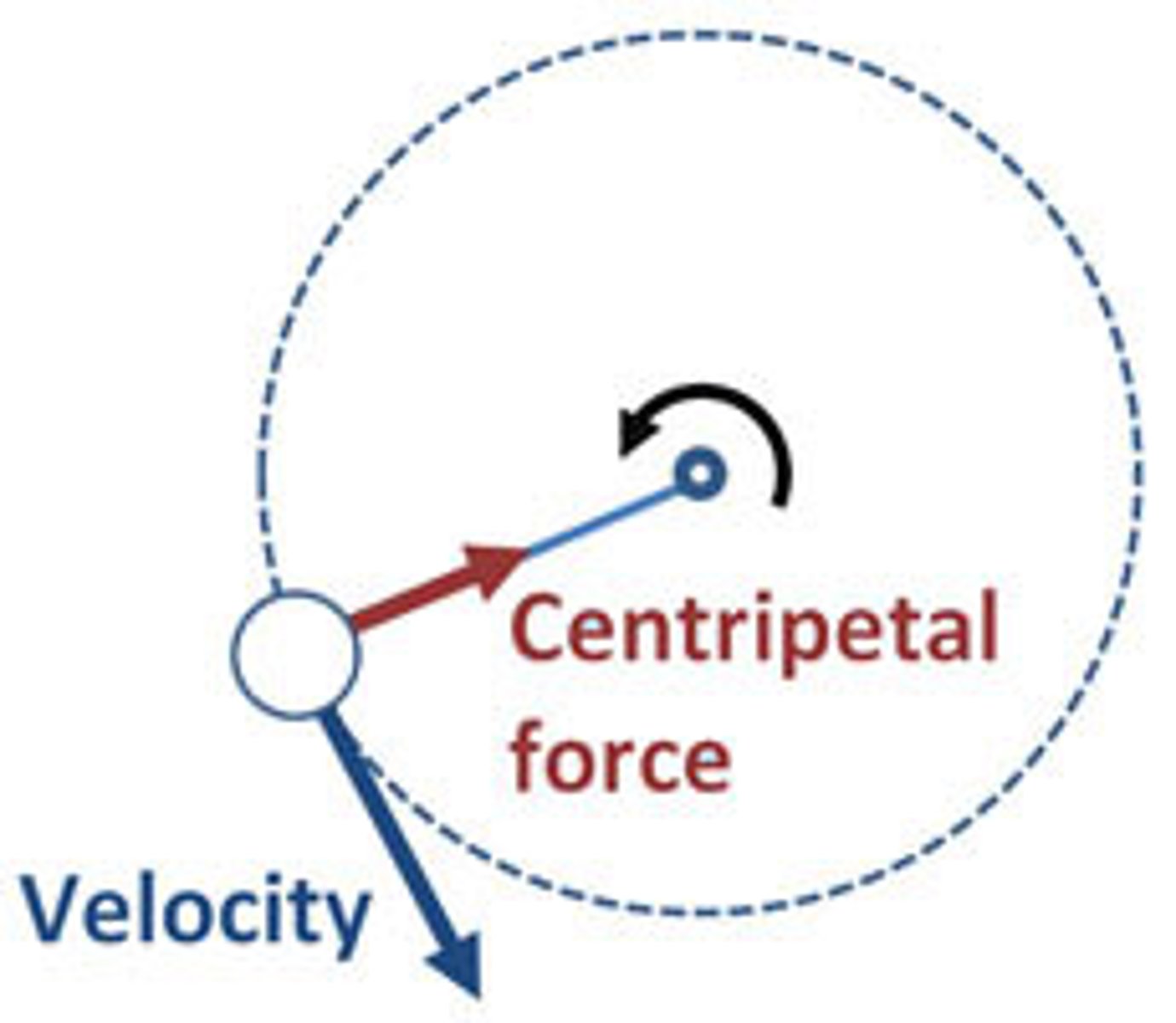
Define Centripetal force
a force that pushes or pulls a object inward follow a curved path. Will always be pointed to the center at right angles to velocity. continuously changes the direction of an object to make it move in a circle
Define period and average speed in circular motion.
period (T)= time for 1 revolution to take place, measured in seconds.
Average speed= distance/time, in circular motion distance = circumference.
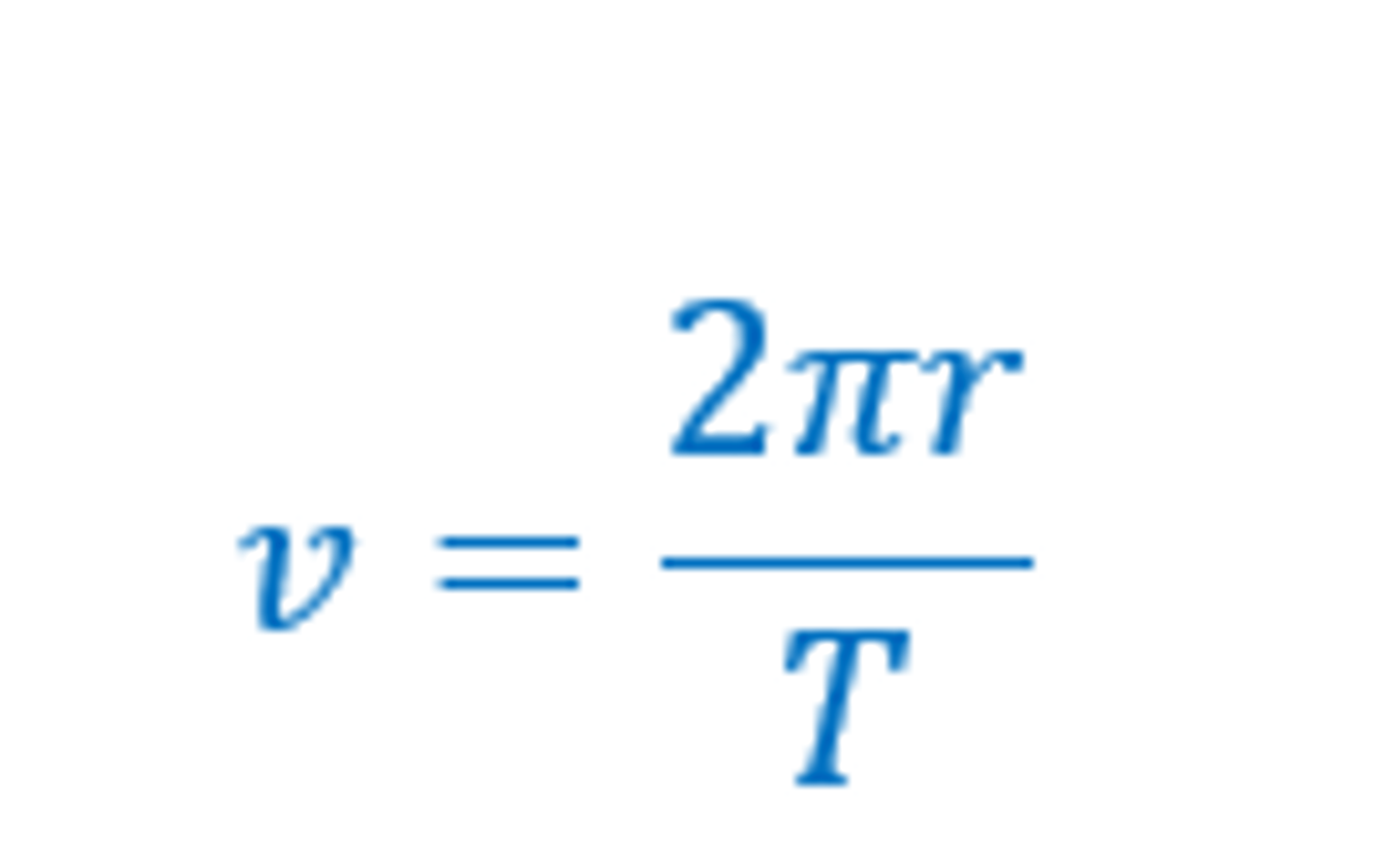
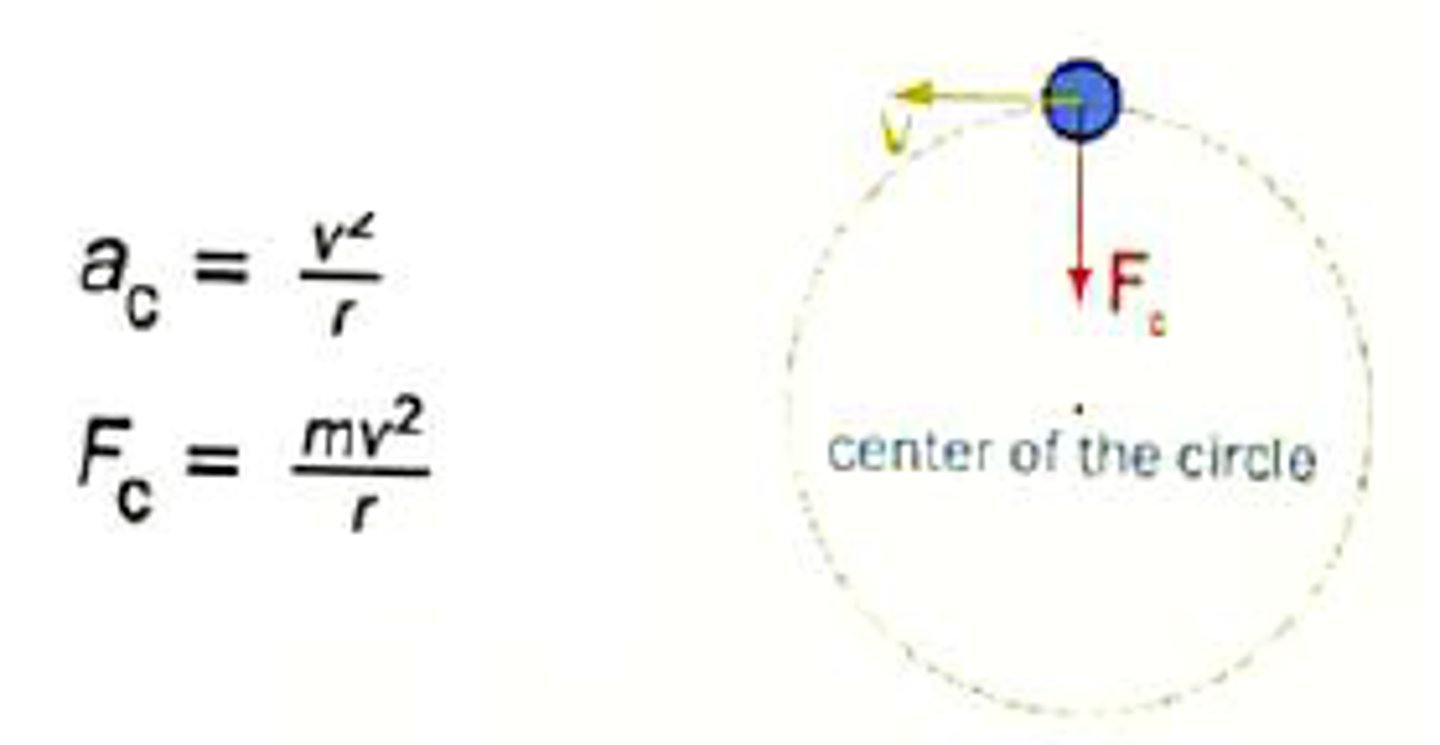
differentiate in centripetal acceleration and force
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration an object experiences when moving in a circular path, always directed toward the center of the circle, and it changes the direction of the object's velocity. Centripetal force is the net force required to maintain this circular motion, also directed toward the center. Essentially, centripetal force causes centripetal acceleration, keeping the object moving in a curved path.
Recall Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
states that the force of attraction between each pair of point particles is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
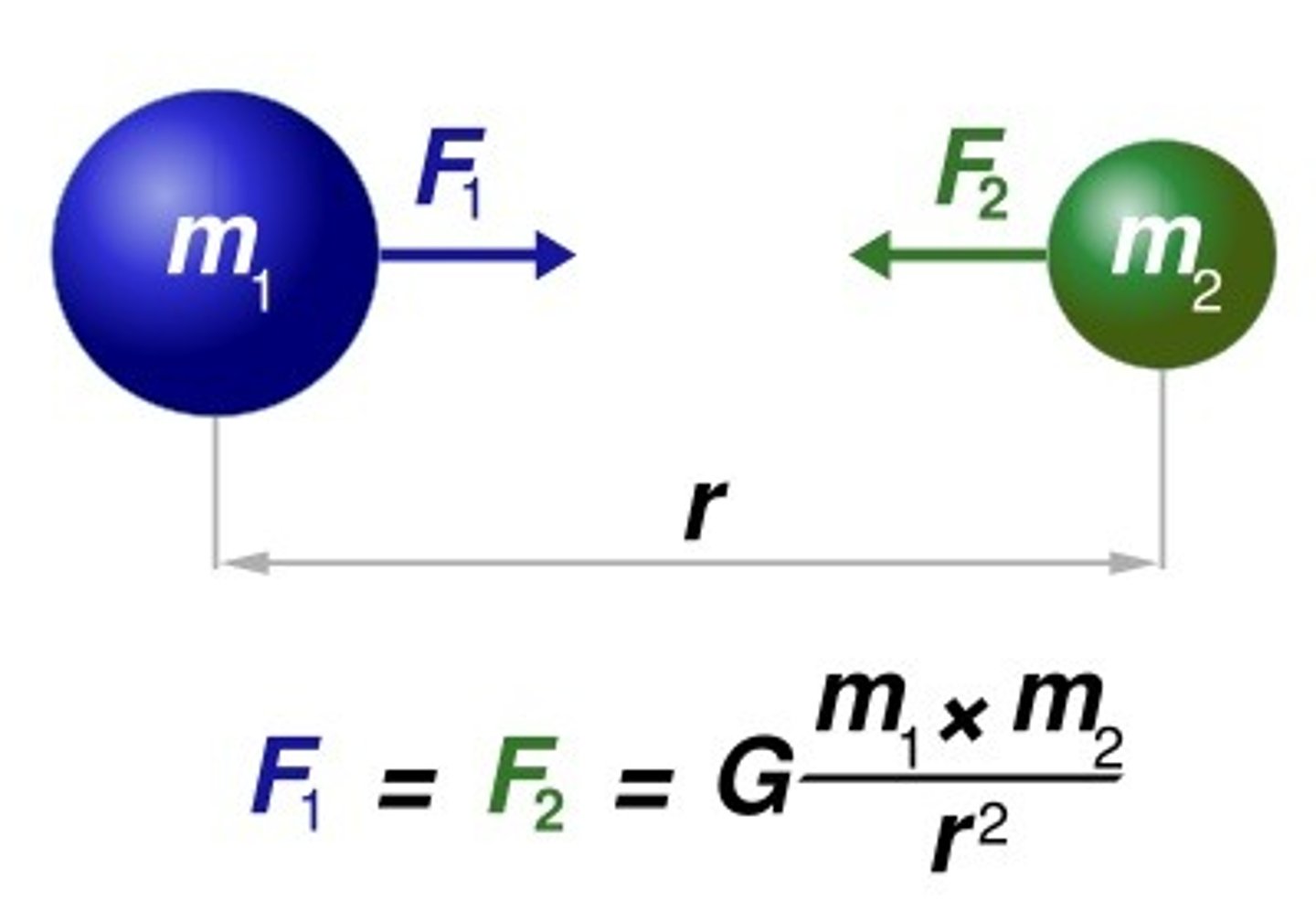
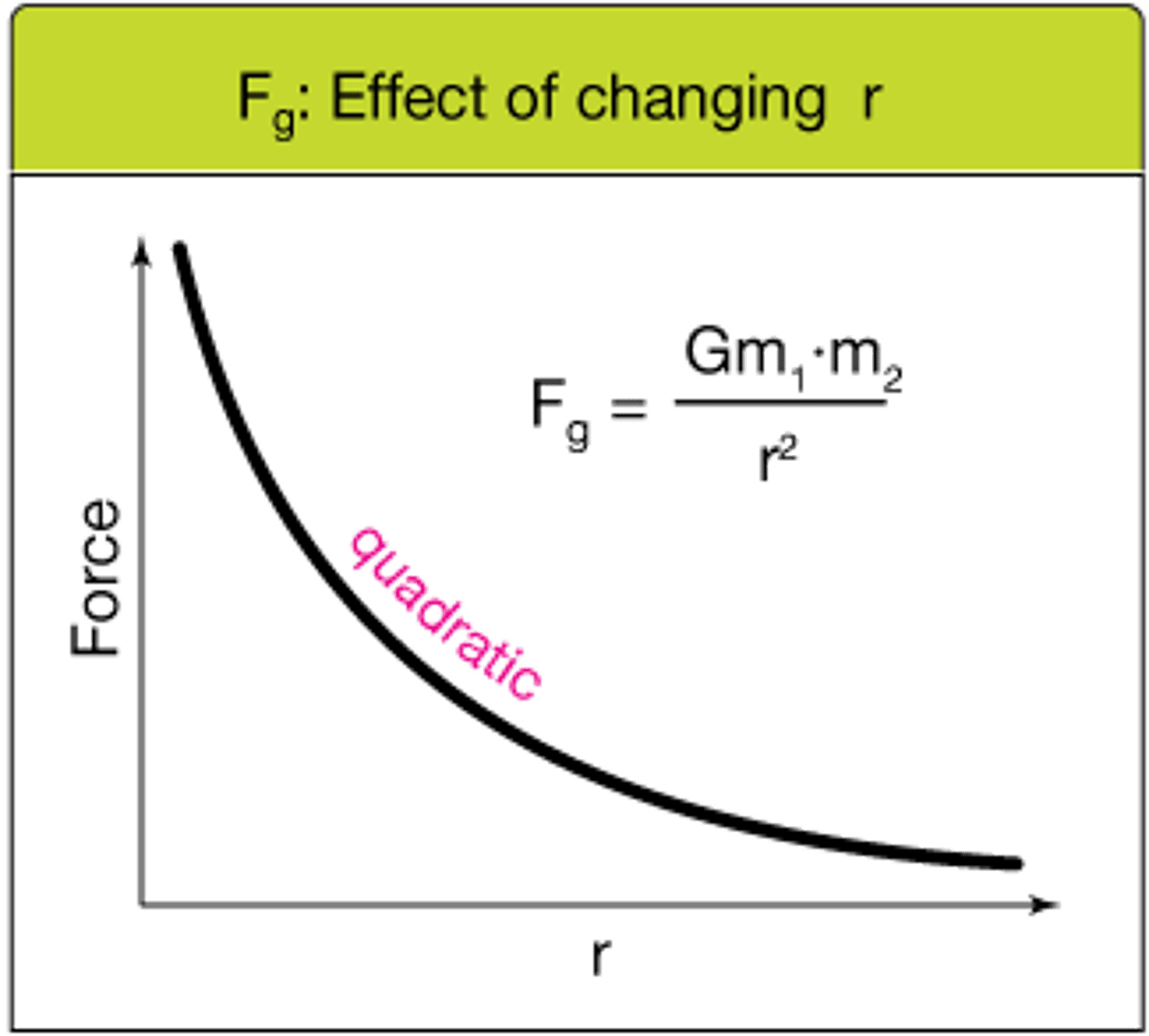
Draw the relationship between Fg and r
Draw the relationship between Fg and 1/r^2
Where y is Fg and X= 1/r^2
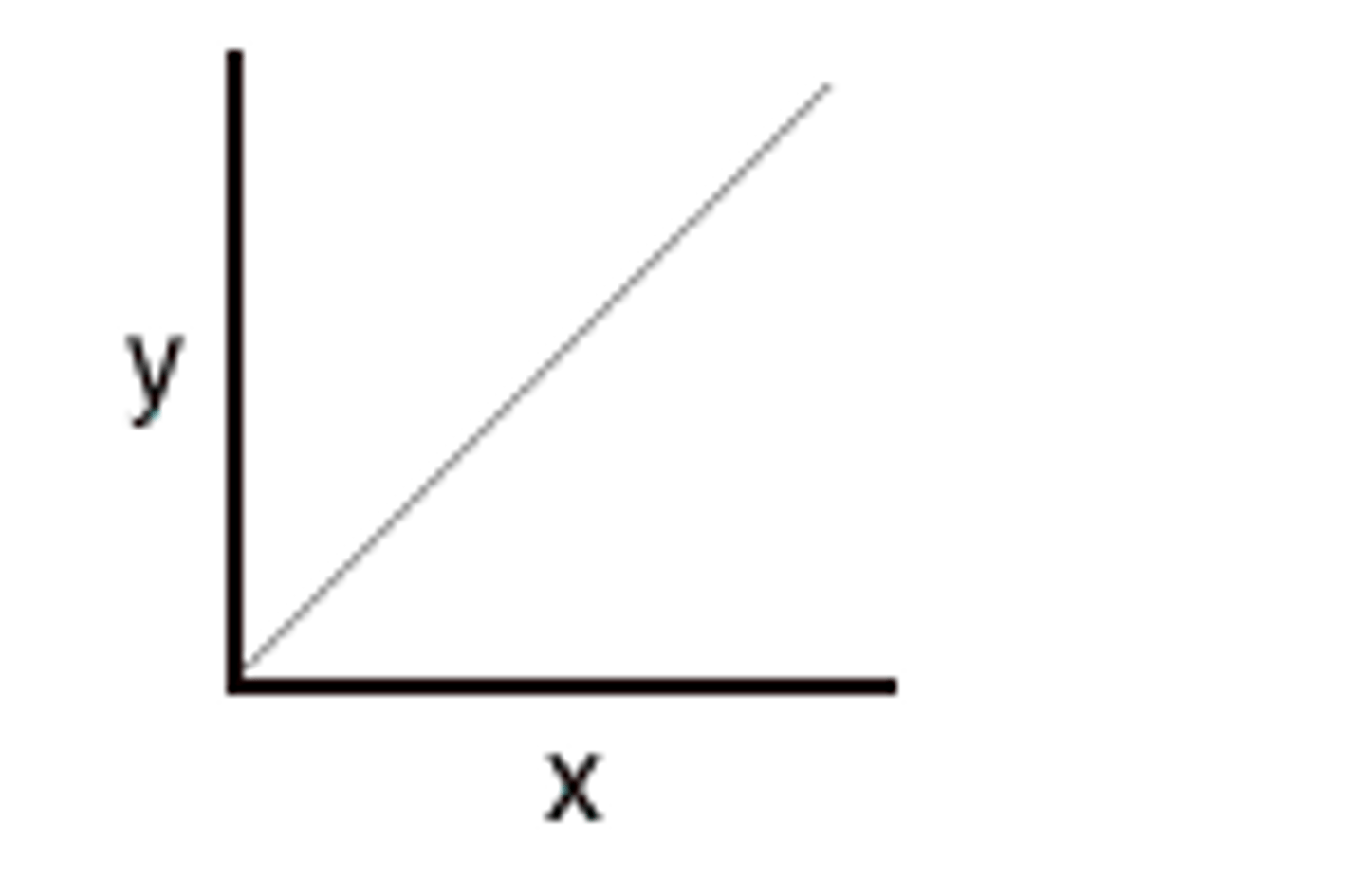
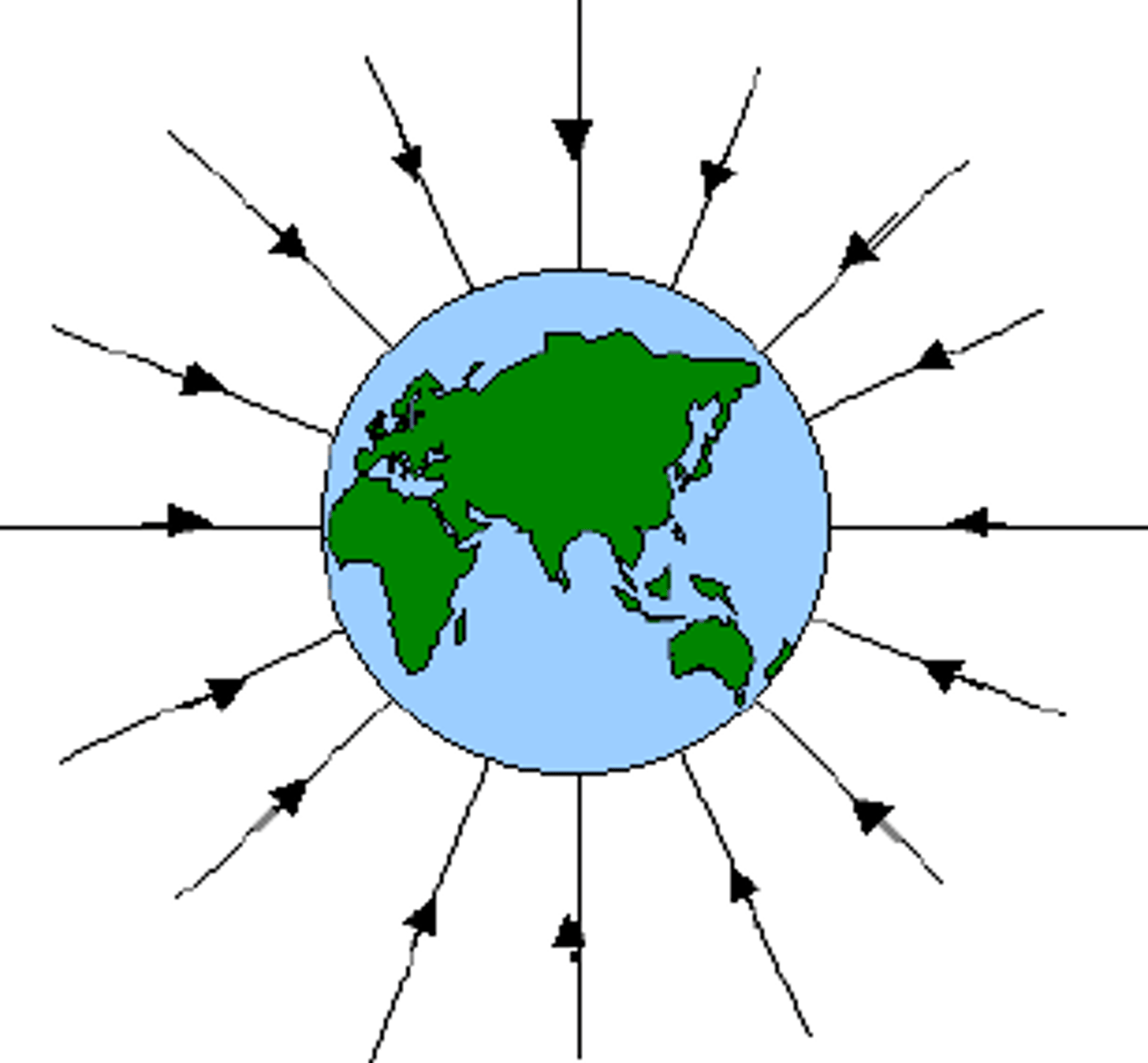
Define a gravitational field
the region of space surrounding a body in which another body experiences a force of gravitational attraction.
g=GM/r^2

Write some conventions for drawing a gravitational field
diagram
-equally spaced arrows indicate the relative magnitude of the fields and constant/uniform field strength.
-the direction of arrows show the direction of the gravitational field
-Gravitational field lines NEVER cross
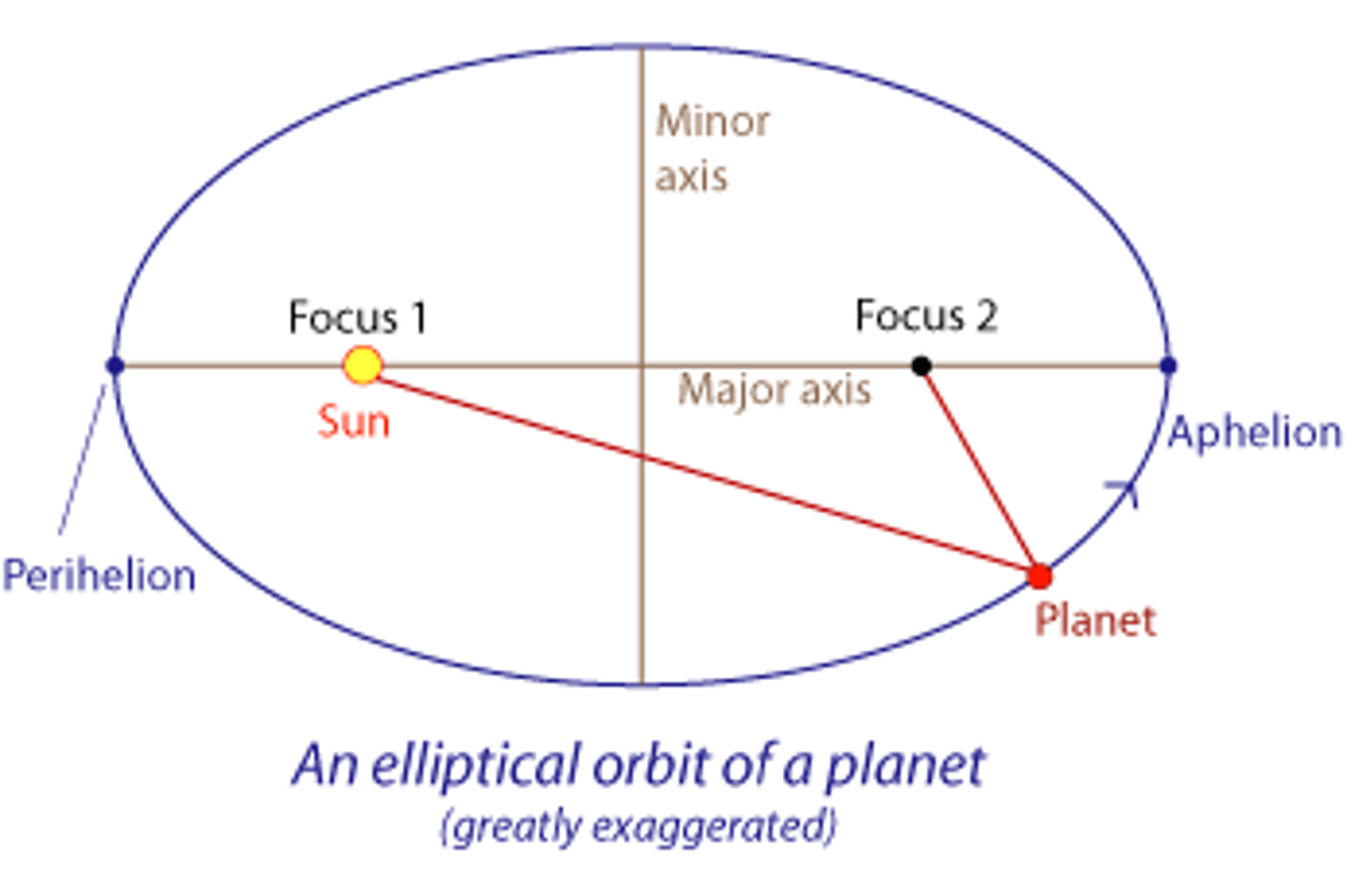
recall Kepler's first law of planetary motion
1: Law of ellipses
The orbits of planets are ellipses, with the Sun at one focus
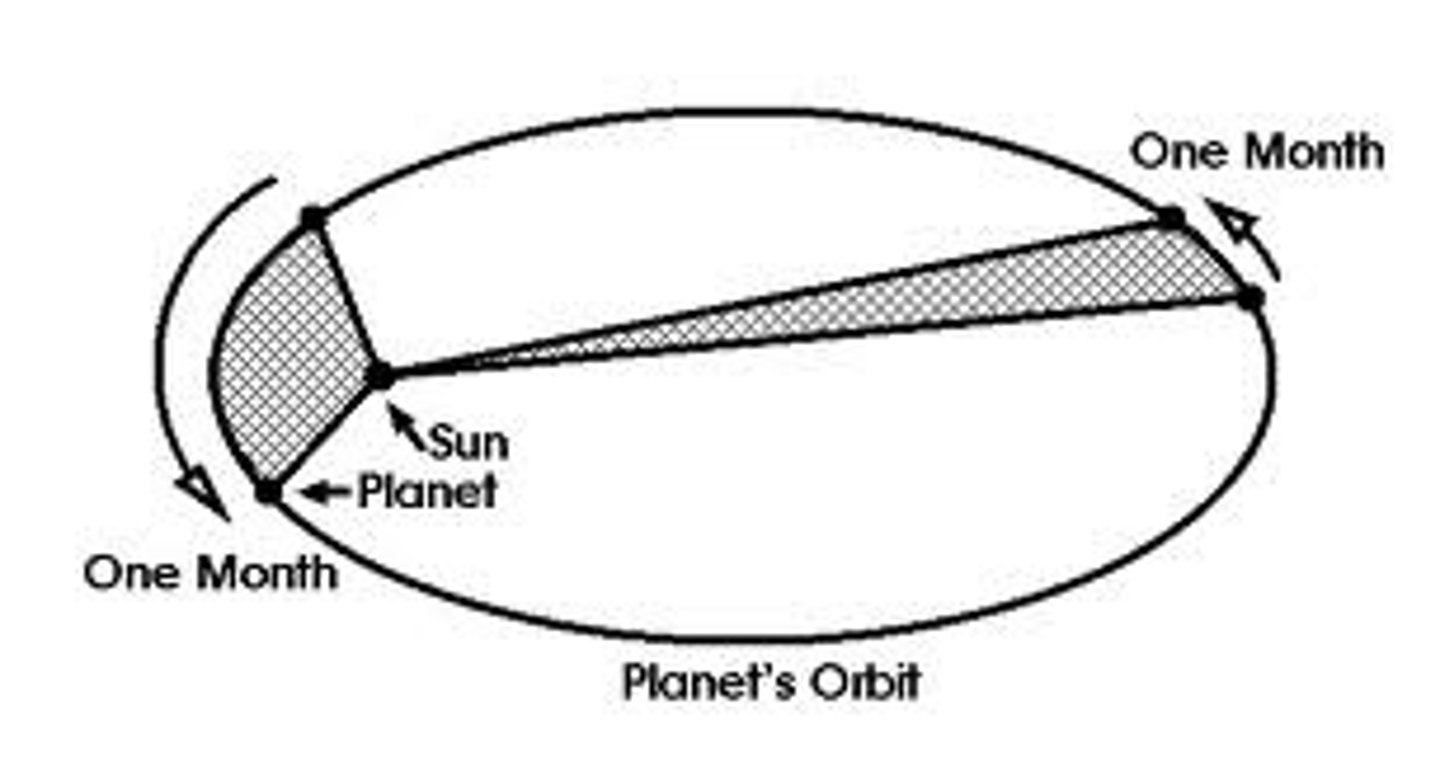
recall Kepler's second law of Planetary motion
2: Law of equal areas
A line drawn from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time, as the planet moves in its orbit.
(planet must move faster when closer to sun and slowly when further from the sun)
recall Kepler's 3rd law of Planetary motion
the square of the periods is directly proportional to the cube of their distance from the sun. Mathematically T^2 is proportional to r^3. Therefore:
T^2 = r^3
Hence:
T^2/r^3= k (Kepler's constant)
Kepler's constant can be found using Fg=Fc and rearrange the equations such that
T^2/r^3= 4pi^2/GM
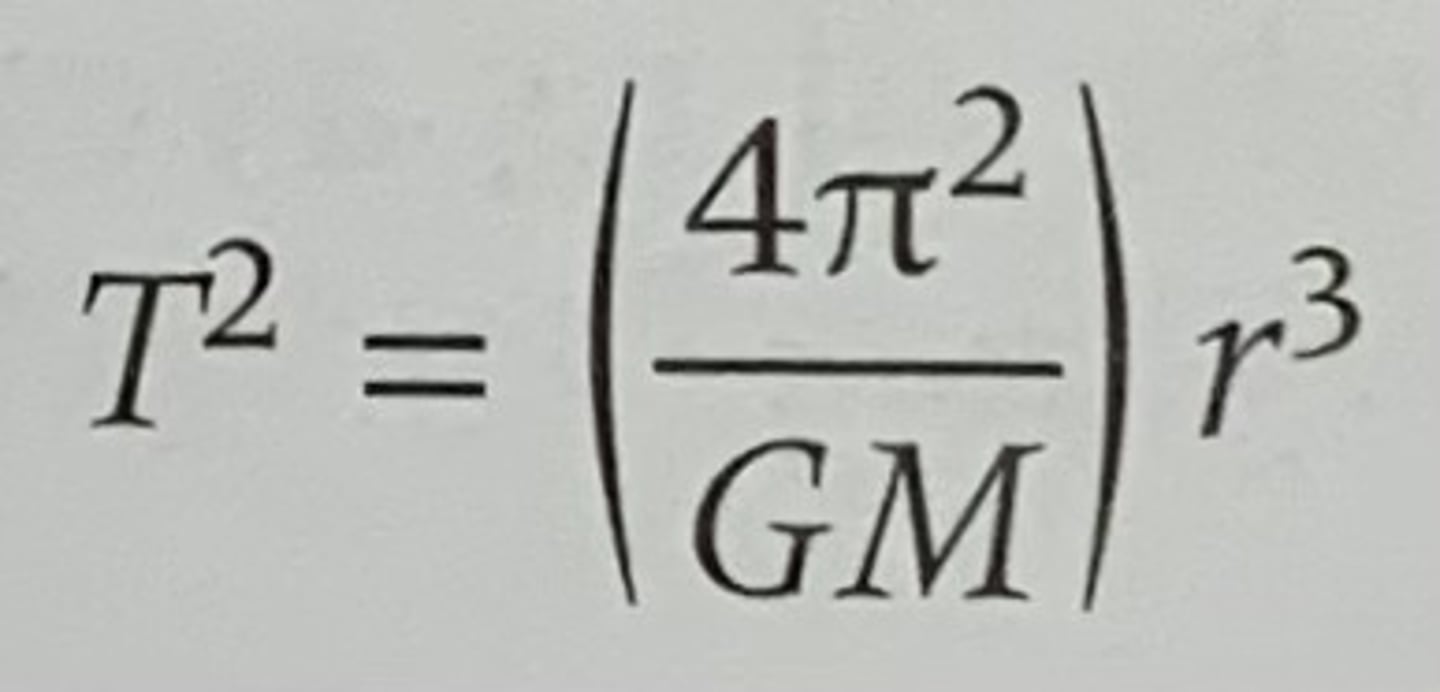
Explain how Fg=Fc works
Gravitational force equals centripetal force when an object is in a stable circular orbit. In this situation, the gravitational pull acts as the centripetal force needed to keep the object moving in its circular path, balancing the forces to maintain the orbit.
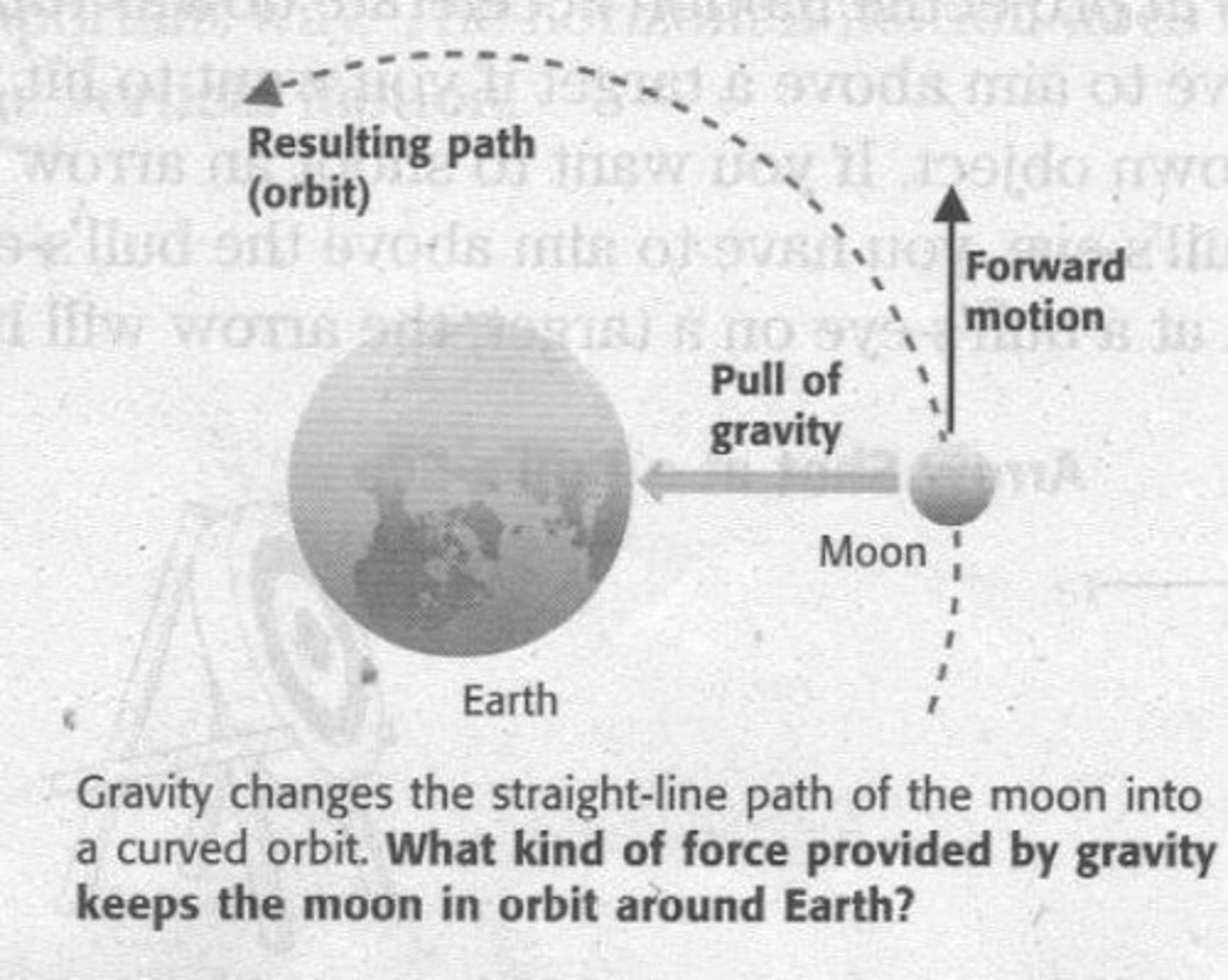
Define Coulomb's law
Coulombs law states that the force between two charged particles, q1 and q2 is inversely proportional to the square of the distances between them.
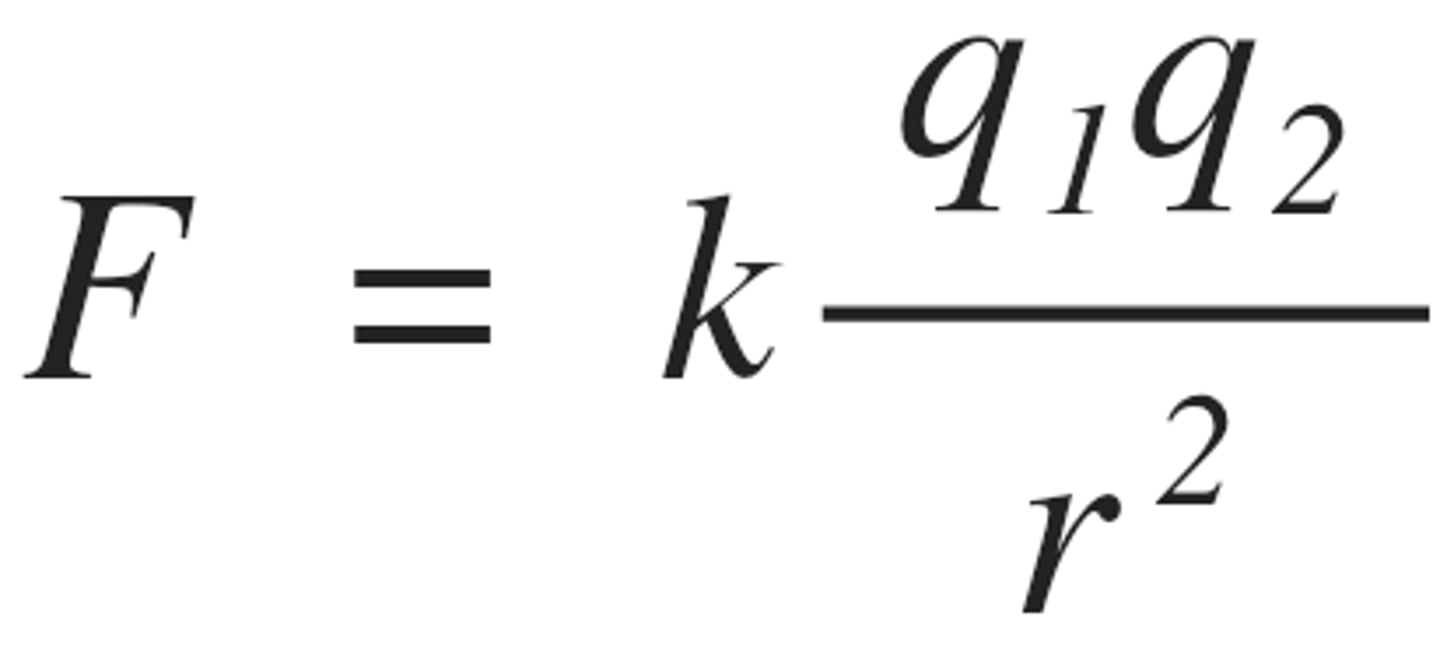
True or False: Increased charge increased force experienced when the distance remains the same
True as force is stronger when the numerator (kQq) is greater than the distance or when the distance is constant.
Do like charges repel or attract?
repel
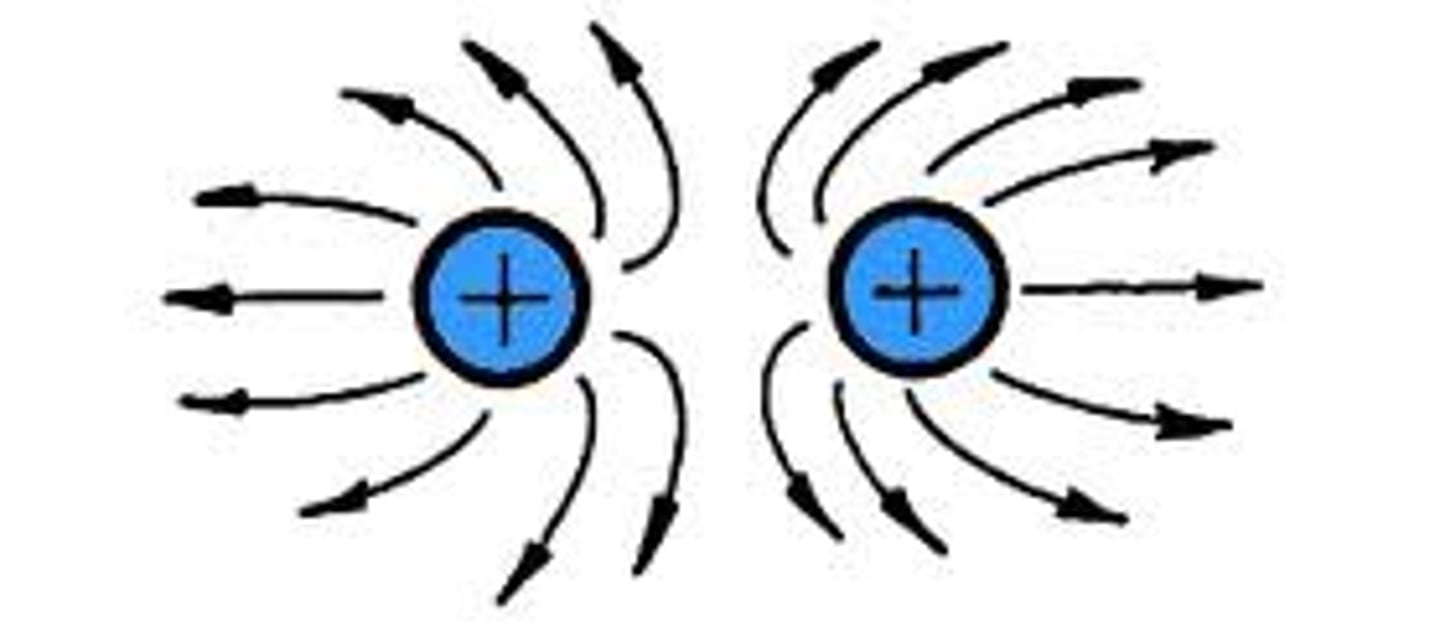
What is an electric field?
a region around a charged particle or object within which a force would be exerted on other charged particles or objects. This force maybe attractive or repulsive.
Define electric field strength
The intensity of an electric field at a particular point in the field. It is the measure of the of force acting on a- unit of charge. (N/C)
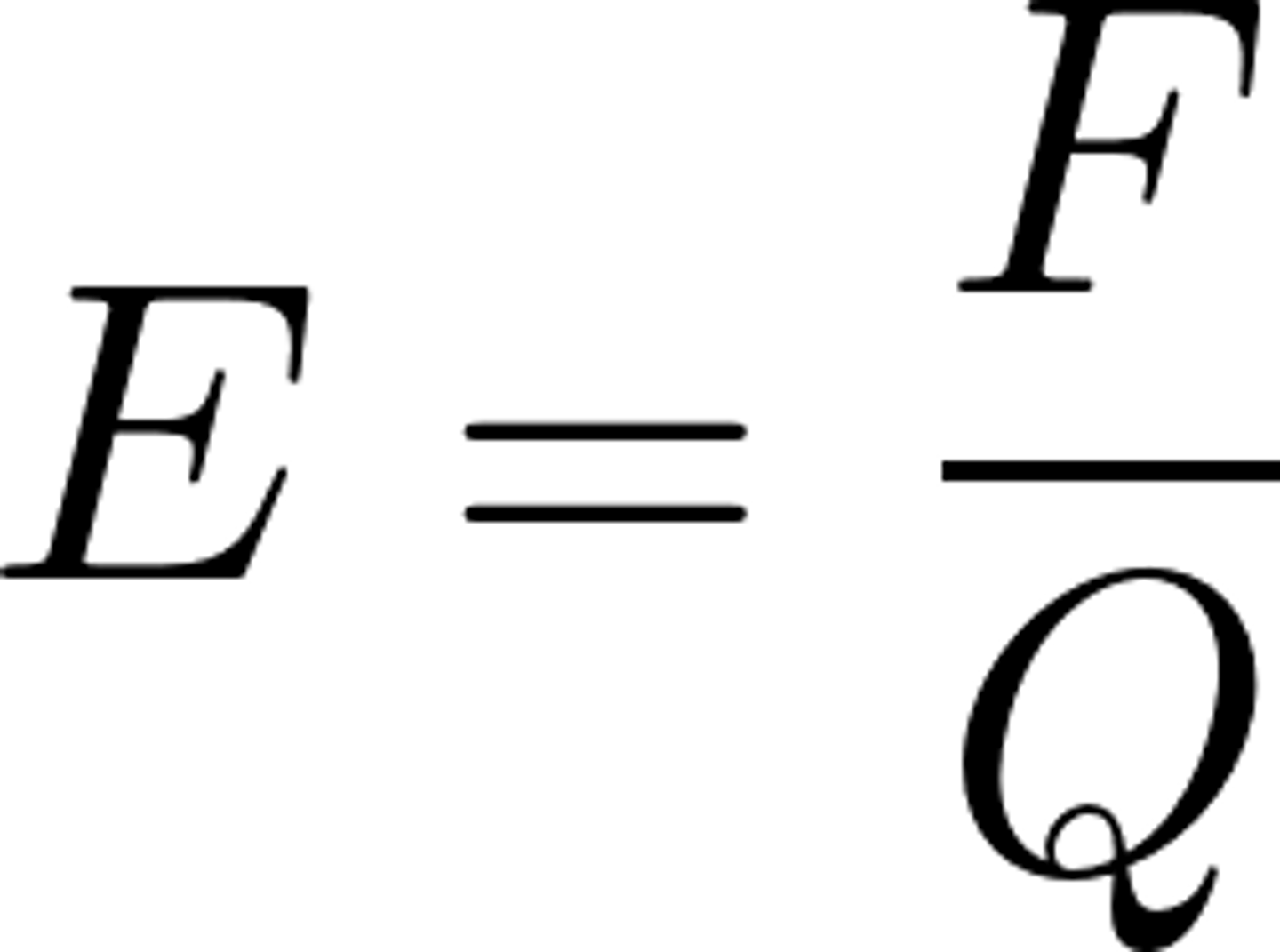
What is an alpha particle?
2 protons and 2 neutrons
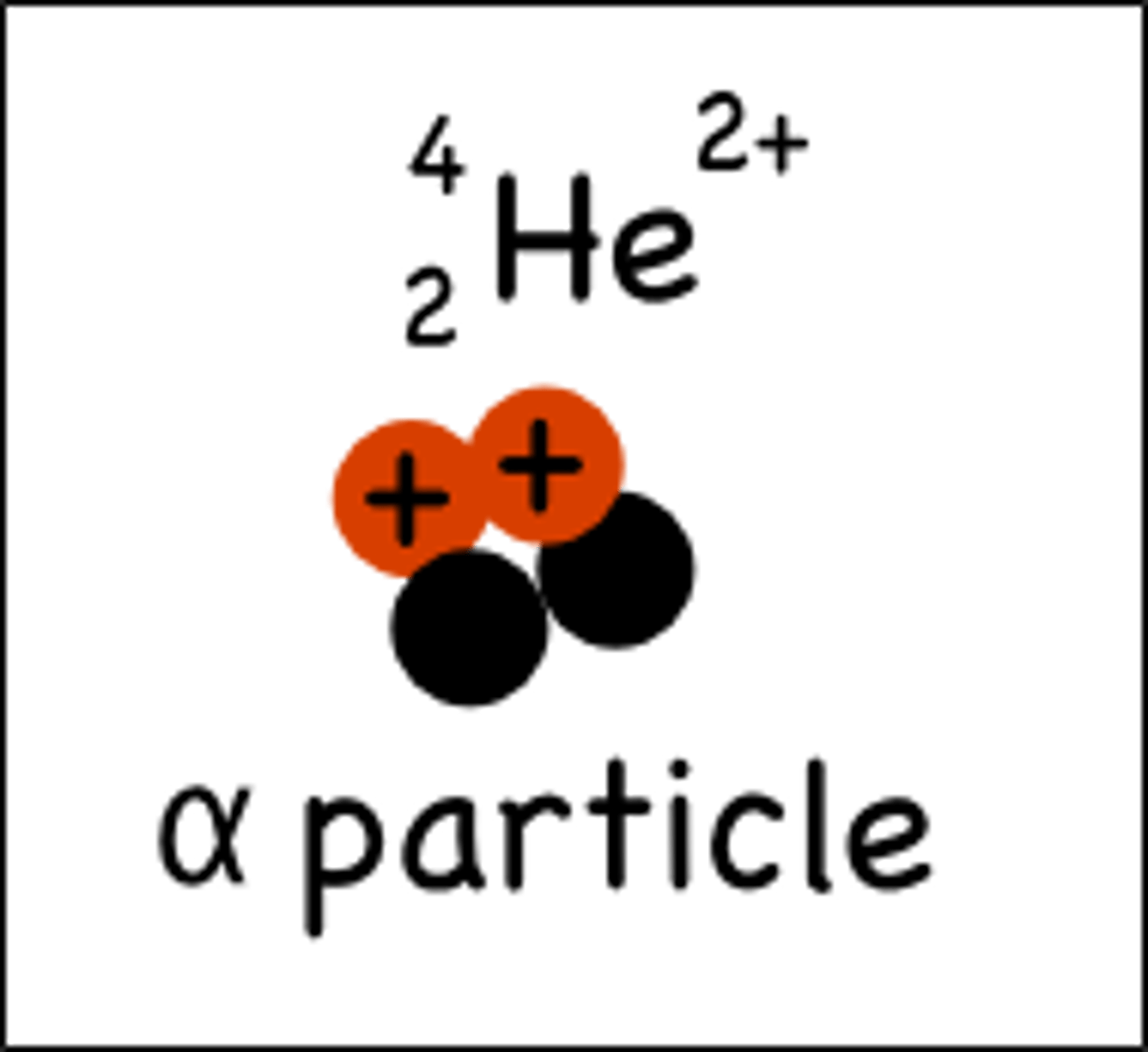
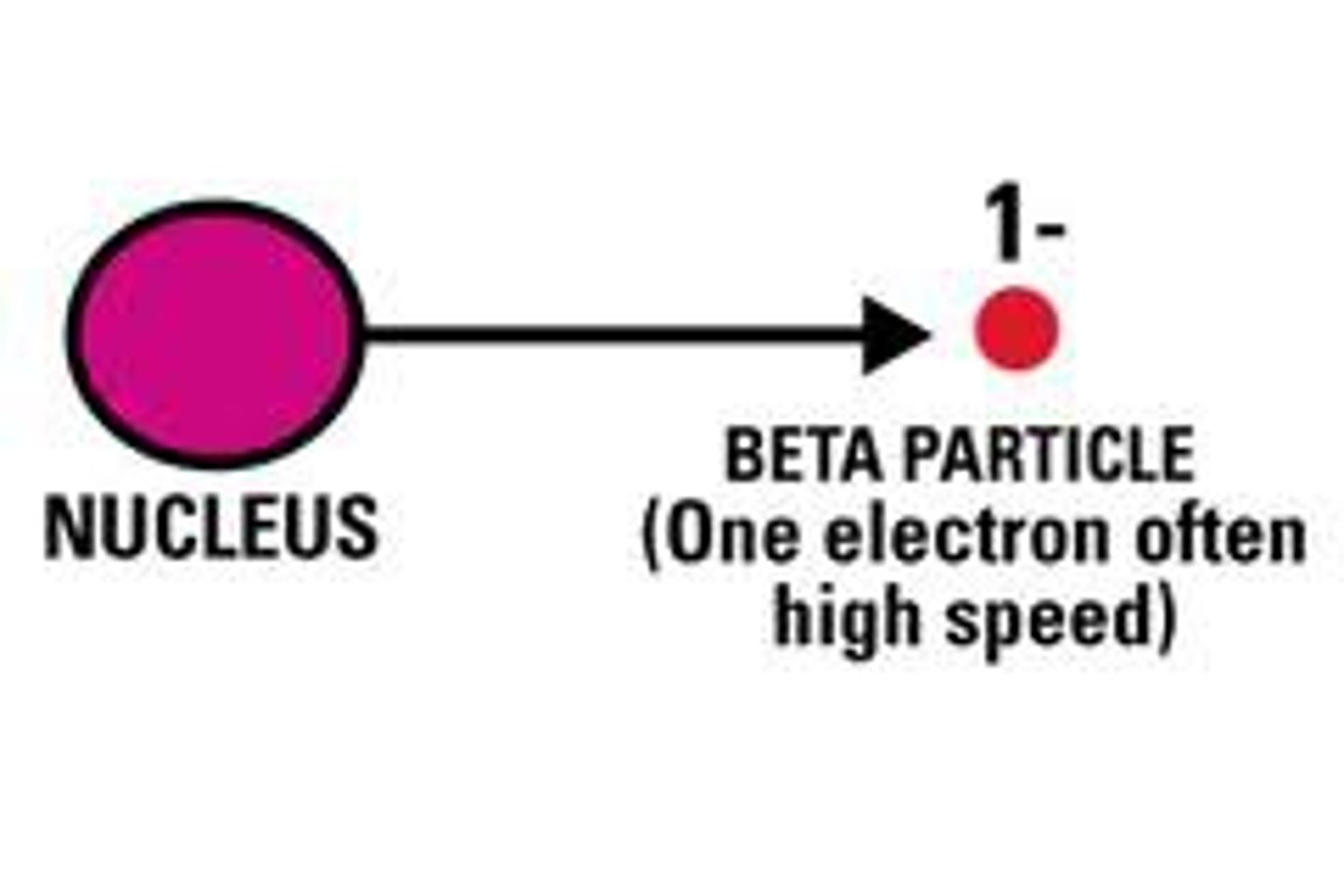
What is a beta particle?
high speed electron
what is an electrostatic charge?
An electrically charged object that is moving (static)
what is the unit of charge?
Coulombs, C
what is the charge of an alpha particle?
2 times the charge of an electron but positive
How do electrostatic fields interact?
opposite charges attract and like charges repel
what is a constant electric field?
An electric field with constant field strength, found between 2 oppositely charged parallel plates.
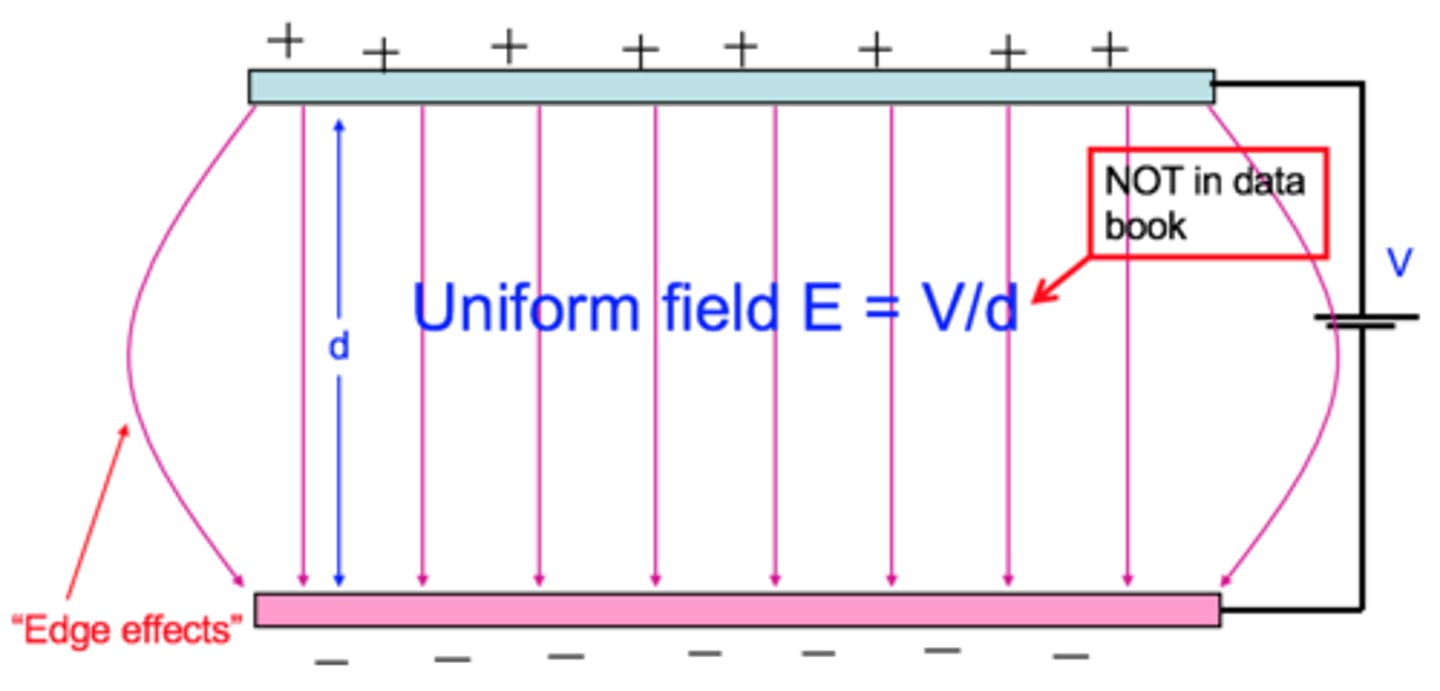
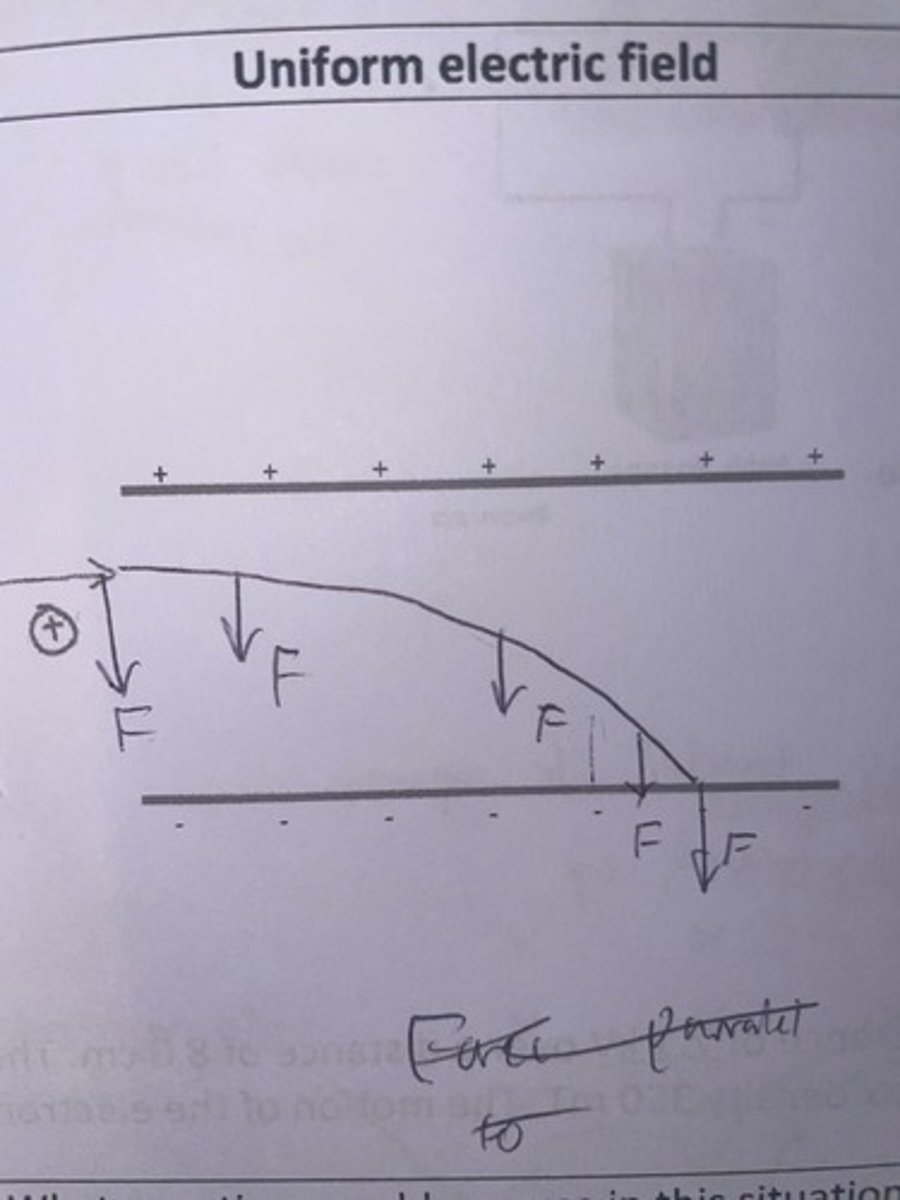
Explain what would happen to a positive charge starting at the positive plate in a uniform electric field (2 parallel plates) in terms of its force and its potential energy.
The positive charge starting at the positive plate would be repelled by that plate pushing it towards the negative plate, as the charge moves further away the repulsion force gets weaker but the attraction force from the negative plate gets stronger. This means that the net force acting in the scenario always stays the same, hence force on the particle is constant at any point in the whole field. Considering the equation E= F/Q, this means that force and charge are always constant is a uniform electric field. Energy on the other hand is always conserved however it does change. As the positively charged particle is repelled it's potential energy is converted into Kinetic energy it gains as it moves towards the negative plate. As potential energy (PE) is converted into KE, PE is not constant. Hence the equation E= V/d, where V is the potential energy of the electric field measured in volts. Therefore as the positively charged particle moves from a location of High potential energy, the energy is converted into kinetic energy.
what equation would you use to determine the Electric field strength of an uniform field if it has an Electrical potential of 12V and the distance between the plates is 3m. Solve for the electric field strength.
E=V/d
therefore, E= 12/3
4 NC^-1

Formulate an expression for work give that E= F/Q and E= V/d.
If E= F/Q and E= V/d
then: F/Q = V/d
we know that work = Fd
if we rearrange we get that
Fd= VQ
therefore W= VQ.
True or False: Neutrally charged objects experience electrostatic force from charged objects.
False Neutrally charged bodies will not experience electrostatic force from charged bodies as they have no charge to interact with an electric field.
what is Coulomb's law?
F=kq1q2/r^2
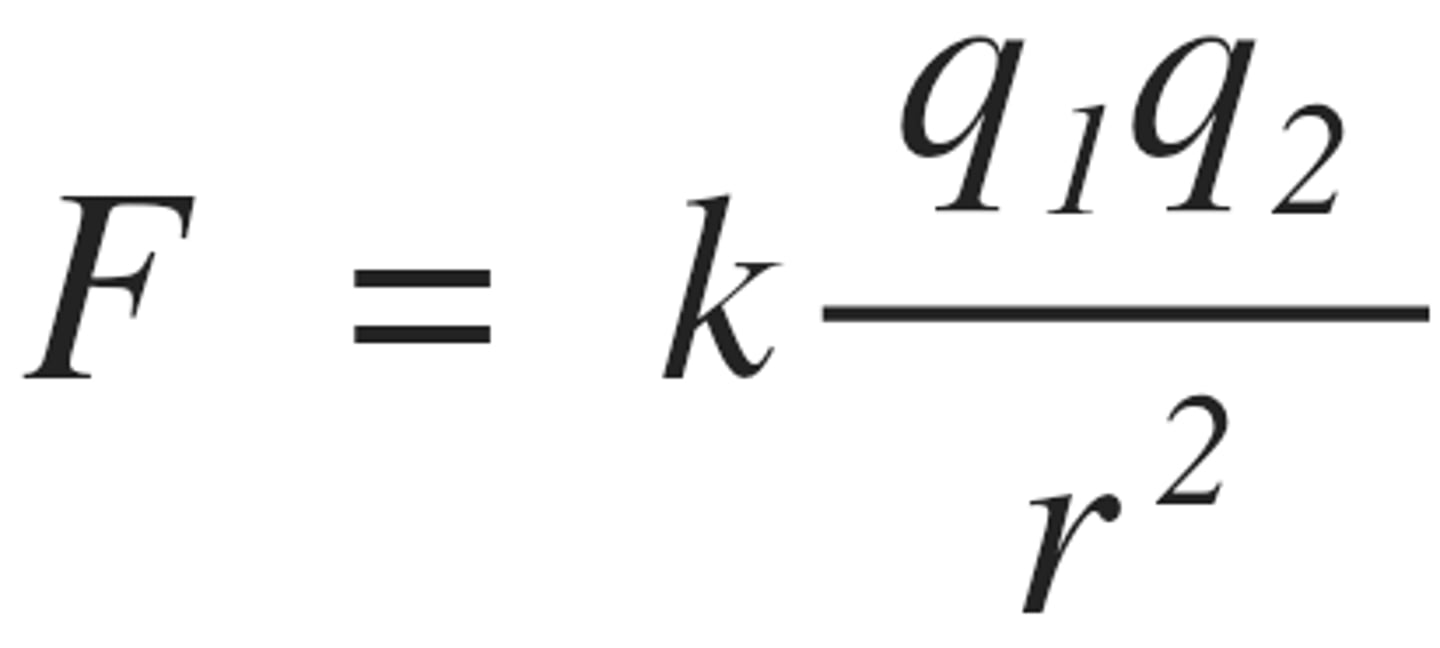
True or false: according to Coulomb's law when charge is increased force will also increase if r (distance) remains the same.
True.
If you Double the distance between 2 charges how does the force change?
We know that F is proportional to the inverse square of the distance. This means that when is doubled the force will decrease by a factor of 4 (2^2) as the further away is gets the weaker the force gets.
what is the equation for the electric field strength on a point charge at any distance in the field?
Consider the 2 equations: E=F/Q and F=kQq/r^2
If we sub the 2 equations into one another we know that:
E=kQq/Qr^2
the Q's cancel and we are left with:
E=kq/r^2, using this equation we can calculate the field strength experienced by a charged particle at any point in the field.
what is does the constant k, mean?
Coulomb's constant = 9x10^9 N/C
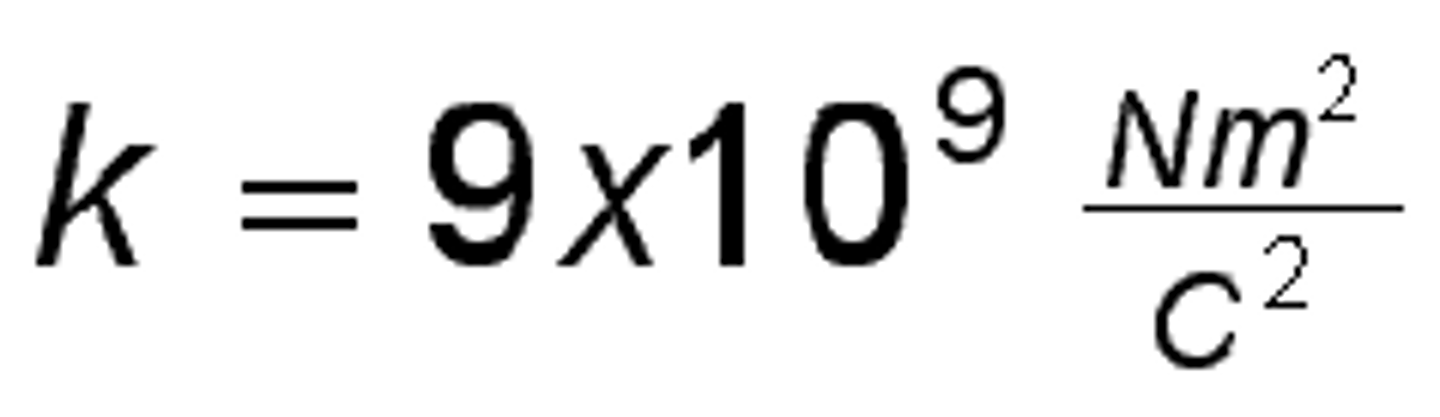
True or false: Work done is the same as the change in Electrical potential energy
True.
Electrical potential energy (U) is the energy a charge (q) has due to its position in an electric field (E). When a charge moves in the electric field, its potential energy changes.
Work is the process of transferring energy by applying a force over a distance. The work (W) done on a charge by an electric field when moving from one point to another is equal to the change in its electrical potential energy ΔU.
W=ΔU
This means the work done on the charge is exactly the amount by which the electrical potential energy changes.
predict the path of a positive electric charge entering a uniform electric field, (positive plate on the top and negative plate on the bottom)
We know that like charges repel and opposite charges attract. so, if the particle entering the field is positive it will be attracted to the negative plate and repelled by the positive plate, hence it will accelerate towards the negative plate. (moving down)
predict the path of an electron charge entering a uniform electric field, (negative plate on the top and positive plate on the bottom)
We know that like charges repel and opposite charges attract. so, if the electron entering the field is negative it will be attracted to the positive plate and repelled by the negative plate, hence it will accelerate towards the positive plate. (moving down)
If a positive charge is moving against the field (uniform electric field) describe the work being done in the field. (positive plate on the top and negative plate on the bottom)
If the charge moves against the field work is done by the charge on the field because as it moves to oppose the field, it loses kinetic energy and slows down.
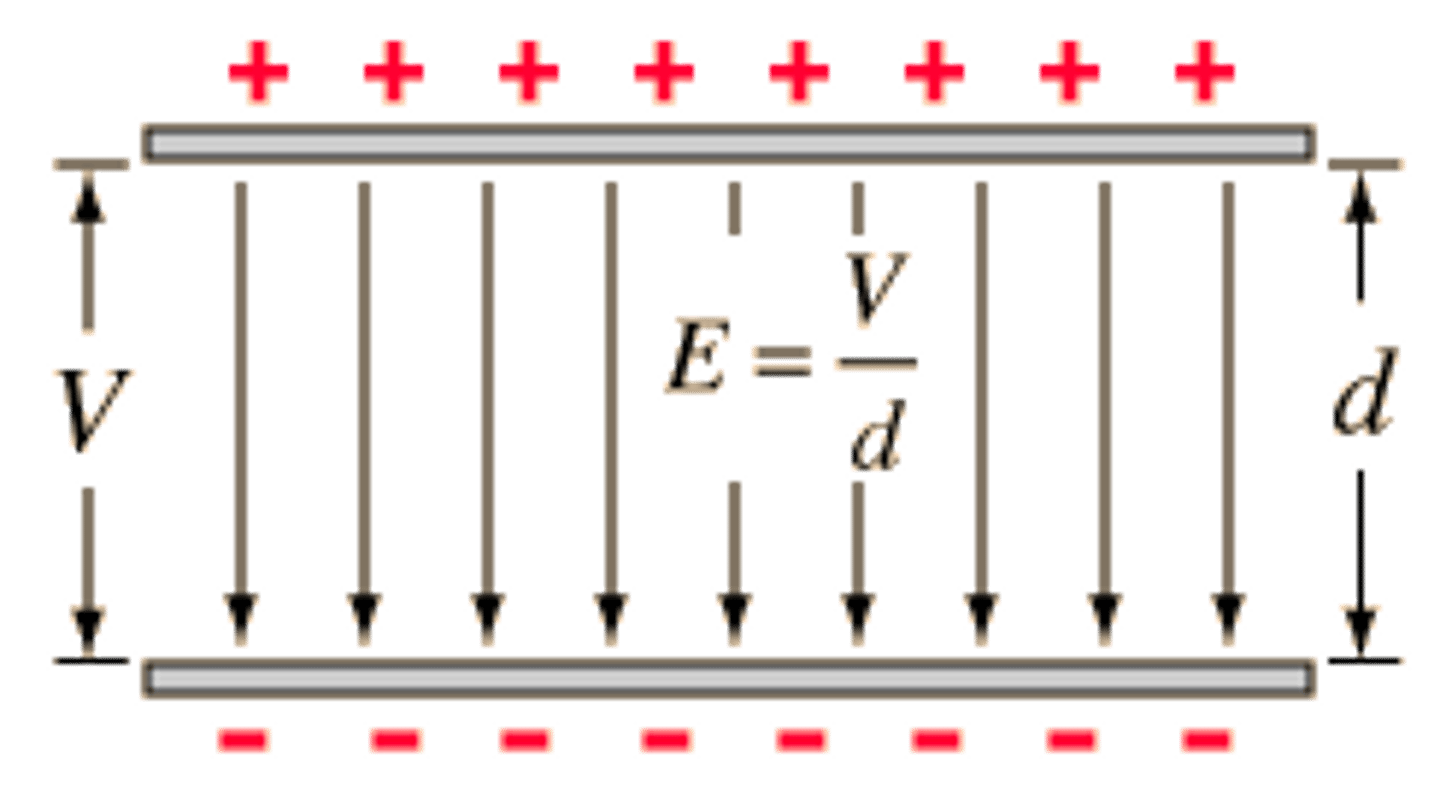
If a positive charge is moving with the field (uniform electric field) describe the work being done. (positive plate on the top and negative plate on the bottom)
If the charge moves with the field work is done by the field on the charge. As the paricle is gaining kinetic energy because the field is pushing it to lose potential energy and travel.
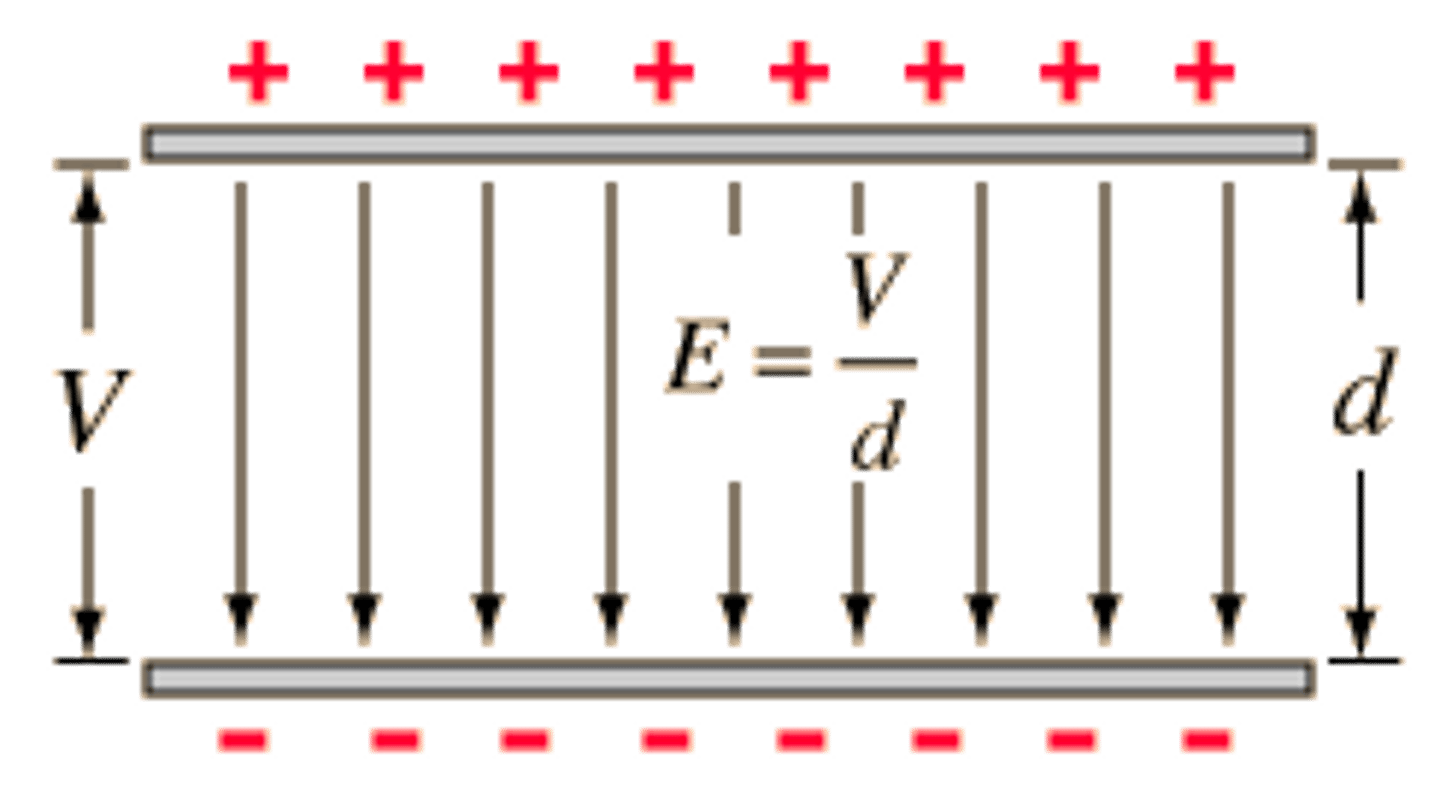
If a negative charge is moving with the field (uniform electric field) describe the work being done. (positive plate on the top and negative plate on the bottom)
If the negative charge is moving with the field it is moving towards the negative charge (which will repel it) work is done by the charge on the field, as it moves it will slow down and lose kinetic energy.
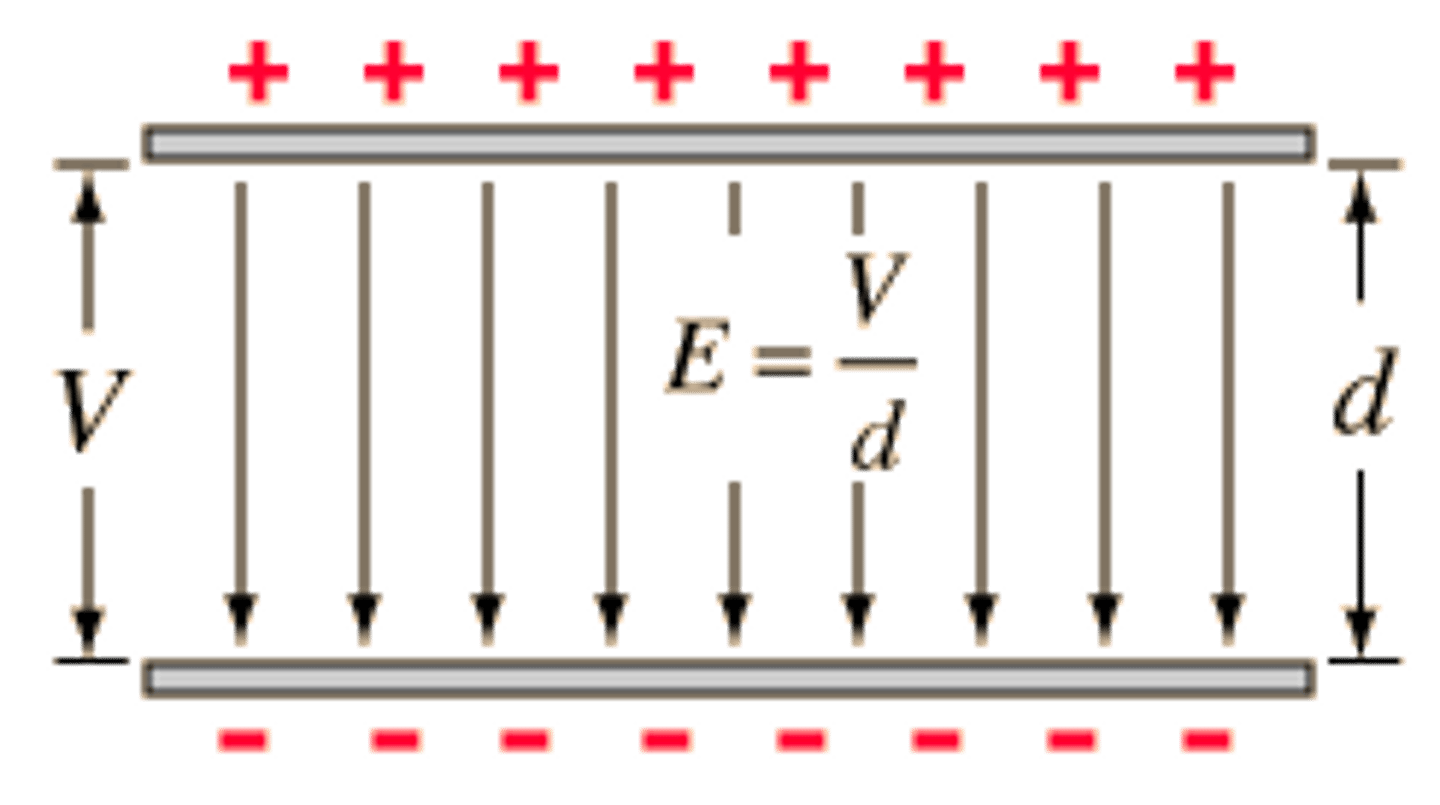
If a negative charge is moving against the field (uniform electric field) describe the work being done. (positive plate on the top and negative plate on the bottom)
If the negative charge is moving against this field it is moving towards the positive charge (which will attract it) this means that work is done by the field on the charge, as the charge will accelerate towards the positive plate attracting it while being repelled by the negative plate hence it loses the potential energy being converted into kinetic energy.
what is 1 eV (electron volt)
it is the energy required to move 1 electron through a potential of 1 volt.
1eV= 1.6x10^-19
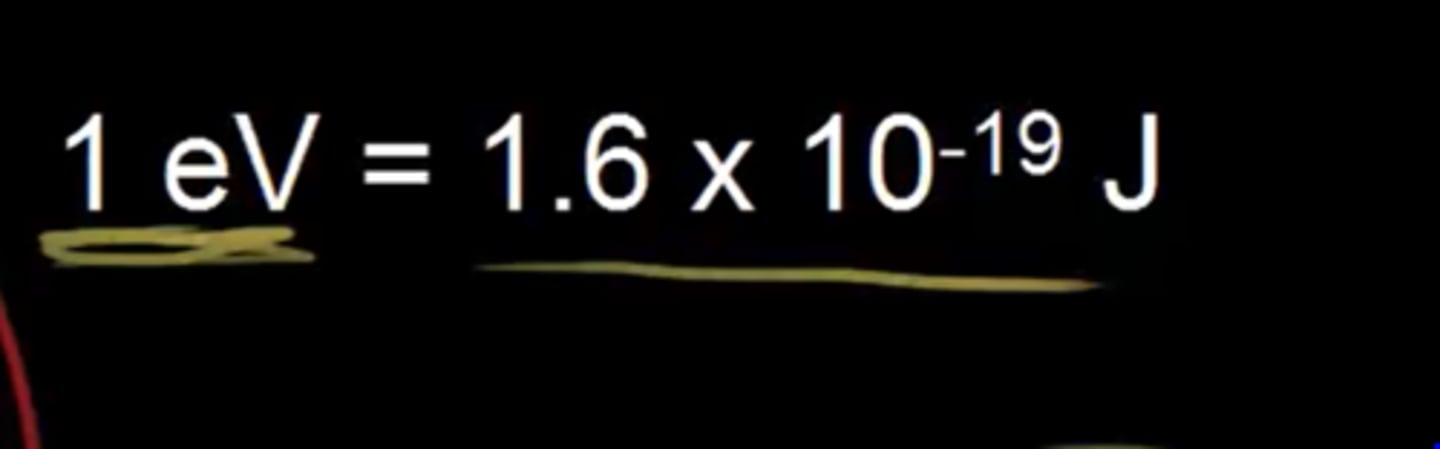
A Sphere has a mass of 12Kg and charge of 2C, is at rest with an electric potential of 12V, It is released from rest and travels freely to a point of no electric potential. What is its speed on arrival?
We know that the work done = the change in potential energy.
therefore:
W=VQ
W= 2x12=24J Initailly.
W=2x0=0J finally
therefore change in PE = -24J.
Now we know that that is energy is conserved the 24J of energy has successfully been converted into Kinetic energy.
Therefore:
KE=0.5mv^2
24= 0.5 x 12 x v^2
therefore if we rearrange and solve
v= 2m/s
2 parallel plates are separated by 2m and have a voltage of 12V between them. A projectile of mass 2kG and charge 3C is launched from the -ve plate with a speed of 3m/s how far does it travel before stopping?
The projectile will only stop when all of the kinetic energy has been converted to potential energy therefore using KE=PE.
Given KE= 0.5mv^2
KE= 0.5x2x3^2
KE= 9J=PE
using W=QV
we know that
9=(3)V
if we rearrange we get that V= 3V
Now if we know that a 2m distance cover 12V, 3V is 1/4 of the original therefore 1/4x2m=0.5m
Hence the projectile will travel 0.5m before stopping
True or False: A positively charged particle in an uniform electric field will experience a constant acceleration towards the negative plate.
True as if F=ma, we know that Force is constant in a uniform electric field and the mass of an object is not subject to change as it travels through the plates, therefore its acceleration must be constant.
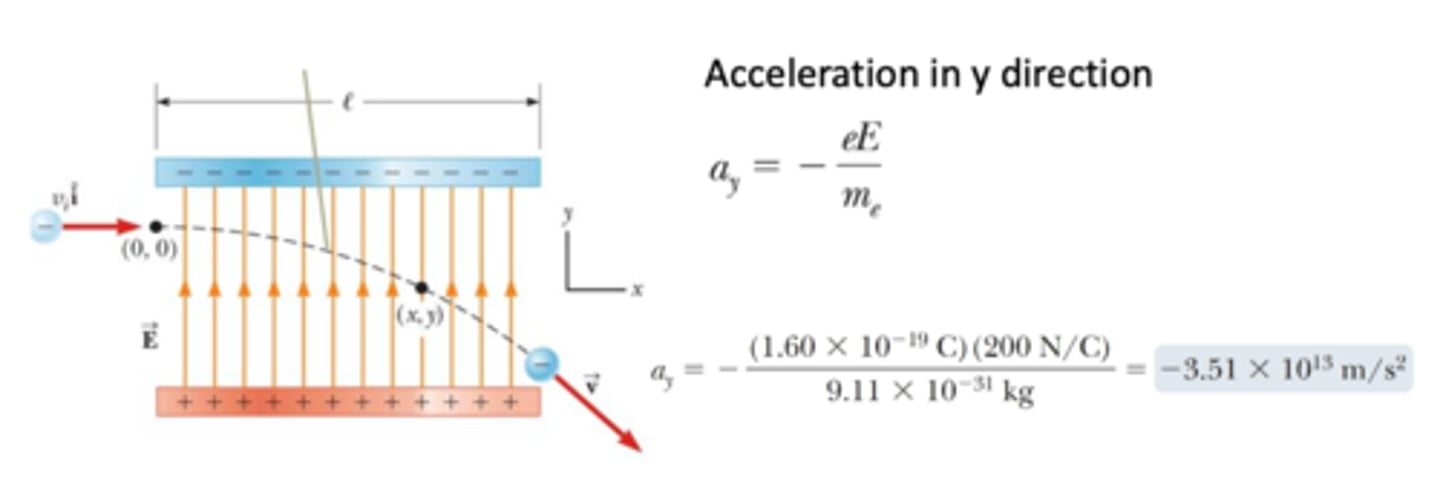
A charged particle moves through a uniform electric field in the direction parallel to the plates. The particle enters the field with a constant velocity in this direction. Describe the direction of acceleration.
The charged particle will always accelerate perpendicular to the plates as the electric force acts in the direction of the electric field and isn't affected by initial motion of the particle. This means that depending on the charge of the particle it will either accelerate up or down ( depending on the attractive plate), this acceleration in the y- direction will always be perpendicular to the horizontal plates.
What is the Right-hand rule for straight current carrying wires.
Thumbs in the direction of current ( Always points from S to N)
Fingers wrap in the direction of magnetic field (B)
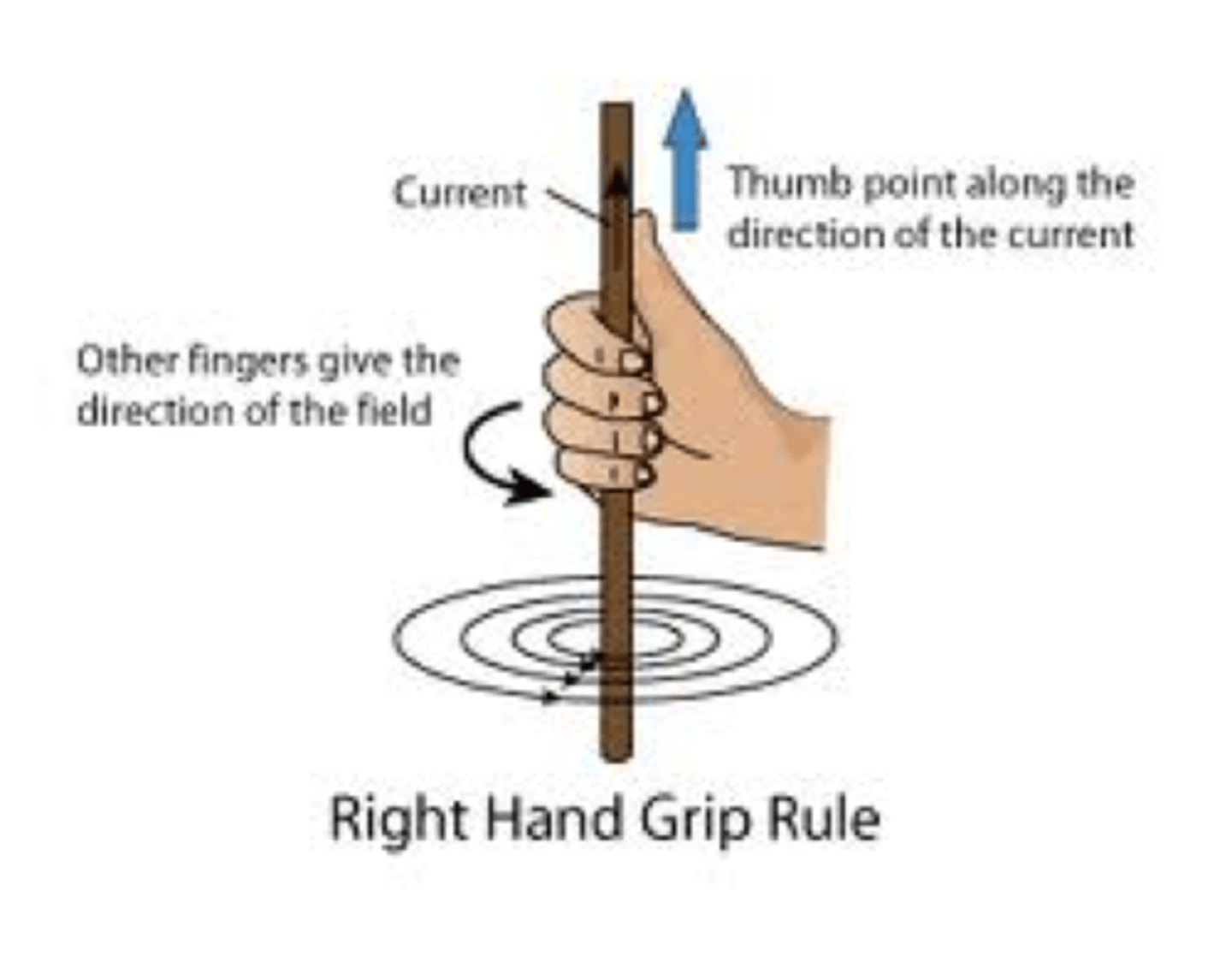
What is the Right-hand rule for Solenoids?
Thumbs point in the direction of the magnetic field ( magnetic field always flows from south to north, therefore thumbs still point to the North end)
Fingers wrap in the direction of the current ( they typically wrap clockwise or anti-clockwise from a given perspective on the solenoid)
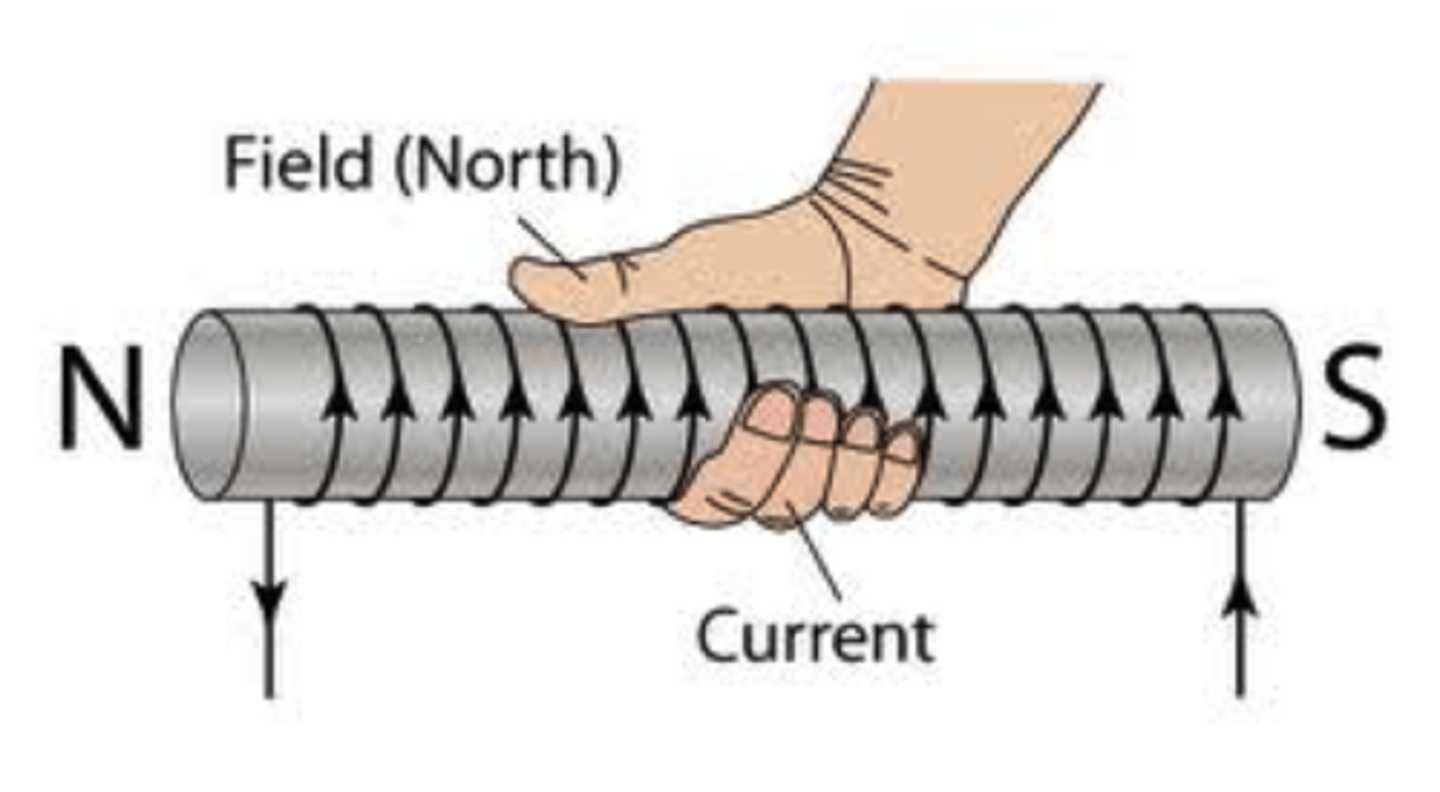
what is the rule for magnetic field strength of straight current carrying wires?
where r is the distance in the field where the field strength is being experienced.
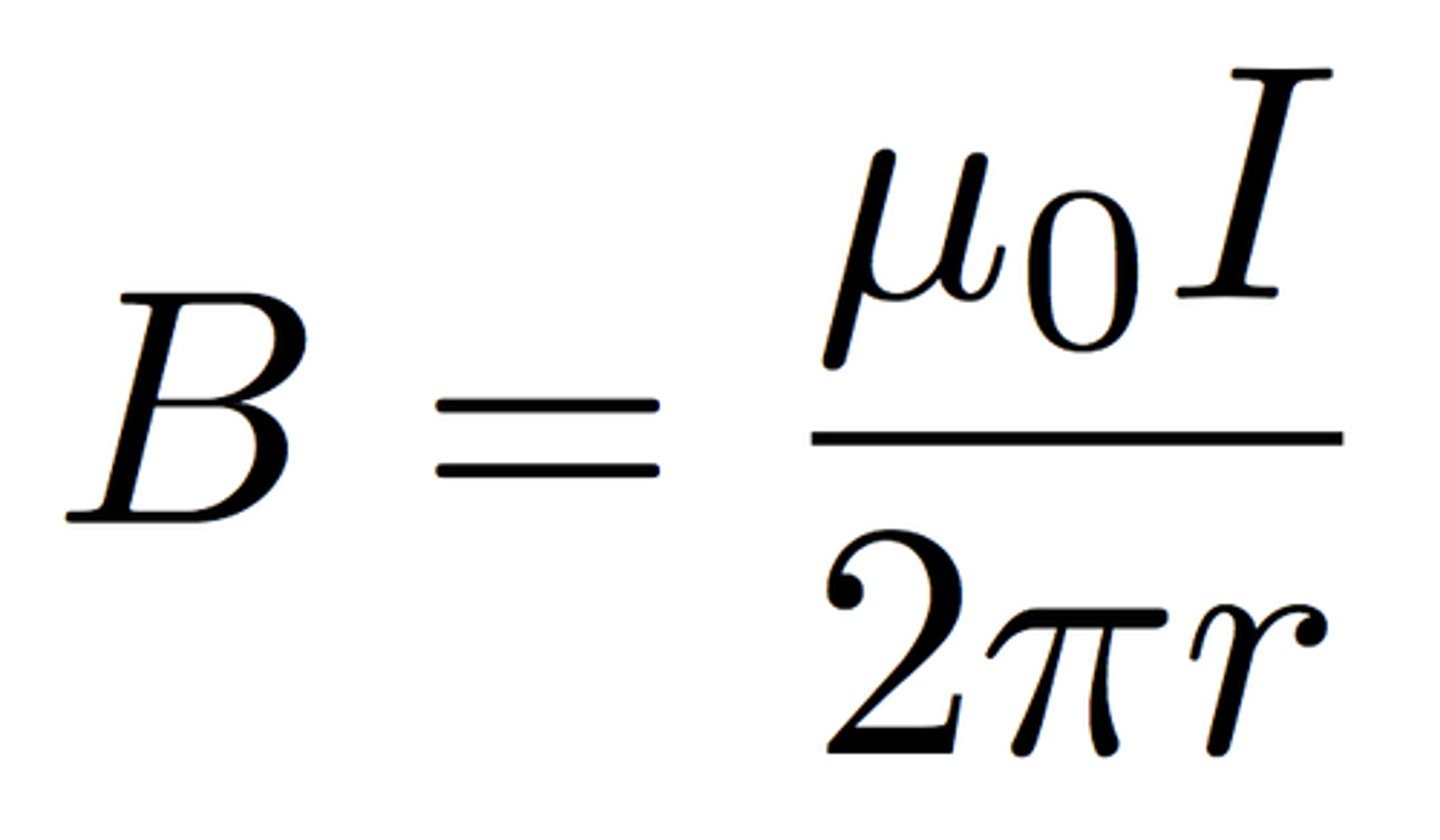
what is the rule for magnetic field strength for solenoids?
where n is the number of turns and L is the length of the solenoid.
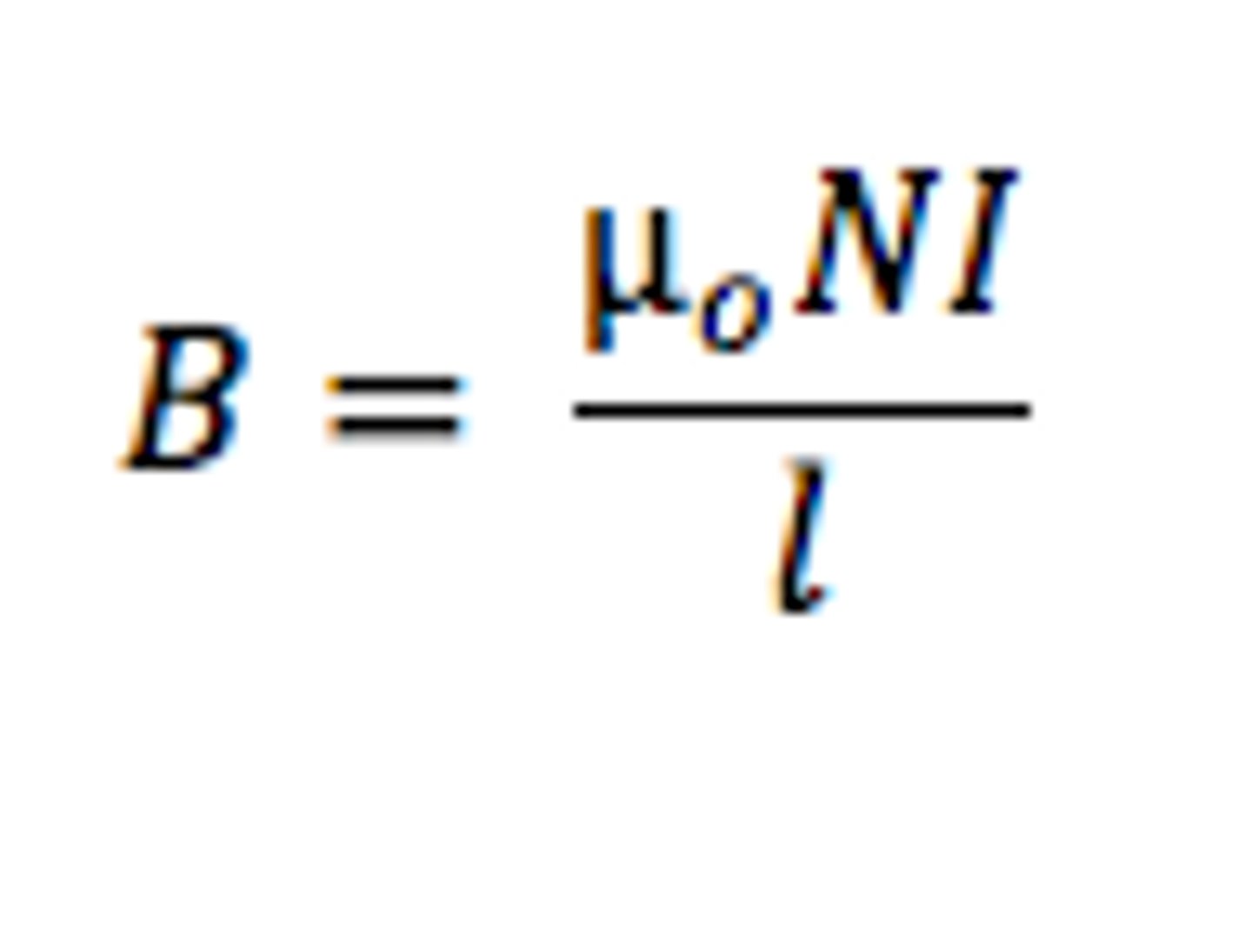
True or False: For the same length of the solenoid if the number of turns of current carrying wire is increased the magnetic field strength B will also increase?
True
what is the unit of measurement for magnetic field strength?
Tesla, (T)
what happens when a current carrying conductor is added to an already existing magnetic field.
A current carrying conductor will produce it's own magnetic field, interacting with the already existing Magnetic field resulting in a resultant field. In this field the direction if the force is always perpendicular to the current and the external magnetic field.
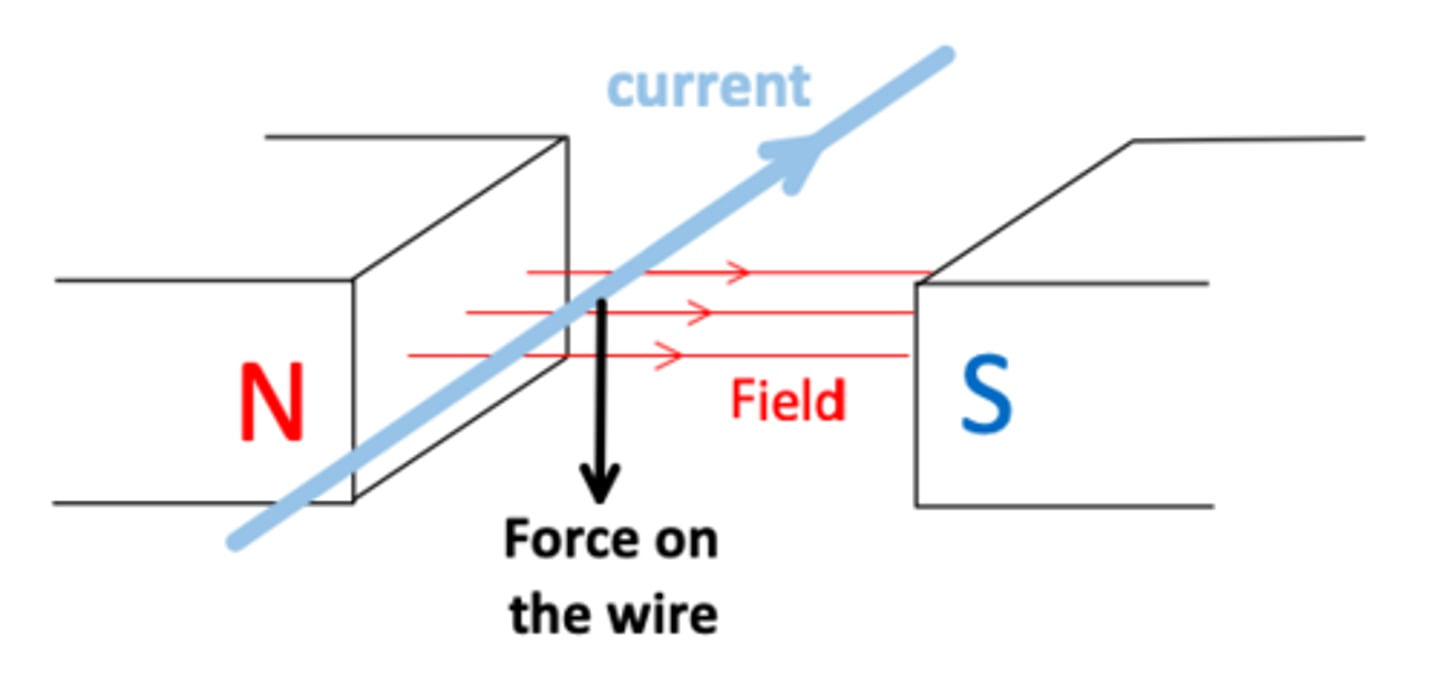
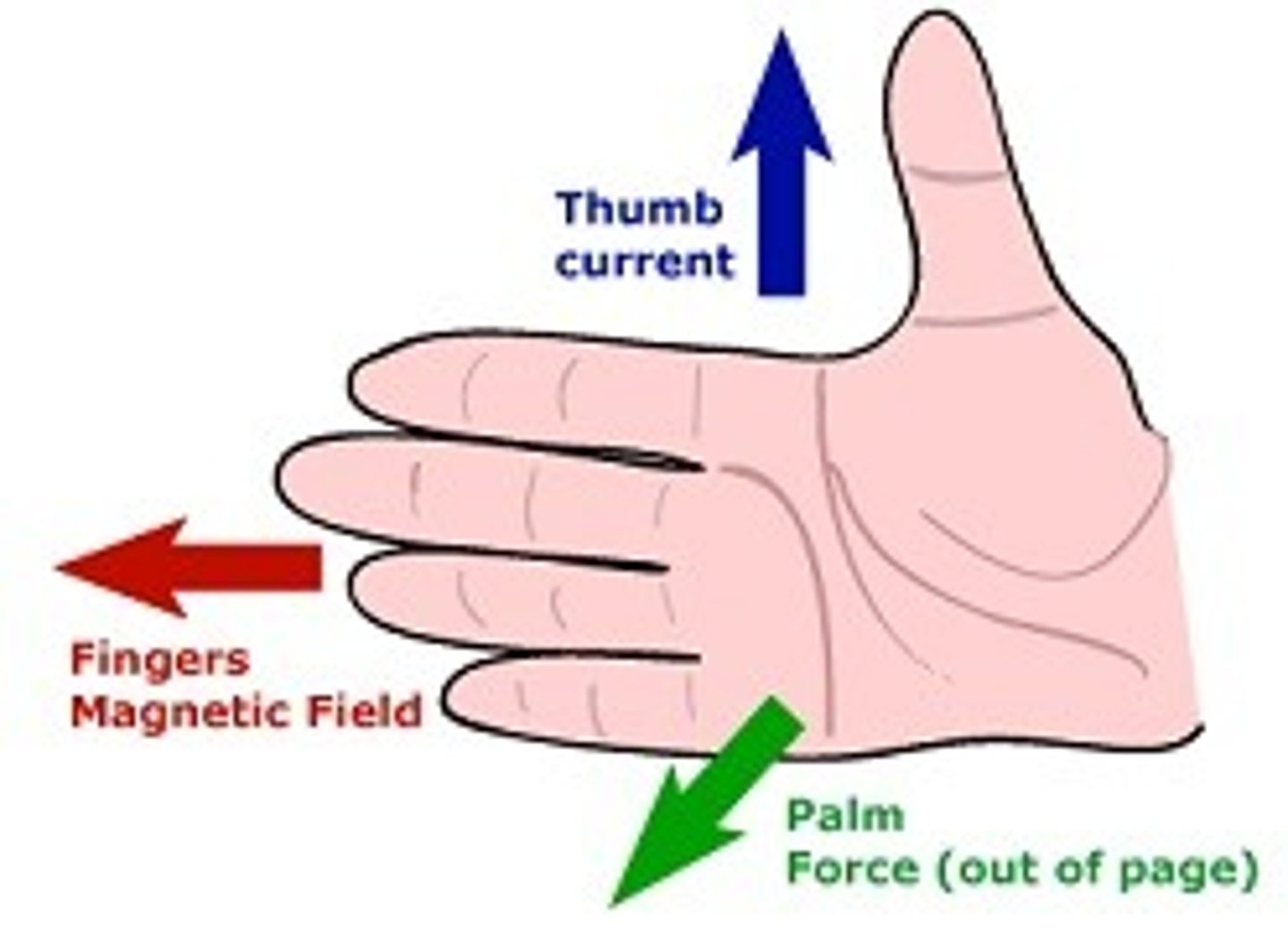
what is the right-hand rule for finding force when there is current and an external magnetic field?
Fingers: Wrap in the direction of magnetic field
Thumb: Point is the direction of current S to N
Palm: direction of Force
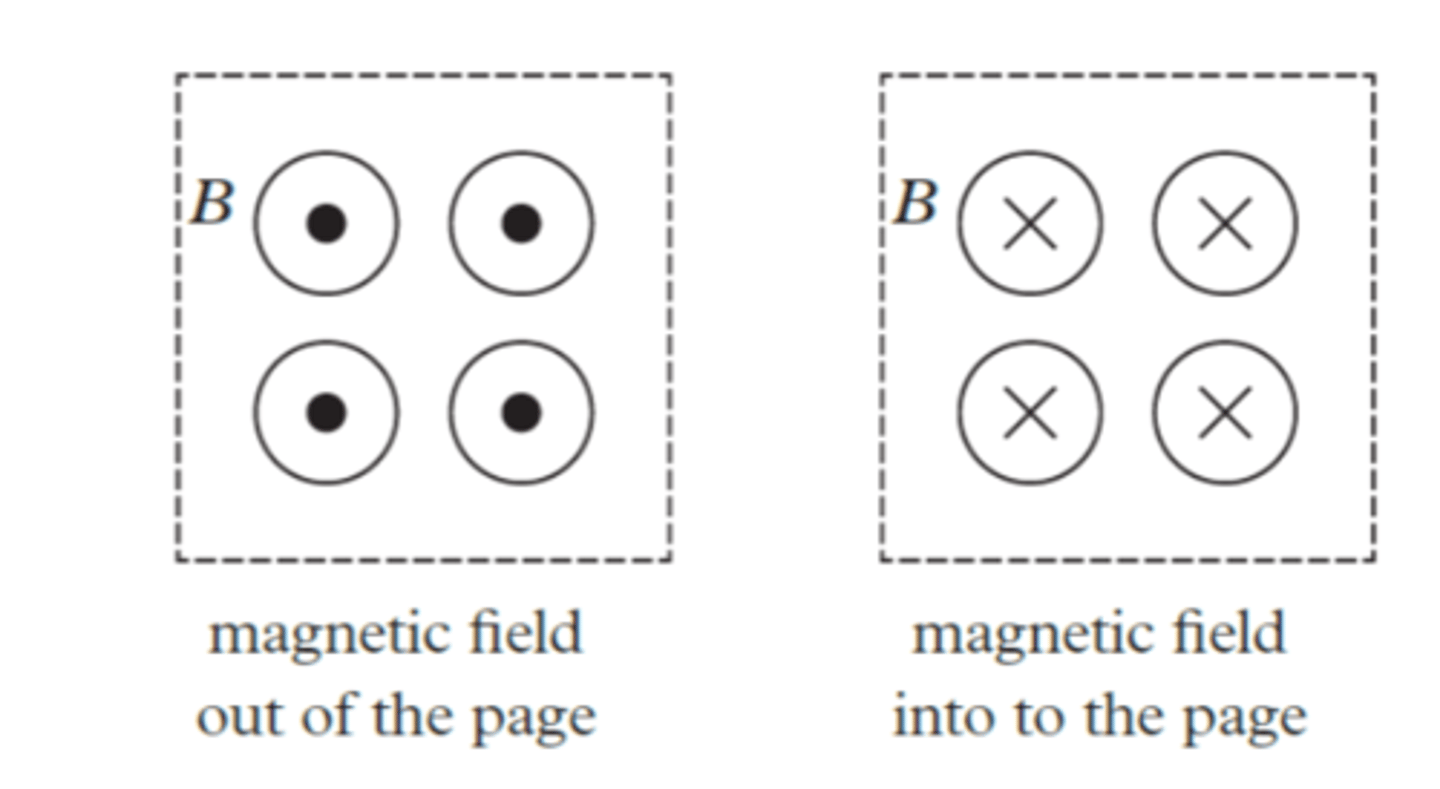
when representing a magnetic field what does a x on the page mean?
Magnetic field into the page
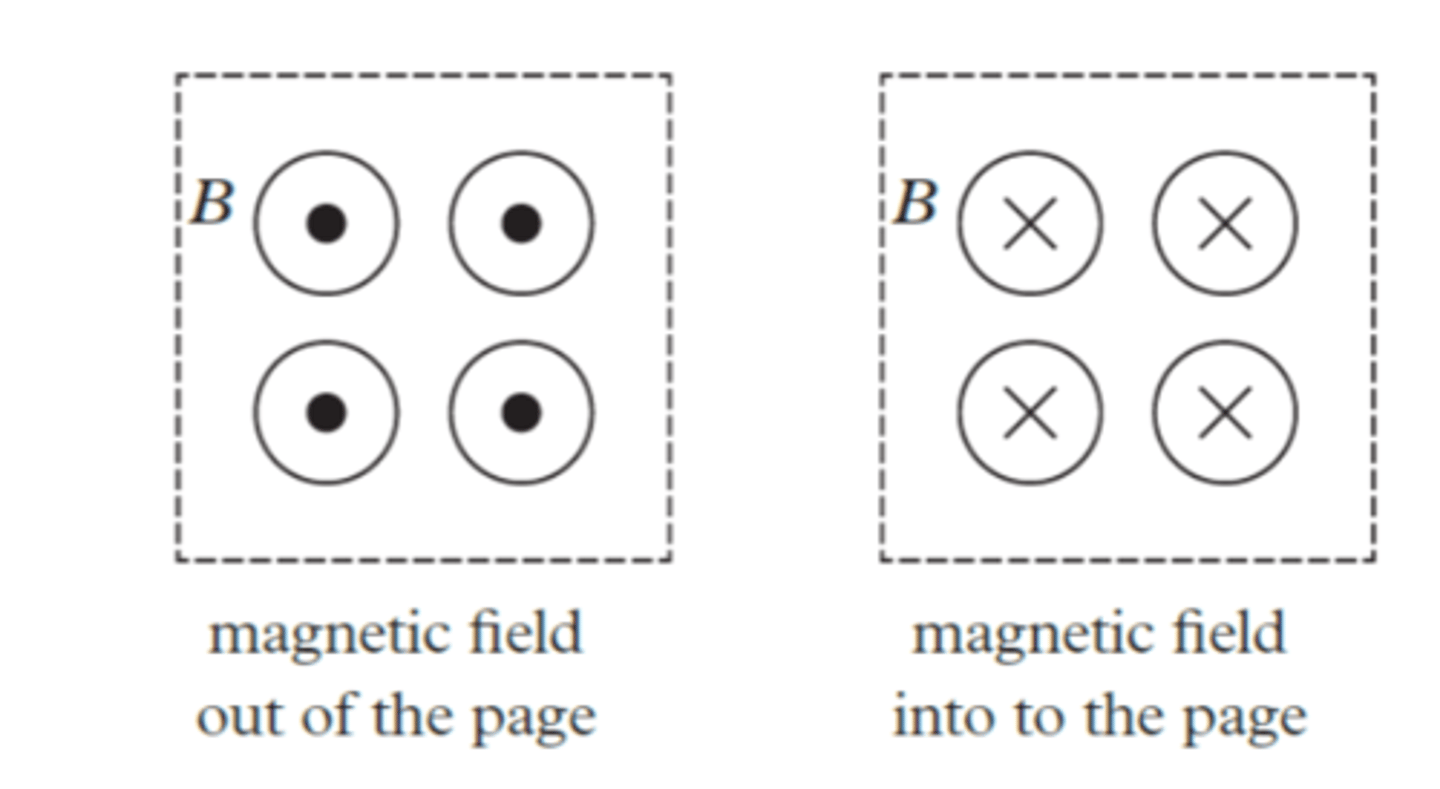
when representing a magnetic field what does a dot on the page mean?
Magnetic field out of the page
what is the formula for force experienced between a straight current carrying wire and an external magnetic field?
F= BILSin(theta)
B= magnetic field strength (T)
I= Current through the wise (Amps)
L= length of the wire on which the force acts
Theta= angle at which the wire lies with respect to the field ( because we need force to be perpendicular so we can only account for the sin, or the y component of the wire's force)
True or False: when a current carrying wire is parallel to the external magnetic field, it will still experience a force.
False if the wire is parallel then theta=0, and Sin(0)=0 , subbed into the equation there will be no force experienced.
2 parallel current carrying wires have the current flowing in the same direction will these wires attract or repel?
Using the right hand rule to determine the direction of the magnetic field on either side of the wire. After we have determined the direction of magnetic field and the direction of current, we can find the force using our other right hand rule, we notic3 that if both parallel conductors have the same current flow the force will attract each other.
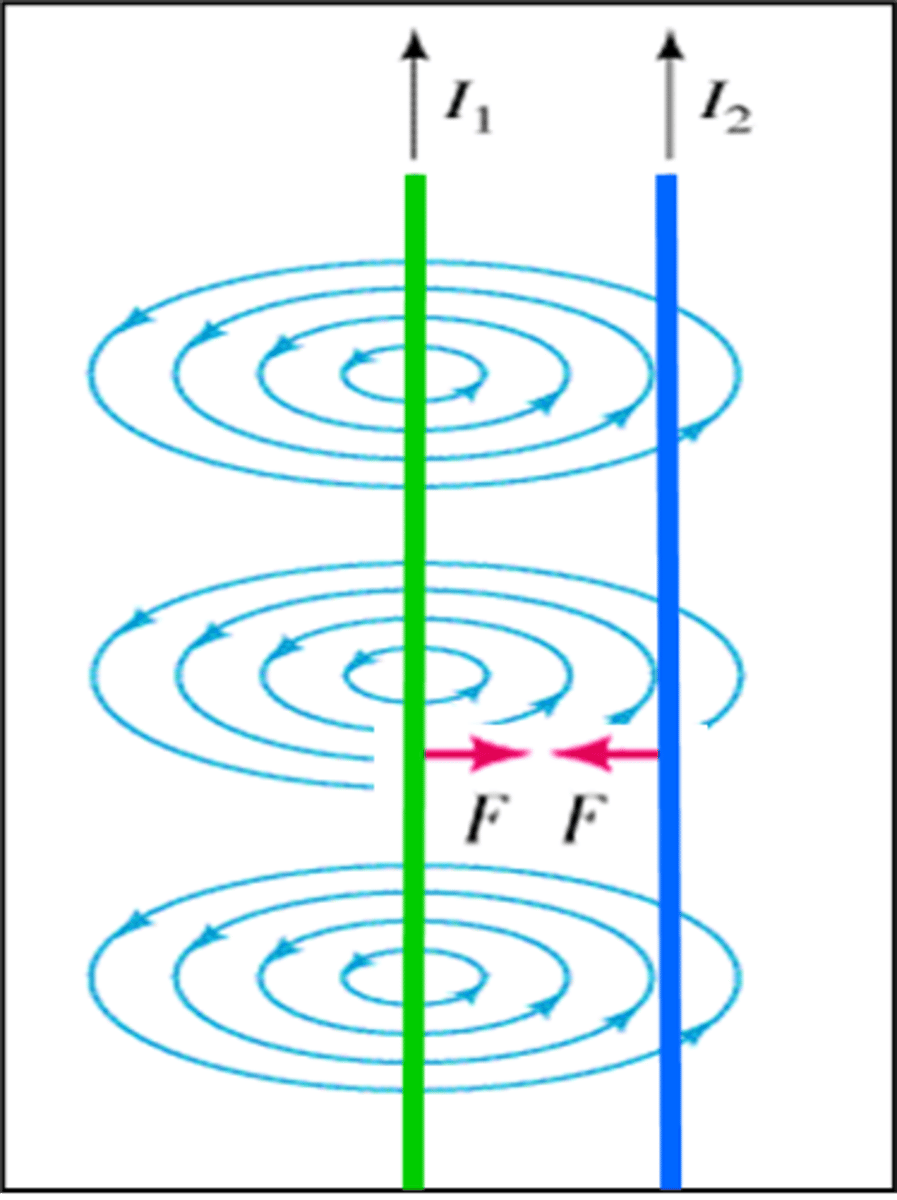
what is the equation to determine the force between 2 current carrying wires.
F= (k x I1 x I2 x L)/d
where k= 2x10^-7
Where L= length of the conductor on which the force is action on.
d= distance between the 2 wires
how do we solve for the force of charged particles in Magnetic fields?
F=BQVsin(theta)
where:
Q= charge of particle in coulombs
B= magnetic field strength (T)
V= velocity of particle (m/s)
what is the right hand rule for determining the force for charged particles
-Thumb in direction of positive charge ( if the charge us negative change the direction of the thumb)
-fingers in direction of magnetic field
-palm points in the direction of force
True or False: A charged particle entering a magnetic field follows a circular path.
True
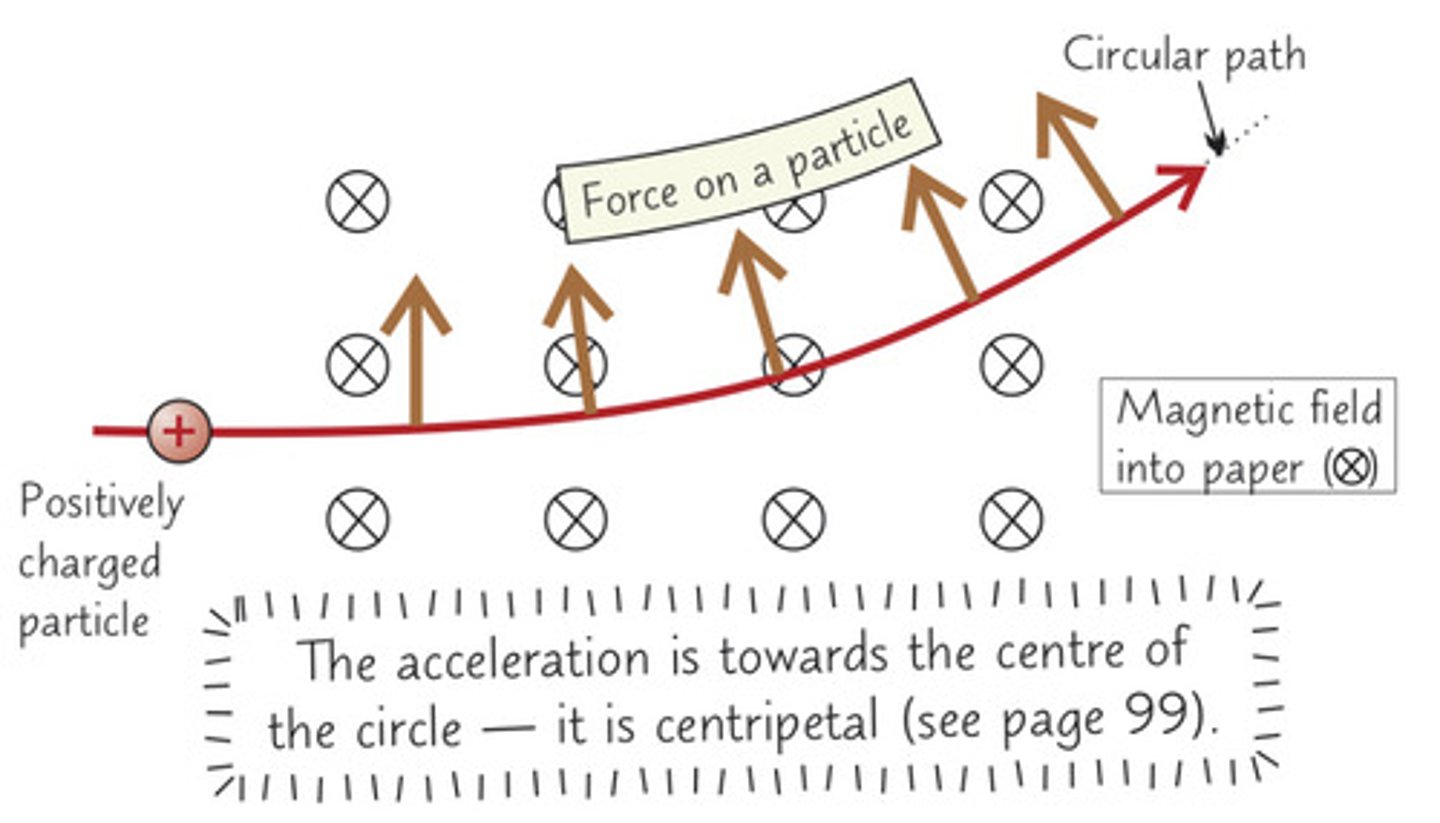
write an expression that allows us to find the radius of the path that a charged particle would follow once it has entered a magentic field.
If we know that the particle follows a curved path it abides by the laws of circular motion therefore we know:
F=mv^2/r and we know that F=BQVsin(theta)
the following can be rearranged with r as the subject giving us the equation:
r= mv/BQ sin( theta)
Note: sin(theta) can typically be ignored as most particles enter the plane perpendicular to field which means sin(90)=1
what is magnetic flux
the number of magnetic field lines passing through a surface.
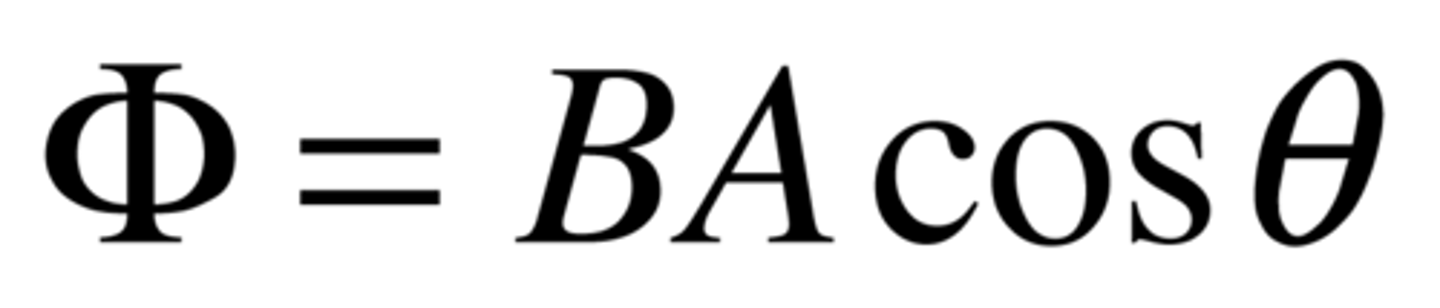
what is magnetic flux density?
A measure of the strength of a magnetic field same as B
At what point is magnetic flux the greatest?
Magnetic flux is maximum when the angle θ between the magnetic field and the normal to the surface is 0°
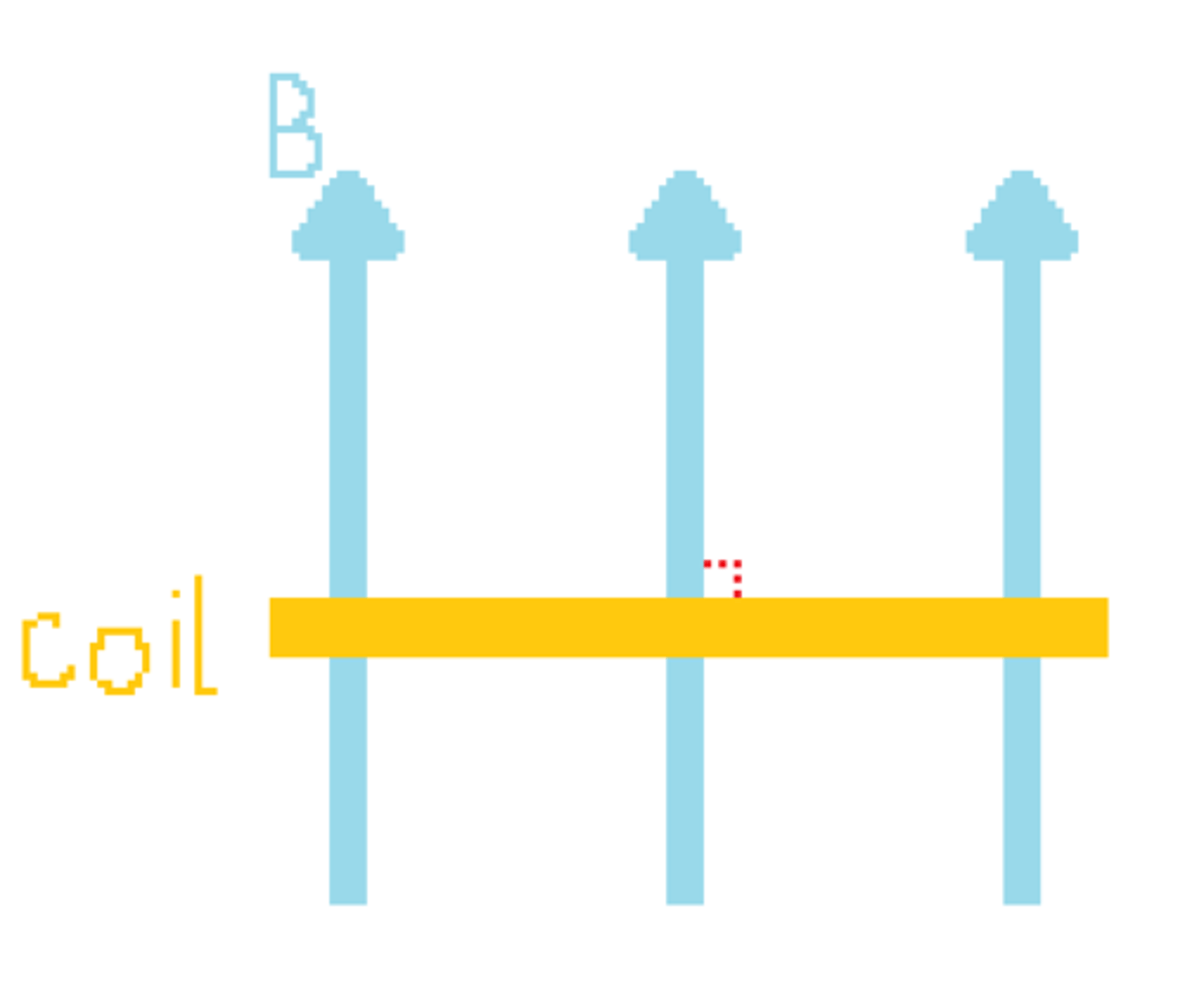
what is electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction is the process of generating an electric current in a conductor by changing the magnetic field around it. When a magnetic field around a wire (or coil) changes—either by moving the magnet or the wire—an electric current is created in the wire. This induced current, is what we call electromagnetic induction
what is the formula for EMF
EMF= (-n x Δflux)/Δt
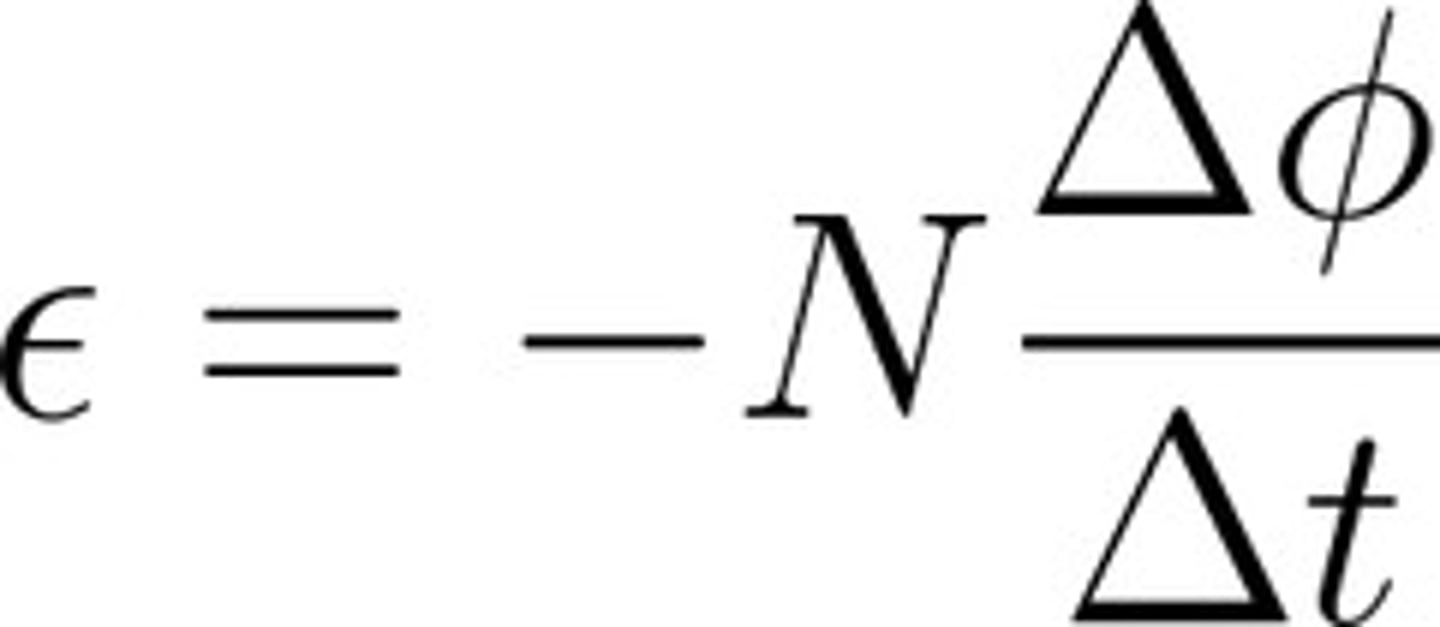
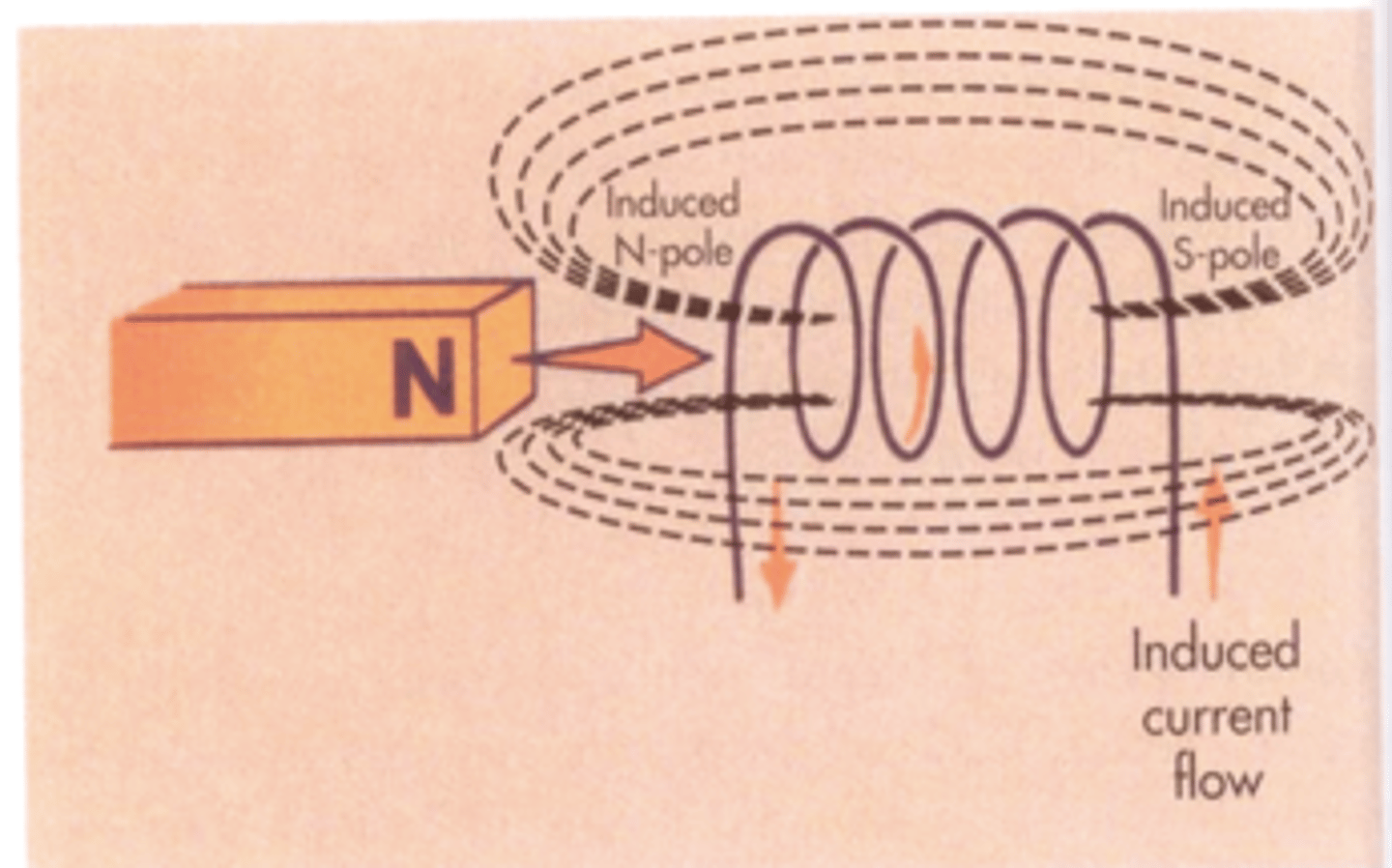
What is EMF?
Electromotive force: the electrical pressure that causes electrons to flow through the conductor. Consider this: There is an existing magnetic field. A current carrying wire is pushed into the magnetic field (left to right or right to left), the force of the magnetic field causes the current in the wire to displace, now instead of flowing as usual the electrons bunch up on one end while the protons bunch up and the other end with a distance in between them. This build up of charge on the 2 terminals replicates the positive and negative terminals of a battery and just as a battery has its voltage, this induced current also has a potential difference (voltage). Therefore, any conductor moving through a magnetic field will generate an electromotive force (EMF) that is the voltage or potential difference generated by a source. EMF is the "push" or energy that causes electric charges to move in a circuit, and it's the reason current flows.
What is Faraday's Law?
The induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage. change in flux linkage simply means that magnetic field lines cut differently as a current-carrying conductor moves through the field. Hence the constantly changing flux linkage induces and emf.
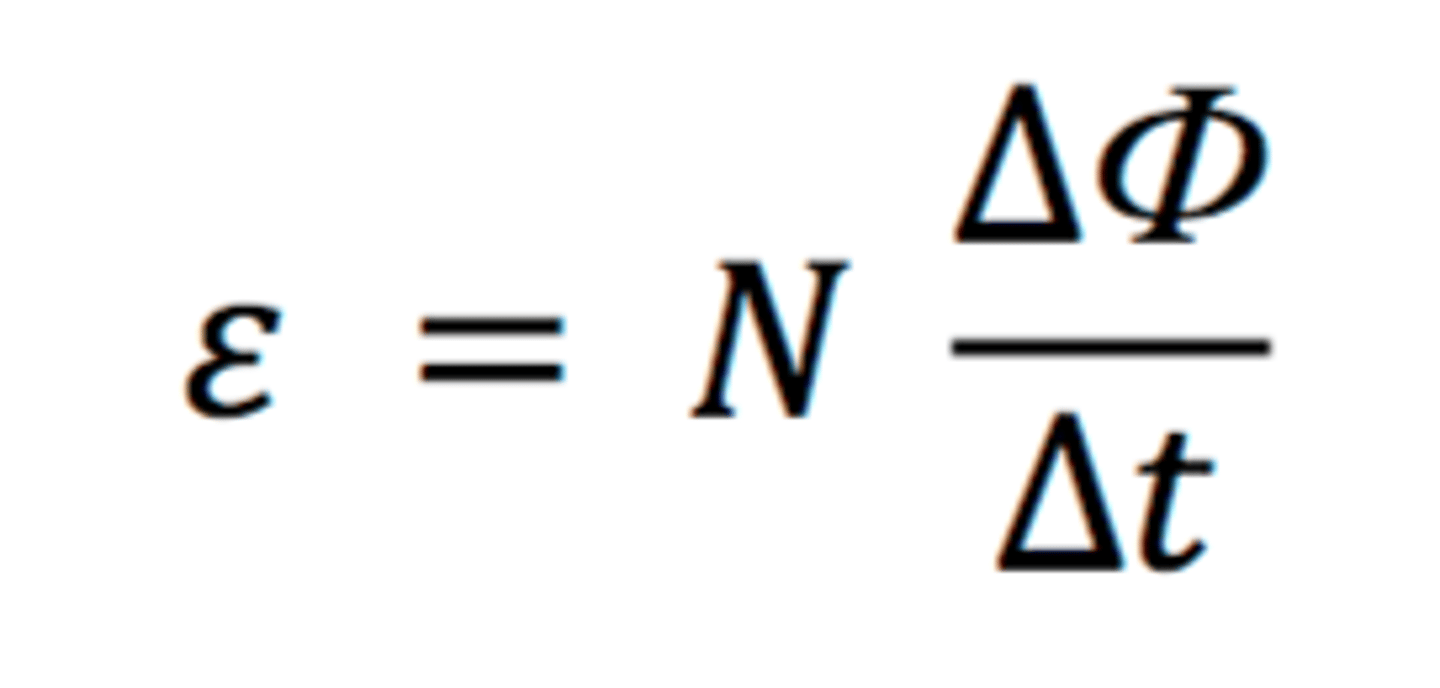
True or False: An increased rate of flux linkage = increased EMF.
True, the faster the current carrying conductor cuts through the magnetic field lines the greater the flux linkage will be and hence EMF will increase as Δt remains fairly small.
what is the Rule for magnetic flux linkage
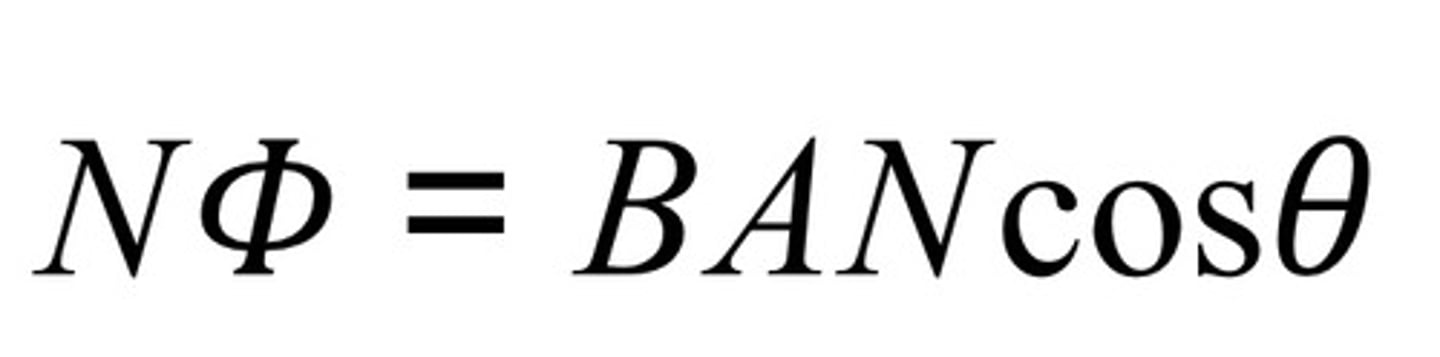
True or False: If a current-carrying conductor is parallel to the magnetic field, the magnetic flux through the surface of the conductor will be zero
True
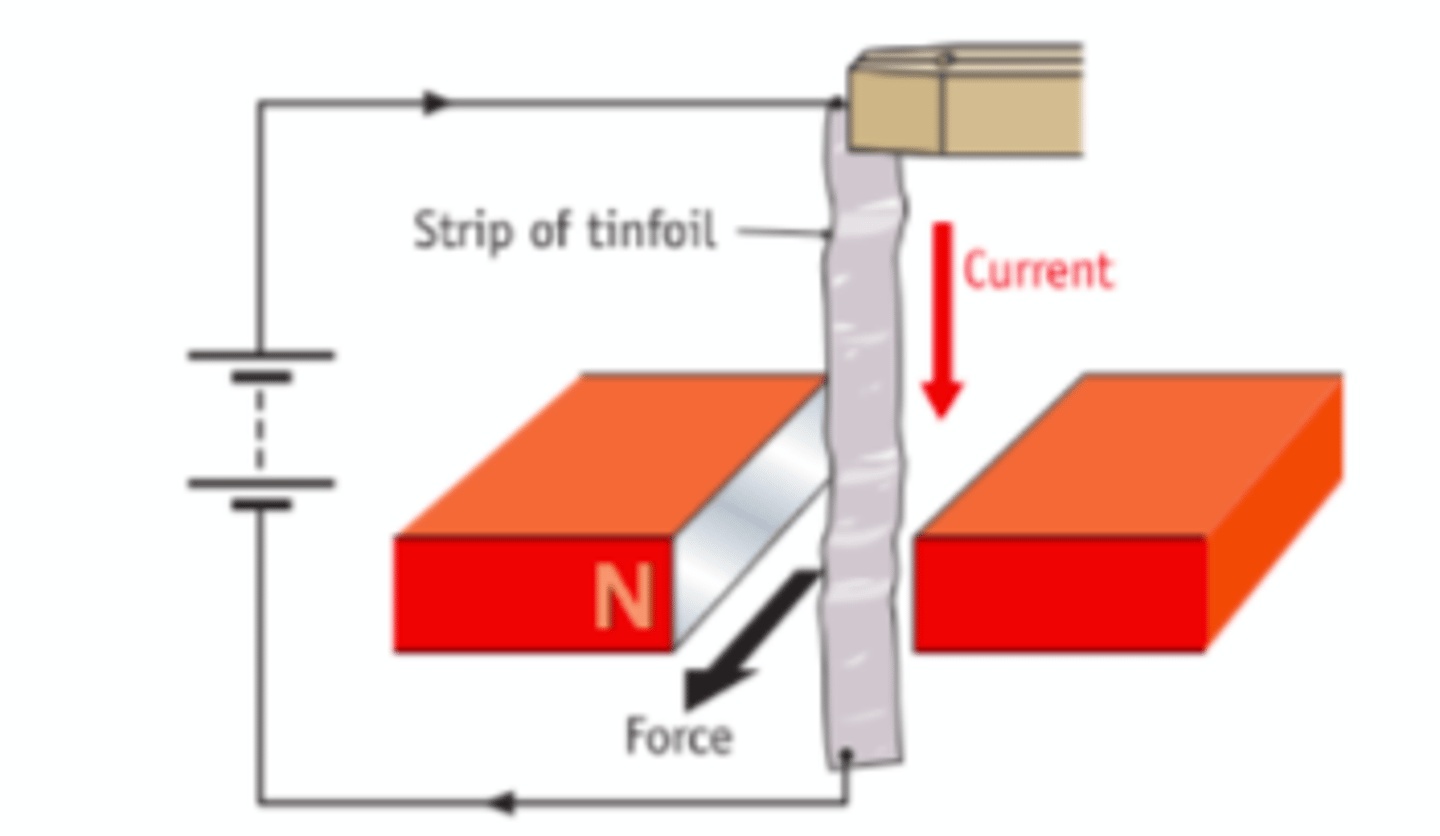
True or False: If a current-carrying conductor is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the magnetic flux through the surface of the conductor will be zero
False, if it is perpendicular to the field then most of the magnetic field lines are passing through the conductor which mean that magnetic flux is at maximum.
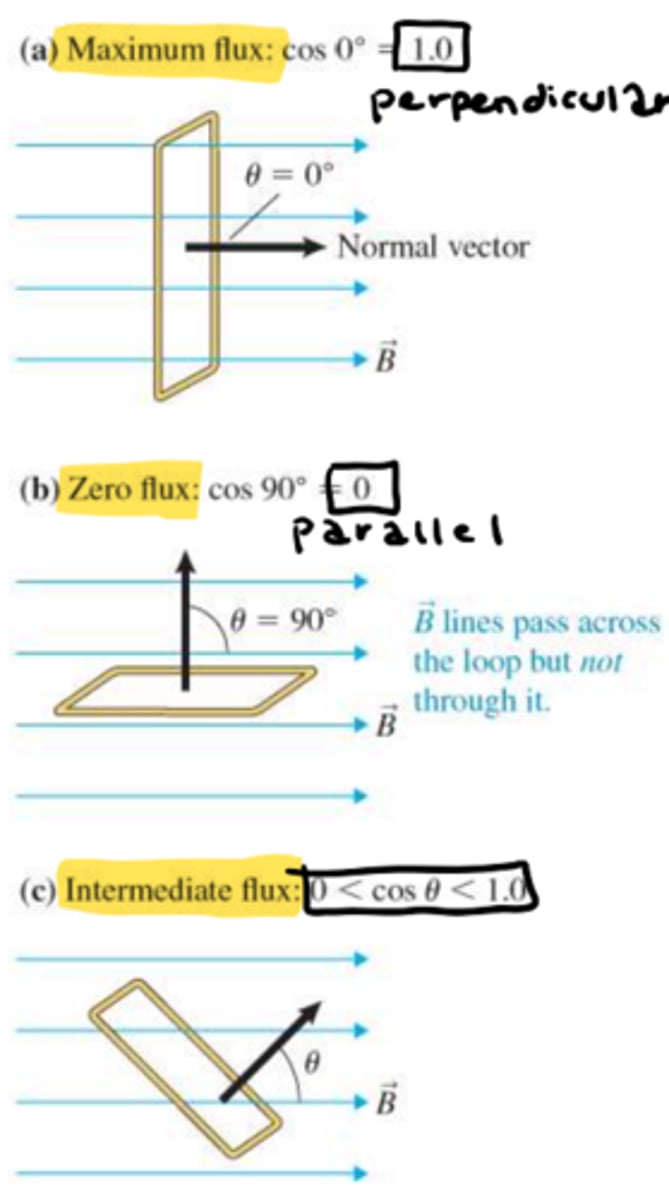
What is Lenz's law?
The induced e.m.f is always in such a direction as to oppose the change that caused it.
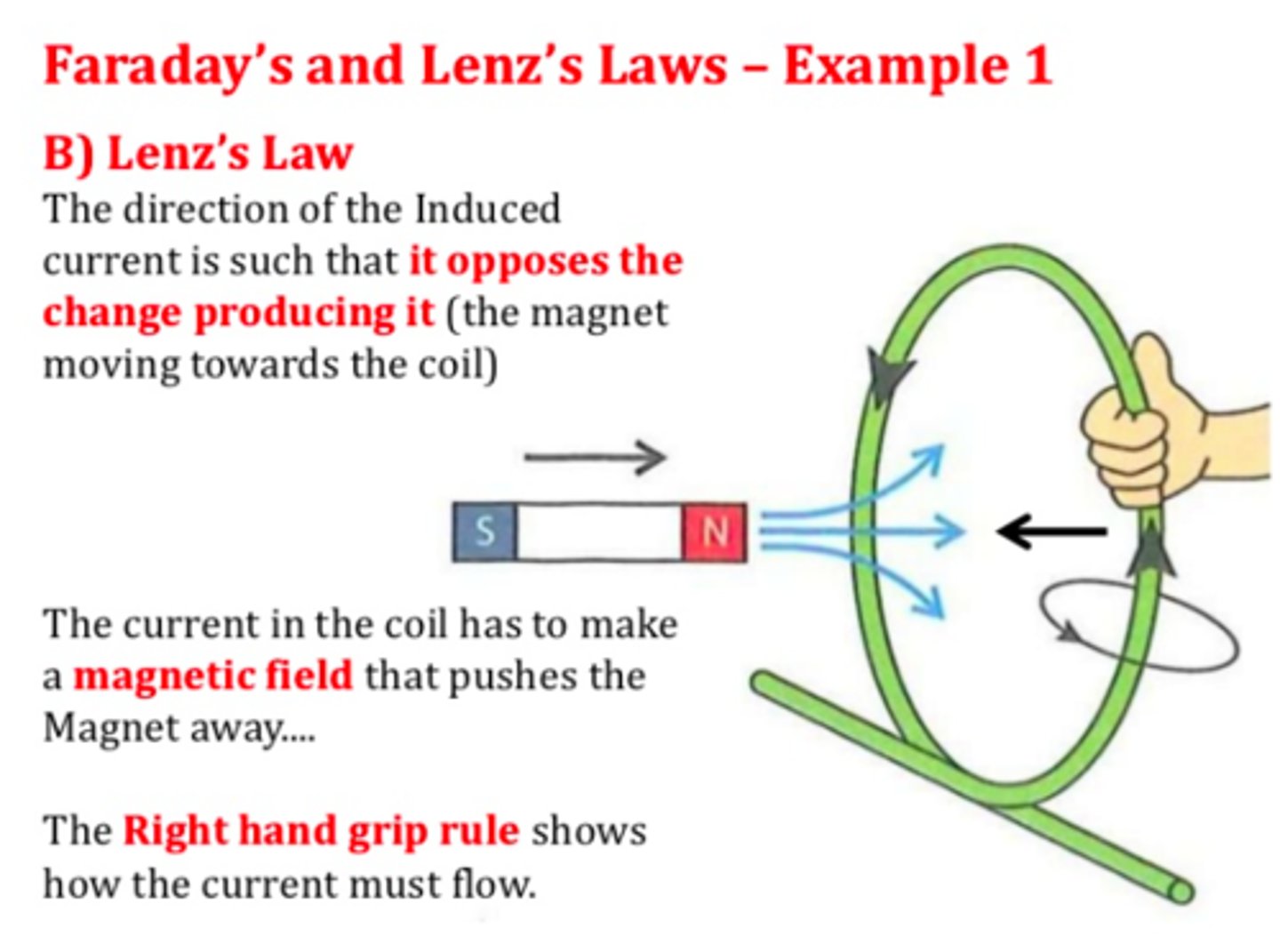
A magnetic field is set up so that it points out of the page. A horizontal conductor is then dragged from the top of the page, to the bottom of the page.
On which side of the conductor will the negative charge accumulate?
The negative charge will accumulate to the right of the rod.
Let's use our right hand push rule here. The magnetic field points out of the page so our fingers should point toward us. We're also told the wire is dragged down the page, so our thumb should point downward. With this our palm should point to the left.
However, the right hand push rule is used for positive charges and the question asks us where the negative charges gather. Since the positive charges gather on the left, the negative charges must gather on the right! So the right part of the rod will accumulate negative charge.
A coil of wire lays flat on the page. Suddenly, a magnetic field of strength 6T is applied inside of the coil.
If the magnetic field direction is into the page, what direction would current flow in the wire?
The current will travel in a counterclockwise direction. When we have a changing flux through the inside of conductor, we know there must be an induced emf. We know that this emf should oppose changes to the magnetic flux in the coil by Lenz's law. Since the flux lines point into the page, the induced emf should produce flux lines from the coil that point out of the page! Using our right-hand grip rule, with our fingers pointing out of the page inside the loop, we get a counterclockwise current!
The south pole of a magnet is pushed into the top of a solenoid. Which option correctly describes the direction of the current and the magnetic polarity at the top of the coil?
The induced current has to create a magnetic field that repels the magnet, so as to reduce the relative motion. That means the induced current must create a magnetic south pole at the top of the solenoid. By the right hand grip rule, we point our thumb down and curl our fingers clockwise, so the current is directed clockwise.
What happens to the galvanometer if the solenoid and the magnet are moved to the right at the same velocity?
The magnet and solenoid move at the same velocity, the galvanometer stays zero because there is no relative motion between the magnet and the solenoid.
What is a transformer?
A device that increases or decreases the voltage of alternating current
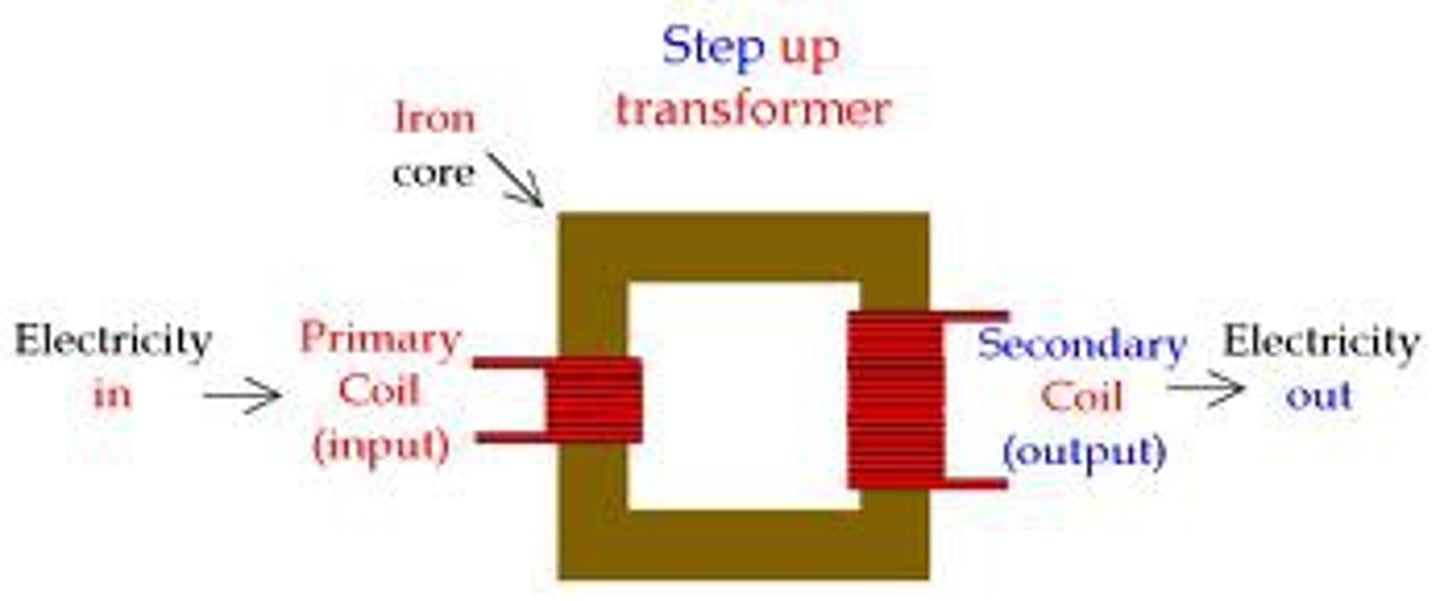
What is a step-up transformer?
a transformer that increases output voltage.
(Vs> Vp) & (Ns>Np)
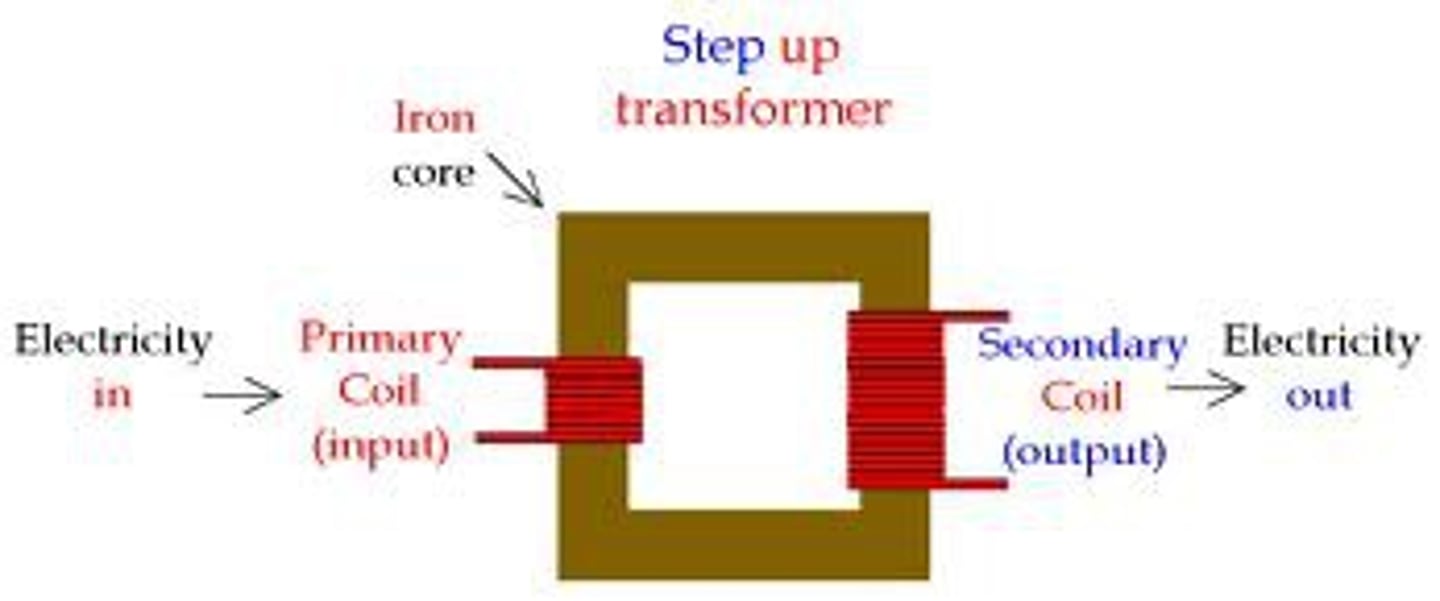
what is the equation for transformers?
Vp/Vs = Np/Ns