Lecture 8: HTML, CSS, JAVA
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
IP Address
32-bit address of a machine used to uniquely identify itself on the Internet which allows it to send information out and also receive information back to the correct location.

IPv6
newest version of IP address that assigns computers to 128-bit addresses

Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
a server whose role is to assign IP addresses to devices.
Domain Name System (DNS)
helps us translate IP addresses to more memorable names that are more human-comprehensible
router
job is to act as a traffic cop that allows data requests from all of the devices on your local network (your home or business, e.g.) to be processed through a single IP address
Internet
an interconnected network comprised of smaller networks woven together and agreeing to communicate with one another
Internet Protocol (IP)/ Connectionless protocol
the protocol for getting information from a sending machine to a receiving machine, but delivery is not guaranteed.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
directing the transmitted packet to the correct program on the receiving machine, guarantees delivery by including information about how many packets the receiver should expect to get, and in what order, and transmitting that information alongside the data
TCP/IP
identifies both where the receiver is and what the packet is for
Steps of the TCP/IP process

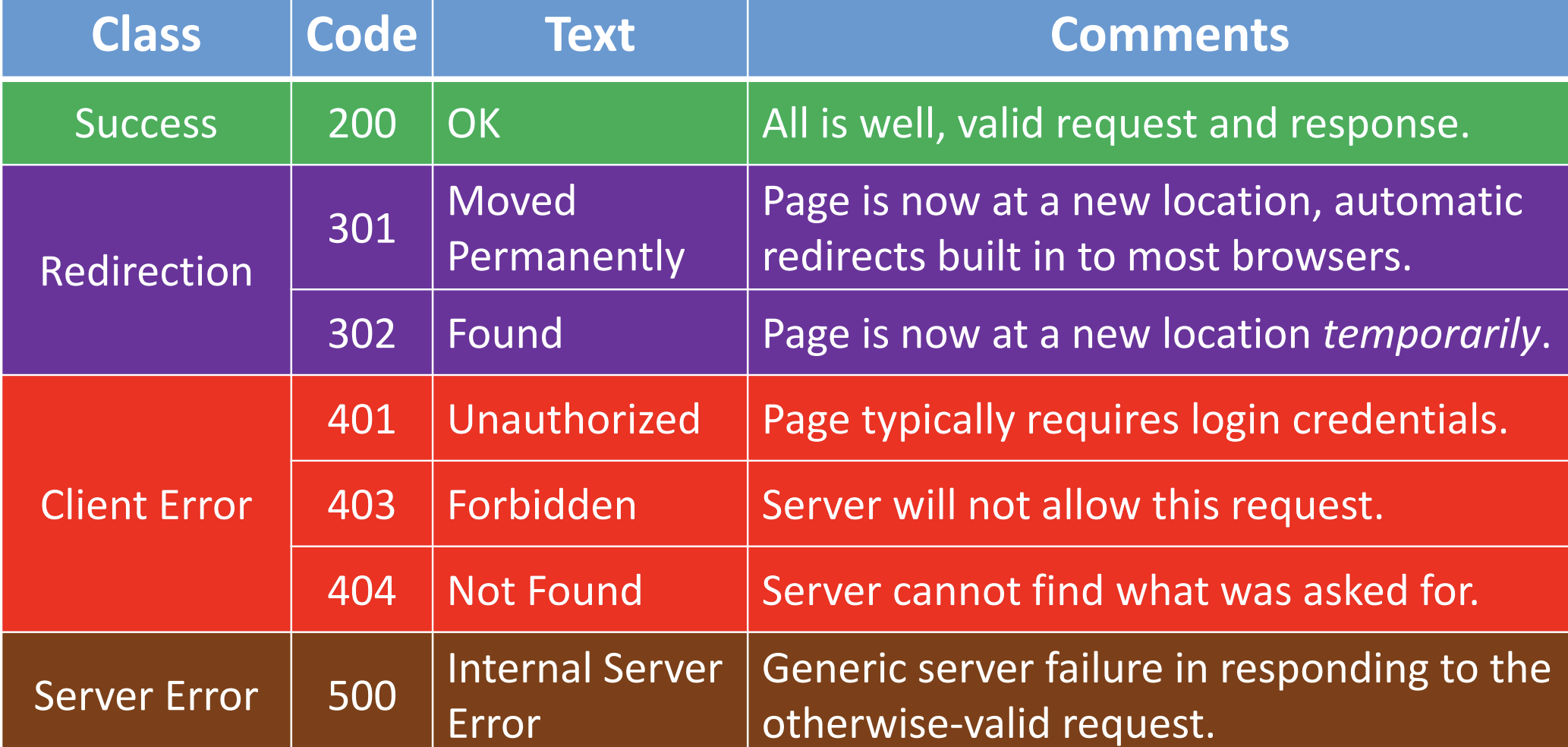
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
an application layer protocol that specifically dictates the format by which clients request web pages from a server, and the format via which servers return information to clients.
Status code
part of the first line that a server will use to respond to an HTTP request.
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language)
a markup (not programming) language that uses angle-bracket enclosed tags to semantically define the structure of a web page, causing the plain text inside of sets of tags to be interpreted by web browsers in different ways.
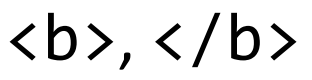
Text between these HTML tags will be rendered in boldface by the browser.
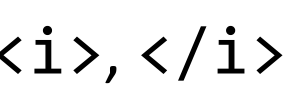
Text between these HTML tags will be rendered in italics by the browser
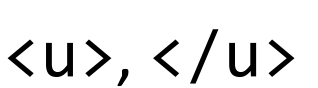
Text between these HTML tags will be rendered underlined by the browser.
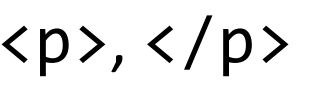
Text between these HTML tags will be rendered as a paragraph by the browser, with space above and below.
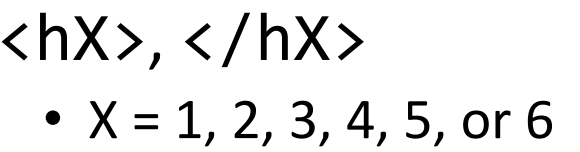
Text between these HTML tags will be rendered as an X-level section header.
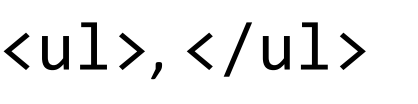
HTML tags that demarcate the beginning and end of an unordered (bulleted) list.
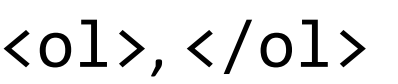
HTML tags that demarcate the beginning and end of an ordered (numbered) list
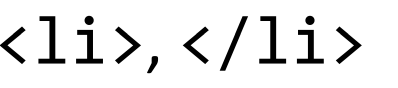
HTML tags that demarcate list items with an ordered or unordered list.
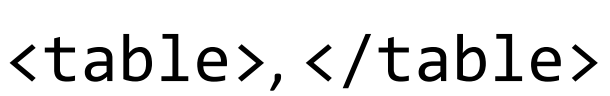
HTML tags that demarcate the beginning and end of a table definition.
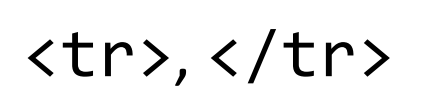
HTML tags that demarcate the beginning and end of a row within a table.
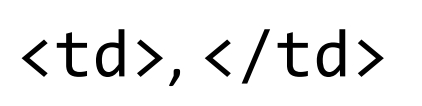
HTML tags that demarcate the beginning and end of a column within a row within a table
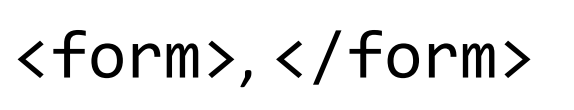
HTML tags that demarcate the beginning and end of an HTML form.
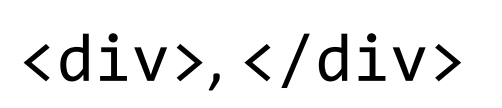
HTML tags that demarcate the beginning and end of an arbitrary HTML page division.
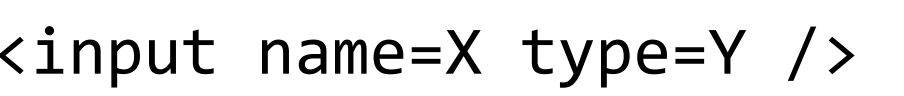
HTML tags that define a field within an HTML form. X is a unique identifier for that field, Y is what type of data it accepts.
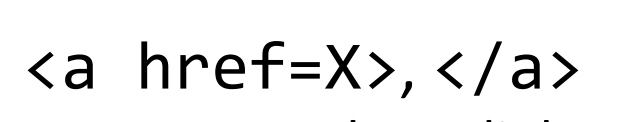
HTML tag that creates a hyperlink to web page X, with the text between the tags rendered and functional as the link text.
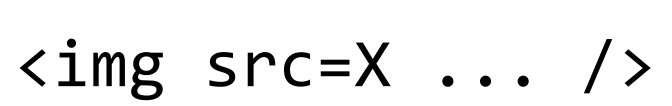
HTML self-closing tag that is for displaying an image located at X, with possible additional attributes (such as specifying width and height).

HTML tag that specifies to HTML5, lets the browser know that’s the standard you’re using
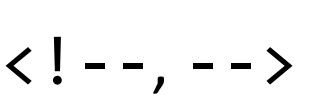
HTML tag that demarcate the beginning and end of an HTML comment.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
styling language/tool used to customize our website’s look and feel with its syntax describes how certain attributes of HTML elements should be modified
How is a style sheet constructed?
by identifying a selector and then an open curly brace to indicate the beginning of the style sheet for that selector. In between the curly brace you place a list of key-value pairs of style properties and values for those properties, each declaration ending with a semicolon. Then a closing curly brace terminates the style sheet
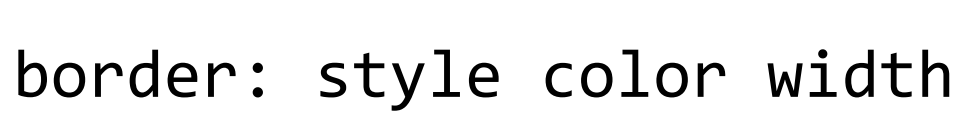
CSS property that applies a border of the specified color, width, and style (e.g., dotted, dashed, solid, ridge…).

CSS property that sets the background color. Some colors are pre-defined in CSS.
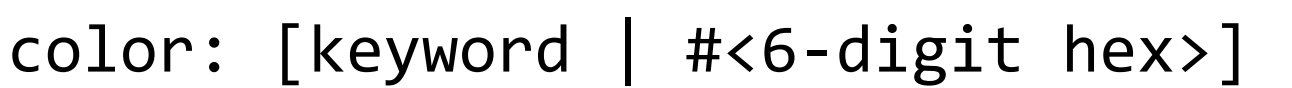
CSS property that sets the foreground color (usually text).
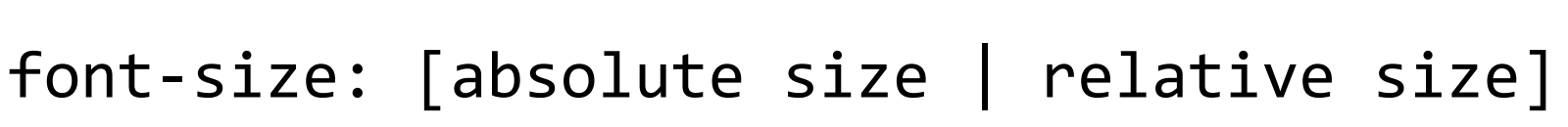
CSS property where you can use keywords (xx-small, medium…), fixed points (10pt, 12pt…), percentage (80%, 120%), or base off the most recent font size (smaller, larger).

CSS property where certain “web safe” fonts are pre-defined in CSS.

CSS property for displaying text
tag selector in CSS
will apply to all elements with a given HTML tag

ID selector
will apply only to an HTML tag with a unique identifier

class selector
will apply only to those HTML tags that have been given identical “class” attributes.

Style sheets can be written in..
both directly into your HTML (Place them within <style tags) within your page’s head) and as separate CSS files and then linked in to your document (use <link> tags within your page’s head)
Javascript
A high-level, client-side scripting language created in 1995 that works alongside HTML and CSS to build interactive websites.
.js file
File extension for JavaScript source code.
Client-side scripting
JavaScript code that runs in the user's browser rather than on the server.
<script> tag
HTML tag used to embed or link JavaScript in a webpage.
src attribute in <script>
Specifies the external JavaScript file to include in an HTML page.
Variable declaration in JavaScript
Use var, let, or const to declare variables; var is the traditional keyword.
var
A keyword used to declare a variable (function-scoped).
Anonymous function
A function without a name, often used as arguments to other functions.
Callback function
A function passed to another function to be called at a later time (e.g., after an event).
map()
An array method that creates a new array by applying a function to each element.
shift()
Removes the first element from an array.
Object
A collection of key-value pairs. Similar to a struct in C or a dictionary in Python.
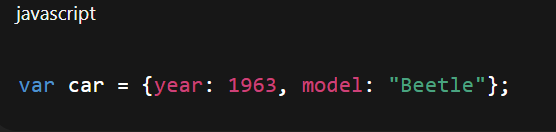
Property
A named value inside an object.
console.log()
A function used to print output to the browser console.
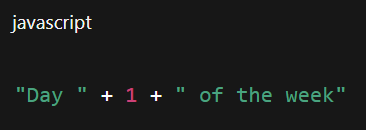
String concatenation
Joining strings with +
parseInt()
Converts a string to an integer in JavaScript
Event
An action or occurrence (like a mouse click or keypress) that JavaScript can respond to.
Event handler
A function that runs in response to a specific event.
onclick attribute
An HTML attribute that binds a JavaScript function to a click event.
event object
Contains data about the event, such as the element that triggered it.
event.srcElement
Identifies which HTML element initiated the event.