1.2 metals
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
meal can divide into
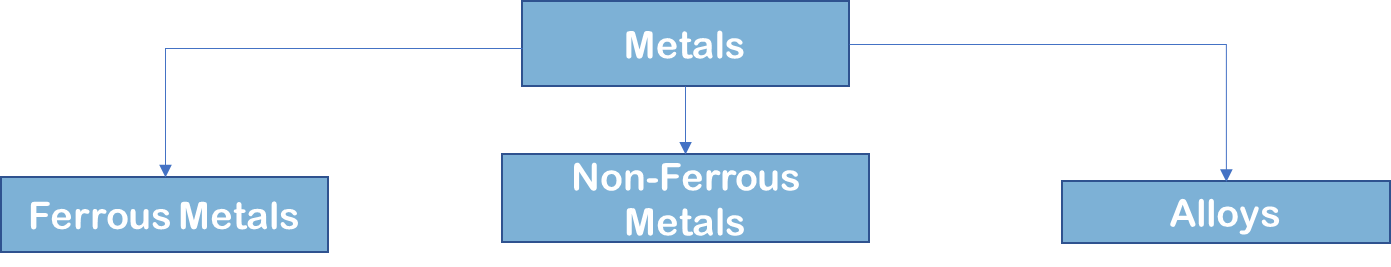
waht is a ferrous metal

wht is a non ferrous metal

alloys are

eg ferrous metls

eg non ferrous metals

eg alloys

25% of the Earth’s crust is made up of
metal ores
) is the most common.
(Bauxite
the second most common.
Iron
Ore Iron
Magnetite, Haematite
Ore Copper
Chalcopyrite
OreAluminium
Bauxite
Ore Lead
Galena
Ore Tin
Cassiterite
Zinc
Zinc Blende
from Iron Ore which is one of the easiest to separate from its ore
using a blast furnace to melt the ore leaving the waste (slag) to float to the top.
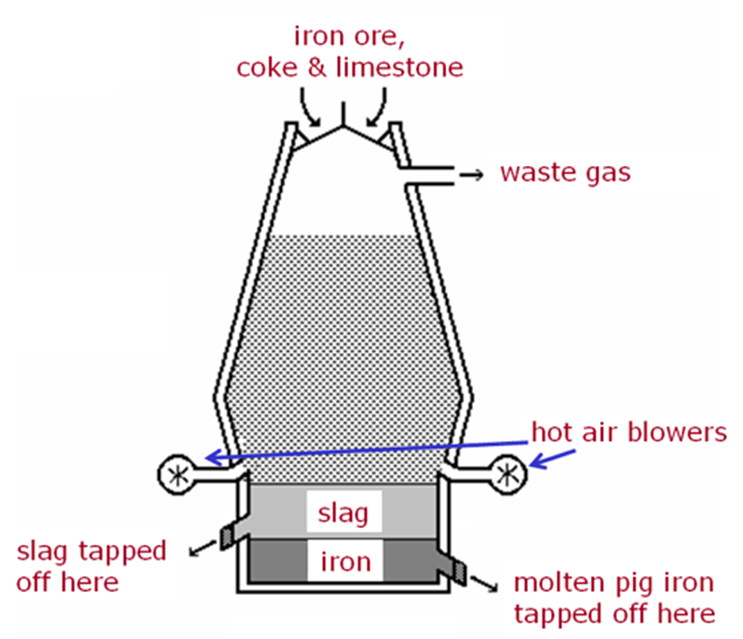
A blast furnace
When Iron is separated from its ore it is know as
Pig Iron
as Pig Iron. This is a very high carbon Iron
3.5-4.5%
Wrought Iron carbon Iron
0.04-0.08% Carbon
Wrought Iron
building material for bridges, fencing, gates and structures as a large as the Eiffel Tower.
Pig Iron It is brittle . unless
it is heat treated to make it malleable
Cast iron is used to make
anvils and cast engine casings.
As the carbon amount is increased so too
so too are the hardness properties of the Steel
However, larger amounts of carbon (over 2%) render the iron
brittle as in Pig and Cast Iron
Mild Steel, sometime known as
Bright Drawn Mild Steel (BDMS
(BDMS used where
is used for the majority of metal construction work from girders in building to the casing on your fridge, from the body of a car to the legs on a table
bdms is iron and
plus 0.15 to 0.3% carbon.
The addition of 0.3-0.7% Carbon produces
Medium Carbon Steel
Medium Carbon Steel used when
which is used for springs and general gardening tools. It is also referred to as Tool Steel
High Carbon Steel
0.7-1.7% Carbon
High Carbon Steel=?
as High Speed Steel (HSS)
as High Speed Steel (HSS) used when
) and is used for tools, cutting and drilling bits, blades etc.
Properties Cast Iron
Hard outer skin but brittle 3.5% carbon content
Properties Mild Steel (low carbon)
Ductile, high tensile strength 0.15-0.3% carbon content
Properties Medium Carbon Steel
Harder than mild steel but less ductile. 0.3-0.7% carbon
Properties High Carbon Steel
Harder than Medium Carbon Steel 0.7-1.7% carbon content
Applications Cast Iron
Engine blocks, disc brakes, cooking pans
Applications Mild Steel (low carbon)
Chair legs, bolts, appliance housings, car bodies
Applications Medium Carbon Steel
Gardening tools
Applications High Carbon Steel
Cutting tools
Processing of Bauxite into Aluminium is difficult and requires a great deal
•of energy.
Aluminium is often 3-4 times more expensive
•than steel.
Aluminium is a third
of the weight of steel
Aluminium is roughly half
as strong as steel.
Copper melts at
1083 degrees
Tin melts at
232 degrees C
Tin Mixed with Lead
to make Solder
Lead is a
very soft but heavy material.
Lead is Often used as
flashing in buildings where the roof meets the wall.
Zinc is used primarily for
coating steels which is known as galvanizing.
Titanium is also classed as a
a modern material.
Titanium has the highest
strength to weight ratio of metals.
Titanium is used in
in high performance sports equipment and in spectacle frames.
Silver melts at
960 degrees C.
Gold melts at
1063 degrees C.
Platinum melts at
1755 degrees C.
Properties Aluminium
Lightweight, ductile, malleable, corrosion resistant
Properties Copper
Ductile, malleable, tough, corrosion resistant, can be soldered
Properties Zinc
Low melting point, god corrosion resistance
Properties Lead
Heavy, soft, malleable
Properties Tin
Ductile, malleable, low melting point, corrosion resistant
Properties Titanium
Hard, stronger than steel but more lightweight
Properties Gold/silver/platinum
Malleable, ductile, corrosion resistant
Applications Aluminium
Drinks cans, aircraft parts, bike frames, MacBook
Applications Copper
Electrical wire, water and gas pipes
Applications Zinc
Galvanising steel, intricate die casting
Applications Tin
Soft solder, coatings for food cans
Applications Titanium
Joint replacements, toot implants, high performance sports equipment
Applications Gold/silver/platinum
Jewellery, electronic components (gold), plating
Applications Stainless Steel
Sinks, kitchenware, cutlery
Properties Stainless Steel
Tough, hard. 18% chrome, 8% nickel
Properties High Speed Steel
Hard, tough, heat resistance 18% tungsten, 4% chromium, 1% vanadium
Properties Die Steel
Hard, tough with carbon, chromium and tungsten depending on grade
Properties Bronze
Tough, corrosion resistant, 90% copper, 10% tin
Properties Brass
Corrosion resistant, good electrical and thermal conductivity. 65% copper, 35% zinc
Properties Duralumin
Equivalent strength to steel but lightweight and ductile 4% copper, 1% magnesium and manganese
Properties Pewter
Malleable, low melting point. 85-99% tin with copper and antimony
Applications Stainless Steel
Sinks, kitchenware, cutlery
Applications Die Steel
Blanking punches and dies, extruder dies, press tools
Applications Bronze
Statues, coins, bearings
Applications Brass
Boat fittings, furniture, valves, ornaments
Applications Duralumin
Aircraft and vehicle parts
Applications Pewter
Tankards, decorative items, trophies
Brass is a mixture of
Copper and Zinc (35%).
Bronze is a mixture of
Copper and Tin (10%).
Duralumin is an
Aluminium alloy
Duralumin contains
4% Copper, 1% Manganese and 0.1% Magnesium.
Duralumin is stronger than
Aluminium yet lighter
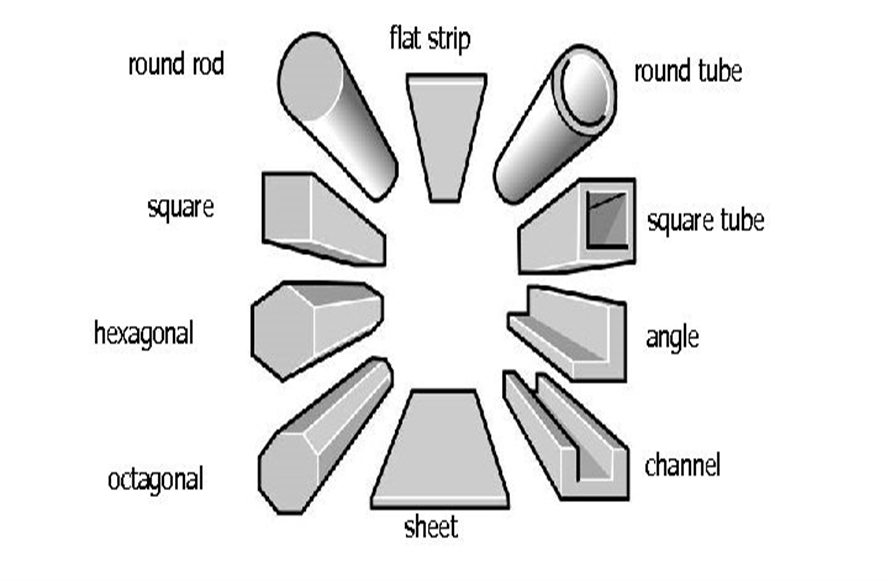
metal stock forms