Heme Lab Final Review Complete
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Clinical significance of Prolonged Bleeding Time
Indicates primary hemostasis issues like dysfunctional platelets or decreased platelet count.
What are the 2 primary bleeding time methods
Ivy
Duke
Ivy Method
Most common bleeding time method using a blood pressure cuff.
Duke Method
less invasive bleeding time method without a blood pressure cuff.
Manual Platelet Count
Counting platelets in multiple fields and calculating the average number per field.
Manual platelet count steps
Count plts in one HP.
Move to another field and count.
5-10 diff fields need to be counted.
Calculate avg number of plts per field.
Multiple your avg by 17,000
What Causes Errors in Automated Platelet Counts
Microcytes and schistocytes may be miscounted as platelets
Platelet clumps or large platelets can be miscounted as white or red blood cells.
Increasing Blood Smear Angle will
make a thicker, shorter smear.
Decreasing Blood Smear Angle will
Make thinner, longer smear
Cause of blue or dark Blood Smear Stain
too thick film
prolonged staining inadequate washing
high pH
Causes of too pink or light of a blood smear stain
Insufficient staining time
Prolonged washing time
Too low pH of stain or buffer
Coagulation Testing Specimen of Choice
Citrated plasma (light blue top).
PT Test Reagents
Tissue factor and calcium.
APTT Test Reagents
Phospholipid-rich preparation
Activator
Calcium chloride.
ACLTOP Coag Testing Principles
Turbidimetric, chromogenic, and immunologic.
How is fibrin clot detected by turbidemetry?
As clot formation takes place, light transmission decreases
Direct chromogenic measurement
Analyte acts directly on specific chromogenic substrate (Protein C)
Indirect chromogenic measurement
analyte of interest reacts under optimized test conditions.
Measures residual enzyme activity then measured using spec synthetic substrate conjugated with chromophore (e.g. heparin, antithrombin).
Immunological vs Turbidimetric are similar except that
Immunological measures Ag-Ab immune complexes.
INR Calculation
Standardizes results for patients on Coumadin
Increased INR indicates
Warfarin/Coumadin use.
Urea test result for normal sample
clot will not be dissolved after 24 hours
Urea solubility test principle
determines if pt sample is factor XIII deficient by placing clot in 5m urea
Urea test result for factor XIII deficiency
clot will dissolve in <24 hours
D-Dimer Formation
Cross-linked D fragments; increased D-dimer indicates cross-linked fibrin breakdown.
FDP Latex Agglutination detects
fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products
D-Dimer assay is specific for
blood-clotting problems.
Stabilized fibrin clot is degraded (support Dx of DIC)
What is the reagent of the FDP latex agglutination assay?
PT
Prolonged PT factors
VII
Prolonged PTT factors
XII, XI, IX, VIII
Prolonged PT and PTT
X, V, II, I
ESR principle
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
how fast the RBCs settle down the tube from plasma.
ESR Monitoring is used for
Rheumatoid arthritis, malignancy, multiple myeloma, bacterial infection, inflammatory disease
What can cause false positives in ESR
anemias, pregnancy, hyperfibrinogenemia states, increase in Igs, poikilocytosis
Cyanmethemoglobin Method principle
Manual hgb determination method using color intensity.
Erythrocytes are lysed by a stomatolytic agent in the presence of surfactant.
hgb released into solution.
hgb oxidized by methemoglobin by ferricyanide.
Methemoglobin is converted to stable cyanmethemoglobin by addition of KCN.
abs measured.
color intensity proportional to hgb conc.
WBC Count Formula using hematocytometer
WBC count = [WBC counted (N)/Volume (V)] X dilution factor
Volume = 4 X (1 X 1 X .1) = 0.4 mm^3
WBC Count = (N/V) X dilution factor = (N/0.4) X 20
RBC Count Formula using hematocytometer
RBC count= [RBC counted (N)/volume (V)] X dilution factor
Volume= 5 X (0.2 X 0.2 X 0.1) =0.02 mm3
RBC count = (N/V) X dilution factor = (N/0.02) X 200
VCS System of cell counting components
Volume, Conductivity, Scatter
VCS Volume principle
VCS utilizes the Coulter Principle of direct current (DC) impedance to physically measure the volume. This method accurately sizes all cell types regardless of their orientation in the light path.
VCS Conductivity principle
Alternating current short circuits the bipolar lipid layer of the membrane. Highfrequency electromagnetic probe determines the conductivity. Collects internal structure information, including chemical composition and nuclear volume.
VCS Scatter principle
Laser beam technology is used to scatter light. Multiple angle light scatter signals are collected an measured. Measures cellular granularity, nuclear lobularity, and cell surface structure.
How are RBC morpholologies quantified?
1+ - 4+
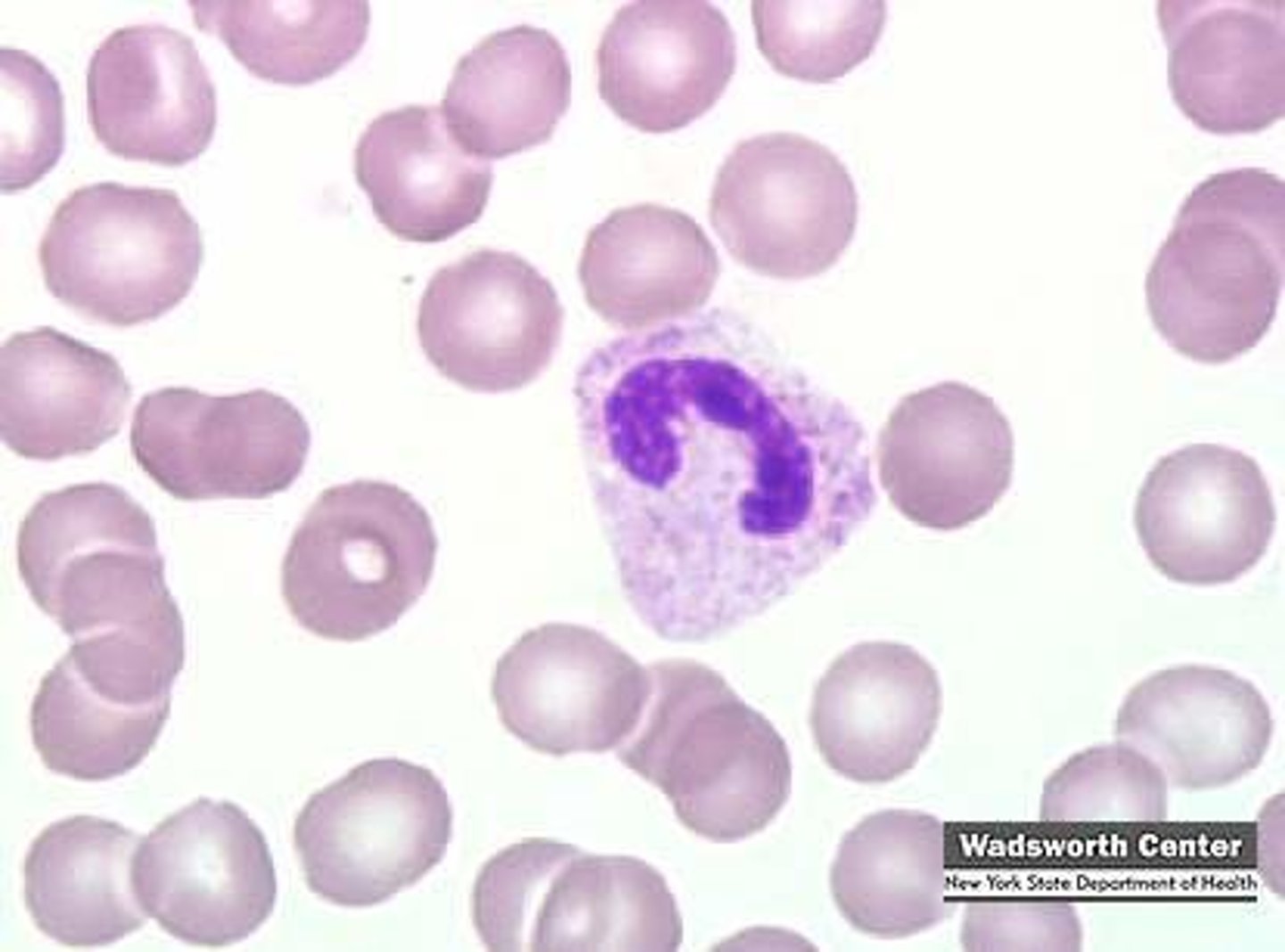
Band
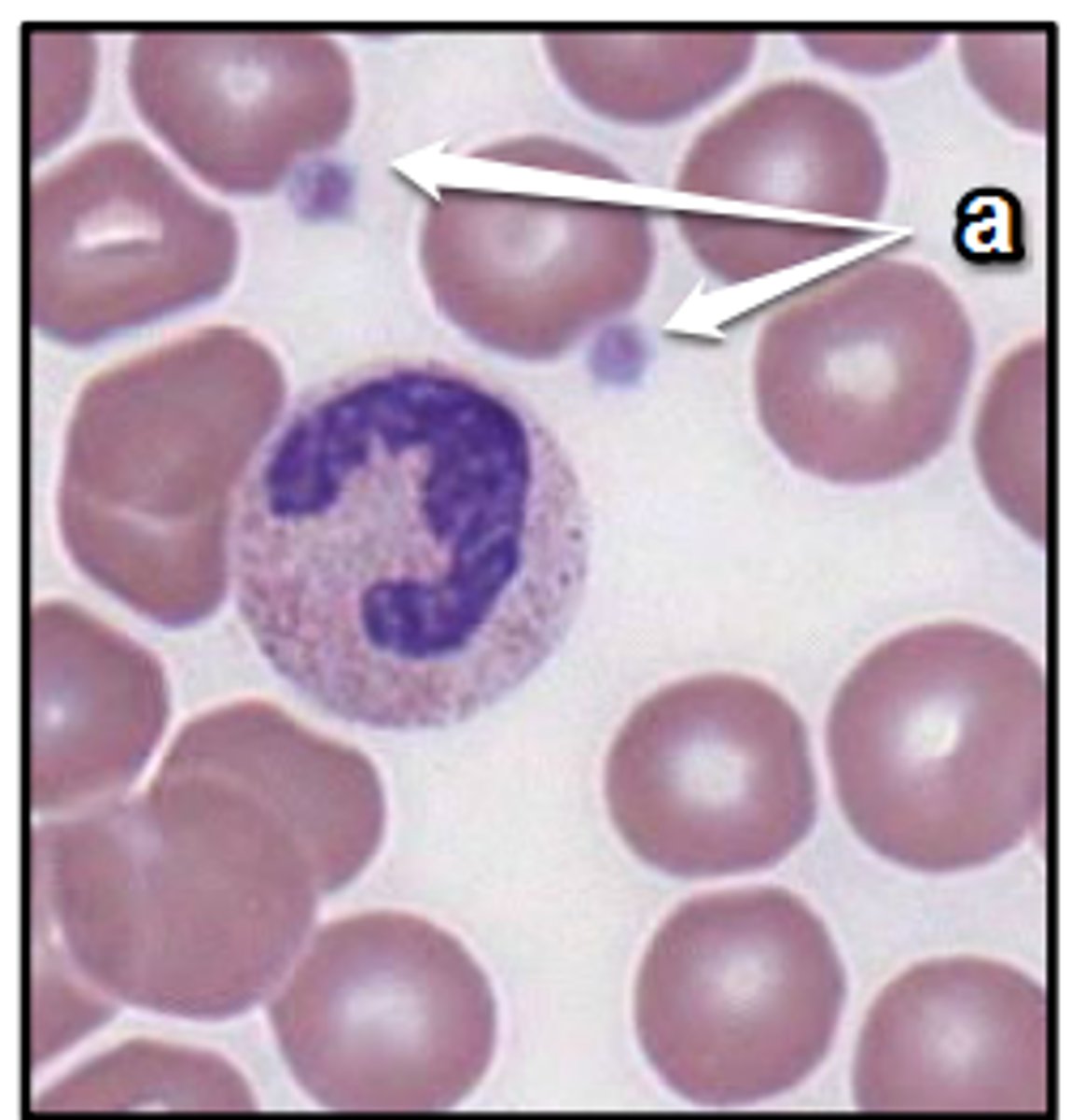
Platelet
Seg
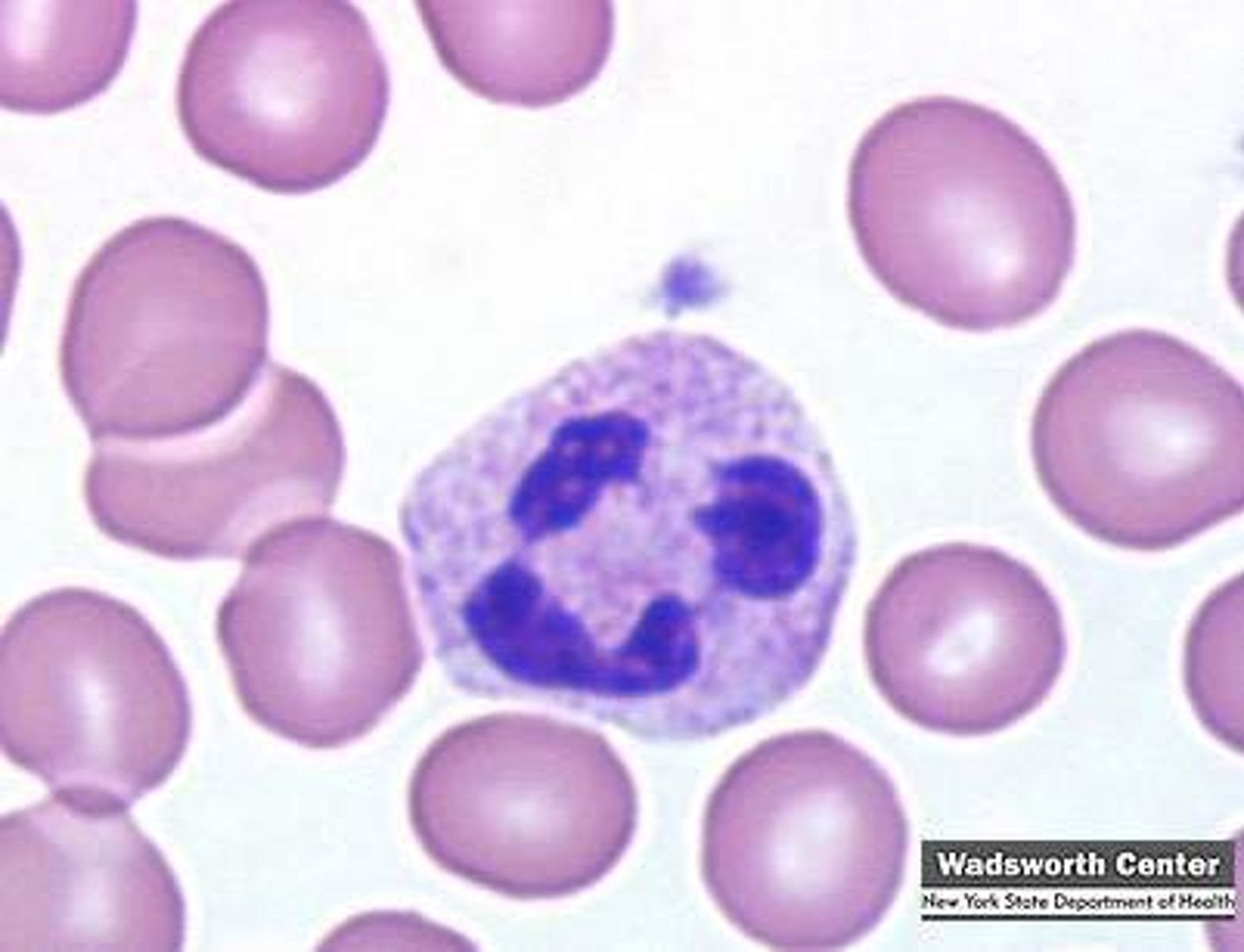
Eosinophil
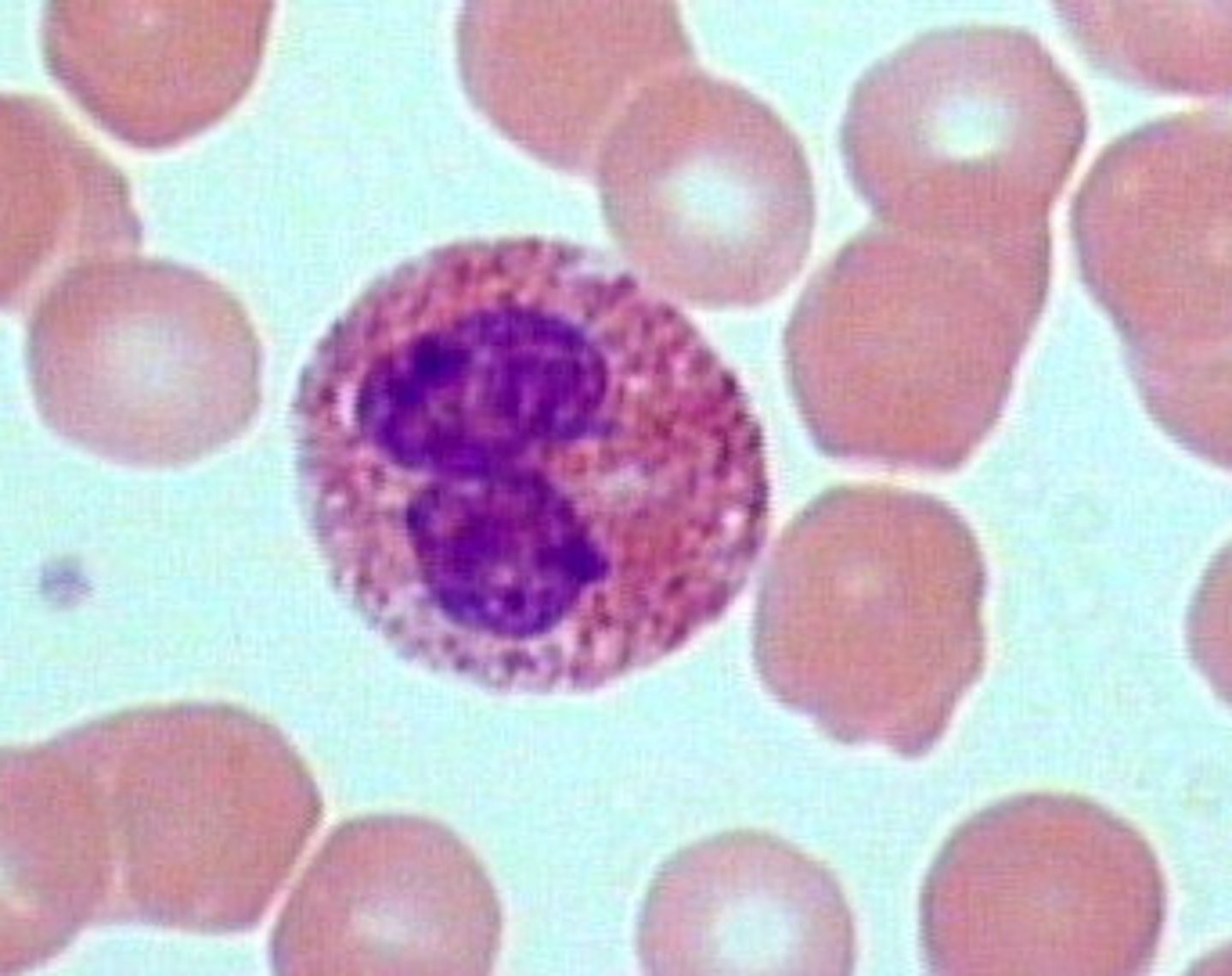
Basophil
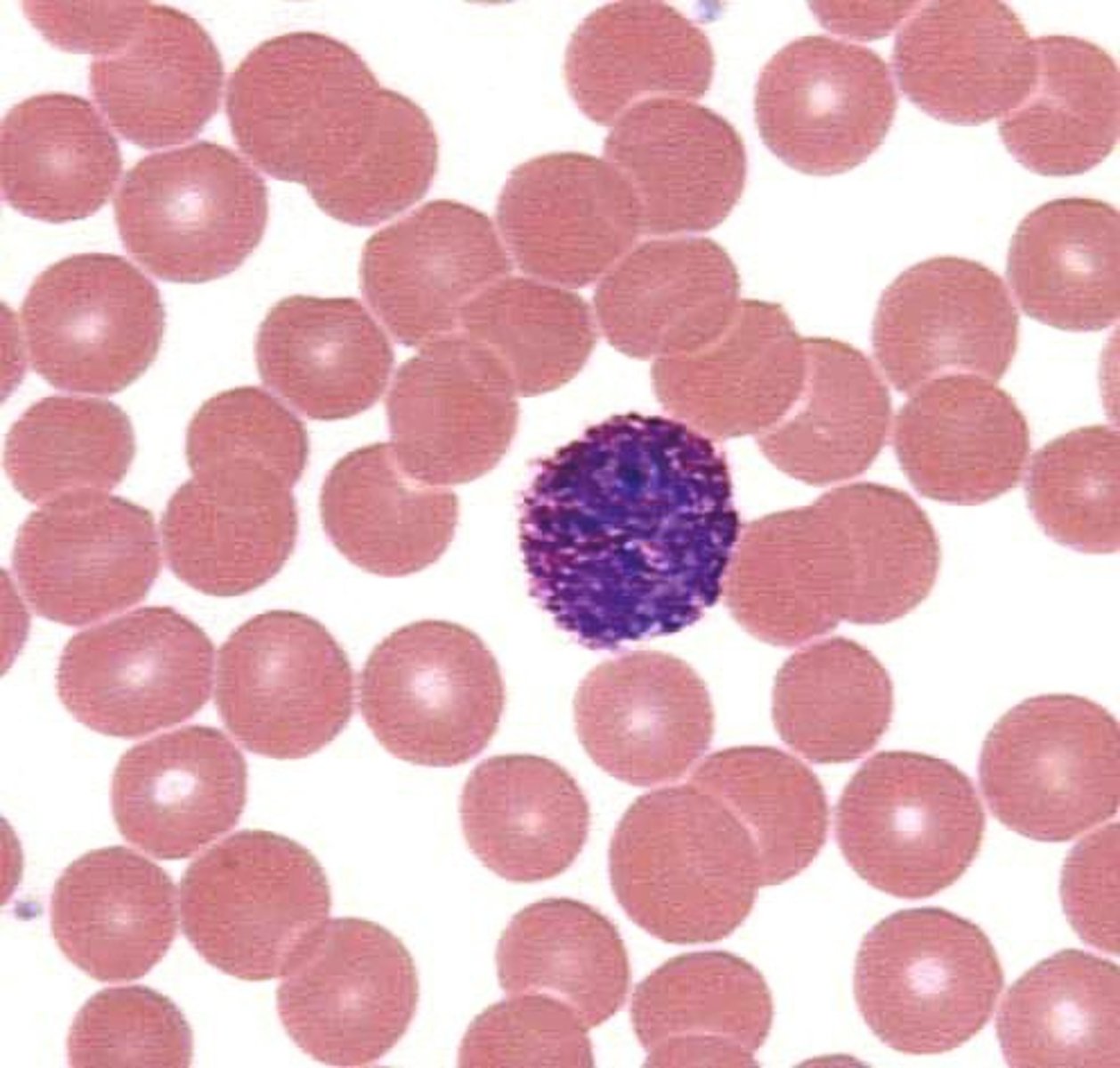
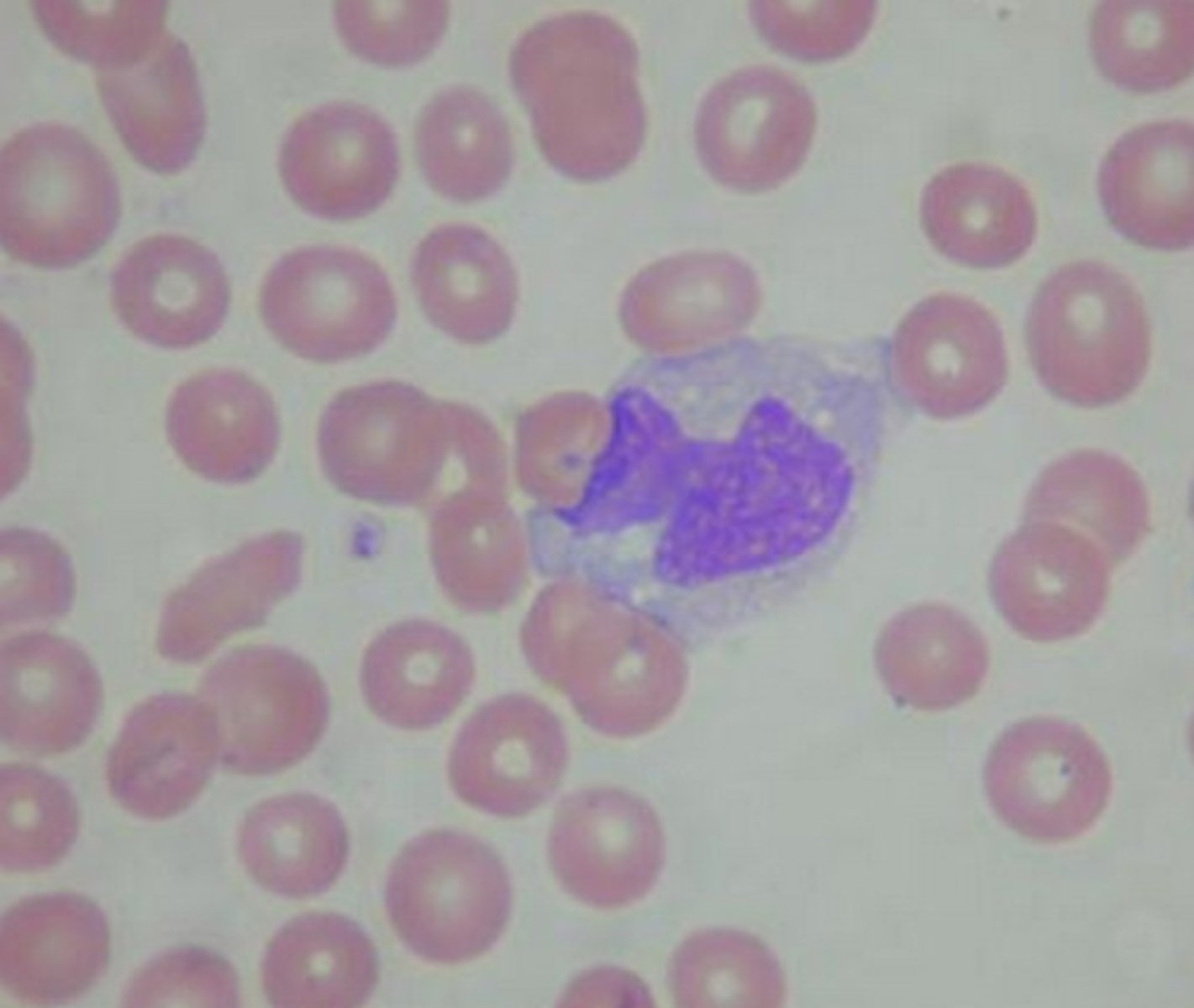
Monocyte
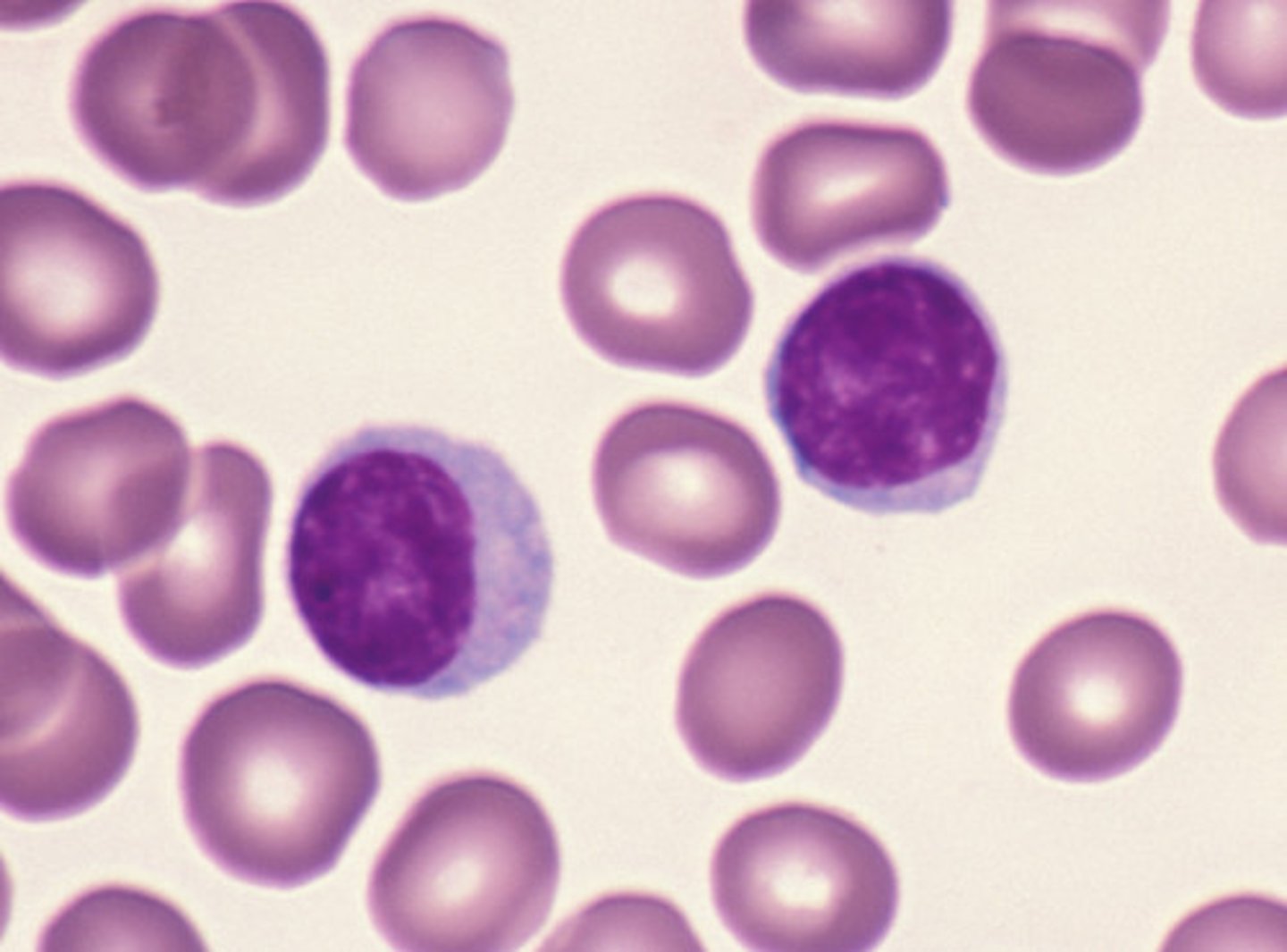
Lymphocyte
WBC (Total)
3.6-10.6 x 10^3/µL.
Neutrophils (absolute)
1.7-7.5 x 10^3/µL.
Neutrophils (relative)
50-70%.
Lymphocytes (absolute)
1.0-3.2 x 10^3/µL.
Lymphocytes (relative)
18-42%.
Monocytes (absolute)
0.1-1.3 x 10^3/µL.
Monocytes (relative)
2-11%
Eosinophils (absolute)
0-0.3 x 10^3/µL.
Eosinophils (relative)
1-3%.
Basophils (absolute)
0-0.2 x 10^3/µL.
Basophils (relative)
0-2%.