[14] Transport in Humans
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
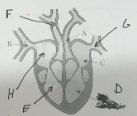
name A and its function
aorta - takes oxygenated blood to the body
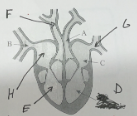
name B and its function
vena cava - carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart
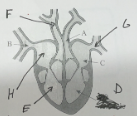
name C and its function
left atrium - to receive oxygenated blood from the lungs and pump it to the left ventricle
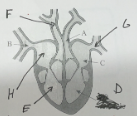
name D and its function
left ventricle - to pump oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
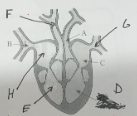
name E and its function
right ventricle - to pump deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated
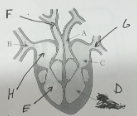
name F and its function
pulmonary artery - to carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated
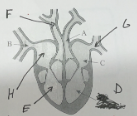
name G and its function
pulmonary vein - carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart, where it's then pumped to the rest of the body
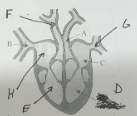
name H and its function
right atrium - receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle
why is the wall of the left ventricle thicker than the wall of the right ventricle (4)
the left ventricle pumps blood to the whole body so it has a very muscular wall which is thicker. The right ventricle only pumps to the lungs so it doesn’t have much muscle and so it is thinner.
Describe how deoxygenated blood from the body passes through the heart to reach the lungs (4)
deoxygenated blood arrives at the heart through the vena cava and enters the right atrium. The blood is pumped into the right ventricle which contracts to pump it to the lungs through the pulmonary artery
what is the role of arteries and veins (2)
arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart
are arteries or veins more elastic, why is _______ helpful in arteries (2)
artery is more elastic, arteries have more elastic fibers to allow them to expand s they carry blood under high pressure
two ways a student can tell which is a vein and an artery (2)
vein has a bigger wall, artery has a thicker wall
two substances that diffuse through capillary walls
oxygen and carbon dioxide
how the structure of a capillary is adapted for its function (6)
very small so they can carry blood close to any cell
They have permeable walls so substances can diffuse in and out of them.
Their walls are only one cell thick to increase the rate of diffusing by decreasing the distance over which it happens
which ventricle has higher blood pressrure and why? (2)
the left ventricle is under higher pressure than the right ventricle as it pumps blood to the whole body
4 components of blood
plasma
red blood cells
white blood cells
platelets
what part of blood is plasma
liquid part of blood mainly water
how have red blood cells have adapted to make them suitable to transport oxygen
they do not have a nucleus and have a biconcave disk structure to increase their surface area and flexibility, which helps them absorb oxygen and pass through small capillaries
what are two types of white blood cells and what do they do
phagocytes - engulf and digest foreign particles
lymphocytes - release antibodies to fight disease, recognize antigens, stimulate immune response
what can lymphocytes do
lymphocytes can release antibodies which can become memory cells they can also recognize antigens and stimulate immune response
what are platelets and what do they do?
cell fragments that help blood clots form they stop bleeding when blood vessels are injured
how do blood clots form
fibrin protein molecules form a mesh, which traps platelets and red blood cells plugging a hole in the blood vessel wall preventing blood loss platelets help clot form
what is the structure of an artery? what does the lining look like and what does it help with?
thick artery wall containing elastic and muscle fibers
smooth lining promotes fast flow of blood through small lumen of artery
where do arteries carry blood and at what speed and pressure and WHY??
arteries carry blood away from the heart at high speed under higher pressure because they receive blood directly from the heart from its powerful contractions
what happens when the heart contracts its muscular wall
arteries pressure fluctuates
what do arteries branch into, what are the diameters of these said branches? why is this helpful?
branch into arterioles, the diameter of the arterioles can vary by the action of muscle fibers in their walls which can be used to adjust the pressure in the circulatory system as well as to divert blood from one organ to another
what do arterioles branch into (2)
the arterioles branch into the capillaries, by which stage the blood is moving slowly under lower pressure
what is the structure of the veins
thin vein wall containing no muscle fibres, large lumen to reduce resistance to flow of blood under low pressure, valves in the lumen.
describe how thickness of the capillary wall can help
a single layer of cells form wall of capillary, substances diffuse across capillary wall into and out of plasma,
describe where capillaries are found
the tissues of the body
why are the walls of the capillaries one cell thick
so that diffusion of gases and other substances can take place through the thin capillary wall, between the plasma and fluid surrounding the cells of the tissues in the body
pulmonary has got to do with what organ?
the lungs
describe 4 factors that make coronary heart disease more likely
heredity - some people inherit a tendency to develop coronary heart disease
high blood pressure - puts more strain on the heart
diet - eating large amounts of saturated fat can lead to fatty deposits forming inside arteries, which can lead to coronary heart disease
smoking - increases blood pressure which can cause damage to the inside of coronary arteries, chemicals in cigarette can damage coronary arteries making it more likely that fatty deposits will form
what is coronary heart disease
when the coronary arteries that supply blood to the muscle of the heart get blocked by layers of fatty material building up
what organ does hepatic got to do with
the liver
what organ does the word renal got to do with
the kidneys
which blood vessel carries blood from the kidneys
which blood vessel carries blood to the kidneys
renal vein
renal artery
which blood vessel carries blood from the liver
which blood vessel carries blood to the liver
hepatic vein
hepatic artery
which blood vessel carries blood from the gut/belly to the liver
hepatic portal vein
where can coronary arteries be found
outside of the heart
name 4 things that plasma transports around the body
urea
minerals
glucose
carbon dioxide
how does the heart rate change during exercise or with adrenalnie
why do humans need a circulatory system
humans have a low volume to surface area ratio so we need a circulatory system we can not rely of diffusion
what is the blood mostly?
plasma
which is the biggest type of white blood cell
phagocytes
which vein links from the liver to the vena cava
hepatic vein
how does vaccination help the body to fight pathogens
vaccines stimulate immune response leading to the production of antibodies and the formation of memory cells that remember the pathogen for swift future responses.
what is the function of semi lunar valves
to prevent backflow of blood from arteries into the ventricles