Anatomy Final
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/140
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomy
The study of structure and shape of the body and its parts
2
New cards
Physiology
Study of how the body and its parts work or function. (structure determines what functions can occur)
3
New cards
Gross Anatomy
Easily observable; large structures - stomach, small intestine, large intestine.
4
New cards
Microscopic Anatomy
Structures are too small to be seen with the naked eye; Cells and tissues can be viewed only with a microscope.
5
New cards
Levels of Structural Organization
* Atoms
* Cells
* Tissues
* Organs
* Organ Systems
* Organisms
* Cells
* Tissues
* Organs
* Organ Systems
* Organisms
6
New cards
Survival Needs
Water, Normal Body Temp, Nutrients, Oxygen Atmospheric pressure
7
New cards
Superior
toward the head or upper part of the body (above)
8
New cards
Other Names for Superior
cranial or cephalic
9
New cards
Inferior
away from the head or lower part of the body (below)
10
New cards
Other Names for Inferior
caudal
11
New cards
Anterior
toward the front of the body (infront of)
12
New cards
Other Names for Anterior
ventral
13
New cards
Posterior
toward the backside of the body (behind)
14
New cards
Other Names for Posterior
dorsal
15
New cards
Medial
toward the midline of the body (inner side)
16
New cards
Lateral
away from the middle of body (outer side)
17
New cards
Intermediate
between a more medial, lateral structure
18
New cards
Proximal
close to the origin of the body/head (attachment points like arms and legs)
19
New cards
Distal
farther from the attachment point (attachment points like arms and legs)
20
New cards
superficial
is towards the surface of the body (skin is most superficial)
21
New cards
deep
more internal/away from the body surface (inside)
22
New cards
Internal Body Cavities
Dorsal and ventral
23
New cards
Dorsal Cavity Subdivisions (posterior; BACK)
Cranial and Spinal
24
New cards
Cranial Cavity
Houses the brain; Protected by the skull
25
New cards
Spinal Cavity
Houses the spinal cord; Protected by the vertebrae
26
New cards
Ventral Cavity Subdivisions (anterior; FRONT)
Thoracic and Abdominopelvic
27
New cards
Thoracic Cavity
**Cavity superior to the diaphragm; Houses heart, lungs, and other organs**; Mediastinum, the central region, houses heart, trachea, and other organs; **Protected by the rib cage**
28
New cards
Abdominopelvic Cavity
**Cavity inferior to the diaphragm**
–Superior abdominal cavity contains the stomach, liver, and other organs; Protected only by trunk muscles
–Inferior pelvic cavity contains reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum; Protected somewhat by bony pelvis
–Superior abdominal cavity contains the stomach, liver, and other organs; Protected only by trunk muscles
–Inferior pelvic cavity contains reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum; Protected somewhat by bony pelvis
29
New cards
Abdominopelvic Cavity Subdivisions
Four Quadrants and Nine Regions
30
New cards
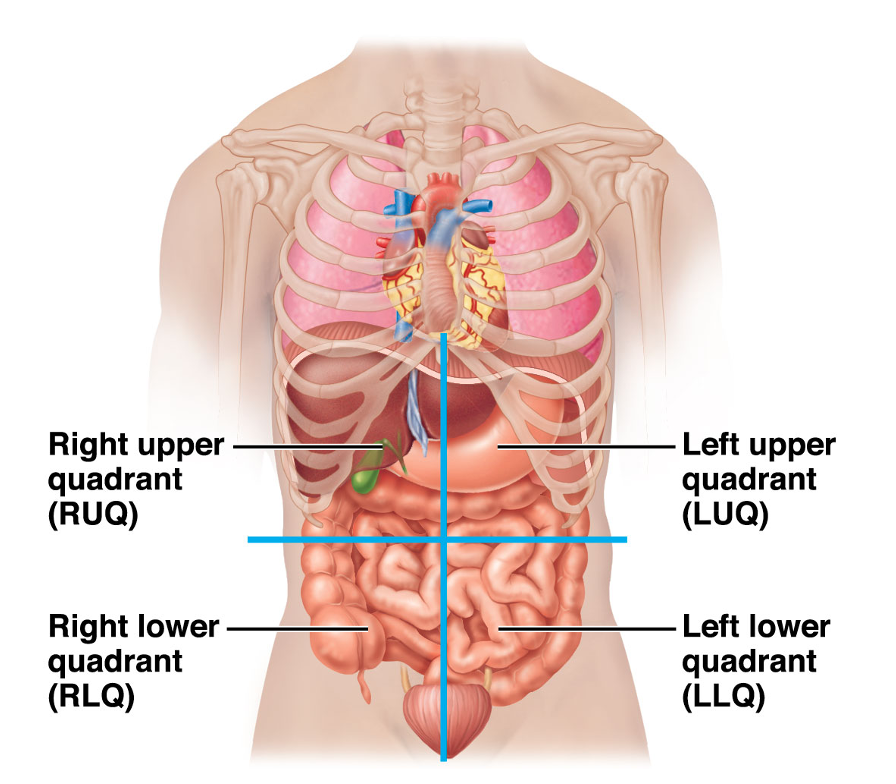
Four Abdominopelvic Quadrants
* abdominal and pelvic cavity are divided into four quadrants, anteriorly.
* A line runs from the sternum to the pubis and a second line that crosses horizontally by the navel creating
* the **right upper quadrant**, R U Q, the **left upper quadrant**, L U Q, the **right lower quadrant** R L Q, and the **left lower quadrant**, L L Q.
* A line runs from the sternum to the pubis and a second line that crosses horizontally by the navel creating
* the **right upper quadrant**, R U Q, the **left upper quadrant**, L U Q, the **right lower quadrant** R L Q, and the **left lower quadrant**, L L Q.
31
New cards
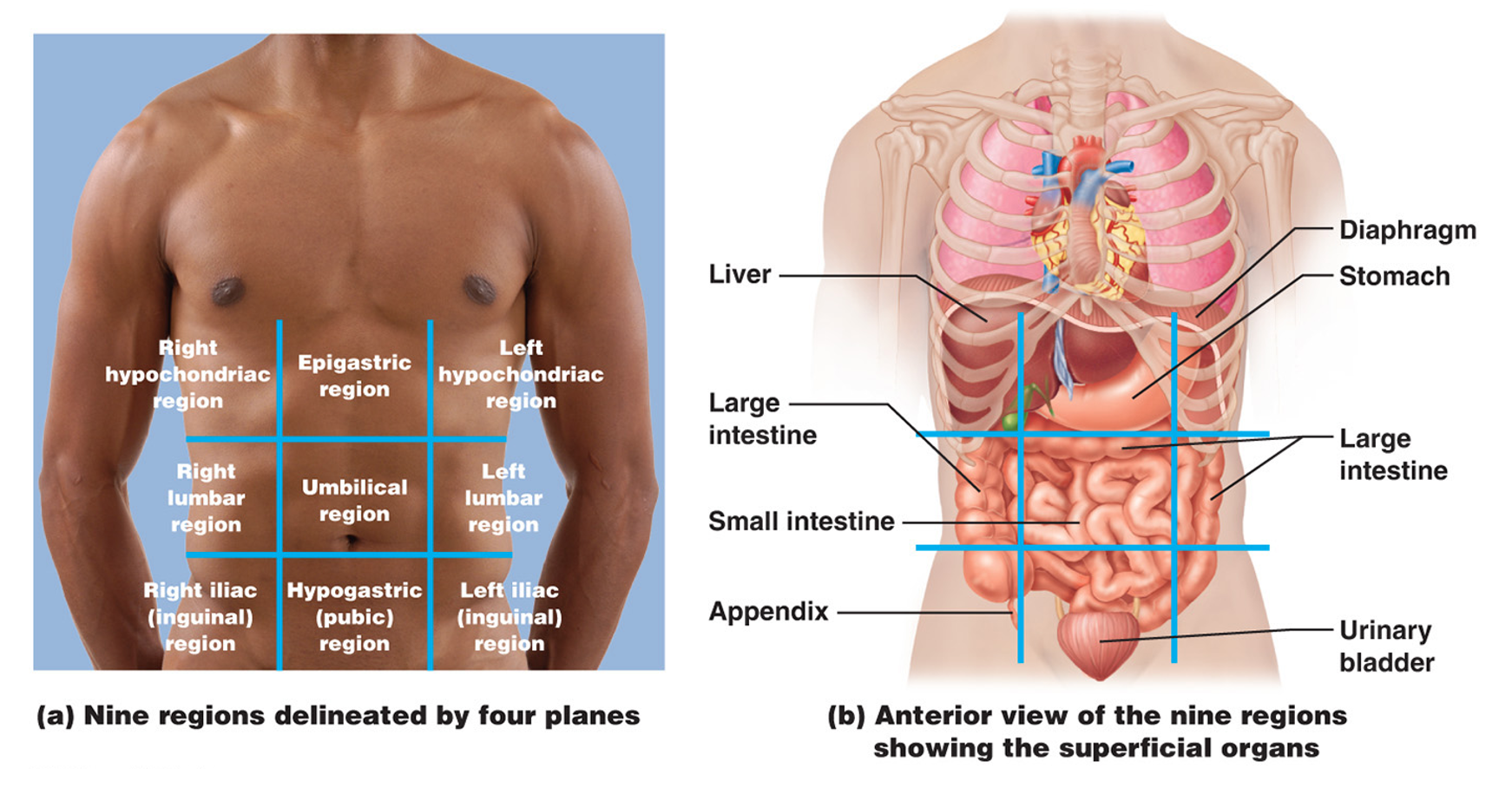
The Nine Abdominopelvic Regions
The nine regions are created by two midclavicular lines running down vertically, and two horizontal lines, one above the umbilicus and one below the umbilicus.
32
New cards
Right Hypochondriac Region
Right side top region; contains the liver
33
New cards
Epigastric Region
Middle top region; contains the stomach
34
New cards
Left Hypochondriac Region
left side top region; contains the diaphragm
35
New cards
Right Lumbar Region
Right side middle region; contains the large intestine
36
New cards
Umbilical Region
Middle region; Contains small intestine
37
New cards
Left Lumbar Region
left side middle region; contains large intestine
38
New cards
Right Iliac Region (inguinal region)
Right side bottom region; Contains the appendix
39
New cards
Hypogastric Region (pubic region)
bottom middle region; Contains the urinary bladder
40
New cards
Left Iliac Region (inguinal region)
Left side bottom region
41
New cards
Planes
cuts sections into imaginary lines
42
New cards
Body Sections
Transverse, Midsagittal, Frontal, Sagittal (4)
43
New cards
Transverse (cross) Section
divides the body into superior and inferior
44
New cards
Midsagittal (Median) Section
Divides the body into **equal** left or right
45
New cards
Frontal (coronal) Section
Divides the body into anterior or posterior (front and back)
46
New cards
Sagittal Section
divide the body into left or right parts
47
New cards
Body Systems
Endocrine, Urine, Cardiovascular, Skeletal, Muscle, Reproductive, Integumentary, Nervous, Lymphatic, Digestive
48
New cards
Endocrine System
* **Secretees chemical molecules, called hormones into the blood**
* Body functions controlled by hormones include: Growth, Reproduction, Use of nutrients
* Body functions controlled by hormones include: Growth, Reproduction, Use of nutrients
49
New cards
Urinary System
* Includes: kidneys, uterus, urinary bladder, and urethra.
* Maintains acid-base balance
* Regulates water and electrolyte balance
* Maintains acid-base balance
* Regulates water and electrolyte balance
50
New cards
Cardiovascular System
* Includes: heart and blood vessels.
* Blood transports: oxygen and carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones.
* Blood transports: oxygen and carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones.
51
New cards
Skeletal System
* Consists of bones, cartilages, ligaments, and joints.
* Provides muscle attachment for movement, Protects vital organs, Site of blood cell formation, Stores minerals
* Provides muscle attachment for movement, Protects vital organs, Site of blood cell formation, Stores minerals
52
New cards
Muscular System
* Skeletal muscles contract (or shorten)
* Produces movement of bones
* Produces movement of bones
53
New cards
Reproductive System
* For male, it includes: the testes, scrotum, penis, accessory glands, and duct system.
* Testes produce sperm
* Duct system carries sperm to exterior
* For female, includes: the ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina
* Ovaries produce eggs
* Uterus provides site of development for fetus
* Testes produce sperm
* Duct system carries sperm to exterior
* For female, includes: the ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina
* Ovaries produce eggs
* Uterus provides site of development for fetus
54
New cards
Integumentary System (Skin System)
* Forms skin, hair, and fingernails; waterproofs the body
* Protects deeper tissue from injury, Produces vitamin D with the help of sunlight, Excretes salts in perspiration (sweat), Helps regulate body temperature, Location of cutaneous nerve receptors
* Protects deeper tissue from injury, Produces vitamin D with the help of sunlight, Excretes salts in perspiration (sweat), Helps regulate body temperature, Location of cutaneous nerve receptors
55
New cards
Nervous System
* Fast-Acting control system
* Consists of brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors
* Responds to internal and external stimuli
* Consists of brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors
* Responds to internal and external stimuli
56
New cards
Lymphatic System
* Includes: lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymphoid organs
* Heart pumps blood
* Houses white blood cells
* Heart pumps blood
* Houses white blood cells
57
New cards
Digestive System
* Includes: the oral cavity (mouth), esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum, and accessory organs
* Breaks down food
* Allows for nutrient absorption into blood
* Breaks down food
* Allows for nutrient absorption into blood
58
New cards
Homeostasis
Stimulus, Receptor, Control Center, Effector, Input, Output, Positive vs Negative feedback loops, Afferent pathway, efferent pathway; Responsiveness
59
New cards
Homeostasis
maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions
60
New cards
What are the main control systems for homeostasis?
Nervous system and Endocrine system
61
New cards
The Elements of a Homeostatic Control System
Receptor, Control center, effector
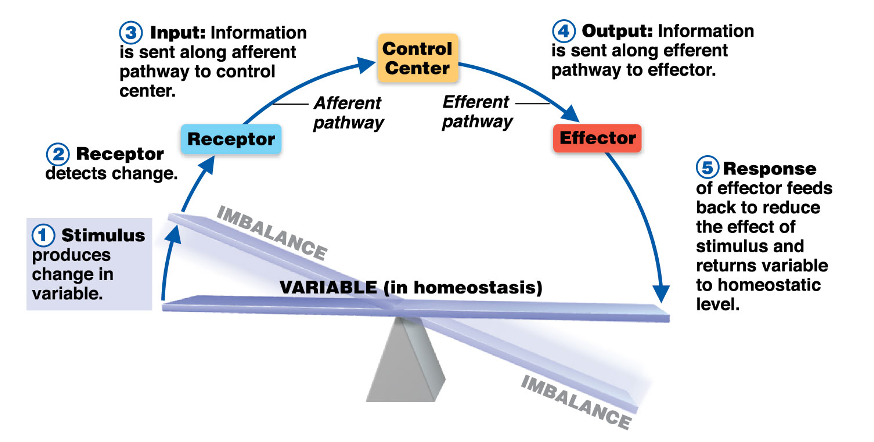
62
New cards
Stimulus (HCS)
produces a change in the variable; causes a reaction (RECEPTOR IS THE NASAL PASSAGE?)
63
New cards
Receptor (HCS)
* Responds to changes in the environment (stimuli)
* Sends information to control center along an afferent pathway
* DETECTS CHANGE
* Sends information to control center along an afferent pathway
* DETECTS CHANGE
64
New cards
Input (HCS)
Information is sent along afferent pathway to control center.
65
New cards
Control Center (HCS)
* Determines set point
* Analyzes information
* Determines appropriate response
* Sends information down efferent pathway to effector
* Analyzes information
* Determines appropriate response
* Sends information down efferent pathway to effector
66
New cards
Effector (HCS)
* Provides a means for response to the stimulus
* Information flows from control center to effector along efferent pathway
* Information flows from control center to effector along efferent pathway
67
New cards
Response (HCS)
The response of the effector feeds back to reduce the effect of stimulus and return the variable to homeostatic levels.
68
New cards
Feedback Mechanisms (loops)
Positive and negative feedback
69
New cards
Negative feedback
* most common feedback type
* Includes most homeostatic control mechanisms
* Shuts off the original stimulus or reduces its intensity
* Opposite thing will put you back into balance (if you are cold, you need heat)
* Works like a household thermostat (ex: when you sweat you cool down, when its dark you turn on light, when you are hungry you eat)
* Includes most homeostatic control mechanisms
* Shuts off the original stimulus or reduces its intensity
* Opposite thing will put you back into balance (if you are cold, you need heat)
* Works like a household thermostat (ex: when you sweat you cool down, when its dark you turn on light, when you are hungry you eat)
70
New cards
Positive feedback
* Rare in human body
* Increases the original stimulus to push the variable farther
* Reaction occurs at a faster rate
* Same thing will put you back into balance (if you cut yourself, you keep bleeding till it stops)
* In the body, positive feedback occurs in blood clotting and during the birth of a baby
* Increases the original stimulus to push the variable farther
* Reaction occurs at a faster rate
* Same thing will put you back into balance (if you cut yourself, you keep bleeding till it stops)
* In the body, positive feedback occurs in blood clotting and during the birth of a baby
71
New cards
Cell Types
Fibroblast, Erythrocyte, Epithelial, Fat, Macrophage, Neuron, Oocyte, Sperm, Red Blood Cells
72
New cards
Fibroblast (cell)
Cells that make fibers; Secretes cable-like fibers
73
New cards
Erythrocyte (cell)
Red blood cell; Carries oxygen in the bloodstream
74
New cards
What is another name for a red blood cell?
Erythrocyte
75
New cards
Epithelial (cell)
**Covers and lines the body’s organs**; Packs together in sheets; intermediate fibers resist tearing during rubbing or pulling
76
New cards
Fat (cell)
Stores nutrients; lipid droplets stored in cytoplasm
77
New cards
macrophage (cell)
fights disease; another name for white blood cell; Digests infectious microorganisms
78
New cards
What is another word for a white blood cell?
Macrophage
79
New cards
Neuron (cell)
gathers information and control body functions; Nerve cell; ▪Receives and transmits messages to other body structures
80
New cards
Oocyte (cell)
female reproductive cell; Largest cell in the body; Divides to become an embryo upon fertilization
81
New cards
Sperm (cell)
male reproductive cell; Built for swimming to the egg for fertilization; Flagellum acts as a motile whip
82
New cards
Red blood cells
Isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic
83
New cards
Cell Organelles
Mitochondria, ribosomes, rough ER, smooth ER, golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, lysosomes, microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments, centrioles, nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, chromatin
84
New cards
What is a solution?
Homogeneous mixture of two or more components
85
New cards
What is a solvent?
dissolving medium present in the larger quantity; the body’s main solvent is water (DISSOLVES)
86
New cards
What is a solute?
components in smaller quantities within a solution. (IS DISSOLVED)
87
New cards
Osmosis
Active and Passive transport
88
New cards
Active Transport
the cell provides the metabolic energy (ATP) to drive the transport process.
89
New cards
Passive Transport
substances are transported across the membrane without any input from the cell
90
New cards
Diffusion (passive)
* Molecule movement is from high concentration to low concentration, down a concentration gradient
* Particles tend to distribute themselves evenly within a solution
* Kinetic energy (energy of motion) causes the molecules to move about randomly
* Size of the molecule and temperature affect the speed of diffusion
* Particles tend to distribute themselves evenly within a solution
* Kinetic energy (energy of motion) causes the molecules to move about randomly
* Size of the molecule and temperature affect the speed of diffusion
91
New cards
What will cause a molecule to move by diffusion?
–The molecules are small enough to pass through the membrane’s pores (channels formed by membrane proteins)
–The molecules are lipid-soluble
–The molecules are assisted by a membrane carrier
–The molecules are lipid-soluble
–The molecules are assisted by a membrane carrier
92
New cards
What are the types of diffusion?
Simple diffusion
* ▪Unassisted movement of solutes
▪Solutes are lipid-soluble or small enough to pass through membrane pores
* –Osmosis—simple diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
* ▪Unassisted movement of solutes
▪Solutes are lipid-soluble or small enough to pass through membrane pores
* –Osmosis—simple diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
93
New cards
What is the smallest unit of all living things
Cell
94
New cards
The skeletal muscles that contract and shorten to move bones form the ________ system.
muscular
95
New cards
The right and left lumbar regions are lateral to the ________ region.
umbilical
96
New cards
A young child sustained a baseball hit to his pelvic cavity. Which bones were fractured?
Hips
97
New cards
The epigastric region is ________ to the umbilical region.
superior
98
New cards
The navel is located in the ________ region of the abdominopelvic cavity.
umbilical
99
New cards
The two major internal body cavities are the ________ cavity and the ________ cavity.
ventral and dorsal
100
New cards
Which of these internal body cavities is the most inferior?
pelvic cavity