APHug Unit 5 Agriculture
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Climate’s Role in Agriculture
Affects how crops grow, when to plant, and how much is produced.
Shifting Cultivation
A farming method where farmers clear a piece of land to grow crops, then move to another area and let the first one recover.
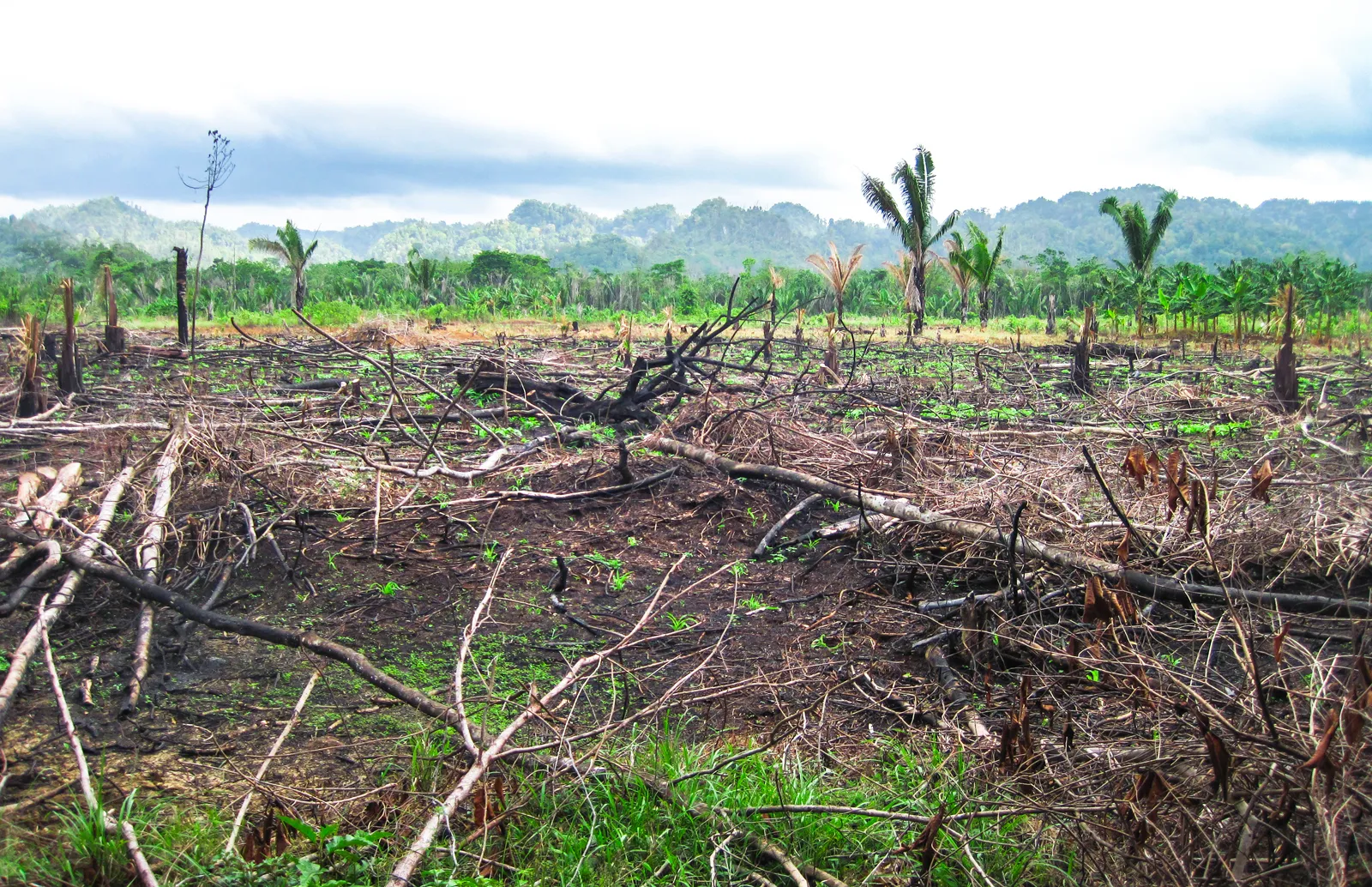

Intensive Subsistence
Farming where a lot of work is done on a small piece of land to grow enough food for a family.
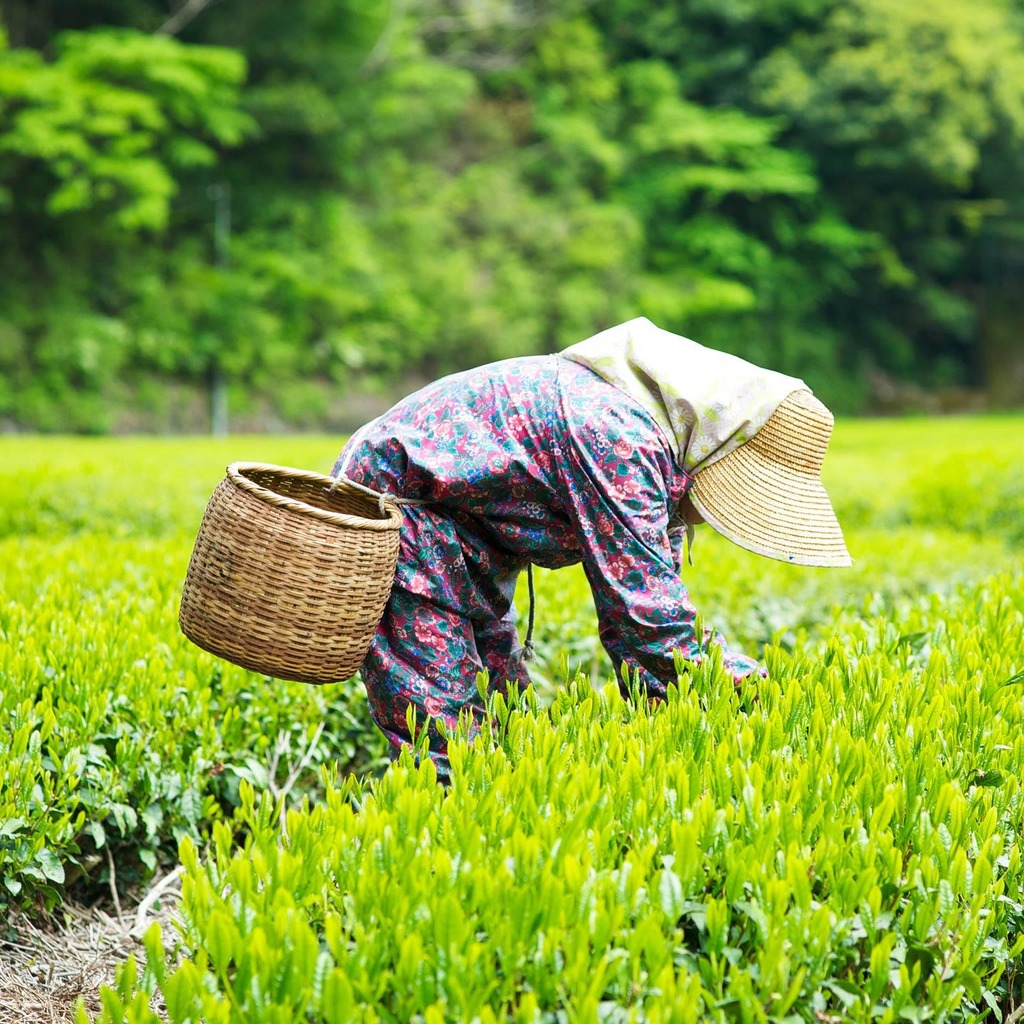

Pastoral Nomadism
Moving with animals to find food and water

Plantation
A large farm that grows one main crop for sale

Mixed Crop and Livestock
Growing crops and raising animals on the same farm. Crops feed the animals.

Dairying
Raising animals for milk and dairy products.

Grain
Farming crops like wheat or corn for food.

Ranching
Raising animals on large open land for meat or wool.

Mediterranean
Farming crops like olives, grapes, and wheat in warm, dry climates near the Mediterranean or similar areas.

Commercial Gardneing
Growing fruits, vegetables, and flowers to sell.

Extensive Agriculture
Big land, low effort
Intensive Agriculture
Small land, high effort
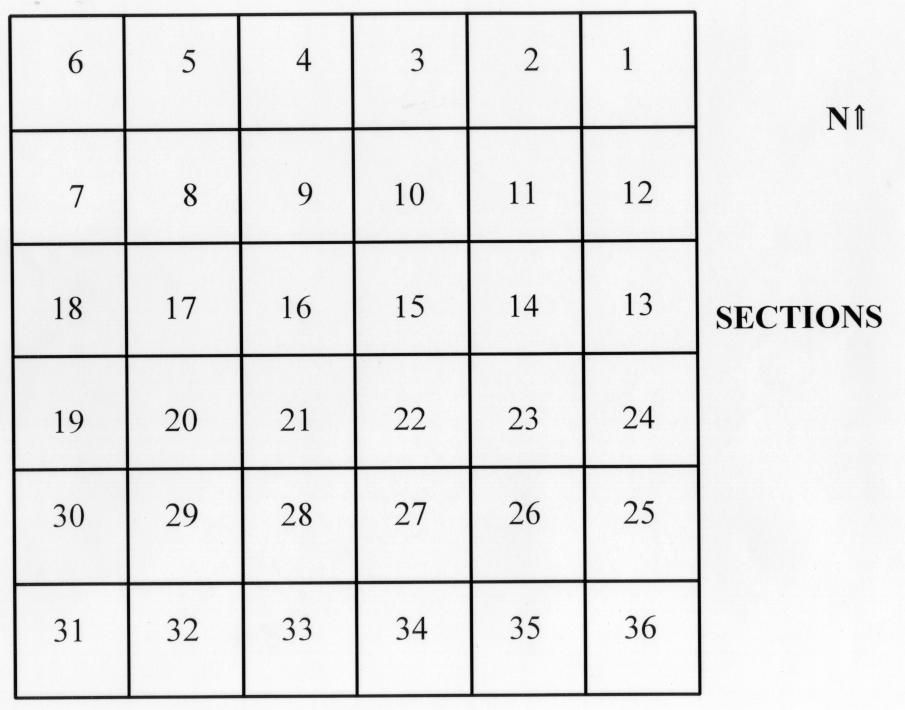
Township and Range
A land surveying method that’s in square patterns
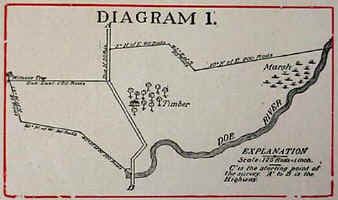
Metes and Bounds
A land surveying method using natural features
Long Lots
A land surveying method that divides land into long narrow strips to provide water and resources

First Agricultural Revolution
When humans transitioned from hunting to gathering
Second Agricultural Revolution
A period of when humas improved agricultural techniques by using innovation and technology.
Third Agricultural Revolution (Green Revolution)
A period marked by the introduction of high-yield crops, advanced agricultural techniques, and the use GMOS.
Bid-Rent Theory
A theory that explains how land value decreases as the distance from the city increases
Subsistence Agriculture
Farming systems that grow food for their own consumption
Commerical Agriculture
Farming systems that produce food to sell
Colonialism’s Role in Agriculture Today
It established plantations and cash crops that are still in global trade systems.
Globalization of Agriculture
The worldwide connection of agriculture through trade, technology, and markets, making food and products move across countries.
Agribusiness
Large scale farming operations
Economies of Scale
Producing more of something at a lower cost per unit.
Von Thünen Model
A model that shows how crops are grown around a city based on cost of land and transport.

Von Thünen Original Model
Farms closer to the city grow perishable goods; farther away grow things that are cheaper to transport.
Von Thünen Modern Model
Explains farming choices today, including factors like technology, global markets, and transportation, not just distance.
Commodity Chains
Steps to produce and sell a product, from making it to delivering it
Transnational Corporations
Companies that operate in many countries.
Environmental Impacts of Agriculture
Deforestation, soil erosion, pollution, loss of diversity
Food deserts and Other Inequalities Related to Agriculture
Some people lack access to healthy food, fair wages, or land, showing unequal distribution in agriculture.
Counter Movements to Modern Agriculture
roups support organic, local, and fair farming instead of big industrial farms.
Women’s Role in Agriculture
Women work on farms, grow food, and support families, often with less access to land or resources.
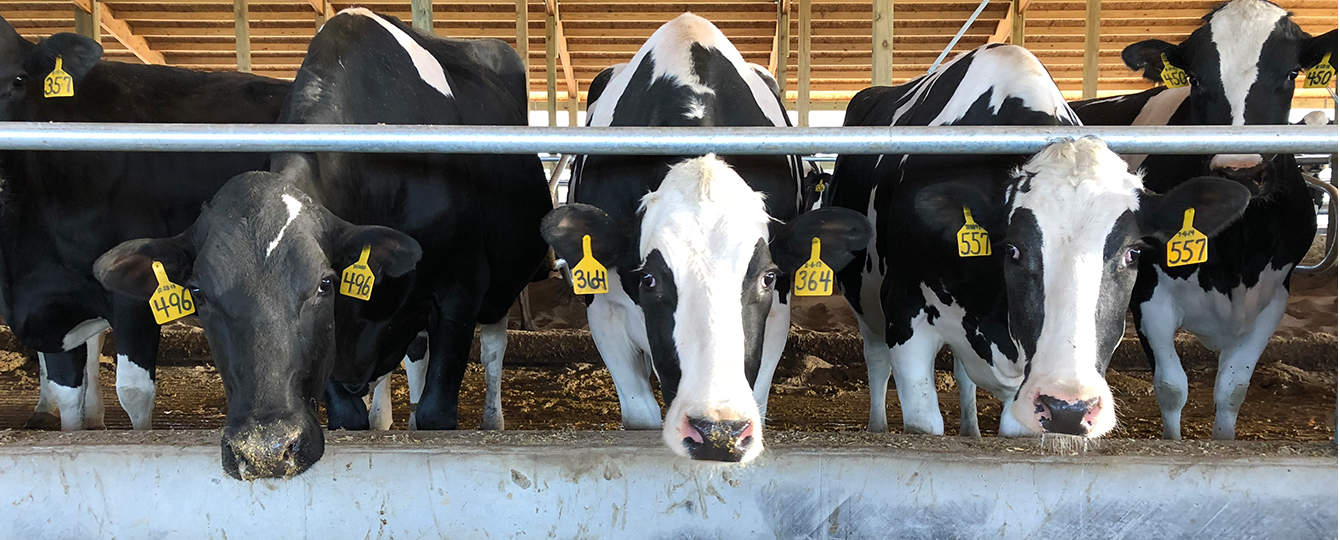
CAFO
Concentrated Animal Feeding Operation