Enzymes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Enzymes
Biological catalysts
made of proteins (sometimes RNA)
rate of reaction
Enzymes increase the ?
more product in same amount of time
activation energy
Enzymes reduce ?
free energy, consumed
Enzymes do not change ? released or required nor are they ?
Substrate
Reactants for a specific enzyme
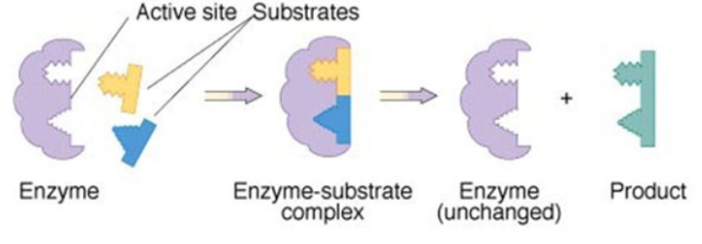
Lock and Key Model
Substrates precisely fit into the active site of a specific enzyme
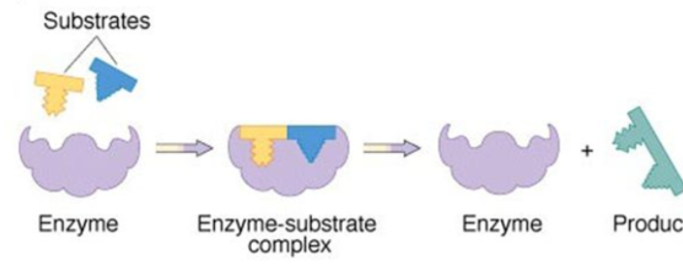
Induced Fit Model
Substrate binds to an active site and both change shape slightly, creating an ideal fit
chemical
There is a ? fit between the active site and substrate
temporary H-bonds and ionic bonds link
compartmentalize
Cells are organized into organelles to ? the enzymes
Activation Energy
Minimum amount of energy that must be added to reactants to start the chemical reaction
Allosteric Regulation
Regulation of an enzyme by a molecule that binds to a site other than an enzyme’s active site
the molecule can increase / decrease enzyme activity
Carbohydrase
Enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates
Catalyst
Substances that increase the rate of a chemical reaction and are not used up
all enzymes are catalysts but not all catalysts are enzymes
Coenzymes
non-protein organic substance that is necessary for an enzyme to work
Cofactors
Organic or inorganic substance (e.g. metal ion) that is necessary for an enzyme to work
temperature, pH
Enzymes need an optimal ? and ? to work correctly
if they don’t have the right conditions, they’ll denature or change in shape
Enzyme inhibitor
Substance that stops an enzyme from catalyzing a chemical reaction
Enzyme Regulators
Substances that affect the rate at which an enzyme catalyzes a chemical reaction
Lipase
Enzyme that breaks down lipids
Protease
Enzyme that breaks down proteins
Negative Feedback Loop
signal causes response that lowers signal
intermediate, product
sometimes an ? or ? of a pathway will act as an inhibitor of enzymes in that pathway