histology test
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Histology
The study of tissues
Epithelial tissue
Covering or lining, stomach/skin
Connective tissue
Holds things together, knee, shoulder, pelvis
Nerve tissue
Responsible for sending messages
Muscle tissue
Can produce own movements
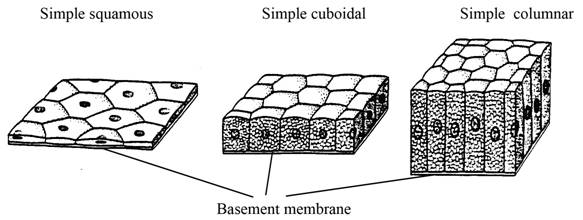
Squamous cells
Thin layer of cells, moves oxygen quickly throughout the body, lungs/aorta
Cuboidal cells
Produces and moves things out, adrenal/saliva glands
Columnar cells
Long thin cells on edge of epithelial cells, absorbs through intestine edges
Goblet cells
Produces snot, sinuses
Transitional cells
Stretchy, can change shape, needed when something needs to expand, stomach lining/bladder
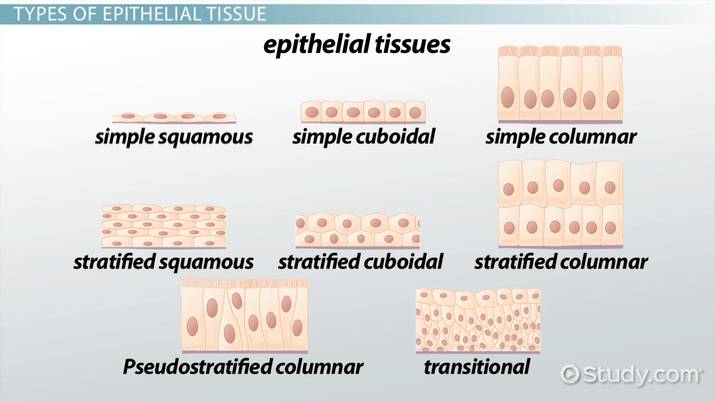
Simple
Stratified
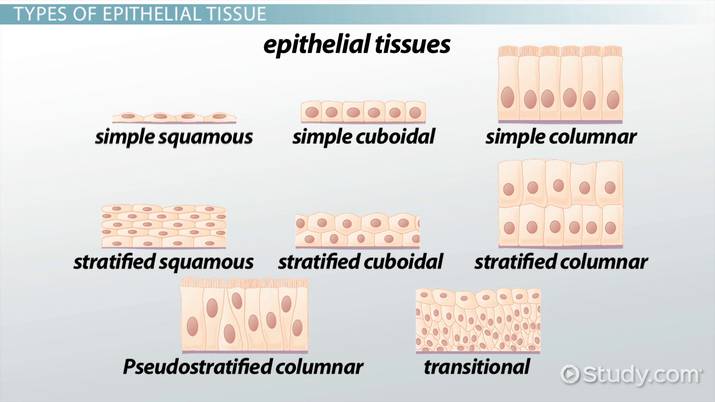
Psudostratified
Osseous tissue C
Bone tissue
vascular tissue C
Blood (red, white, platelets)
Hyline cartilage
Rigid, nose, ribs, spinal disks, surrounding joints
Elastic cartilage
Stretches, ear
Fibrocartilage
Like the sole of a shoe, a mixture of tissue and cartilage
Loose proper connective tissue areolar
Holds the body together
Proper connective tissue Dense
Tendon and ligaments
Proper connective tissue Loose adipose
Fat storage in the body
Features of connective tissue
Cells (grapes), Fibers and maybe blood (noodles), matrix (jello)
Smooth muscle tissue
Lines stomach/bladder, it expands
Cardiac muscle tissue
Heart, Cells divided and converge, one nuclei per cell, intercalated disks
Skeletal muscle tissue
Muscles surrounding bones
Stratum corneum
The outermost layer, most protective
Stratum lucindum
Thin, translucent layer present in the thicker region of epidermis
Stratum granulosum
Layer Where keratinization begins
Stratum spinosum
Composed of multiple layers of polygonal keratinocytes (keratin producing cells)
Reticular dermis
Thick, bottom layer, soles of feet, palms
Papillary dermis
Thin, top layer
Whorls
Finger print types that form a swirl shape

Arch
Finger print types that form a small arch shape
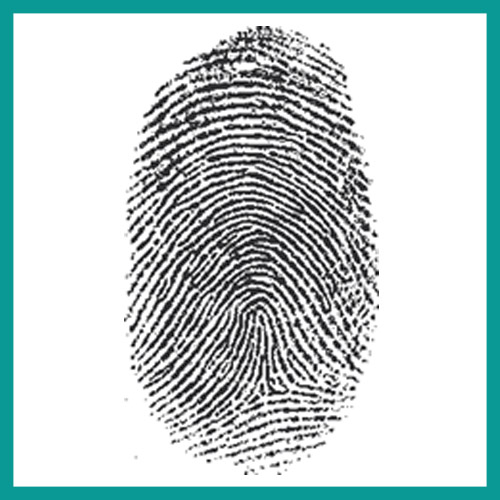

Loop
Finger Print type that forms a small loop shape

Deep tissue receptors
A nerve ending found in the deep layers of the skin, they are bare endings
Light touch receptors
A nerve ending found in the epidermis, they are flattened epithelial cells
Specialized nerve ending
Found in the dermis, on fingers, palms, tongues, they have encapsulated nerve endings
Sebaceous glands
Releases sebaum, causes acne, protects skin from moisture loss, brittle hair, bacteria and fungi, found in the second layer of the dermis.
Sudoriferous glands
Secretes sweat, two types; eccrine (small/simple)- open directly into skin, and apocrine (large/branched)- opens to a hair follicle.
Ceruminous glands
Modified glands in the ear canal, protects and lubricates the ear canal with an antibacterial layer, they are coiled and tubular. cerumen=earwax
Mammary glands
Females primarily use them, they create lactose for an infant, men have evolved to not create the lactose.
1st degree burn
Burn on the epidermis, sunburns
2nd degree burn
Burn on the top two layers of the skin (epidermis/dermis), causes blisters to form front the fluid buildup between the layers.
3rd degree burn
Nerve endings are destroyed, no pain, burns through all three layers of the skin and sometimes fat and muscle below
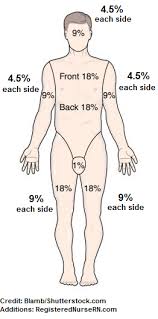
9% rule
Used to estimate total burn damage, and used to determine treatment needed for a patient
Hair
Protein filament, grows in follicular, found in dermis, made of keratin, sebaum, and melanin
Nails
Hard structure of dead keratin filled skin cells, protects digits, enhances tactile sensation and tool
Hair matrix
Located at each follicle base, rapidly dividing cells, cells undergo keratinization
Nail matrix
Tissue under nail base, growth center for nail plate, cell division
Dorsal
Cavities, vertebral, cranial
Ventral
Cavities, thoracic, upper abdominal, pelvis
Long bones
Arms and legs
Short bones
Chunky
Flat bones
Ribs, sternum, scapula, cranial
Irregular bones
Pelvis, facial, vertebra
Skeletal system functions
Protection, support, structure, shape, movement, blood cell production, mineral storage, stores fat
Hypodermic
The deepest layer of skin
Dermis
The middle layer of skin
Epidermis
The most superficial layer of skin
Skin functions
Protection- dehydration, microorganisms, uv light, mechanical damage
Mobility- allows smooth body movement
Immunity- development against pathogens
Tempature regulation- conserving/releasing heat (sweat and Goosebumps)
Endocrine activity- initiates biochemical process involved in vitamin d production