Biology 172- Exam 1 Review-February 21
1/325
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
326 Terms
What is a protist?
Any eukaryote that is not a fungus, plant or animal
List the taxonomy levels in order
Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
How do protists obtain energy?
Autotrophically, Heterotrophically, Mixotrophically
What is endosymbiosis?
the process in which a unicellular organism engulfs another cell, which becomes an endosymbiont and then organelle in the host cell.
How did mitochondria evolve?
through endosymbiosis of an aerobic prokaryote.
How did plastids evolve?
through endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic prokaryote
Name the four eukaryotic supergroups
Excavata, "SAR" clade, Archaeplastida, Unikonta
Supergroup Excavata
The supergroup Excavata share a similar cytoskeleton and some have an "excavated" feeding groove on the side of the body.
Diplomonads
anaerobic metabolism, two equal-sized nuclei and multiple flagella, reduced mitochondria called mitosomes. example: Giardia intestinalis (lamblia)
Antonie von Leeuwenhoek 1632-1723
father of microbiology, discovered protists and bacteria
Parabasalids
have hydrogenosomes (anaerobic energy), example: Trichomonas vaginalis
Euglenozoans
A diverse clade that includes predatory heterotrophs, photosynthetic autotrophs, and parasites. The main feature distinguishing them is a spiral or crystalline rod inside their flagella. This clade includes the kinetoplastids and euglenids.
Example:Trypanosoma brucei (African sleeping sickness)
Name the four Eukaryotic Supergroups
Excavata, SAR clade, Archaeplastida, Unikonta
Alveolates
SAR clade, have membrane bounded sacs (alveoli) just under the cell membrane. They include dinoflagellates, apicomplexans, and ciliates.
Dinoflagellates
-have two flagella and each cell is reinforced by cellulose plates (cellulose is the main structural molecule in plants, so this is a case of convergent evolution).
-They are abundant components of both marine and freshwater plankton and can be autotrophs, heterotrophs or mixotrophs.
dinoflagellate
identify this microorganism
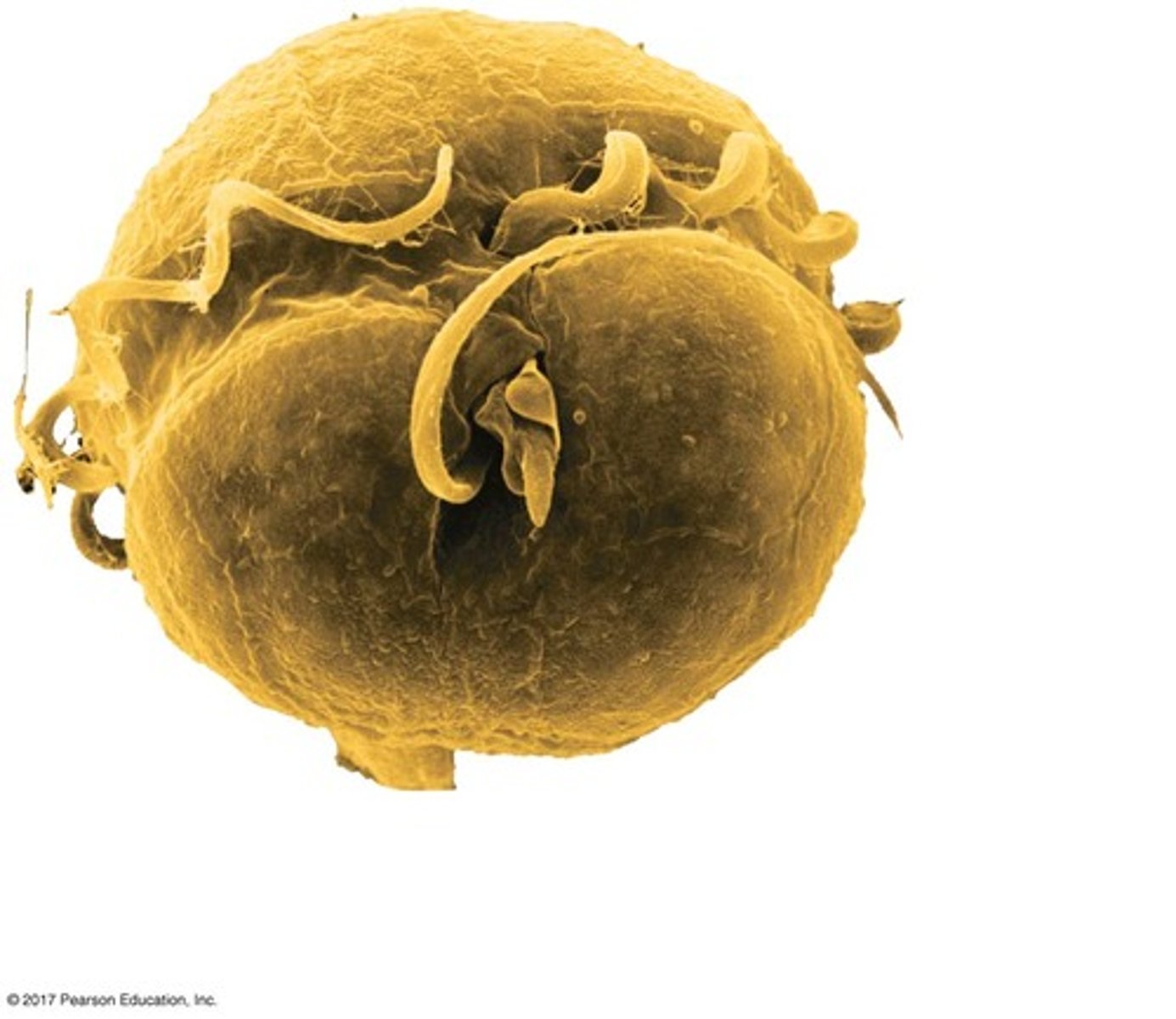
cartenoid
pigment found in all three domains of life, seen in red algae blooms
What is the "red tide"
A bloom of dinoflagellates, releasing a powerful but short lived toxin, kills lots of fish
What are Apicomplexans?
Specialized parasites of animals, some of which cause serious human diseases.
Reproduction of Apicomplexans
Most have sexual and asexual stages hat require two or more different host species for completion.
How do apicomplexans spread
through their host as infectious cells called sporozoites.
Structure of apicomplexan
One end, the apex, contains a complex of organelles specialized for penetrating host cells and tissues....
The APICAL COMPLEX will connect to the red blood cell
What are the two most common apicomplexans?
Plasmodium and Toxoplasma
What illness is associated with plasmodium?
4 types of malaria
What is the vector for malaria?
Anopheles mosquitoes (through infected blood)
Figures about malaria?
Over 40 percent of the world's population lives in contact with malaria and there are about 200 million cases each year.
Steps of a human infection with malaria
1. A sporozoite form is transmitted from the mosquito to a person's blood.
2. A merozoite form reproduces in the liver and then infects red blood cells.
3. A feeding form consumes the hemoglobin of blood cells.
4.Rupture of cells leads to symptoms of chills and fever.
What is one reason most endemic Hawaiian birds have gone extinct?
avian malaria following introduction of mosquitoes in the 1800's
important characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii
- parasitic alveolate
-affects the host behavior
-ex... rat being comfortable around a cat
ciliates
a large varied group of protists, are named for their use of cilia to move and feed.
example of a ciliate
Paramecium
what is a macronuclei?
part of a ciliate that is responsible for protein subscription
Conjugation in cilliates?
sexual process, physical exchange of genetic material with haploid mICROnuclei, SEPARATE from reproduction
Reproduction in cilliates
binary fission, one cell simply splits into two
what is a micronuclei?
stores the complete genome, is diploid, germ cells, do NOT transcript anything
what does the contractile vacuole do?
osmoregulation... expands to collect, shrinks to expel it
purpose of cilia
locomotion
purpose of food vacuole
digests food particles with aid of lysosomes
oral groove
mouth opening of the paramecium
cell mouth
Opening through which food passes into the gullet of a paramecium.
Stramenophiles
-important autotrophs, some heterotrophs
-most have a hairy and a smooth flagella
-diatoms, golden algae, brown algae
Diatoms
-unicellular algae
-unique two-part, glass-like wall of hydrated silica
-reproduce asexually, occasionally sexually
-approximately 100,000 species
major component of phytoplankton?
diatoms
What is diatomaceous earth?
Ground sedimentary rock made up of the fossilized cell walls of diatoms
Which is the largest, most complex algae, including seaweeds and kelp?
Brown algae
what are cell walls of brown algae made of?
Algin
What is algin used for?
to thicken processed foods
what is a stipe?
a stem-like region between the holdfast and blade of some seaweeds
what is a blade?
place where photosynthesis occurs (leafish) of brown algae
What is a holdfast?
root-like structure, anchors brown algae into water
Supergroup Unikonta
includes animals, fungi, and some protists
Amoebozoans
- amoeba that have lobe- or tube-shaped pseudopodia (foot-like extensions).
-They include single-celled, free living and parasitic amoeba as well as colonial slime molds.
What are plasmodial slime molds?
Amoeba 'supercells' containing many nuclei.
Where do plasmodial slime molds typically inhabit?
Moist soil or decaying vegetation.
How do plasmodial slime molds feed?
By phagocytosis (cell-feeding, engulfing and drawing within).
What are cellular slime molds?
Microscopic amoeba that feed as individual cells.
What do cellular slime molds form to migrate?
Multicellular aggregates.
What do cellular slime molds disperse?
Reproductive spores.
Dictyostelium discoideum
experimental model for studying the evolution of multicellularity
What organelles are associated with the first cases of endosymbiosis?
Mitochondria and plastids
heteromorphic
sporophytes and gametophytes are structurally different
isomorphic
Referring to alternating generations in which the sporophytes and gametophytes look alike, although they differ in chromosome number.
oomycetes
-water molds/friends
-hyphae (multinucleated filaments)
-cell wall of cellulose
-responsible for potato blight
-decomposers and parasites
amoeba
protists that move and feed with pseudopodia
rhizarians
include radiolarians, forams, and cercozoans
forams
A marine protozoan that secretes a shell and extends pseudopodia through pores in its shell
what are foram tests?
porous shells hardened with calcium carbonate, symbiotic algae can live inside.
What are fungi?
-single OR multicellular heterotrophic eukaryotes
How many species of fungi are there?
100,000 known, probably over a million
Habitat of fungi
many habitats including the arctic, tropical rainforest, fresh and salt water. However, most fungi live in soil.
Cell wall of fungi is made of…
chitin (like bug exoskeleton)
Are fungi vascular or non vascular?
nonvascular
Can fungi move?
No, they’re non-motile
biggest organism ever?
honey mushroom Armillaria
What are hyphae?
thin, thread-like filaments that make up the main “body” of the fungus
What are mycelium?
a mass of hyphae
How do SPORES structure relate to their role in ecosystems?
enable fungi to colonize new environments. The spores germinate and grow when conditions are favourable.
How do hyphae decompose?
EXTRACELLULAR DIGESTION; secret enzymes into the environment to break materials down, then absorb said materials.
How are most hyphae cells divided?
By septa, with pores allowing movement of organelles.
What are Coenocytic fungi?
Have hyphae that lack septa and have a continuous cytoplasmic mass with hundreds or thousands of nuclei.
fungi can be…
decomposers, parasites, predators
Example of a parasitic fungi
ringworm
Unique factor of some predatory fungi
have specialized hyphae for capturing prey.
What are haustoria?
Structures that allow fungi to extract or exchange nutrients with plants by penetrating host cells.
What are mycorrhizae
Symbiotic associations between fungi and plant roots that enhance nutrient exchange.
Where do mycorrhizae grow ?
into the extracellular spaces of the root or extend hyphae directly through the cell walls of the root.
How do plants rely on fungi?
the mycorrhizae allow the plant to obtain phosphate ions and minerals.
What is a lichen?
a symbiotic association between a photosynthetic protist (algae) or bacteria and a fungus.
How do the parts of the lichen interact?
The algae provide carbon compounds, bacteria also provide organic nitrogen, and fungi provide the environment for growth.
Where do the algae/bacteria occupy in a lichen?
underneath the fungal hyphae
How do fungi reproduce?
with spores, both asexually (more common) and sexually
Which is more common in a fungi life cycle: haploid or diploid?
haploid!
What is plasmogamy?
the union of cytoplasm from two parent mycelia.
What is karyogamy?
the fusion of nuclei to produce diploid cells.
What is a heterokaryon?
a fungal mycelium that contains genetically different nuclei within the same cytoplasm.
What is a dikaryon?
A type of fungal mycelium characterized by containing two genetically distinct nuclei within a single cell, allowing for dual genetic material.
How do dikaryon and heterokaryon differ?
blah
What are molds?
fungi that produce visible mycelia and produce haploid spores through mitosis.
What is a yeast?
asexual, unicellular fungi that reproduce with simple cell division and buds
What is a chytrid?
widespread in lakes and soils and include decomposers and parasites.