basic locomotor system
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
which embryonic structure does the locomotor system come from?
mesoderm : somites
screrotome: bone and cartilage
myotome: muscles
dermatome: skin and subcutaneous tissue
What is the function of the locomotor appartus ?
- carry out the body movement
- organ protection
- mineral reserve
- production of blood in the bone marrow
- heat production
What is osteology?
it's the osteogenesis, classification of bones and bone structure
What is the Arthrology ?
it's the arthrogenesis, the joint classification and joint elements. But also the joint biomechanics
What is the myology ?
it's the myogenesis, the types and classification of the muscle and how they are organised
What are the muscle accesory structures ?
Can be the fasciae, tendon/ fibrous sheath, the synovial bursa and sheath
What is hematopoiesis?
The formation of new blood cell
What is the function of the skeleton ?
support the weight and give protection
give an example of a long bone
femur
give an example of a short bone
carpal bone
give an example of a flat bone
scapula
give an example of an irregular bone
vertebra
give an example of a sesamoid bone
patella
where do tendons connect
muscle to bone
what do ligaments connect
bone to bone
give the structure of a bone
-osseous/bone tissue
-cartilage
-periosteum
-bone marrow
-vessels and nerves
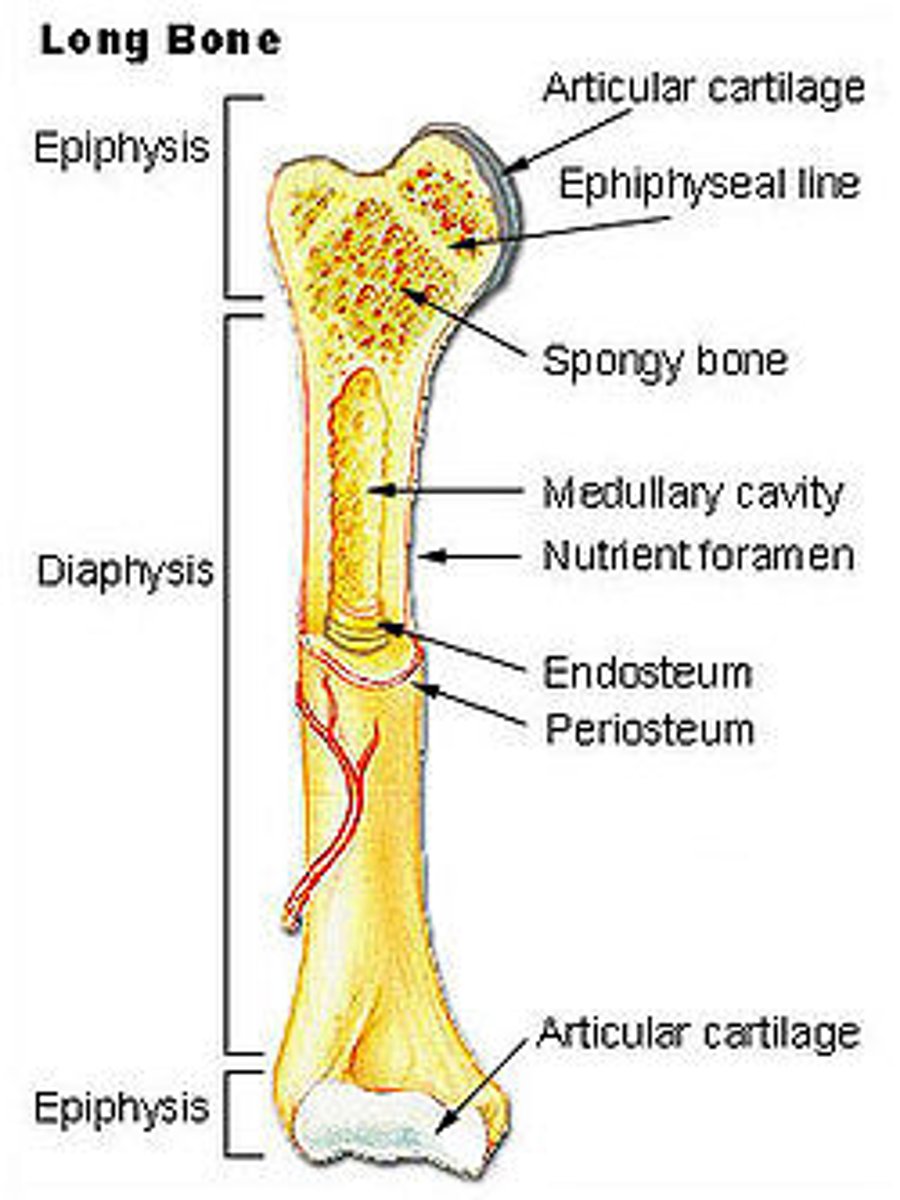
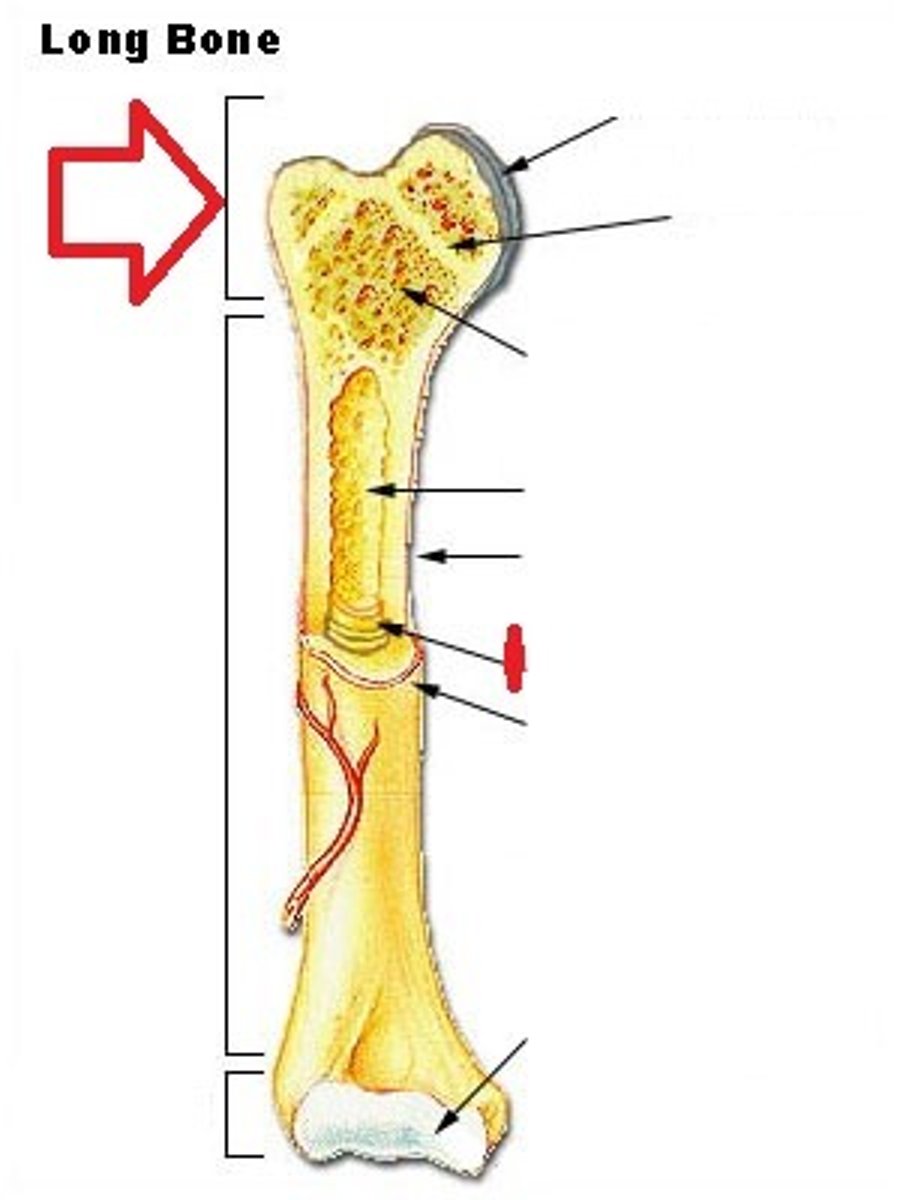
Where is located the growth plate or epiphyseal line ?
It's the area of cartilage near the end of long bones in youngs animals, it stop growing after 1 years
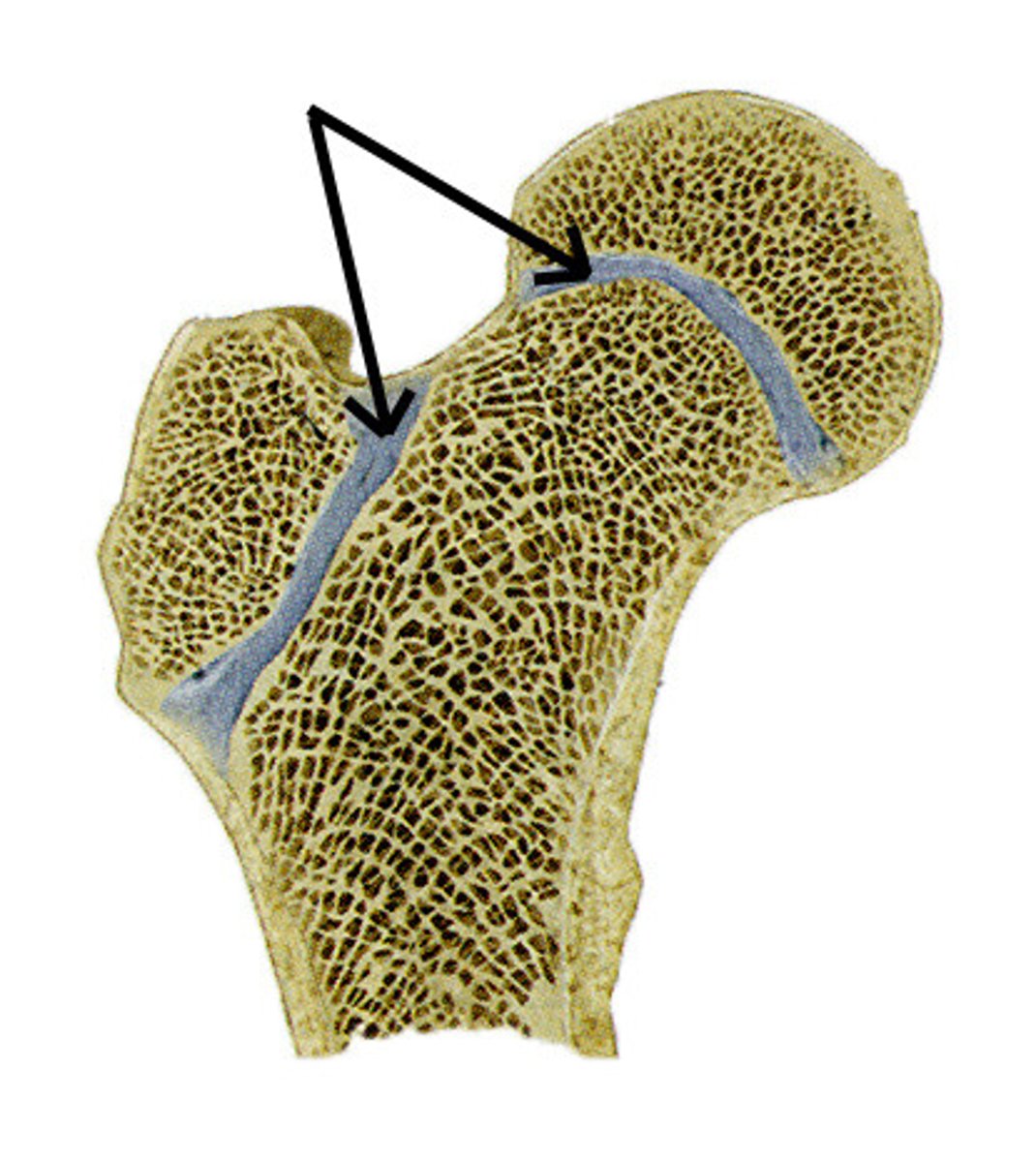
Why we need to be careful while looking at a paw x-ray in young animals?
because we can mistake the growth plate with a broken bone
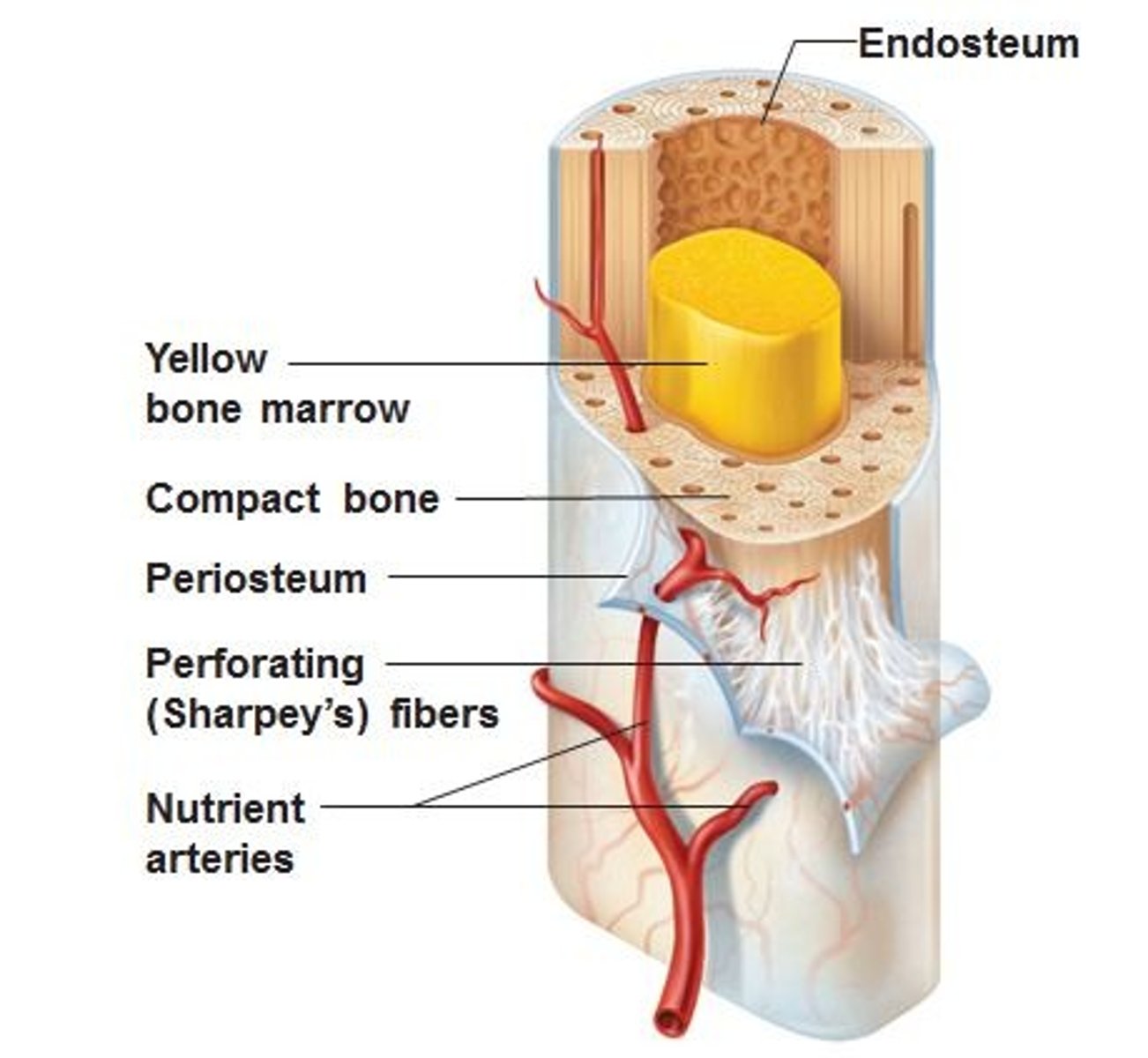
What is the periosteum?
the tough membrane that covers the outside of the bone
What is the proximal epiphysis
end of the bone closest to the body trunk
What is the diaphysis?
shaft of a long bone
shaft of a long bone
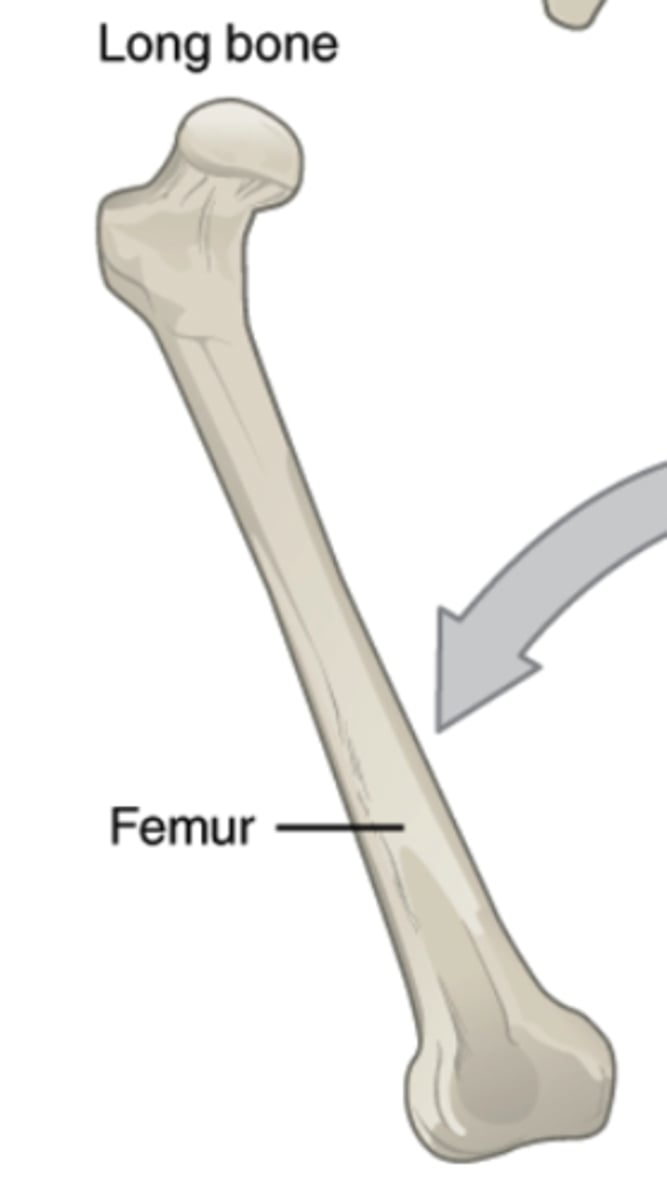
What is the distal epiphysis ?
end farthest from trunk of a bone
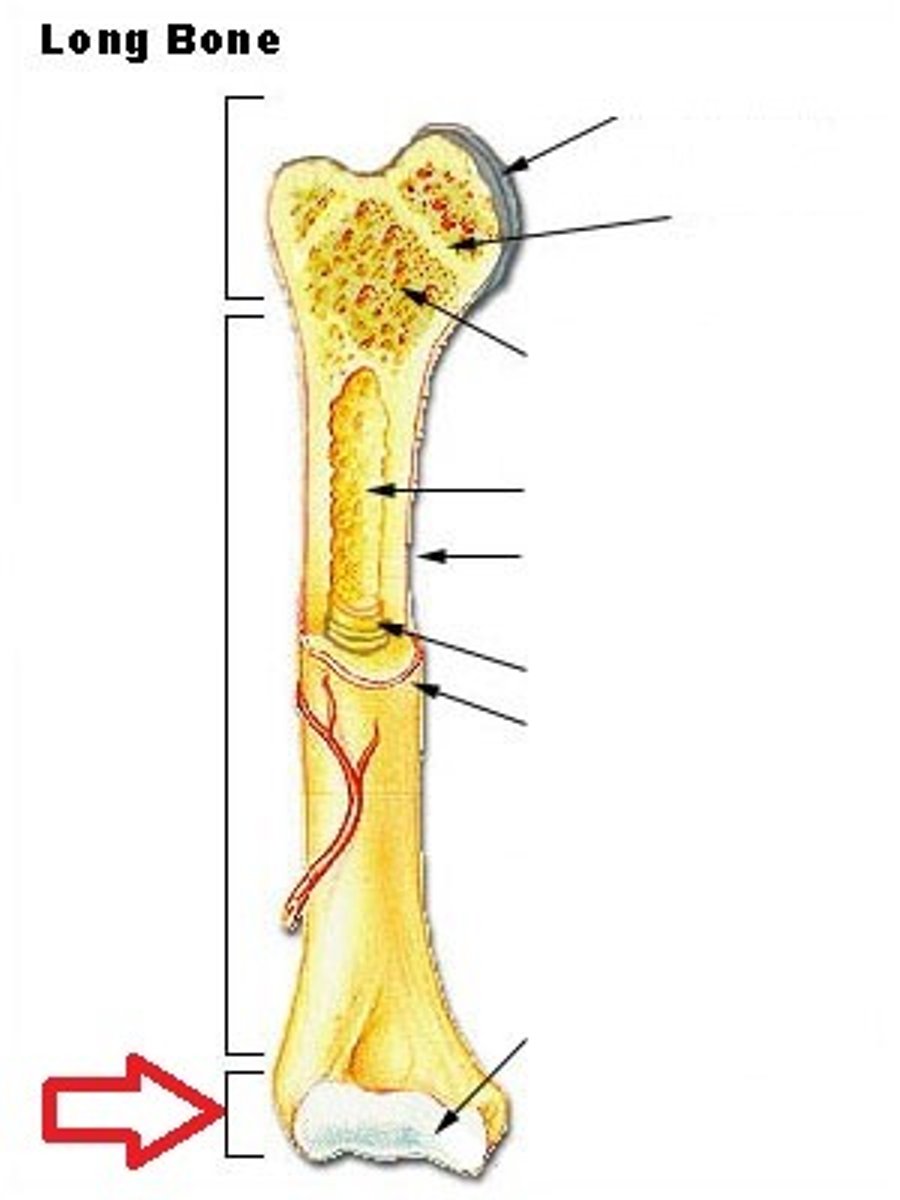
What kind of bone marrow can we find inside a long bone ?
yellow bone marrow
What are the two types of bone tissue ?
compact and spongy
What is direct primary bone development ?
When the bone is formed without using a cartilagenous tissue (embryonic stage)
Give an example of a direct primary developed bone
skull

What is indirect primary bone development ?
transform a cartilagenous model into bone
what is secondary ossification
bone remodeling, forms a mature bone to improve mechanical action
example of mature bone
lamellar bone
What are the fuctions of osteoclasts and osteocytes?
store minerals
reorganize bone structure
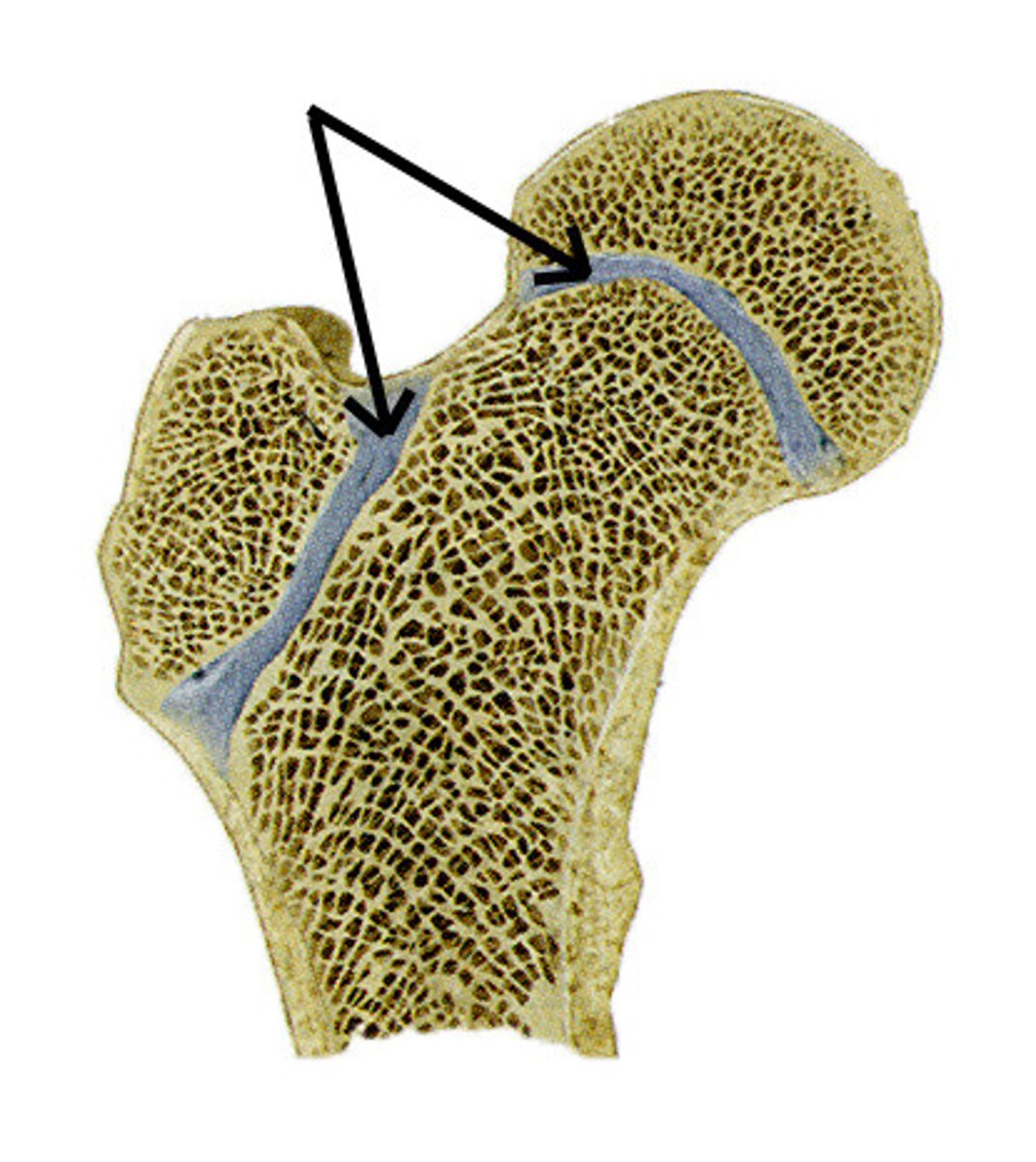
what are the 2 types of cartilage tissue in bones
articular and epiphyseal
articular cartilage
surrounds every articular surface
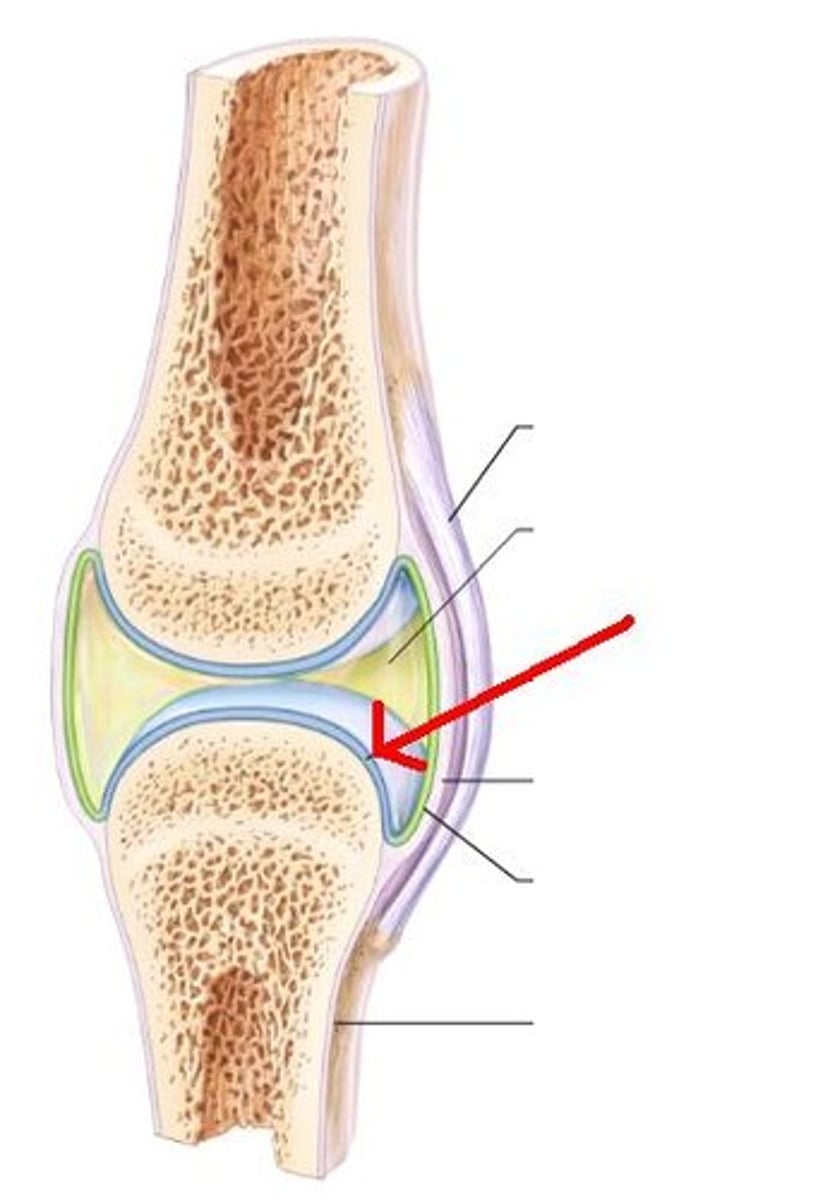
epiphyseal cartilage
for longitudinal growth
how does bone marrow change with age
red --> yellow --> grey
what is the afferent system of blood vessels?
oxygenated blood to bone (arteries)
what is the efferent system of blood vessels?
deoxygenated blood away from bones (veins)
What are the vessels in the afferent system ?
- nutrients arteries
- epiphysis and metaphysis
- periosteal arteries
what is the function of vasomotor nerves
stimulates blood vessels pumping to bone
what is the function of sensitive nerves
pain and heat detection
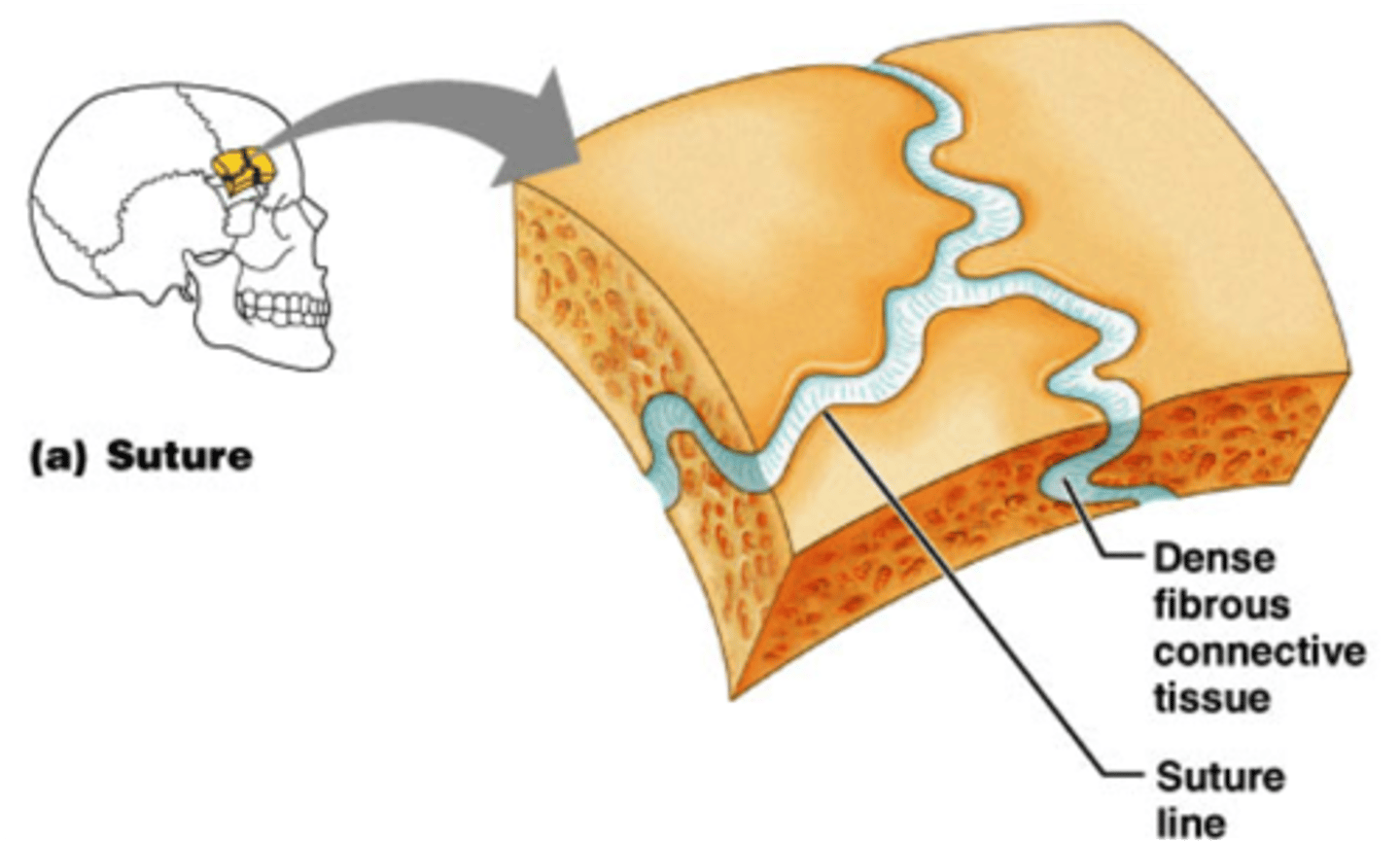
fibrous joints
do not allow any movements (syndesmosis)
sutures (eg skull)
gomphosis (eg teeth and alveolar bone)
no articular cavity (synarthrodial)
cartilagenous joints
synchondrosis - hyaline cartilage
symphysis - fibrocartilage
no articular cavity (synarthrodial)
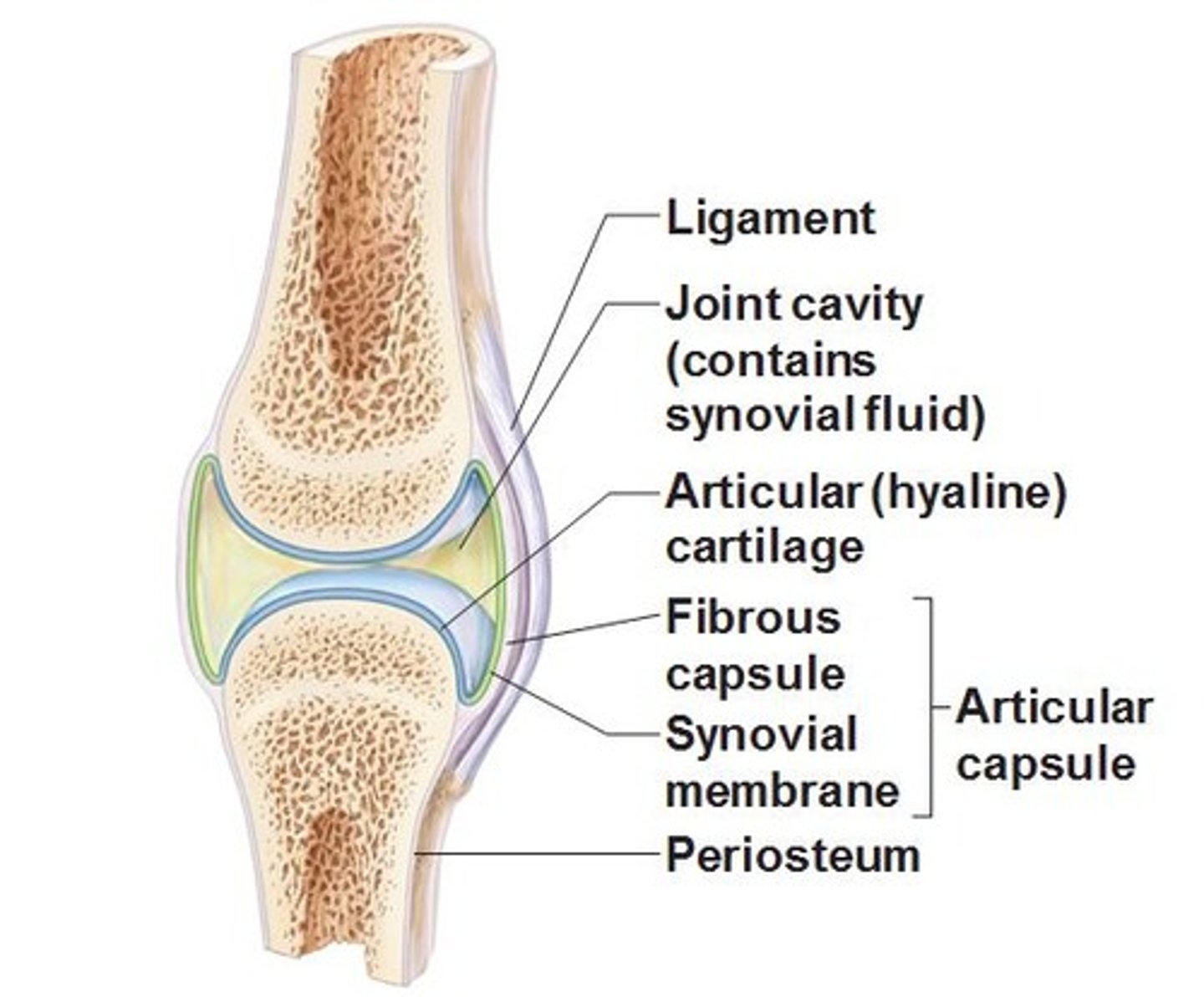
synovial joint
free movement (diarthrodial)
joint cavity surrounded by capsule:
- articular labrum
- articular disc
- meniscus
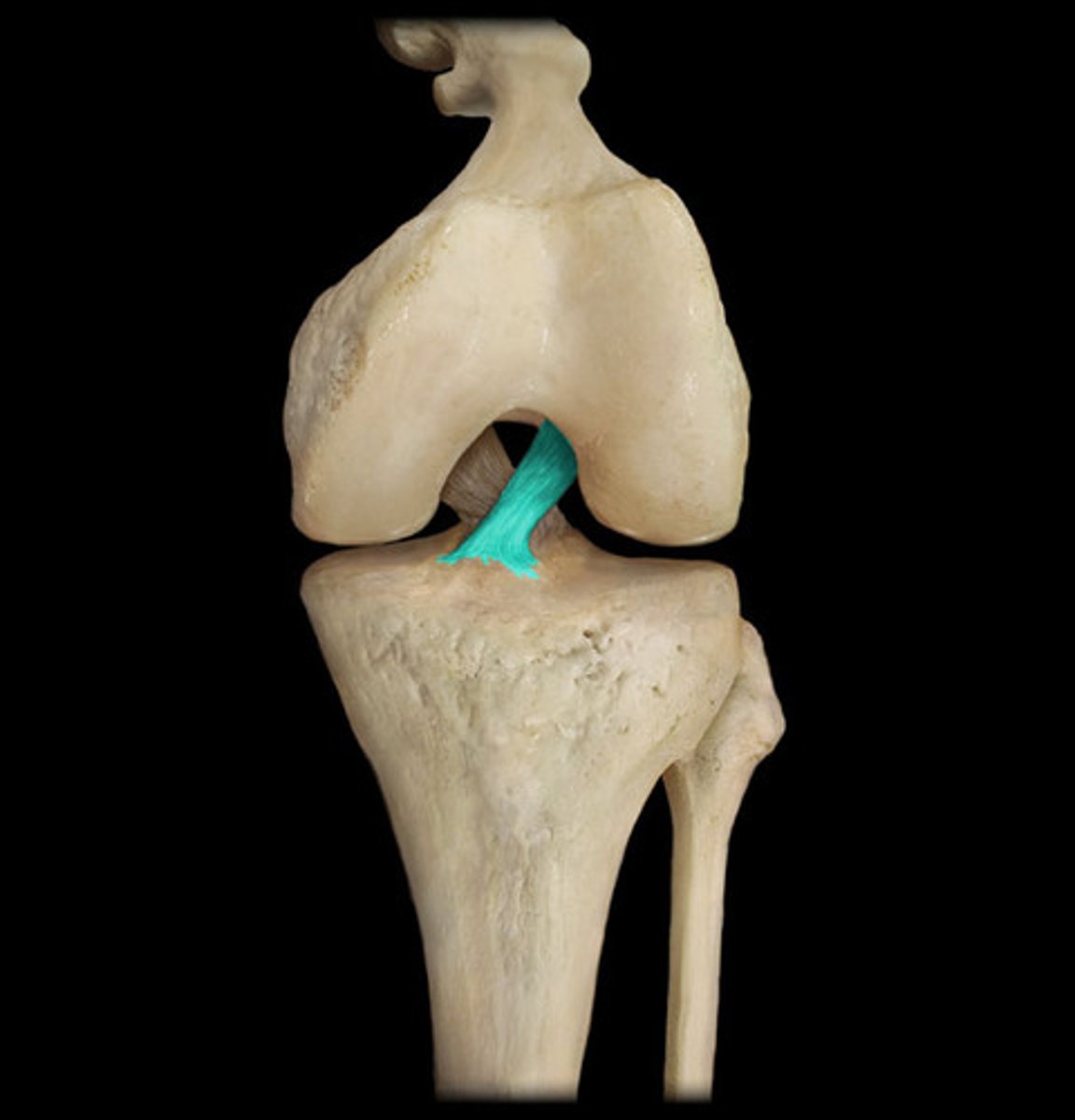
what is an intracapsular ligament
inside the joint cavity
what is an extracapsular ligament
outside joint cavity - stabilises joint externally
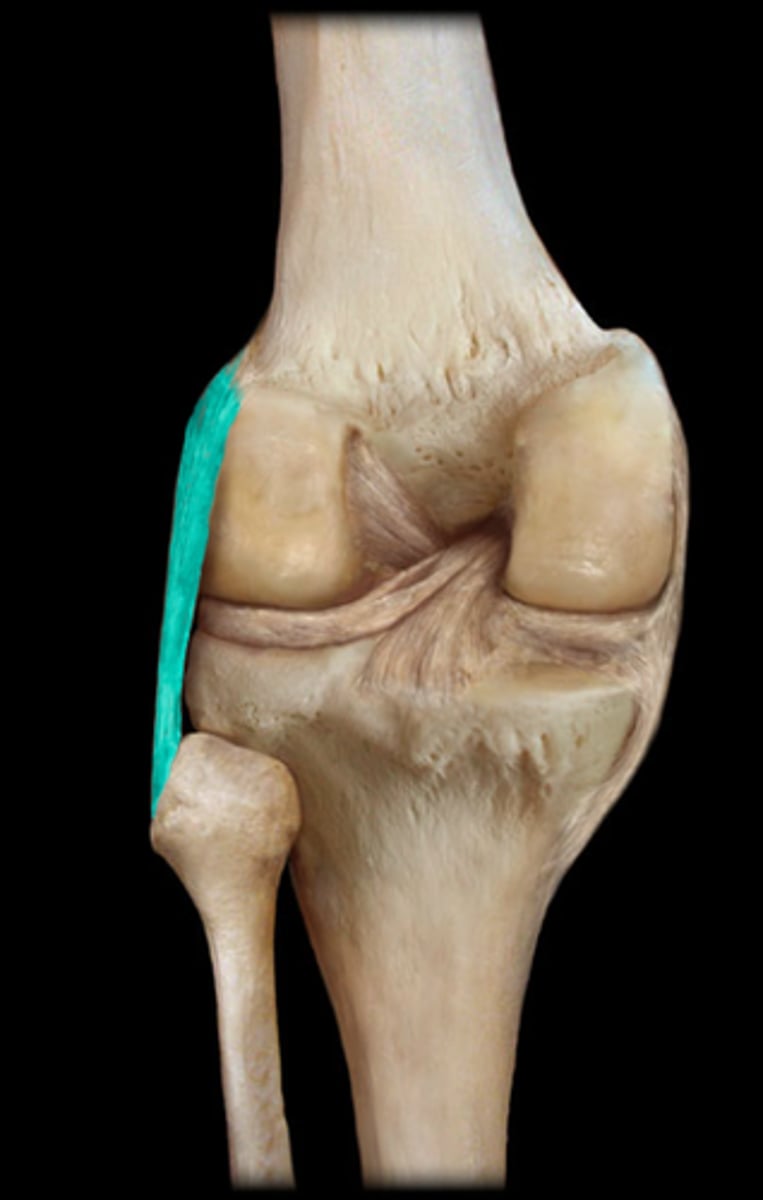
types of synovial joints
- ball-and-socket joint
- hinge joint
- compressive joint
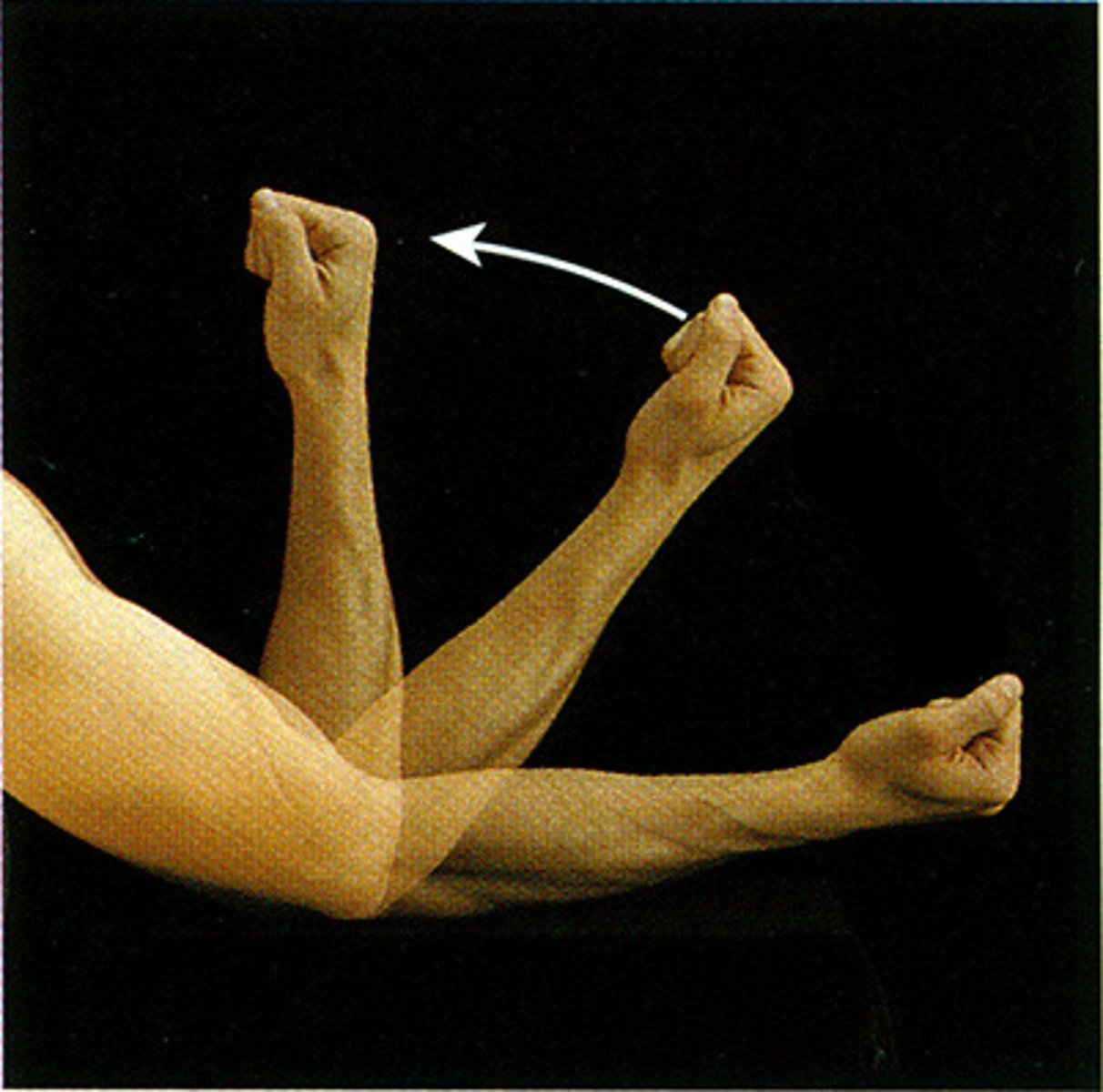
flexion/ extension
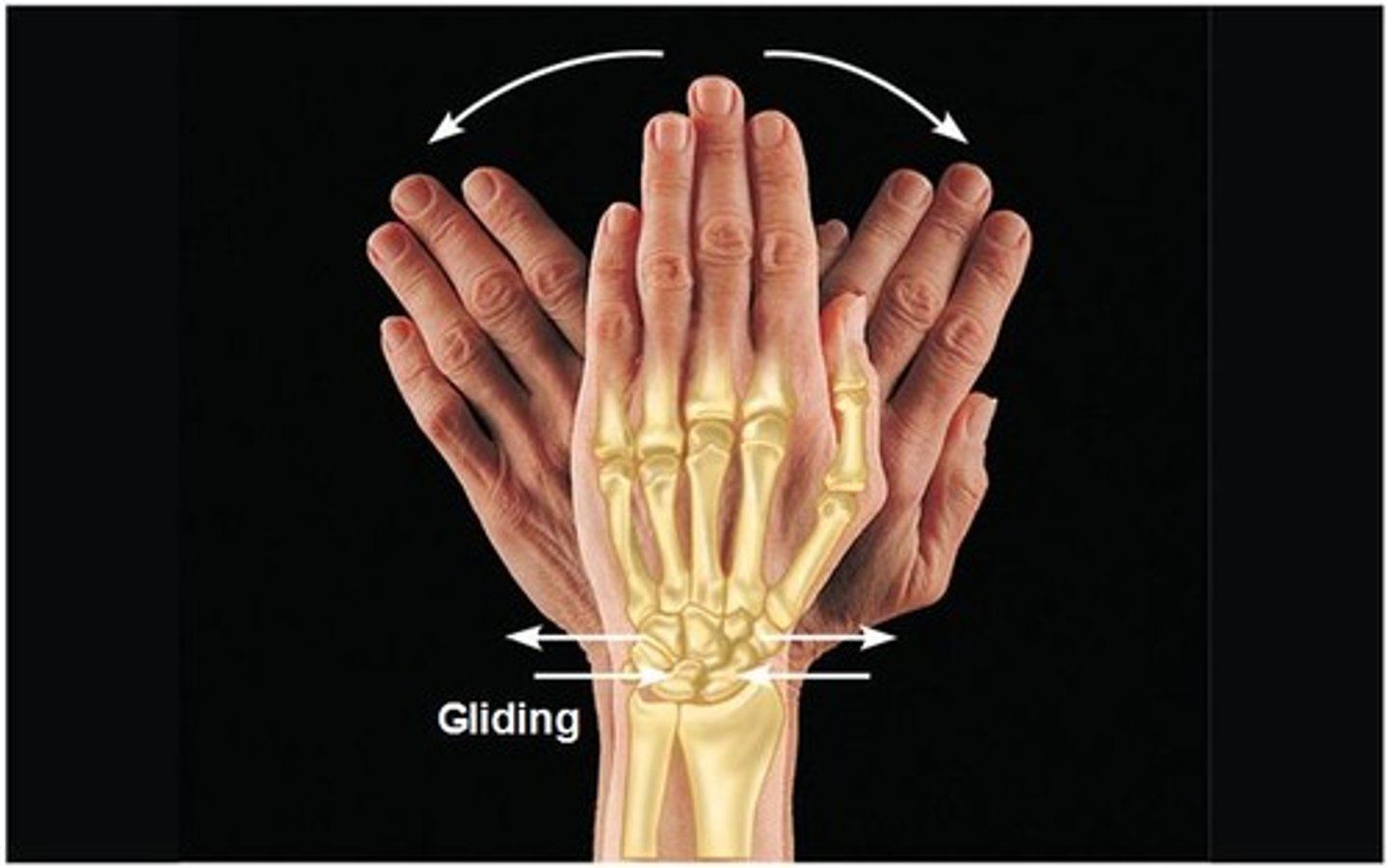
gliding movement
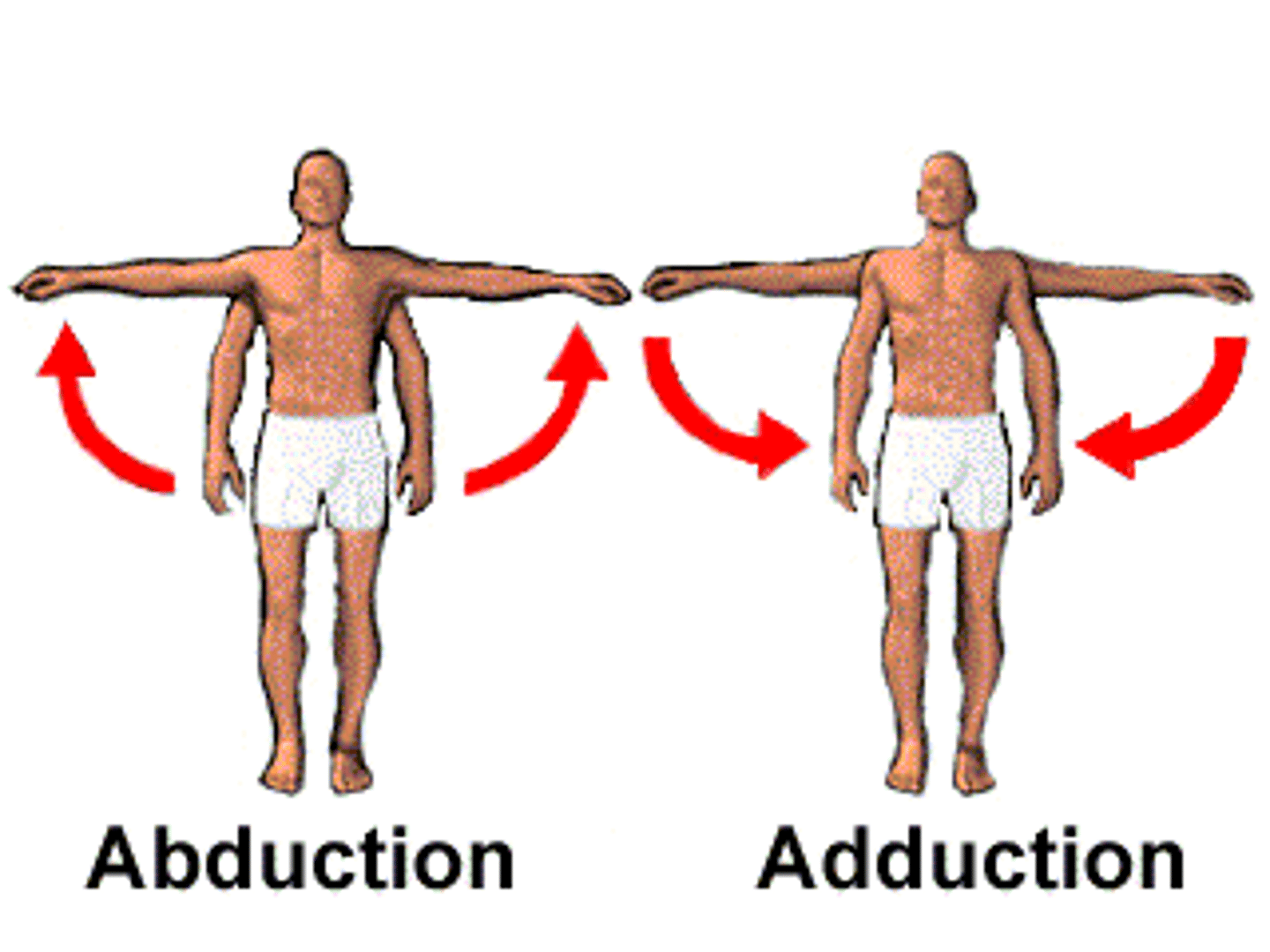
abduction/adduction
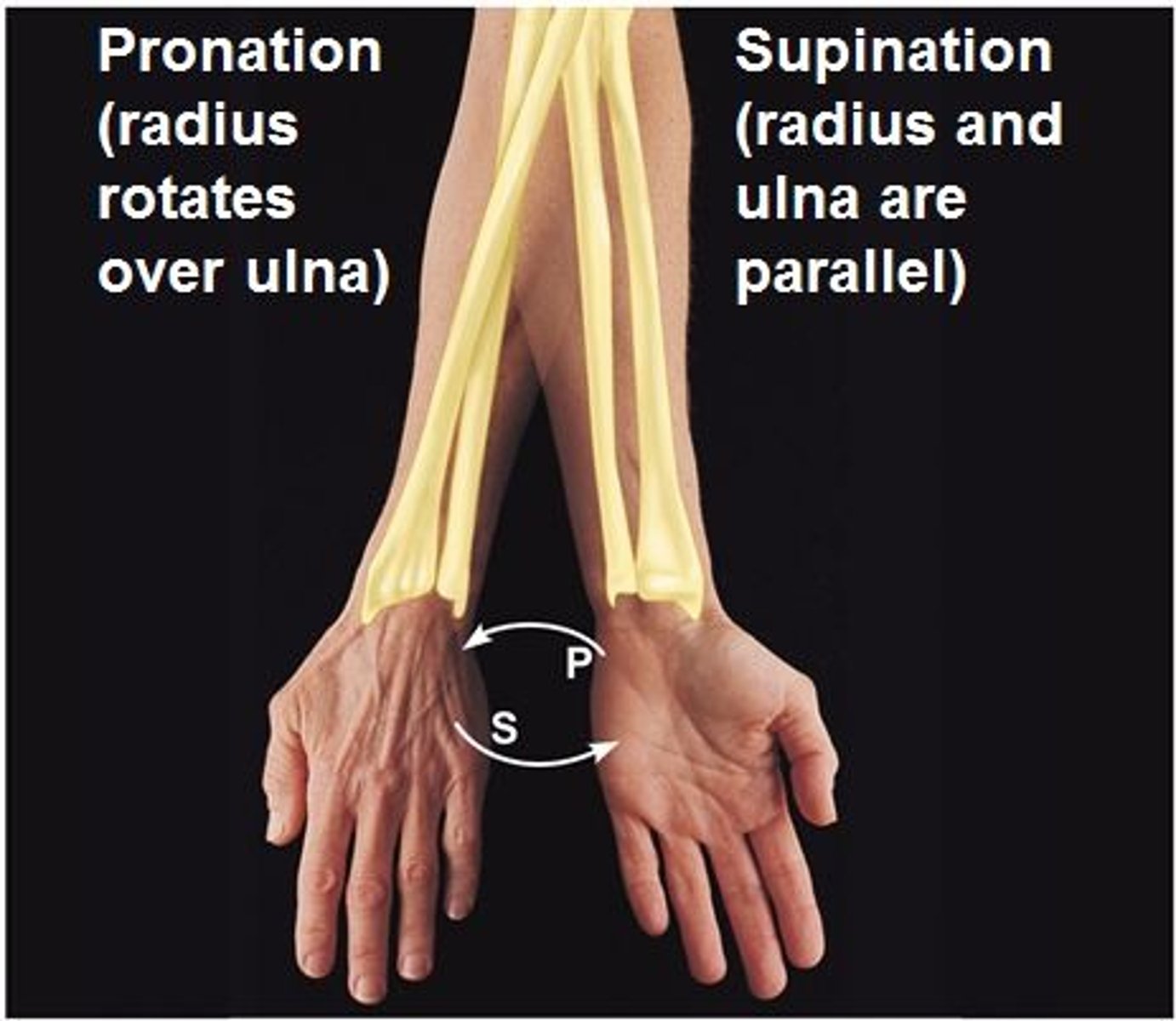
pronation / supination
antroversion
forwards
retroversion
back
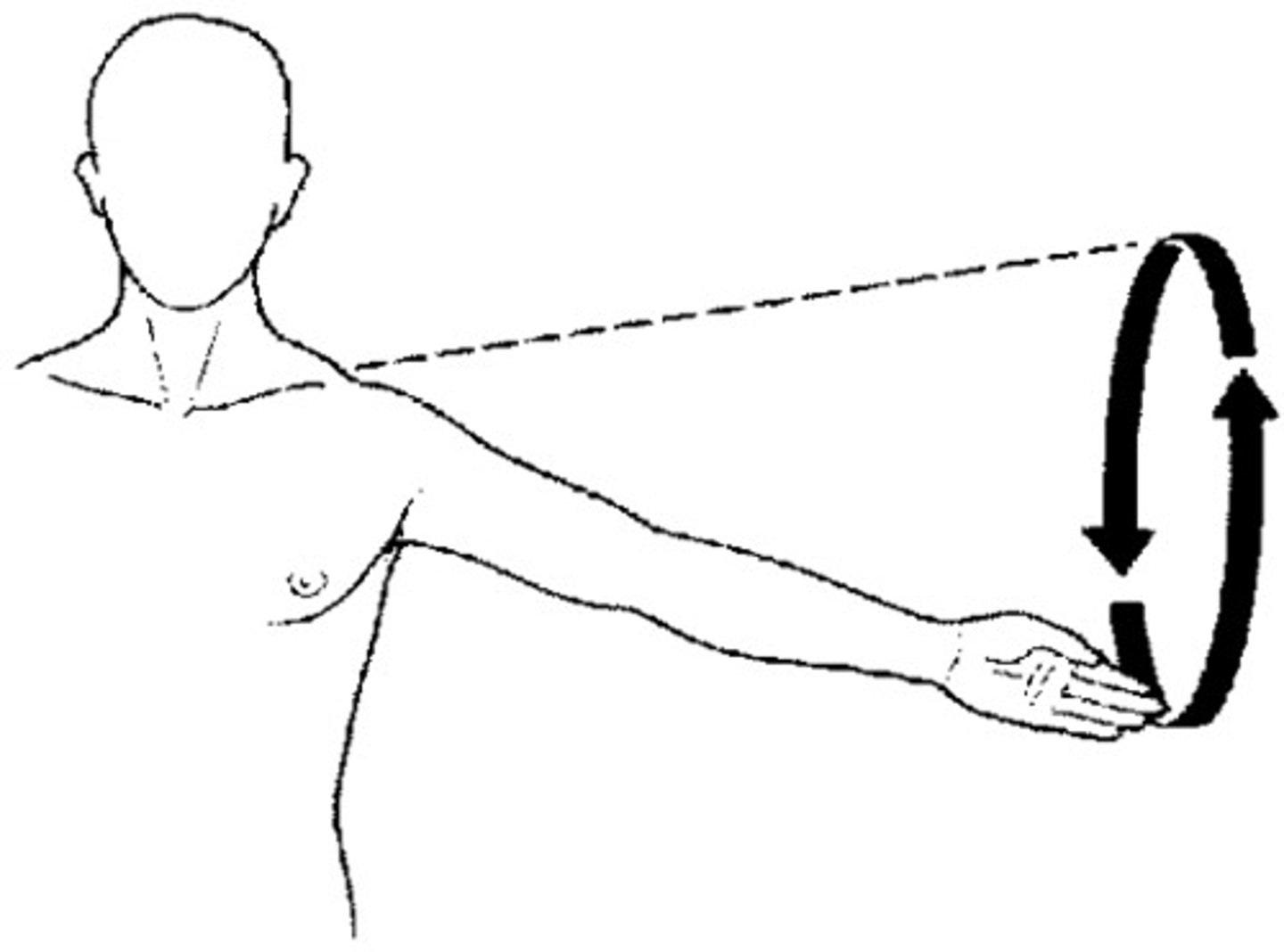
Circumduction
what is the muscle hilium ?
provide vascularization to the muscle and the nerves
what is a fasciae ?
Can be superficial or deep, surrounds the muscle
What is a fibrous sheaths?
support the fascia, tendon, and keep everything joined to a bone
What is a synovial bursas ?
sac filled with synovial fluid for protection
What is a synovial tendon sheaths?
special sinovial bursa