Thermal Physics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is the internal energy of a body?
The sum of all the randomly distributed kinetic and potential energies of the particles
What 2 ways can the internal energy of the system be increased?
Doing work (e.g moving it)
Increasing the temperature
Why does internal energy change when state changes?
The potential energy of the system changes due to a change in the separation of the particles (however KE is constant)
State the formula for specific heat capacity.
change in energy = mass x shc x change in temperature
Define specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1K without changing its state
State the formula for specific latent heat.
change in energy = mass x slh
Define specific latent heat.
The energy required to change the state of 1kg of a substance without changing its temperature
What are the 2 types of SLH?
SLH of fusion
SLH of vaporisation
What are gas laws?
Laws the describe the experimental relationship between pressure, volume and temperature for a fixed mass of gas
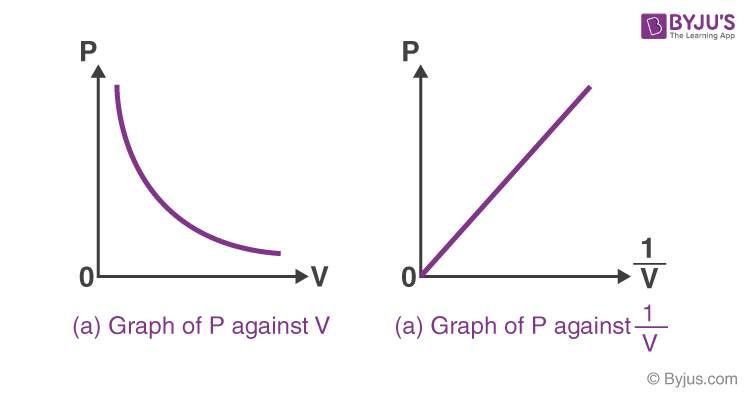
State Boyle’s law and its equation.
When temperature is constant, pressure and volume are inversely proportional
pV = k
What is the effect of using a higher temperature experiment on a Boyle’s law graph?
The curve moves further from the origin
Draw 2 graphs to represent Boyle’s Law.
State Charles’s law and give its equation.
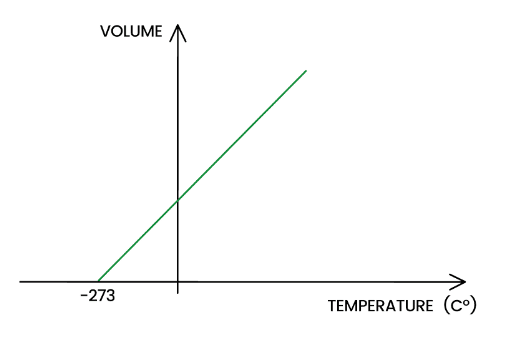
When pressure is constant, volume is directly proportional to absolute temperature
V/T = k
Draw a graph to represent Charles’ Law.

State the pressure law and give its equation.
When volume is constant, pressure is directly proportional to absolute temperature
p/T = k
Draw a graph to represent the Pressure Law.
State how to convert from degrees to kelvin.
+273
What is absolute zero.
0K (-273*)
Particles have no kinetic energy and pressure and volume are 0
State the ideal gas equation.
pV = nRT
State the value of R.
8.31 JK-1mol-1
State how to convert from cm³ to m³.
x10-6
State how to convert from dm³ to m³
x10-3
How many molecules/atoms are in 1 mole of a substance?
6.022 × 1023
State how to convert between moles and molecules?
x avogadro’s constant
State the equation for k.
k = R / NA
State the ideal gas equation using number of molecules.
pV = NkT
What is the value of k?
1.38 × 10-23
What is molar mass?
The mass (g) of one mole of a substance
How can work done be calculated when changing the volume of a gas at a constant pressure?
change in W = p x change in V
How is work done found from a pressure-volume graph?
Calculate the area under the graph
What is Brownian motion?
The random motion of larger particles in a fluid caused by collisions with surrounding particles
List the assumptions made when deriving the kinetic theory equation.
No intermolecular forces between particles
Duration of collisions is negligible in comparison to time between
Motion of particles is random and collisions are completely elastic
Motion follows Newton’s laws
Molecules move in straight lines
Derive the kinetic theory equation.
consider a cube of side length l, a molecule has a mass m and is travelling at velocity u. It collides with the wall and the change in momentum = mu - (-mu) = 2mu
The molecule travels to the opposite wall before colliding again, so the time between collisions is t = 2l/u
F = change in momentum = 2mu / (2l/u) = mu²/l
Pressure on one wall = F/A = mu²/l(l²) = mu²/l³ = mu²/V
Sum the pressures on each molecule in the cube = p = N(mu²/V)
Consider all directions of movement (c² = 3u²) and u² = v² = x²
State the kinetic theory equation.
pV = 1/3(Nmcrms²)
What is an ideal gas?
There are no intermolecular forces between the gas particles and the particles have negligible volume
What is the potential energy of an ideal gas?
0
What is the internal energy of an ideal gas?
The sum of the KEs of all the particles
State how to calculate the kinetic energy of a single gas molecule.
1/2mcrms2 = 3/2kT = 3RT/2NA
What property is kinetic energy of a gas molecule directly proportional to?
The temperature (in K)