Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Bio (Chapter 6+7) LMK if I'm missing any terms that could be helpful by emailing me :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
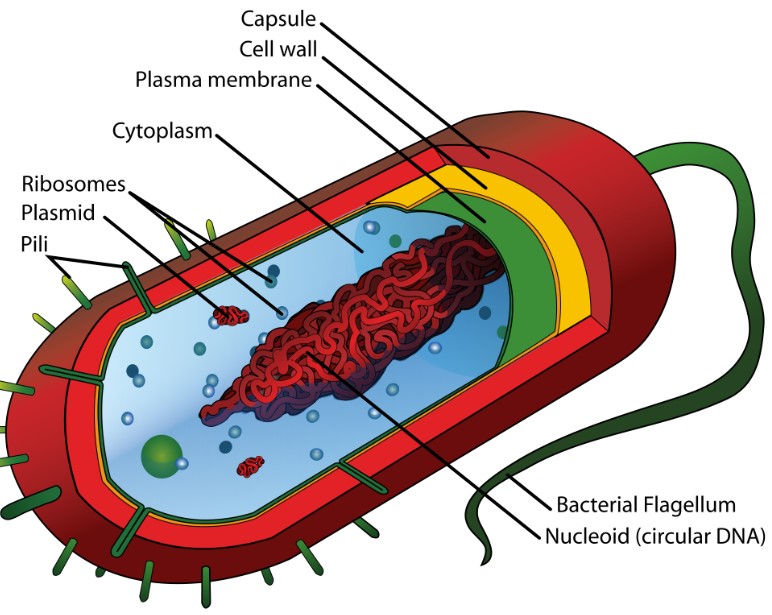
Prokaryotic
Always unicellular
Smaller, simpler structure
Lacks membrane bound organelles
Lacks true nucleus
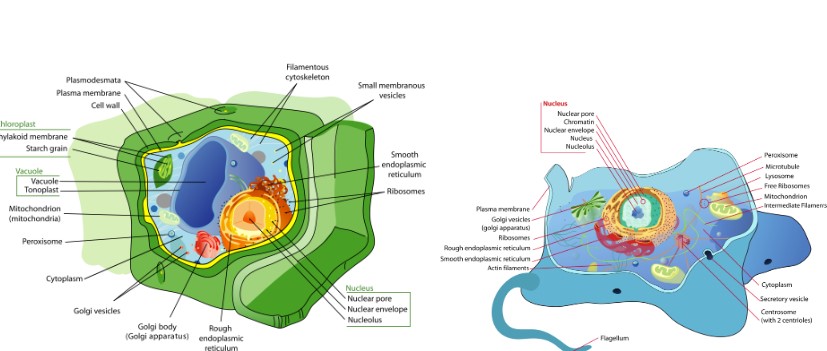
Eukaryotic
Can be unicellular or multicellular
Larger, more complex structure
Has many organelles
Has a nucleus
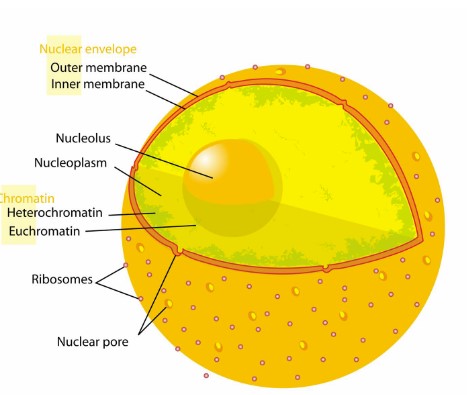
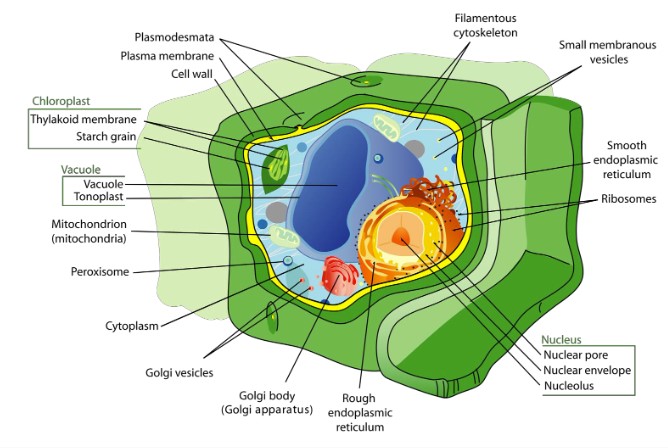
Nucleus
contains DNA and directs cellular functions
Nuclear Membrane
Structure to allow the storing of information & allowing for it to flow from nucleus -> ribosomes in the cytoplasm
porous membrane separates cell’s DNA genome from rest of cellular environment
Ribosomes
converts nucleic acid information (DNA) into polypeptide chains
site of protein synthesis
Free ribosomes
make proteins that will stay inside the cell for use by the cell, like enzymes associated with metabolism or DNA replication
exists in the cytoplasm (in ALL types of cells)
Bound ribosomes
make proteins that will leave the cell to be used elsewhere
Most are for communication between cells, such as antibodies for fighting infection
bound to the ER
Cell Wall
Fibers of structural polysaccharides that provide structural support and protection for cell
Cell Membrane
controls passage of organic molecules, ions, water, & oxygen in and out of the cell (waste products leave by passing through)
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
membranous channels that run through cell, producing membranes and transporting proteins
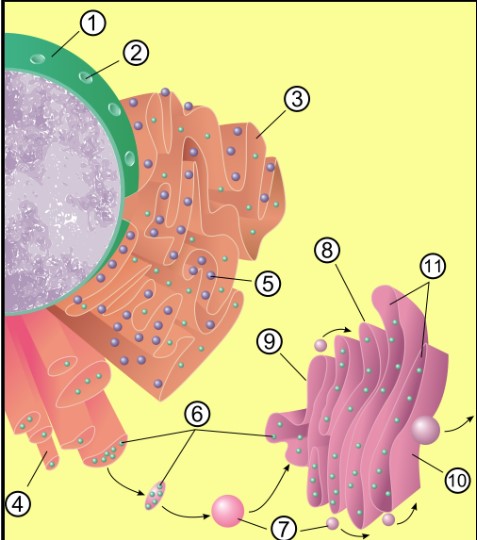
Smooth ER
Helps with synthesis of lipids, phospholipids, steroids
Helps carbohydrates (glycogen/stored sugar) breakdown into (glucose/useable sugar)
Detoxify blood as liver cells have lots of SER (smooth ER)
Store Ca++ needed for muscle contraction
ER 3 and 4 (depicted above) make up the Endomembrane System, involved in production/transport of membrane & membrane proteins
ER not covered in ribosomes
Rough ER
Provides safe folding area for proteins
Ribosomes bound to outside, deposits proteins as they are made inside ER
Proteins can fold into 3D structure needed to function
ER covered in ribosomes
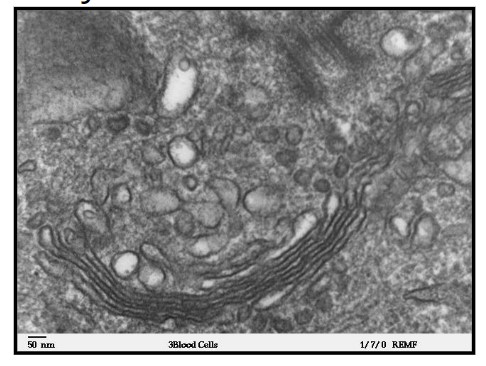
Golgi Apparatus
flattened membranous compartments that receive material from ER, modify it before targeting it for delivery to other areas of cell
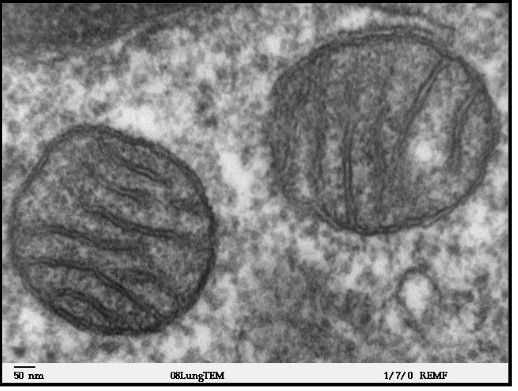
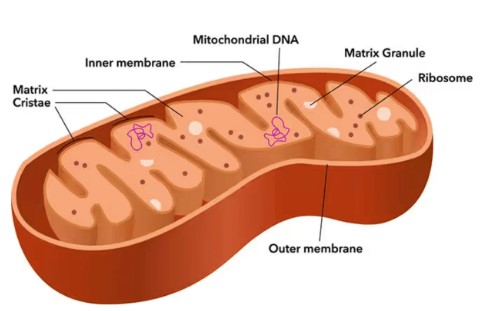
Mitochondria
site of aerobic cellular respiration
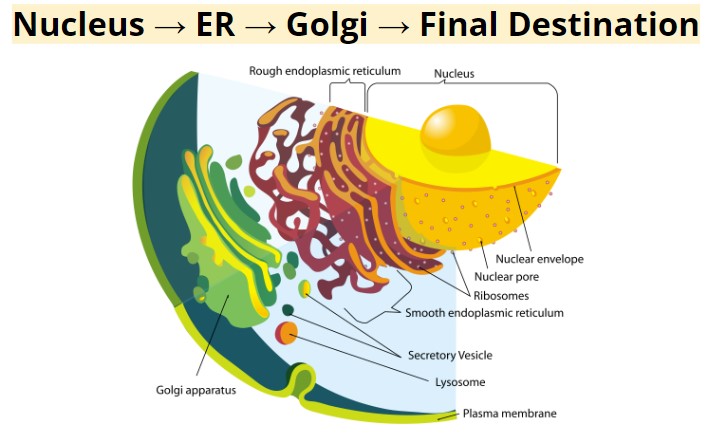
Endomembrane System
The flow of information from the nucleus to proteins. Nucleus → ER → Golgi → Final Destination
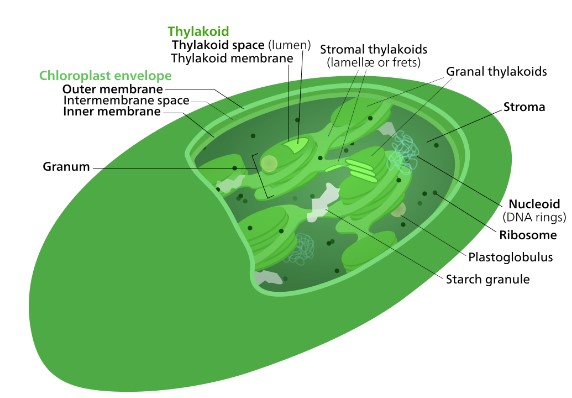
Chloroplasts
site of photosynthesis in plants and algae
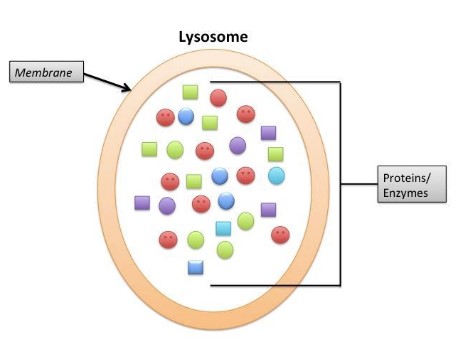
Lysosomes
plays a part in molecule digestion,
recycling of cell’s damaged components
programmed cell death
membrane enclosed sacs containing collections of digestive and hydrolytic enzymes
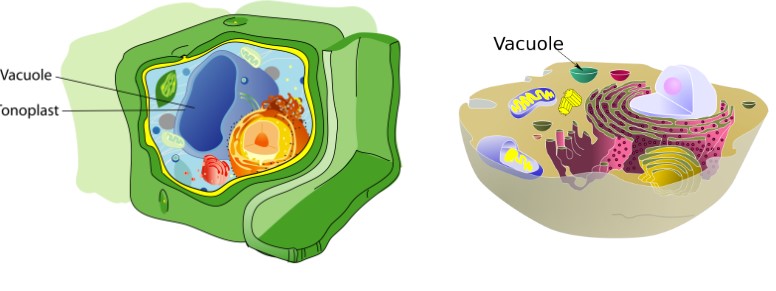
Vacuoles / Vesicles
plant cells have large, central vacuole which store nutrients/material and support cell structure
animal cells have smaller, individual
membrane bound sacs that store material w/ different structures for different products needed by the cell
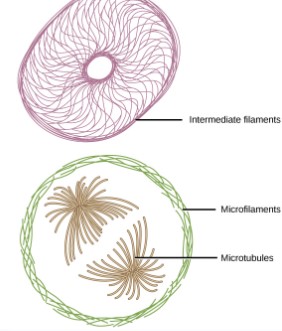
Cytoskeleton
Keeps inner organelles organized
Facilitates cell organelle movement
Supports and protects the cell
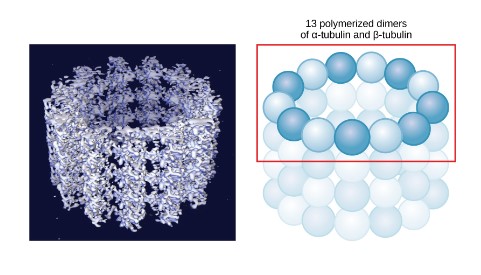
Microtubules
supports movement and function of cell & organelles Important structures made of microtubules within a cell that you should know:
large, hollow tubes made of Tubulin protein
Centrosomes and Centrioles
Centrosomes contain a pair of centrioles and are the region where microtubules grow from.
Spindle Fibers
microtubules that grow out of the centrosome region (seen in mitosis and meiosis)
Cilia
microtubule extensions that project from cells (usually many) and are involved in movement of fluids/substances over the surface of the tissue
Flagella
Microtubule extensions that project from cells (usually just one or a few) involved in movement of a cell (like a tail)
Microfilaments
provide pulling force
abundant in muscle tissue cells in animals
solid rods made of actin or myosin protein

Intermediate filaments
helps reinforce and brace large microtubules
permanent solid rods made of keratin protein
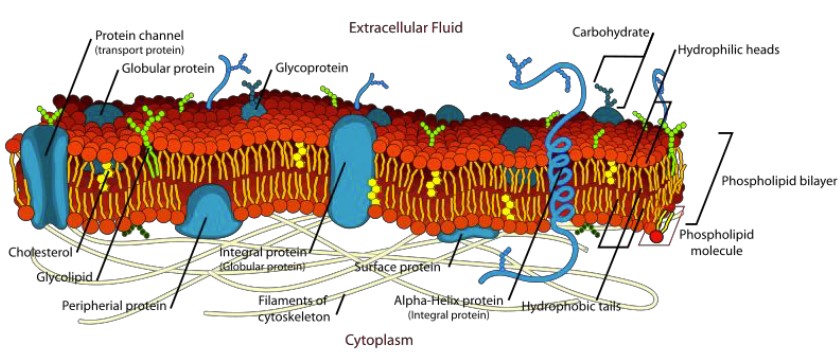
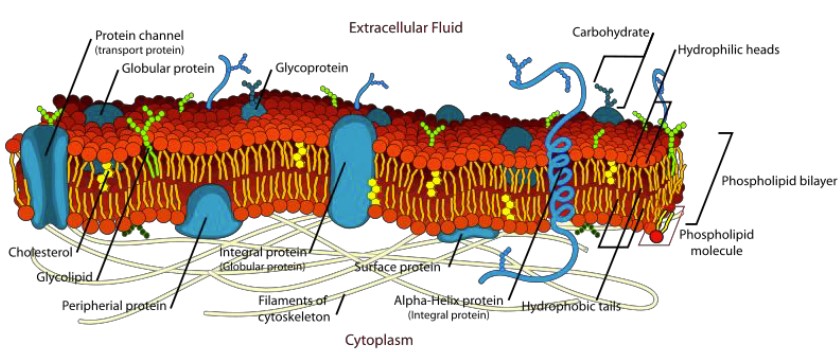
Fluid Mosaic Model
Connects membrane structure to function. 2 components: phospholipids and proteins
Selective Permeability
Only small nonpolar molecules move through bilayer
Gets oxygen and co2 in and out fast
Cell needs o2 & wants to get rid of co2 fast because it is waste
Other materials move through protein pores
A property of biological membranes that allows them to regulate the passage of substances across them
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are amphipathic.
They spontaneously form a bi-layer in aqueous environments.
The inside of the bi-layer is hydrophobic.
Cholesterol
Reduces membrane fluidity at moderate temperatures by reducing phospholipid movement.
At low temps, hinders solidification by disrupting regular packing of phospholipids.
Fluidity buffer
Passive Transport
Doesn’t require energy
Diffusion, moves with the concentration gradient
Simple Diffusion
Ex: oxygen, carbon dioxide
Small, nonpolar molecules are able to diffuse across the phospholipid bilayer
Facilitated Diffusion
Protein pores
Large, polar/charged molecules must defuse through protein pores in cell membrane
Primary Active Transport
moves ions across a membrane against their gradient and creates a difference in charge across that membrane, which is directly dependent on ATP
Secondary Active Transport
describes the movement of material that is due to the electrochemical gradient established by primary active transport that does not directly require ATP
Co-Transport
Cells can transport multiple molecules simultaneously
Bulk Transport
Cells transport bulk molecules by surrounding them with membrane (“vesicles”)
Endocytosis
Internal vesicular transport
Exocytosis
External vesicular transport
Tonicity
A measurement of the relative concentrations of solute between two solutions (inside and outside of cell)
Hypertonic
Solution has more solute/less solvent
Hypotonic
causes water to flow into the cell
Animal cell = shrivel
Plant cell = flaccid
Solution has less solute/more solvent
Isotonic
Equal concentrations or equal exchange rate of solute and solvent
Water Potential Ψ
LOW water potential:
LESS water molecules are free to move around.
HIGH water potential:
MORE water molecules are free to move around.
The potential energy of water per unit area compared to pure water. A measurement of how likely it is that water will move in/out of a solution. Water moves from an area of HIGH water potential to LOW (more negative) water potential.
Proteins (role in cell)
act as channels that molecules can enter/exit the cell membrane through
integral and peripheral
Carbohydrates (role in cell)
signal to other cells
Cholesterol
In cold temperatures, cholesterol acts a roadblock to prevent molecules from packing together too tightly (and stiffening too much)
In warm temperatures, cholesterol acts a roadblock to hinder phospholipid movement, preventing excessive fluidity
acts as fluidity buffer to prevent cell membrane from being too fluid or too stiff
Phagocytosis
takes IN PARTICLES used for nutrients
Pinocytosis
takes IN FLUID droplets to use for nutrients
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis
Specific molecules bond to receptors (which can only accept specific molecules) and are brought into the cell
Aquaporins
Channels that allow water to diffuse
Osmosis
Diffusion of water in cell membrane
Sodium Potassium Pump
Cells move molecules against the concentration gradient by using energy. The energy is used to operate “pump proteins”.
Flaccid
when plants cells are isotonic
Turgid
when plants cells have excess water (hypotonic)
Plasmolysis
when plants cells have too little water (hypertonic)