UA: Crystals, Cells, and Casts
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcard Sets Combined
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Casts in Urinary Sediment
Casts in urinary sediment → differential diagnosis of renal disease
Pure Hyaline casts may be seen in Proteinuria
Small Hyaline cast seen transiently may occur with marked exercise or febrile conditions
Casts with inclusions, such as RBC’s or WBC’s may be formed without a protein matrix
Types of Casts
Hyaline, Granular, WBC, RBC, Cellular and other casts (such as hyaline casts with inclusions), Waxy, Fatty, Epithelial
Hyaline Casts
Hyaline casts = Renal Proteinuria: They form only with urinary protein.
Tamm-Horsfall protein is key: This nephron-secreted protein is the main cast component.
Acid/Concentration = Casts: Low pH and high solutes cause cast formation.
Hyaline Casts Appearance
Transparent, cylindrical with parallel sides and rounded ends; seen more when urine flow is slow and proteinuria is high, less in alkaline urine.
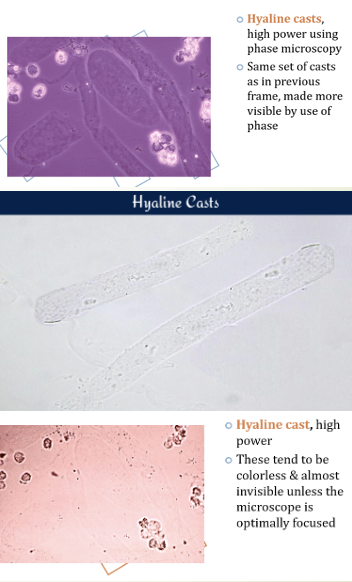
Hyaline Casts Clinical Implications
Casts formed from protein leakage through damaged glomerular membranes, indicating conditions like nephritis, chronic renal disease, or diabetic nephropathy.
Granular Casts vs Hyaline Casts
Granular casts are renal casts that contain granules and indicate damage to the renal tubules, whereas hyaline casts are clear, homogeneous structures that can be found in normal urine or in cases of dehydration and concentrated urine.
Fine vs Course Granules
fine: appear grey or pale yellow in color)
coarse: appear as darker
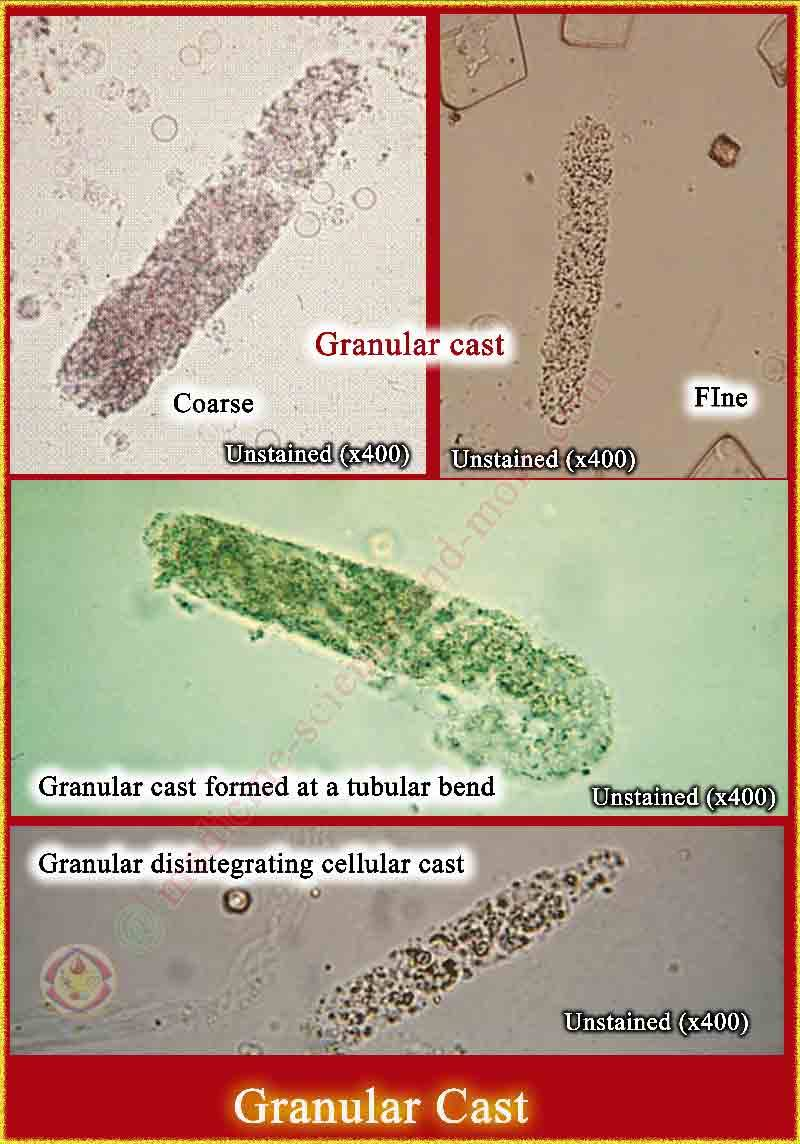
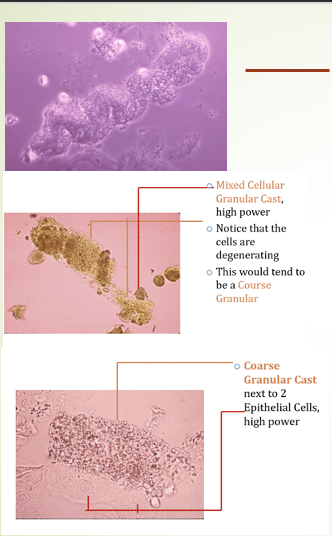
Granular Casts
Degenerated cellular components or aggregated serum proteins within Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein, indicating significant renal disease.
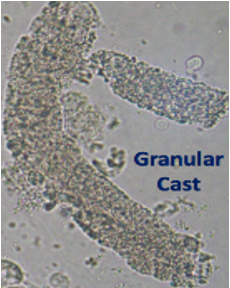
Granular Cast Under Phase Contrast
Granular Cast Clinical Significance
may be seen in:
Acute tubular necrosis
Advanced granulonephritis
Pyelonephrities
Malignant nephrosis
Chronic lead poisoning
Cellular Casts
when concentrated proteins in the distal tubule entrap cells, leading to Hyaline Casts with cellular inclusions → WBC Casts. Mucus threads found in urine samples can indicate irritation or be a normal finding.
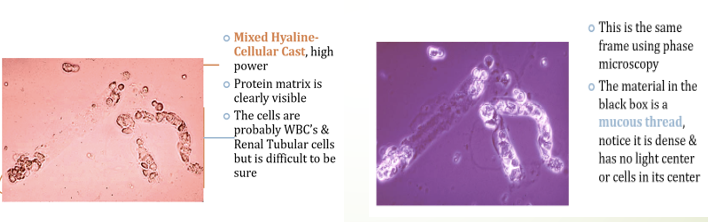
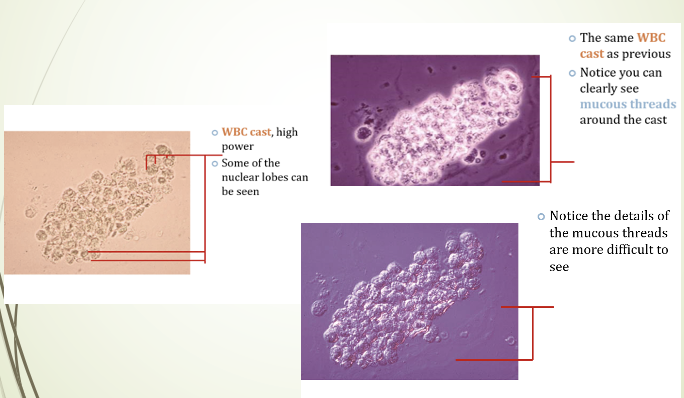
WBC Casts
Formed by aggregates of WBCs trapped in protein matrix in the renal tubular lumen.
An excess of WBCs singly or in clamps, in the urine may indicate inflammation
of renal origin
seen in acute pyelonephritis and occasionally in glomerulonephiritis.
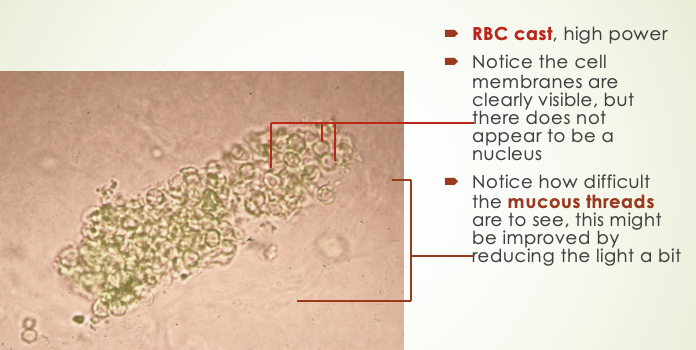
RBC Casts
Usually, they found in hematuria
brown to almost colorless
usually diagnostic of glomerular diseases.
Normal range: normally not seen in normal individual
Formed usually after accumulation of cellular element in the renal tubules
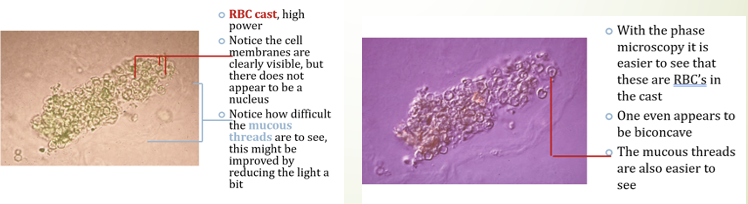
RBC Casts Appearance
clear membranes and lack nuclei, formed from RBCs trapped in renal tubules. Mucus threads present but difficult to see
Waxy Casts (Renal Failure Casts)
Not seen in normal individuals.
shorter and broader than hyaline casts.
Composed of homogeneous, yellowish materials.
May occur from cells (WBC, RBC, or Epithelial) casts, hyaline casts.
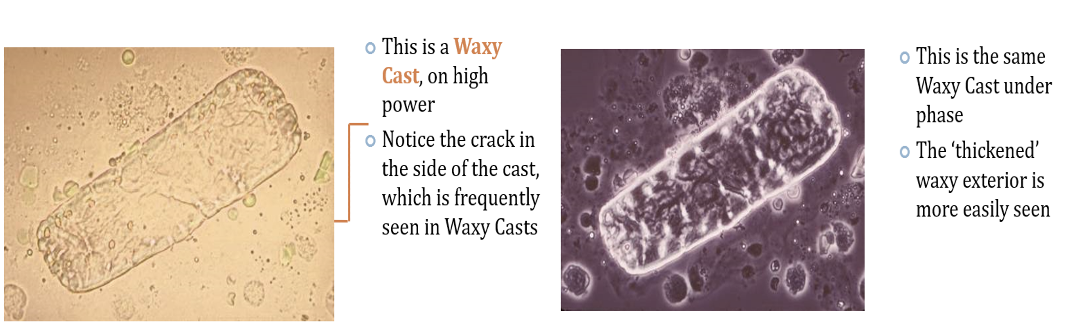
Waxy Casts are found in what possible diseases?
Chronic renal disease
Tubular inflammation
degeneration/Localized nephron
obstruction/malignant hypertension
presence indicates severity of renal disease.
Fatty Casts
normally not seen in health individuals.
contain fat droplets inside them.
formed after accumulation of fat in the tubular vessels, especially tubular epithelial and finally disintegrated.
fat droplets, oval, fat bodies, or fat casts → nephrotic syndrome.
Chronic renal disease/Inflammation and degeneration of renal tubules/ lupus and toxic renal poisoning

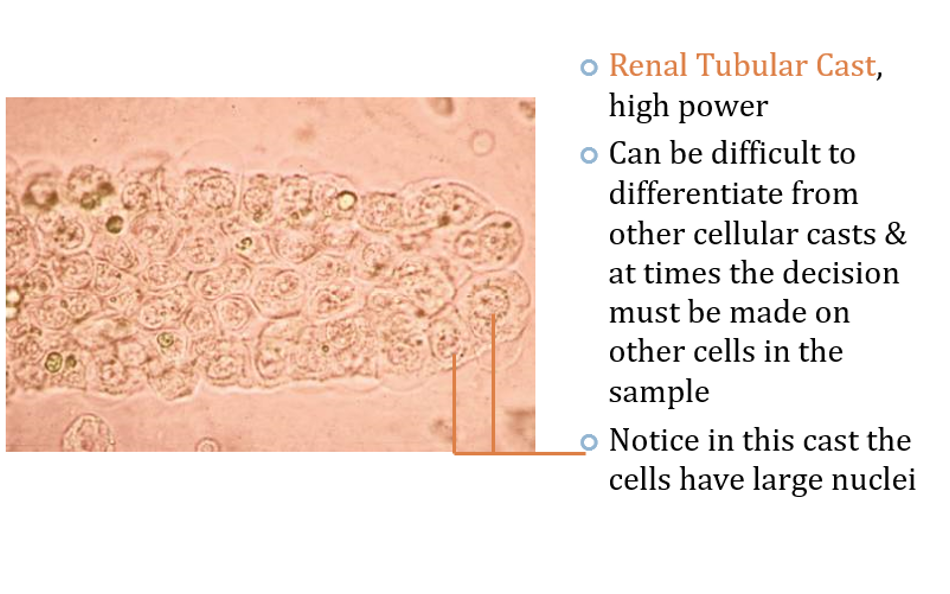
Epithelial Casts
consist mainly of desquamated tubular epithelial cells
appear as two rows of cells in a protein matrix.
A large number indicates renal parenchymal disease with tubular damage.
Procedure for Microscopic Examination - Key Steps
Centrifuge: Centrifuge urine (1500-2000 rpm, 3-5 minutes).
Discard Supernatant: Remove the liquid (supernatant).
Resuspend Sediment: Mix the remaining sediment.
Prepare Slide: Place a drop of sediment on a slide and cover.
Microscopy: Examine under 10x, then 40x objective.
Source of Errors During Microscopic Examination of Urine
Drying of specimen on the slide.
Improper pouring off of supernatant decreases sediment concentration, leading to false results.
Discarding whole sediment with supernatant can cause false negatives.
Collect another sample and repeat test if errors occur.
Microscopy Types and Key Findings
Bright Field: Frequently used, low light via rheostat control not lowering condenser
Phase Contrast: Advantageous for low refractive casts, mucous threads and Trichomonas
Polarizing: Crystals and lipids: confirm fat droplets, oval fat bodies and fatty casts
Interfering Contrast: 3D image – fine structures
Dark-Field: spirochete Treponema pallidum
Fluorescence: immunofluorescence
Classification of Urinary Sediments
Organized (Formed)
Ex in HPF: WBCs, RBCs, Bacteria
Ex in LPF: Muscus, casts, yeast cells, miscellaneous
Non-Organized (Non-Living Material)
Slightly Acidic Crystal
Acidic, Neutral, or slightly alkaline
Alkaline, Neutral, or slightly acidic

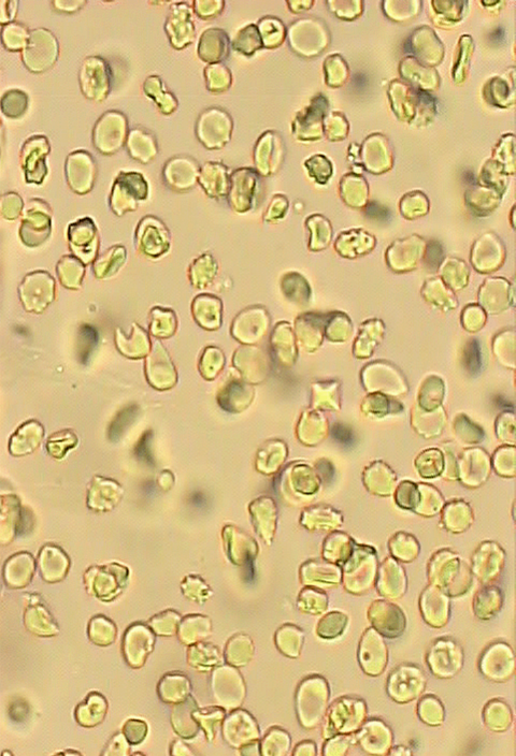
RBCS in Urine
organized urinary sediment
NOT usually present in normal urine 0-5/HPF
Appearance:
fresh sample: intact, small and faint yellowish discs, darker at the edges
RBCs will lyse in acetic acid while other elements will stay intact.
RBC Variations in Urine
In conc. (hypersthenuric) urine: RBCs may be crenated and small
In diluted (hyposthenuria) urine: RBCs may be turgid, large, and may lyse.
In alkaline urine: small or destroyed, forming brownish granules.
In diluted and alkaline urine: RBCs rupture, releasing hemoglobin, forming 'ghost' cells (colorless cell membranes).
Dysmorphic RBCs: vary in size, show protrusions or fragments.
To get rid of RBC’s so that WBC’s are more visible – acetic acid is very helpful, Why?
RBCs will lyse in acetic acid while other elements will stay intact.
Microscopic Examination of RBCs
OCCURS AT 40X OBJECTIVE
presence of a few is normal
higher numbers are indicator of renal disease
result of bleeding at any point in urinary system
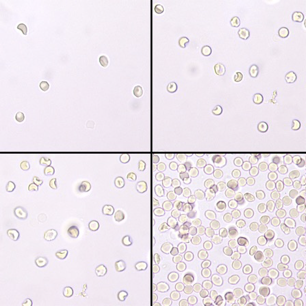
Clinical significance of RBCs in Urine
An elevated RBC count (typically exceeding 5 RBCs/HPF, averaged over 10 HPFs) may indicate:
Macroscopic hematuria: TNTC (>100/hpf)
Disease conditions in the urinary tract
Too many RBC = presence of disease conditions in the urinary tract, such as
Acute and chronic glomerulonephritis
Tumor that erode any part of the urinary tract
Renal stone
Cystitis
Prostates
Trauma of the kidney
traumatic catheterization
Yeast Cells compared to RBCs
smaller and are oval in shape flattened, vary considerably in size with one specimen, and have budding at the surface

Bubbles (oil droplets) compared to RBCs
vary considerably in size and are extremely refractive or shiny → polarizing microscopy to find Maltese Shaped Cross

Leukocytes compared to RBCs
larger and have granular appearance upon addition of 2-5% acid the RBCs will disappear
Interfering factors for RBCs
Factors that may result falsely in high number of RBCs, i.e. without the presence of actual renal or other normal physiological disturbances included:
Menstrual bleeding, Vaginal bleeding, Trauma to peranal area in female patients
Following traumatic cateterization
Some drugs:
Aspirin ingestion or over dose
Anticoagulant therapy over dose
Leukocytes (WBCs)
Normal range: 0-4 WBC/HPF.
Appearance: normally, clear granular disc shaped, the nuclei may be visible.
In alkaline urine, they may increase their size and become irregular.
Predominantly, polymorph nuclear neutrophils are seen
WBCs (Pus Cells)
occur due to predominance of neutrophils and the occurrence of bacterial cells together with polymorphonuclear cells, WBCs are called pus cells → may be seen in clumps.
Microscopic Examination of WBCs
Occurs at 40X OBJECTIVE; a few are normal while high numbers indicate inflammation or infection somewhere along the urinary or genital tract
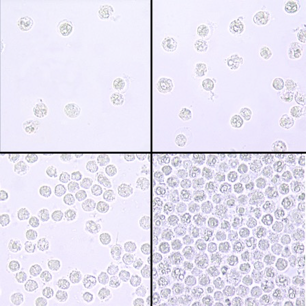
WBCs Result Reporting
under 40x objective, at least 10 fields of microscope
0-5/HPF → normal
5-10/HPF → few leukocytes/HPF
10-20HPF → MOD/HPF
20-30/HPF → MANY/HPF
Above 30 leukocytes/HPF →full/field
Clinical significance of leukocytes
Increased number of leukocyte urine are seen in case of:
UTI such as renal tuberculosis
All renal disease
Bladder tumor
Cystitis
Prostates
Temporarily increased during:
Fever
After strenuous exercise
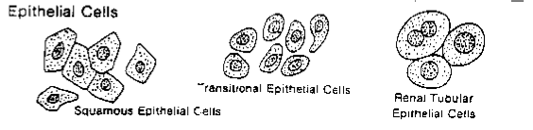
Epithelial Cells
Squamous epithelial cells
Transitional epithelial cells
Renal tubular epithelial cells
Oval Fat Bodies
Clue Cells
Order of Epithelial cells from smallest to largest
Renal tubular epithelial cells
Transitional epithelial cells
Squamous epithelial cells
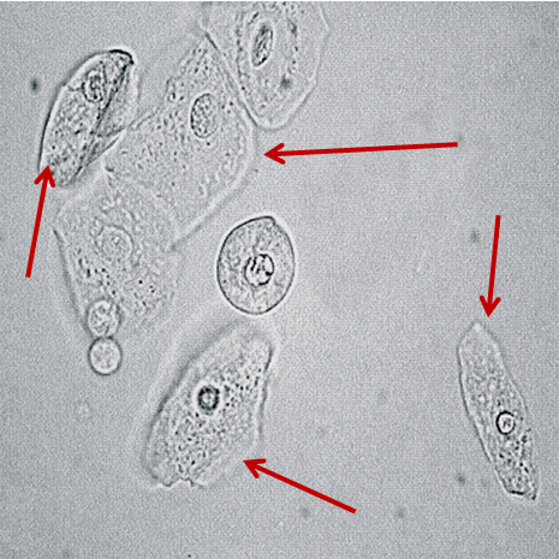
Squamous Epithelial Cells
large, flat cells with small nuclei
nucleus is usually distinct & centered
Appear flat with abundant cytoplasm
Originate from the superficial lining of the vagina, female urethra, and lower portion of the male urethra
Common contaminant; seen in female voided specimen
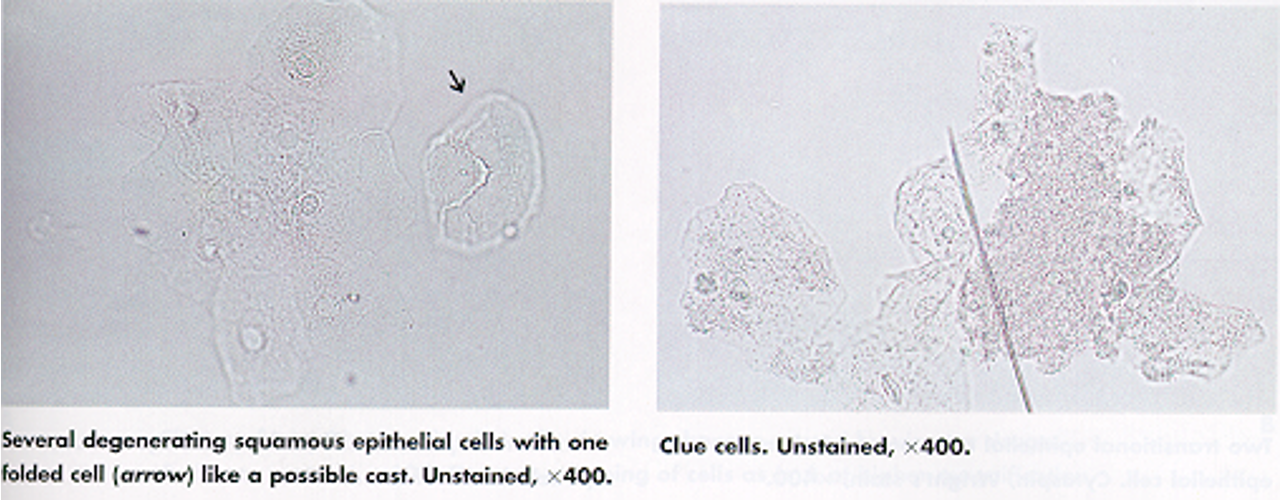
Clue Cells
Squamous epithelial cells covered with coccobacilli, Gardnerella vaginalis
Transitional Epithelial Cells
Shape: Polyhedral; swells to spheroidal in urine.
Appearance: Round/pear-shaped contours, small central nucleus (may be bi-nucleated).
Origin: Transitional lining of renal pelvis, ureter, urinary bladder.
Normal: Few in urine; large clumps may suggest carcinoma.
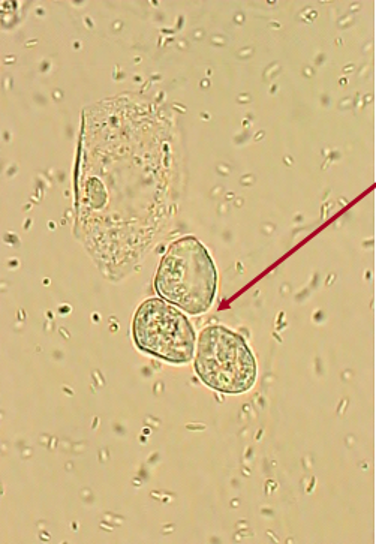
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells (RTE)
Origin: Proximal and distal convoluted tubules
Shape: Single, oblong or egg-shaped
Appearance: Coarsely granular eosinophilic cytoplasm
Nuclei: Small, dense chromatin (may be multiple)
Clinical Significance: Indicative of acute tubular necrosis, drug, or heavy metal toxicity
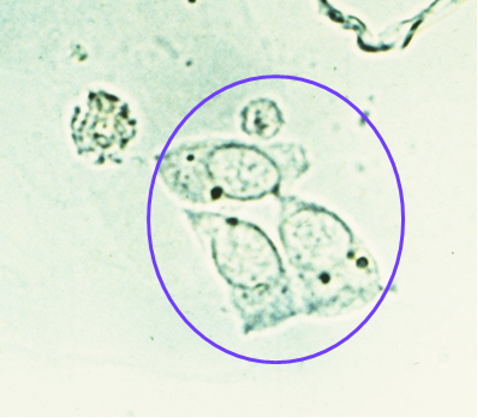
What are RTEs associated with?
Presence of more than 2 RTE/HPF indicates tubular injury
Usually seen in association with proteins or casts
Clinical significance: increased amts indicative of necrosis of the renal tubules.
Clinical significance of Epithelial Cell Presence
Presence of epithelial cells in large number, mostly renal types may indicate:
Acute tubular damage
Acute glomerulonephritis
Silicate overdose
TRUE OR FALSE: The presence of large # of epithelial cells with large # of Leukocytes and mucus trades (filaments) may indicate Urinary Tract Infections (UTI).
True, as this presence suggests inflammation and potential infection.
Oval fat bodies
RTE absorb lipids present in filtrate
Make RTE highly refractile
Seen with free floating fat droplets
ID with stain: Sudan III or Oil Red O
Polarizing light: maltese cross
Extremely significant finding. Seen in lipid nephrosis and terminal kidney disease.
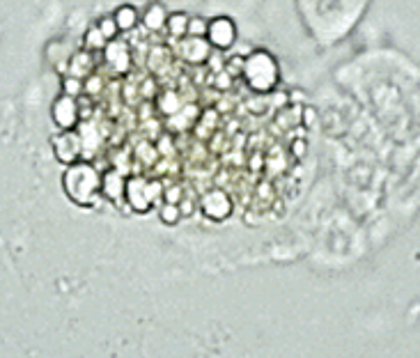
What disease is associated with Oval Fat bodies in urine?
Lipiduria frequently associated with damaged glomerulus due to nephrotic syndrome
Reporting of epithelial cells
under 10X objective, semi-quantitatively
1-3/LPF
2-4/LPF
6-14/LPF
15-25/LPF
Full Field/LPF
Bacteria
Normally not present in the urine
Unless sterile collection a few may be non-pathological→Contamination
Multiply rapidly in room temp conditions – increase pH
Accompanied by WBCs significant for UTI (lower or upper)
Motility (Trichomonas)
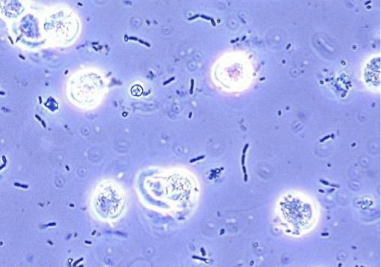
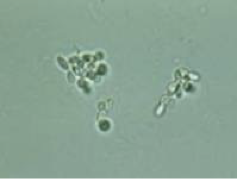
Yeast Cell
fungi that are not normally seen in healthy individuals.
Appearance
Variable in size
Colorless.
Oval in shape, and usually form budding
Have high refractive index.
Usually confused with RBCs
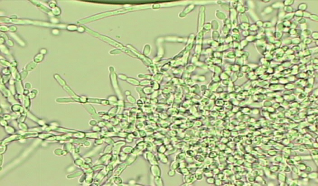
Branching Pseudohyphae
obscure specimen features & may indicate that the specimen is not a clean catch
candida species (candida albicans)
UTI
Vaginites
DM
Intensive antibiotic or immunosuppressive therapy
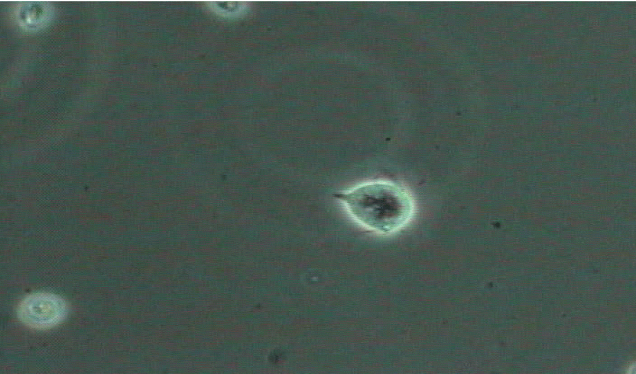
Why are yeast cells found in specimens with high glucose levels? What does it indicate?
because they thrive in environments with abundant sugar, indicating a possible underlying issue such as diabetes or a UTI
Parasites
Trichomonas vaginalis
Schistosoma haematobium
Wuchereria bancroftie
others such as Entrobious vermicularies also may occur due to contamination of the urine with stool.
Trichomonas Significance in urine
small parasite that is very active in a fresh specimen
multiple flagella as well as an undulating membrane = MOTILE
absence of movement → mistaken for WBCc
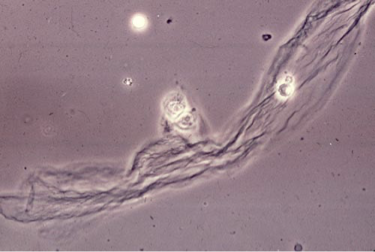
Spermatozoa - Miscellaneous
Small, motile structures with a head and tail, often seen in the urine of males and occasionally in females after coitus.

Mucus
Protein material: Tamm-Horsfall protein
Appears as thread like structures (HPF)
Contaminates and Artifact Structures
Muscle fibers
Vegetable fibers
Air pockets or bubbles
Pollen greens
Starch granules
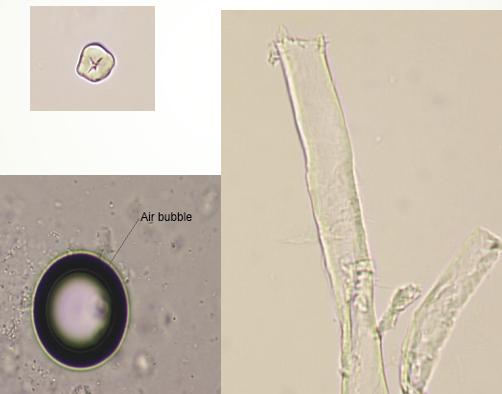
Urine Sediments: Artifacts, Crystals, Mucus

Crystals in Sediment
precipitation of solutes
are not normally present in freshly voided urine
can precipitate on storage
most are not clinically significant
pH critical to differentiating some important crystals
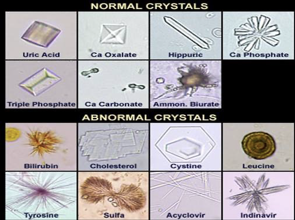
Acidic Urine Includes…
All clinically significant crystal are found in acid urine
Include: cystine, tyrosine, leucine & iatrogenic crystals: sulfonamide & ampicillin
Amorphous Urates
Amorphous Urates
Non crystalline urate salts of Na, K, Mg, & Ca
small & yellow-brown granules and can be in acidic or neutral urine
Will dissolve in alkaline or when heated
If add acetic acid, uric acid crystals will precipitate out

Amorphous Urates vs Amorphous Phosphates
Amorphous urates are non-crystalline urate salts, small yellow-brown granules found in acidic or neutral urine, whereas amorphous phosphates are non-crystalline forms of calcium and magnesium phosphates that typically occur in alkaline urine.
Uric Acid Crystals
Urine pH = 5.0 to 5.5
Common form = diamond shape but may be cube shaped or cluster in rosettes
Usually yellow to orange-brown
Are birefringent under polarizing light
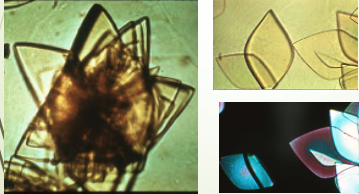
When do Uric Acid Crystals appear?
appear normally BUT can see large #s in gout & in increased purine metabolism such as cytotoxic drugs
What are the two forms that Oxalate Crystals appear as?
Both colorless
Dihydrate Form:
2 pyramids / squares w/ intersecting lines
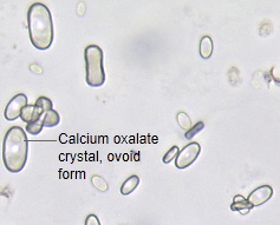
Monohydrate Form:
small ovoid or dumb bell
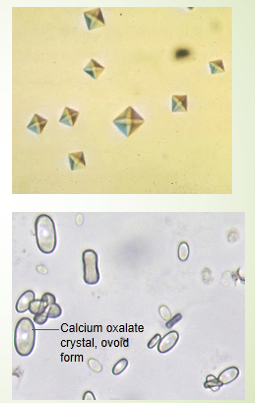
Calcium oxalate Dihydrate Form
Usually octahedral or look like envelope, less common than monohydrate form although both are seen in kidney stones
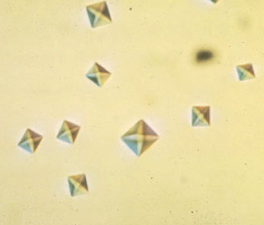
Calcium oxalate Monohydrate Form
A birefringent, colorless crystal that varies in size, often seen in neutral or acidic urine. It can appear due to normal dietary intake (e.g., ascorbic acid, tomatoes, spinach) and also indicates ethylene glycol.
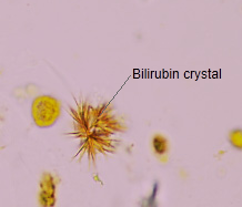
Bilirubin Crystals: Abnormal State
Appear as fine needles, granules, or plates
urine is acidic
always yellow-brown
the bile stains the other components of the sediment
presence of the crystals indicate high concentrations of bilirubin in the urine
What is the next step when bilirubin crystals are suspected in urine?
Confirm the presence of bilirubin with a strip reaction; positive results indicate a pathological process and abnormal crystals, often associated with liver disease.
Amino Acid Crystals and Pathology
Amino acid crystals are ALL ABNORMAL & seen in overflow aminoaciduria
can be seen in rare cases of liver disease, more likely to reflect inherited metabolic disorder
Include: TYROSINE, LEUCINE, AND CYSTINE
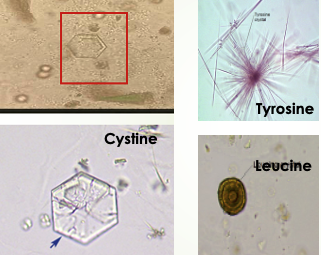
Tyrosine Crystals
fine, delicate needles, colorless or yellow
frequently in clusters or sheaves [as in stacks of wheat]
in acidic urine
less soluble than leucine, so found more often
![<ul><li><p>fine, delicate needles, colorless or yellow</p></li><li><p>frequently in clusters or sheaves [as in stacks of wheat]</p></li><li><p><strong>in acidic urine</strong></p></li><li><p>less soluble than leucine, so<u> found more often</u></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6fb8d3bb-783e-4528-b0d4-20a2dd427eec.png)
Leucine Crystals
Highly refractile yellow to brown spheres in acid urine.
Have concentric/radial striations on their surface
Can be mistaken for fat globules [or vice versa]
will not stain with fat stains or appear as maltese cross under polarization
![<ul><li><p>Highly refractile yellow to brown spheres in acid urine.</p></li><li><p>Have concentric/radial striations on their surface</p></li><li><p>Can be mistaken for fat globules [or vice versa]</p><ul><li><p><u> will not stain with fat stains or appear as maltese cross under polarization </u></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a3e6f00b-030a-4353-bae9-be8c353c24e0.png)
Cystine Crystals
Colorless hexagonal plates
sides may be uneven
primarily seen in acidic urine
Clincally significant, seen in congenital cystinosis or cystinuria
Deposit out in tubules as calculi/stone causing damage

Why are Cystine Crystals confused with Uric Acid Crystals? How do we confirm Cystine Crystal presence?
both may present as hexagonal shapes. To confirm cystine crystal presence, perform cyanide-nitroprusside test using SODIUM CYANIDE which will yield a positive result for cystine (purple color)
Cholesterol Crystals
Clear flat rectangular plates with notched corners
in acidic urine
Rarely seen
Presence indicates both ideal conditions for precipitation & supersaturation
When are Cholesterol Crystals commonly seen?
Always see with positive protein + fat droplets, fatty casts or oval fat bodies
Seen in nephrotic syndrome & other renal damage

Ampicillin Crystals
Appear in acidic urine
Require large dosage for formation, so rarely seen
Calcium Phosphate Crystals
Colorless, thin, star-shaped prisms with one tapered end; they often appear as irregular granular sheets resembling degenerating squamous epithelial cells.

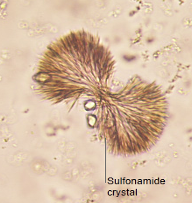
Sulfonamides Crystals
Highly refractile & birefringent
In acidic urine
Closely resemble ammonium biurate but differentiated on
pH & solubility
chemical confirmatory test
Type varies with form of drug prescribed
rarely seen due to recent solubility of sulfa drugs
Alkaline Urine Crystals
Amorphous Phosphate
precipitate white rather than pink-orange of amorphous urate
presence enhanced by refrigeration
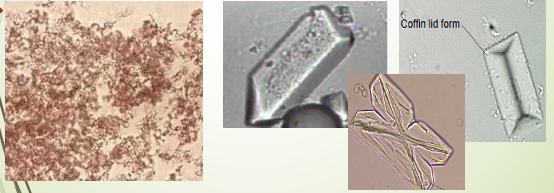
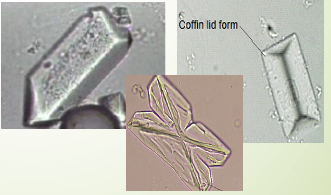
Triple Phosphate
most common are 3 & 6 sided ‘coffin lids’, vary in size
Amorphous Phosphate
alkaline or neutral urine
microscopically not distinguishable from amorphous urates
distinguishable on urine pH & solubility
precipitate white rather than pink-orange of amorphous urates
are soluble in acid & will not dissolve when heated to 60C
presence enhanced by refrigeration
Triple Phosphate Crystals
Colorless & in different forms
most common are 3 & 6 sided ‘coffin lids’
vary greatly in size
may also see a ‘fern leaf’ form, feathery
See in normal healthy individuals but are often present in formation of calculi
are associated with UTI
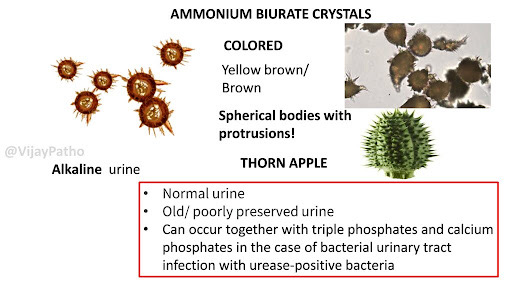
Ammonium Biurate
Yellow brown spheres with striations
Can have irregular spicules ‘thorny apple’
In alkaline or neutral urine
Not significant unless seen in fresh urine
Usually seen in old specimens
Dissolve in acetic acid or heating to 60C
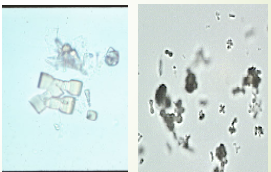
Calcium Carbonate
Very small granular crystals
Can be misidentified as bacteria
Usually found in pairs ‘dumbbell shape’
Acidic Urine (pH < 7) Crystals
Amorphous Urates
Uric Acid
Calcium Oxalate
Bilirubin
Tyrosine
Leucine
Cystine
Cholesterol
Sulfonamides
Ampicillin
Alkaline Urine (pH > 7) Crystals
Amorphous Phosphates
Triple Phosphate
Ammonium Biurate Crystals
Calcium Phosphate Crystals
Calcium Carbonate Crystals
What crystal can appear in acidic AND neutral pH?
Calcium Oxalate Crystals
Clinical Significance of Crystals
kidney stone formation: Calcium oxalate, Uric acid, Cystine, Triple phosphate
metabolic disorders: Cystine, Tyrosine, Leucine
liver disease: Bilirubin, Tyrosine, Leucine, Cholesterol
UTI: Triple phosphate
drug therapies: Sulfonamides, Ampicillin
benign: Amorphous urates, Amorphous phosphates
Shapes of Crystals
Envelope-shaped = Calcium oxalate dihydrate
Needle-shaped = Uric acid, Bilirubin, Tyrosine, Sulfonamides, Ampicillin
Hexagonal = Cystine
"Coffin lid" = Triple phosphate)
"Thorny apple" = Ammonium biurate
Rhombic = Uric acid
Spherical = Leucine