Parasitology Exam 2
1/497
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
498 Terms
Nematoda phylum common name
Roundworm
where do free living nematodes live
freshwater, saltwater, soil
what is a major cause of animal, plant, and human disease
nematodes
copulatory bursa
lateral flat expansion at posterior region of male nematodes
bursate nematodes
hookworm, strongyles, trichostrongyles
nonbursate nematodes
roundworm, filaroides, pinworm, trichinelloid
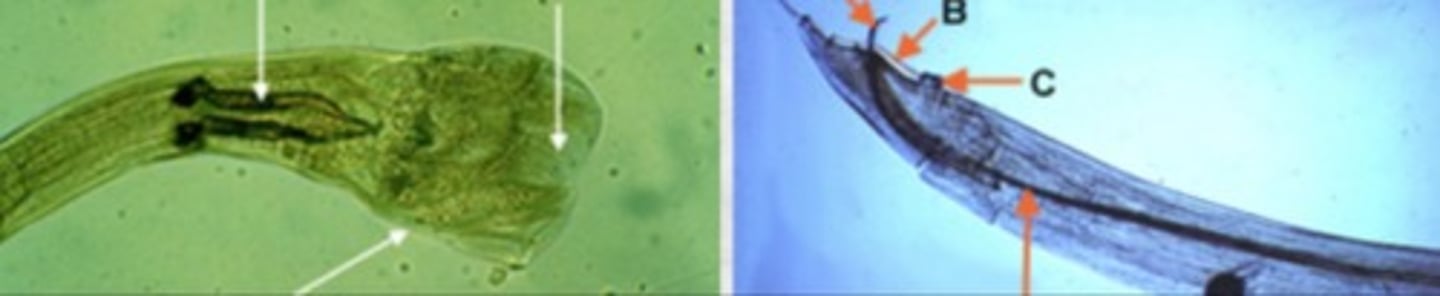
What is on the left
Copulatory bursa of male nematode
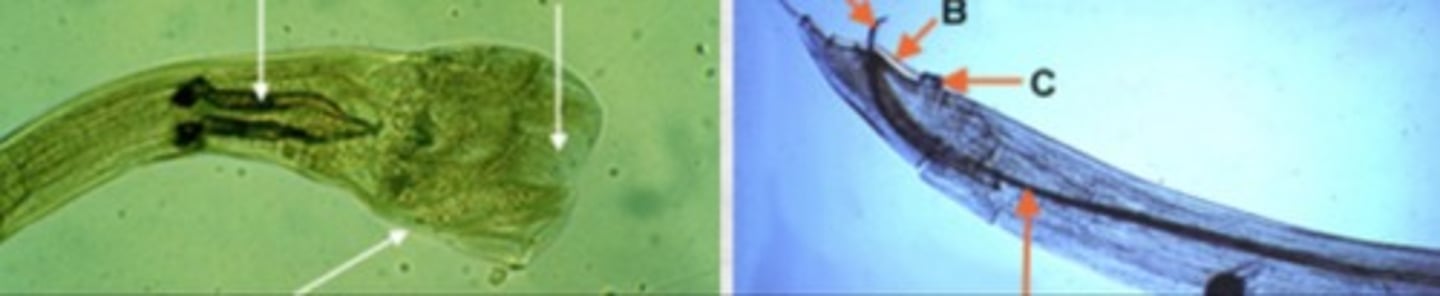
What is on the right
Male nematode without copulatory bursa
what are the most important parts of a nematode
digestive and reproductive
where is the digestive system of a nematode
digestive tube extends from the mouth to the anus and ends at the rectum or cloaca
do nematodes have a circulatory or respiratory system
no
what kind of mouthparts do nematodes have
leaf crown, numerous papillae
what kind of reproductive parts do male nematodes have?
tubular testes
what kind of reproductive parts do female nematodes have?
uterus
what are the 4 kinds of nematode eggs
ascarid, trichostrongyle/strongyle, spirurid, trichinelloid
ascarid egg
round, yellow/brown, single cell stage inside
trichostrongyle/strongyle egg
thin wall, oval, morula with multiple cells inside
spirurid egg
small, oval, thick shell, first stage larva inside, further developed
trichinelloid egg
oval, brown, thick shell, operculum plugs at each end, single cell inside
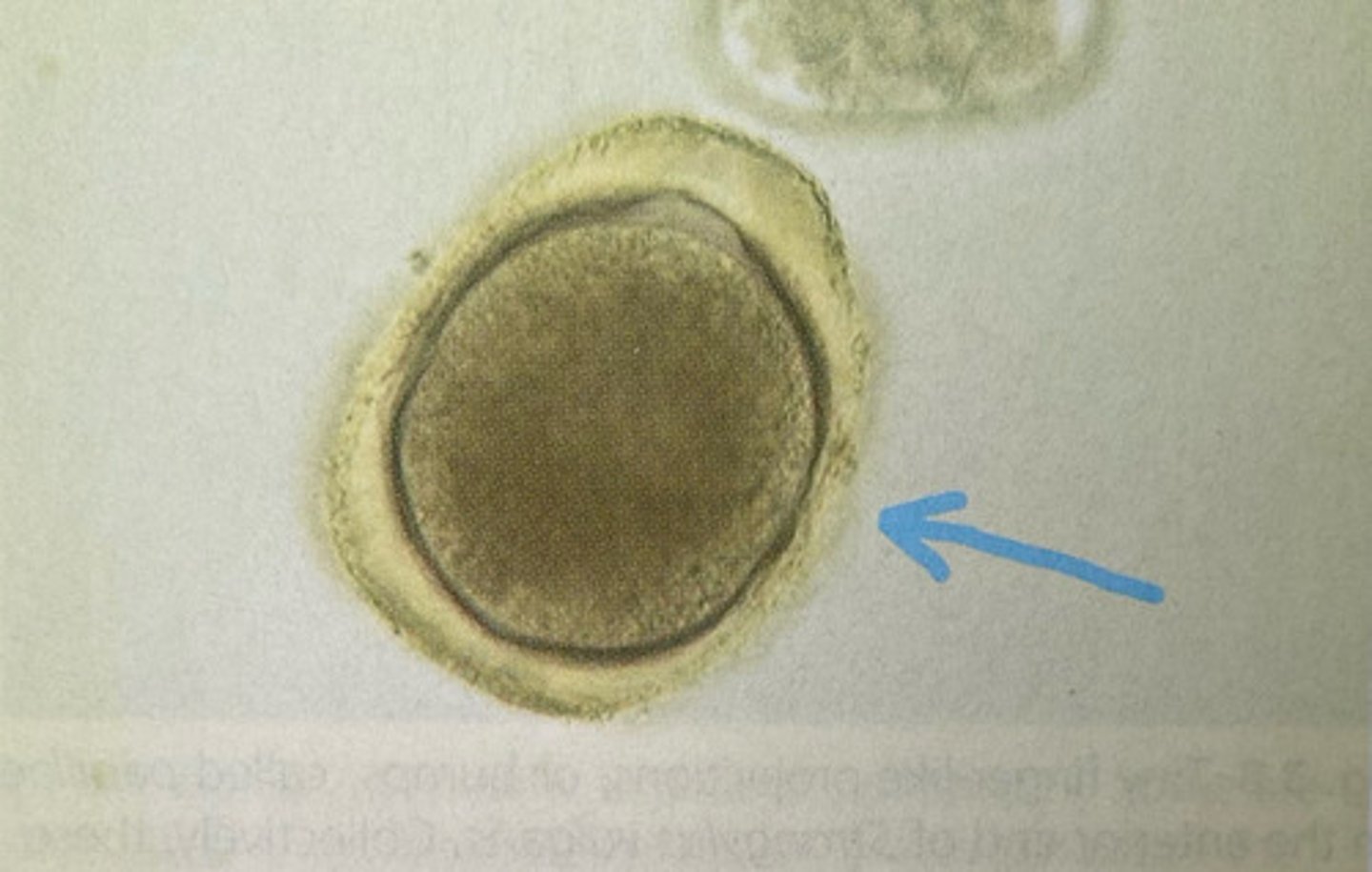
What kind of egg is this
Ascarid egg
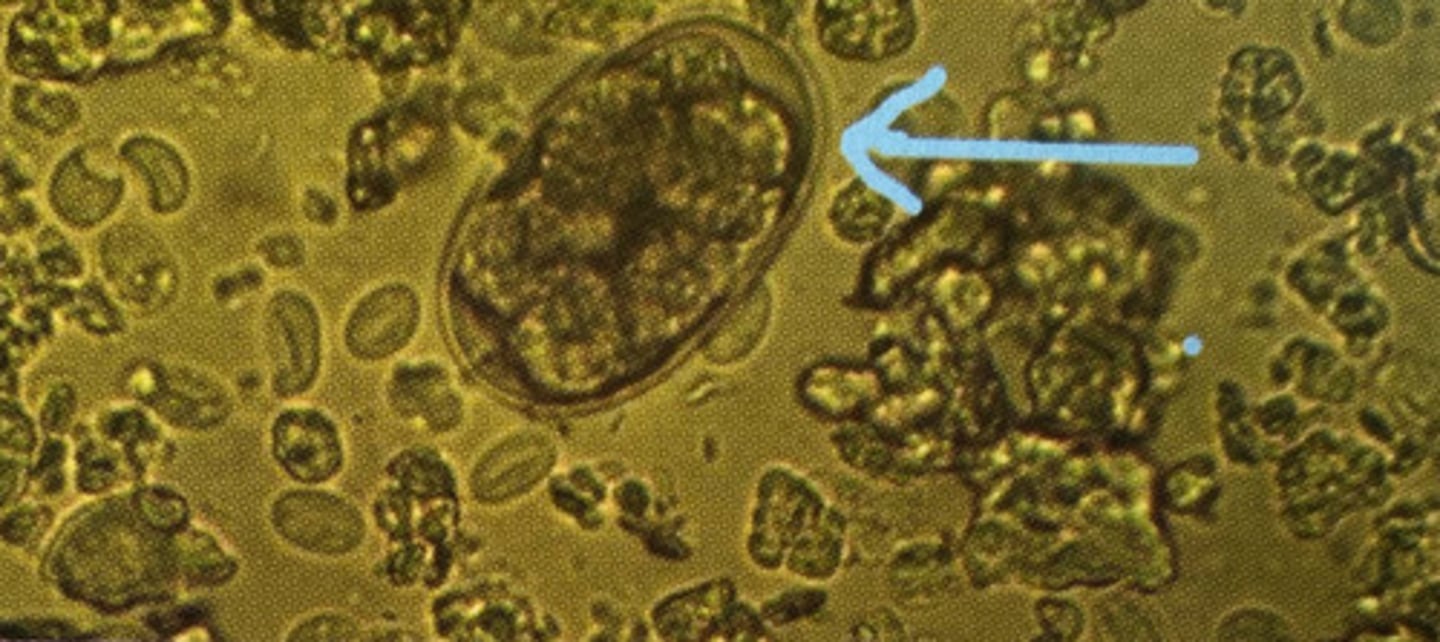
What kind of egg is this
Trichostrongyle egg
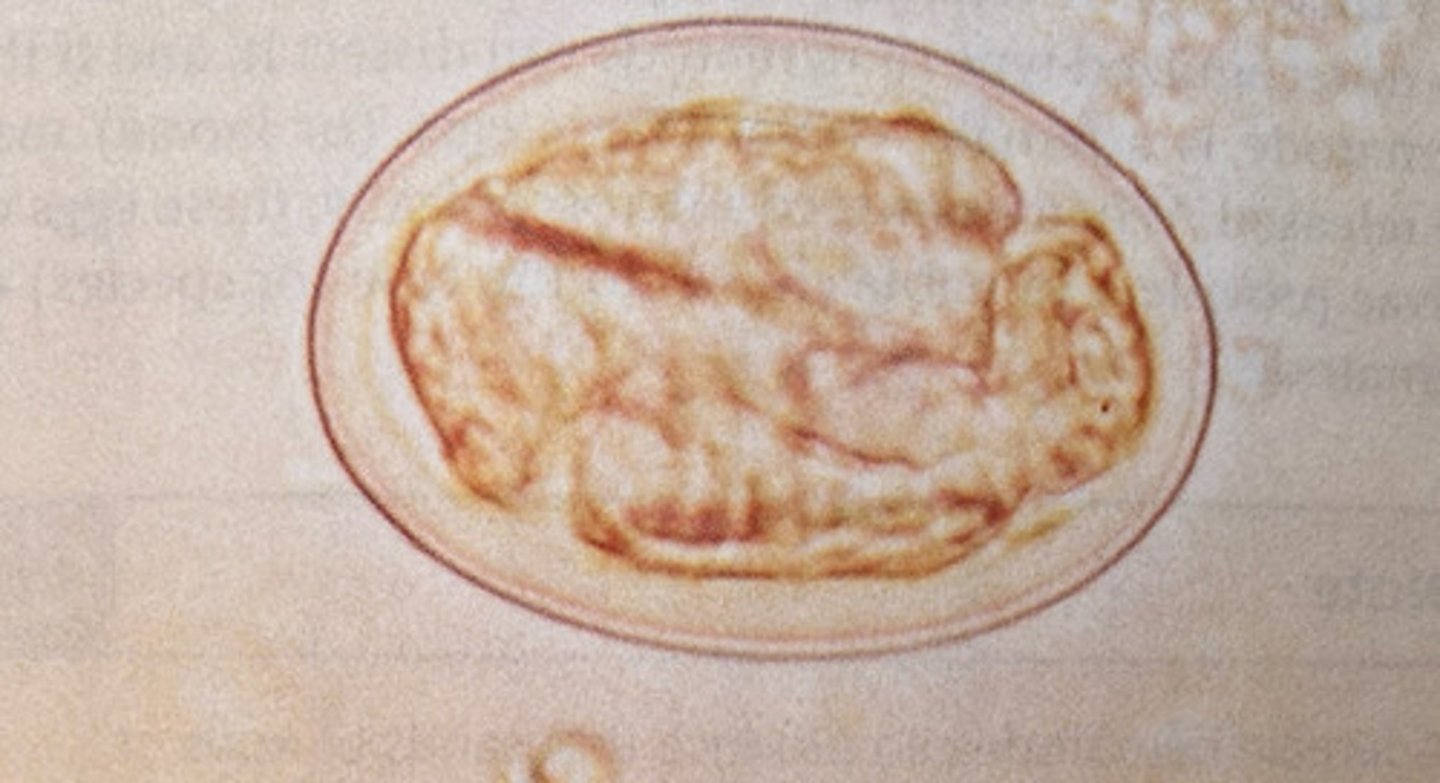
What kind of egg is this
Spirurid egg
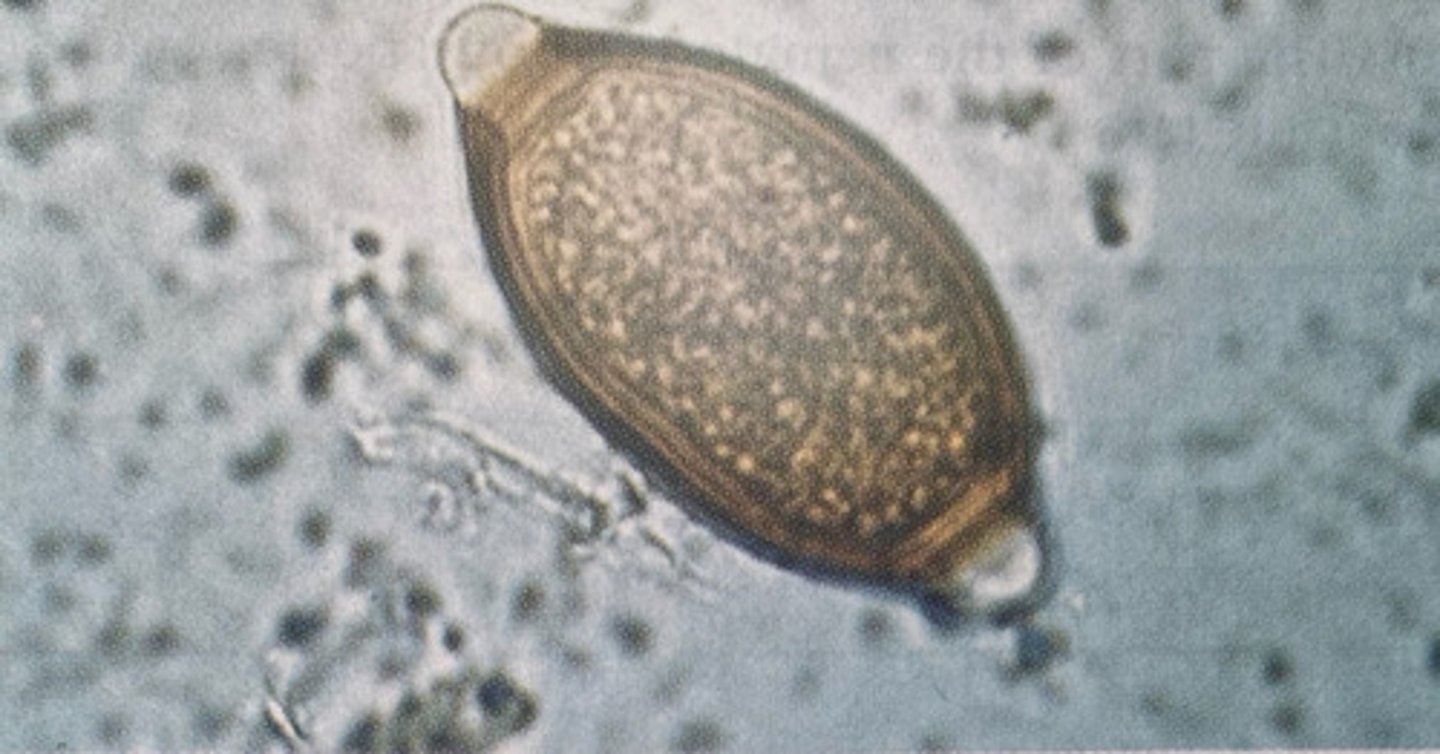
What kind of egg is this
Trichinelloid egg
Oviparous egg
egg hatches after it has been laid, unembryonated egg
Ovoviviparous egg
egg hatches within female before being laid or shortly after
larviparous
female retains egg in uterus and give birth to larvae
what is the normal life cycle of a nematode
adult female produces egg or larva, L1 emerges and molts into L2, L2 molts into L3, L4, L5 within definitive host, L5 migrates into predilection site and develops into mature adult, male and female adult worms breed
which is the infective stage larva of nematodes
L3
which is the immature/preadult nematode stage
L5
direct L3 nematode larva
larva lives in environment
indirect L3 nematode larva
larva is in intermediate host
which stages of nematode larva are inside infected definitive host
L4 and L5
what must L4 and L5 larva do after entering the definitive host
migrate to predilection site
direct life cycle
parasite does not need an intermediate host to complete life cycle
Indirect life cycle
larva needs an intermediate host to finish life cycle
what is the exception to the L3 infective stage larva
some nematodes produce eggs that do not hatch, the eggs contain larva inside that is infective
Prepatent period
the time from infection to diagnostic stage
how are worms diagnosed
by using a fecal sample
how long is the prepatent period for heartworm
6 months
Spirocerca lupi
esophageal worm
what is the prepatent period of Spirocerca lupi
6 months
how does a host get infected with Spirocerca lupi
Dung beetle goes into stool and gets infected, parasite becomes L3, definitive host eats dung beetle intermediate host and becomes infected
which life cycle does Spirocerca lupi have
indirect lifecycle
what is the intermediate host for Spirocerca lupi
dung beetle
where does Spirocerca lupi migrate to after infecting the host
wall of celiac artery and thoracic aorta, develop there for 3 months, migrate to esophageal wall as adults
Physaloptera spp
Stomach worm
Where do adult Physaloptera live in the host
stomach or small intestine lumen attached to mucosa of dog and cat
what symptoms do Physaloptera cause
vomiting, anorexia, dark tarry stool
Melena
dark tarry stool, bleeding source is higher in the GI tract, normally small intestine, and blood has been digested
what does bright red stool mean
bleeding source is in the lower end of the GI tract
what is the intermediate host for Physaloptera
cockroach, beetle, cricket
what is the prepatent period for Physaloptera
56-83 days
paratenic host
host where parasite development does not occur but bridges an ecological gap in the parasite's life cycle
what is the paratenic host of Spirocerca lupi
chicken, reptile, rabbit
what is the paratenic host of Physaloptera
mice, frogs
Toxocara canis
dog roundworm
Toxocara cati
feline roundworm
Toxascaris leonine
cat and dog roundworm
what kind of nematode is Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toxascaris leonine
ascarid
is Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toxascaris leonine zoonotic
yes
where is Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toxascaris leonine located in the host
don't attach to intestine, free floating in small intestine
what are the symptoms of Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toxascaris leonine
vomiting, diarrhea, coughing, potbelly appearance
what kind of eggs do Physaloptera have
Spirurid
What is the difference between Toxocara and Toxascaris eggs
Toxocara have rough pitted outer shell while Toxascaris have a smooth outer shell
Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toxacaris leonine life cycle
eggs in host feces, embryonate on ground until L3 larvae, larvae ingested by new host, L3 released from egg, larvae migrate to tissues and lungs, L3 larvae coughed and swallowed into GI tract, L3 larvae develop into adult in small intestine
what kind of transmission route does Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati
fecal oral transmission
how long is the prepatent period for roundworms
3-4 weeks, 21-35 days
what is the paratenic host for Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toascaris leonine
rodent
How does Toxascaris leonine infect the host
ingestion of rodent paratenic host
Visceral larval migrans
condition where Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, or Toxascaris leonine infects human host and migrates to various organs
Ocular Larval Migrans
condition where Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toxascaris leonine infects a host and migrates to the eyes
how do you diagnose Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toxascaris leonine
fecal float identification of eggs, antigen ELISA to visualize adult worms
how do you treat and prevent Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, Toxascaris leonine
deworming through strongid, ivermectin, panacur, drontal, hand washing
Baylisascaris procyonis
Racoon roundworm
is Baylisascaris procyonis zoonotic
yes
Ancylostoma spp
canine and feline hookworm
Ancylostoma caninum
canine hookworm
Ancylostoma tubaeforme
Feline hookworm
Uncinaria stenocephala
Northern canine hookworm
where do Ancylostoma infect the host
attach to mucosa of small intestine using teeth
what do Ancylostoma feed on
blood using teeth
Ancylostoma life cycle
male and female attach to wall of small intestine and mate, eggs with morula passed into environment through host feces, morula develops into L1 and hatches, develops into L3 in environment, L3 ingested or penetrate skin, migrate into lungs, coughed up, swallowed, migrate to small intestine and attach
Vertical transmission
transmission of parasite from parent to offspring
how do you treat Ancylostoma
deworming through strongid for puppies and kittens, ivermectin, panacur, drontal
how do you prevent Ancylostoma
keep environment clean of feces to prevent Morula from developing, routine fecal sample testing, proper disinfectant cleaning protocols
what is the fecal sample testing recommendations for dogs and cats
4 times during first year of life, 2 times yearly after first year
Strongyloides spp
Intestinal threadworm
Strongyloides westerii
horse intestinal threadworm
which gender of Strongyloides is parasitic
female
how do Strongyloides reproduce
female produces larva without fertilization
autoinfection
parasite reinfects host right away after being passed through stool because parasite is well developed when passed in feces
Strongyloides westerii, Strongyloides spp life cycle
Female in small intestine lays egg, egg hatches in small intestine, free living larvae develop into infective L3, L3 penetrate skin and migrate to small intestine or ingested, larvae can be passed through feces
Trichuris vulpis, Trichuris ovis, Trichuris suis
whipworm
do Trichuris vulpis infect cats
rare in cats
What kind of eggs does Thricuris vulpis have
trichinelloid
Tricuris vulpis, Tricuris ovis, Tricuris suis life cycle
adult attached to cecum or colon wall in large intestine feeding on blood, pass eggs into host feces, infective L1 larva develops in egg, egg ingested by host, larva molts into adult
Enterobius vemicularis
human pinworm
Dirofilaria immitis
canine heartworm
What animals does Dirofilaria immitis parasitize
cats, dogs, ferrets
where do adult Dirofilaria immitis reside
pulmonary arteries, right ventricle