Human Resource Management: Reliability and Validity Concepts
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
Reliability
The degree to which a measurement is free from random error; can be thought of as consistency in measurement or outcomes.
Inter-item reliability
Asking the same thing different ways.
Test-retest reliability
Taking the same test or survey multiple times.
Inter-rater reliability
Multiple interviewers evaluate the same applicant and correlate interviewers' scores.
Validity
The extent to which a performance measure assesses all the relevant -and only the relevant- aspects of job performance.
Criterion
The outcome; it is the y (outcome) in y = mx + b where x (predictor) is your selection measure score.
Criterion-related validity
Show a 'substantial' correlation between selection measure and performance on the job.
Predictive validation
Establish correlation between pre-employment test scores and on-the-job performance.
Concurrent validation
Establish correlation between current employees' test scores and on-the-job performance.
What might be some problems using the criterion-related validity?
- Sampling issues
- Range restriction
- Job experience
Content validity
Requires 'expert judgment' to validate; demonstrating the questions or problems on the test are representative of the situations that are likely to occur on the job.
Discriminant validity
The scale is different from scales it is intended to be different from.
Convergent validity
The scale 'maps onto' or is similar to scales it is intended to be similar to.
Sampling issues
Surveying only those who have had adequate performance and chose to stay with the organization; missing the scores of those who quit or were fired.
Range restriction
All of the current employees may be similar on some trait (not enough variance).
Job experience
Higher performing employees may have gained knowledge that potential new hires would not possess.
Actual Job Performance
Your criterion, your outcome.
Virtual Tryouts
A method for employers to assess candidates in a simulated job environment.
EEOC concerns
Potential legal issues regarding discrimination in hiring practices.
Reliability of virtual tests
Comparison of the consistency of virtual tests with traditional methods such as interviewing.
Validity of virtual tests
Ensuring that virtual tests accurately measure the skills and abilities relevant to the job.
Job suitability for virtual tryouts
The idea that some jobs may be better suited for virtual assessments than others.
Interviews
A dialogue initiated by one or more persons to gather information and evaluate the qualifications of an applicant for employment.
Nondirective interview
Applicant given maximum amount of freedom in determining the course of discussion.
Structured interview
Use of a structured set of questions (increases validity); same questions asked of all applicants.
Behavioral description interview
Questions about what the applicant actually did in his/her last job.
Sequential interview
Interviewers meet one on one with each candidate and compare notes.
Panel interview
Candidate meets with a group of interviewers, providing better reliability and is faster than a sequential interview.
Video interview
Common when separated by geography; can be recorded and viewed by others in the organization.
Physical Ability Tests
Common to jobs requiring some minimum physical strength or capability.
Physical Ability Tests - Reliability
High.
Physical Ability Tests - Validity
Moderate criterion validity, high content validity for some jobs; heavy lifting OTJ.
Physical Ability Tests - Generalizability
Low, pertain only to physically-demanding jobs.
Physical Ability Tests - Utility
Moderate, may prevent expensive injuries and disability.
Physical Ability Tests - Legality
Must establish job relatedness; generally adverse impact on women and individuals with disabilities.
Cognitive Ability Tests
Cognitive ability is positively associated with better performance across the vast majority of occupations.
Cognitive Ability Tests - Reliability
High.
Cognitive Ability Tests - Validity
Moderate criterion validity; generally inappropriate content validity.
Cognitive Ability Tests - Generalizability
High, predictive for most jobs, especially cognitively demanding or complex jobs.
Cognitive Ability Tests - Utility
High, low cost and wide application.
Cognitive Ability Tests - Legality
Often have adverse impact on some minorities.
Personality Inventories
Five-factor Model of personality.
Openness to experience
Curious, imaginative, linked with intelligence.
Conscientiousness
Dependable, organized, achievement-oriented, linked with performance.
Extraversion
Sociable, assertive, talkative, linked with performance in service jobs and leadership.
Agreeableness
Courteous, trusting, good-natured; subordinates want an agreeable supervisor.
Neuroticism (adjustment)
Worried, anxious; linked with better performance in data-driven occupations.
Work Samples
A test to determine whether the individual can perform the work required of the job.
Honesty tests
Polygraph Act (1988)—banned use of 'lie-detecting' machines in most organizations.
Drug tests
Administered systematically to jobs that involve safety hazards, with results reported to individuals and avenues for appeal.
Invasion of privacy
A potential concern regarding the administration of drug tests.
Interview Questions
Questions asked during an interview that can be categorized into acceptable and unacceptable.
National origin
Probably OK to ask about a person's name, origin of name, ancestry, previous names, native language, and pertinent foreign languages.
Age
Probably OK to ask if the person is over 18 or can prove their age; not OK to ask for the date of birth.
Gender
Generally not OK to ask unless it is a bona fide occupational qualification (BFOQ).
Race
Not OK to ask about a person's race.
Disabilities
Probably OK to ask if the person has disabilities that may inhibit job performance or if they are willing to take a physical exam.
Height and weight
Probably OK to ask about weight; not OK to ask about height unless BFOQ.
Residence
Probably OK to ask for an address and how long the person has lived there.
Religion
You may inform the person of the required work schedule; probably not OK to ask about religious affiliation.
Military record
Probably OK to ask about military education or experience pertinent to the job.
Education and experience
Questions about prior work experience, graduation dates, reasons for leaving, and salary history.
Criminal record
Probably OK to ask if the person has ever been convicted of a crime; not OK to ask if they have ever been arrested.
Citizenship
Probably OK to ask if the person is a US citizen or has a legal right to work in the United States.
Marital/family status
Questions about marital status and children may be asked.
Organizations
Probably OK to ask if the person is a member of professional, service, or trade organizations.
Photographs
Not OK to ask for a photograph with the application package.
Facebook hiring process
Consists of three steps, including applicable written tests.
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
A personality assessment tool that categorizes individuals based on traits such as Extraversion vs. Introversion, Sensing vs. Intuition, Thinking vs. Feeling, and Judging vs. Perceiving.
Extraversion (E)
A personality trait indicating a preference for social interaction.
Introversion (I)
A personality trait indicating a preference for solitary activities.
Sensing (S)
A personality trait focused on fact-based information.
Intuition (N)
A personality trait focused on impressions and possibilities.
Thinking (T)
A personality trait that is logical and analytical.
Feeling (F)
A personality trait that is people-oriented and empathetic.
Judging (J)
A personality trait that is task-oriented and planning-focused.
Perceiving (P)
A personality trait that is flexible and spontaneous.
Dichotomized scale
A continuous variable is made into two categories.
Criticism of MBTI
Most modern personality psychologists would be afraid to conduct research based on Jung's theory of types or the MBTI.
Lack of neuroticism reference in MBTI
The MBTI lacks reference to neuroticism.
Test-retest reliability of MBTI
Individual scores change, indicating very little test-retest reliability.
MBTI and managerial effectiveness
Few consistent relationships between MBTI personality type and managerial effectiveness have been found.
Dark Triad
A psychological concept that includes Machiavellianism, Psychopathy, and Narcissism.
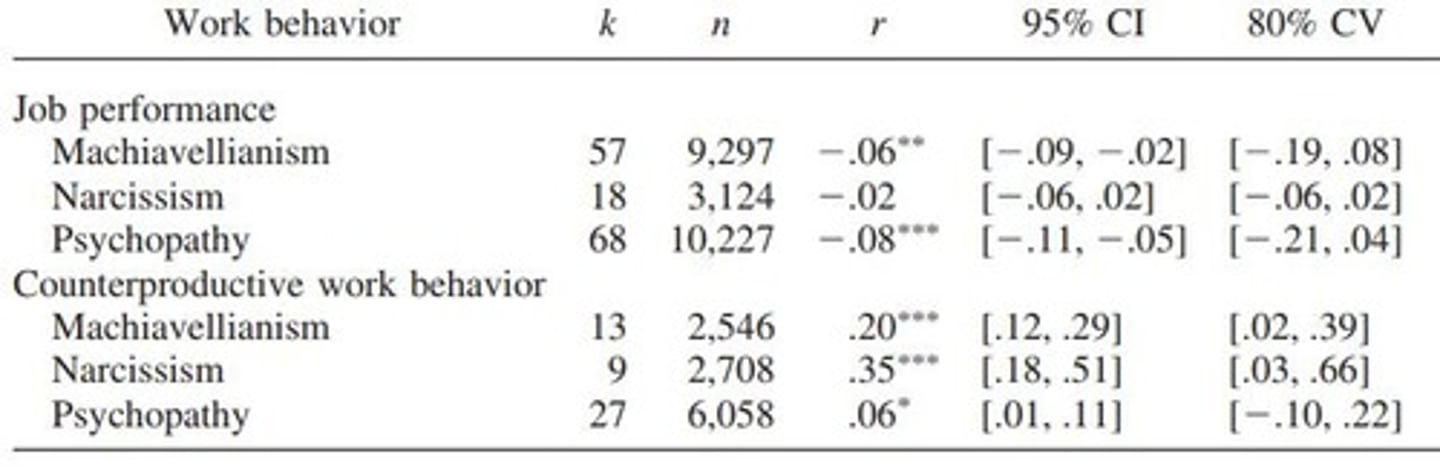
Machiavellianism
Generally includes a cynical worldview, lack of morality, and manipulativeness.
Psychopathy
Deficits in affect (i.e., callousness) and self-control (i.e., impulsivity).
Narcissism
Defined by a clash between a grandiose identity and underlying insecurity.
Annual performance review
Most companies use an annual, paper-based performance review.
Automated performance review process
Less than 30% of companies use an automated process.
Employee satisfaction with performance appraisal
72% of companies are somewhat satisfied to extremely dissatisfied with their performance appraisal process.
Annual review helpfulness
60% of employees say the annual review is not helpful.
Training needs identification
Less than 25% use the reviews to identify training needs and potential leaders.
Comparative approach in performance evaluation
Compare an individual's performance to that of others in the same job.
Forced distribution
Required percentage at the high and low ends in performance evaluation.
Paired comparison
Comparison of each employee with all other employees in the same role.
Time required for paired comparison
Takes a great deal of time, calculated as (n!)/(n-x)!*x!.
Attribute approach in performance evaluation
Extent to which individuals have certain attributes believed to be desirable for the company's success.
Behavioral approach in performance evaluation
Includes behaviorally anchored rating scales (BARS) and behavioral observation scales (BOS).
BOS (Behavioral Observation Scale)
A count of observed behaviors.
Example behaviors for performance criteria
Specific behaviors rated on a scale from 1 to 5 based on performance.
Quality approach
Customer orientation and prevention of errors; Customer satisfaction is the primary goal.