unit 1
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Diff between nervous and endocrine in terms of
mechanism:
area of effect:
signaling mol:
duration of effect:
target tissues:
Diff between nervous and endocrine in terms of
mechanism: nervous electrochemical, endocrine chemical secretion
area of effect: nervous local, endocrine broad
signaling mol: nervous neurotransmitters, endocrine hormones
duration of effect: nervous short, endocrine longer
target tissues: nervous neurons, muscle and glands. endocrine all body tissues
Craniosacral system is
parasympathetic
thoracolumbar system is
sympathetic
list the 3 effector cells of the autonomic nervous system
smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, gland cells
Describe the steps of the parasympathetic system and the neurotransmitters used
action potential in preganglionic
acetylcholine released
Ach binds to nicotinic type Ach receptor on postganglionic neuron
postganglionic neuron releases Ach on target
Ach binds to muscarinic type Ach receptor
BOTH NEURONS RELEASE ACH
4 main subtypes of adrenergic receptors and what pathway uses them
Alpha 1: smooth muscle contraction
Alpha 2: sympathetic postganglionic neurons, negative feedback
Beta 1: cardiac muscle cells
Beta 2: smooth muscle relaxation
USED IN SYMPATHETIC EFFECTORS
Describe the steps of the sympathetic system and the neurotransmitters used
AP in preganglionic
preganglionic releases ACh
Ach binds to nicotinic Ach receptor on postganglionic
postganglionic releases norepinephrine on target
NE binds adrenergic receptor
EXCEPTIONS TO THE SYMPATHETIC PATHWAY
sweat glands target receptor is muscarinic instead of adrenergic
adrenal medulla releases epi into the blood and then binds to adrenergic
2 ways to activate sympathetic system and 1 way to activate parasympathetic system
Sympathetic: CNS preganglionic, or release of epinepherine from adrenal medulla
parasympathetic: CNS preganglionic activation
5 functions of blood
transport,
defend,
regulate pH and ions,
clot
regulate temp
describe the composition of blood
Plasma, buffy coat middle layer, and formed elements
Describe the composition of plasma
mostly water, 8% proteins
describe the composition of formed elements
99.9% RBC/erythrocytes
Difference between hemopoiesis and erythropoiesis?
hemo is all blood cell, happens in red marrow, makes hemocytoblasts to form any blood cells. hemocytoblats can then go through erythropoiesis to form red blood cells.
what speeds up erythropoiesis?
erythropoietin (EPO)
why the structure of RBCs help with their function
biconcave disc create large surface to volume ratio
lack organelles , increases flexibility
How is hemoglobin recycled
heme is broken down to bilirubin and excreted
iron is reused
proteins broken down to AA and reused
Describe jaundice, anemia, myloid and lymphoid leukemia
jaundice: live cant break down RBC and bilirubin builds up
anemia: decrease in O carrying capacity of blood
myloid leukemia: abnormal granulocytes or marrow cells
lymphoid leukemia: abnormal lymphocytes
Describe the 3 granulocytes:
granules- nubs (NEBs)
neutophil: most of WBCs, phagocytic, first reponse to injurt. high levels indicate bacterial infection
eosinophil: attracted to foreign compounds that react w antibodies, phagocytic. high levels indicate allergy or parasite
basophil: release histamine and heparin in damaged tissue
Describe 2 agranulocytes:
lymphocyte: immune system cells
monocytes: leave circulation to become macrophage
Myloid stem cells go to
GRANULOCYTES (neut, eisino, baso) and MONOCYTES
lymphoid stem cells go to
lymphocytes and plasma cells
What does complete blood count measure
hematocrit and hemoglobin
platelet count
wbc count
what are platelets?
fragments of megakaryocytes, NOT CELLS
Describe the role of clotting
vascular spasm reduces diameter of vessel
platelets adhere, release chemicals that form positive feedback loop
thrombin catalyzes fibrinogen to fibrin
fibrin forms a mesh, clot forms
Thrombus vs embolus
thrombus: blood clot formed by platelets, often at disease site
embolus: piece of thrombus that travels and blocks another part of body
describe systemic circulation
aorta carries oxygenated blood to organs
systemic veins carry DEoxygenated blood from organs through superior and inferior venae cavae to pulmonary artery
describe pulmonary circulation
pulmonary artery carries DEoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from lungs to aorta
Describe the 3 layered wall of a blood vessel
tunica intima: innermost, lined by endothelium
tunica media: middle, smooth muscle
tunica externa: outer, connective tissue
Difference between structure of artery vs vein
arteries have stronger thicker walls, and contain more smooth muscle and elastic fibers
Describe vessels of arterial system:
elastic arteries:
muscular arteries:
arterioles vessel:
Describe vessels of arterial system:
elastic arteries: conducting arteries
muscular arteries: distributing arteries
arterioles: resistance vessel, few muscle layers
What are the only vessels that move materials through wall?
capillaries / exchange vessels
Describe vessels of venous system:
veins :
Describe vessels of venous system:
veins : capacitance vessel, just hold blood
What is a venous valve and how is it formed?
valves catch blood if they try to flow back, formed from tunica intima foldings
Describe the difference between
continuous capillaries
fenestrated capillaries
sinusoidal capillaries
Describe the difference between
continuous capillaries: tight endothelial layer, only water and lipid solutes pass through, creates BBB
fenestrated capillaries: pores in endothelial lining, exchange of water and larger solutes. Found in choroid plexus, endocrine organs, kidneys, GI
sinusoidal capillaries: large gaps between endothelial cells, free exchange of water and large proteins. Found in liver, spleen, bone marrow
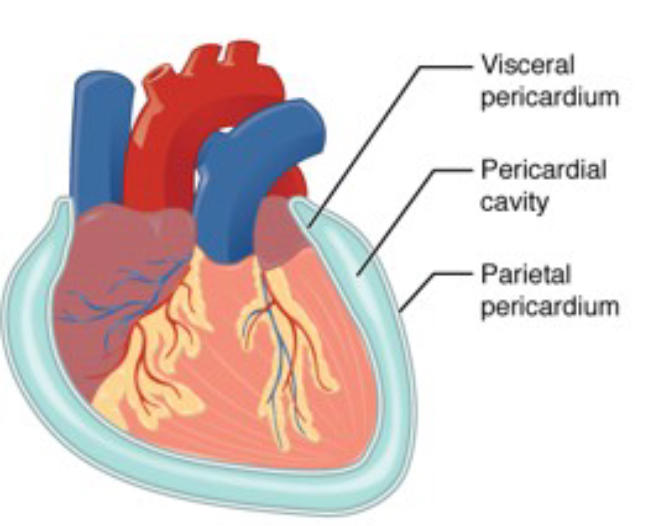
Describe the pericardial sac
surrounds heart:
parietal pericardium is outer
pericardial cavity is fluid filled
visceral pericardium adheres to heart surface
What separates atrium and ventricle?
AV valves
left coronary artery branches into
circumflex artery and left anterior descending
3 layers of the heart wall
epicardium: outer, connective tissue, fat
myocardium: middle layer, cardiac muscle
endocardium: inner, endothelium
Explain the 2 sets of ACTIVE AV valves and AV valve anchors
Tricuspid: right, 3 flaps
Bicuspid/Mitral: left, 2 flaps
flaps anchored to papillary muscle by chordae tendineae
Explain the 2 sets of PASSIVE Semilunar valves and valve anchors
Pulmonary valve leaves the right vent
aortic valve leaves the left vent
anchored to inner wall. no muscles
What determines if a valve is open or closed?
pressure gradients
Explain the steps of blood flow through the right side of the body
blood from body through sup + inf venae enter right atrium
passes through tricuspid valve to right ventricle
passes through pulmonary valve to pulmonary trunk
trunk branches into right and left arteries to go to lungs
Explain the steps of blood flow through the left side of the body
blood returns from lungs through two right and left pulmonary veins into left atrium
passes through bicuspid/mitral to left ventricle
to aortic valve and aorta
aorta ascends to aortic arch
2 types of cardiac muscle cells and percentage of each
contractile cells- 99%
pacemaker cells- 1%
no contraction, initiate APs
Explain 3 steps of pacemaker APs
pacemaker potential, slow depolarization due to opening of Na and closing of K
Depolarization: Ca influx, reaches threshold
Repolarization: Ca inactivation, K opening
Sequence of conducting system
SA node
AV pause
AV bundle
Bundle branch
Purkinje fibers
Describe Ectopic pacemaker
high AP, disrupts contraction, poor blood ejection
Describe the structure of a contractile cell
single central nucleus
made up of sarcomeres arranged into myofibrils, surrounded by sarcoplasmic reticulum
intercalated discs connect cells
Explain steps of contractile cell APs
Depol: Na channels open, then close
Plateau: Ca channels open fast,K channels close
Repol: Ca channels close, K channels open
Resting potential
Difference between pacemaker and contractile APs?
contractile membrane potential gets stable, resting
Difference between cardiac contraction and skeletal muscle contraction APs?
cardiac APs cannot summate, and last as long as the contraction
muscles summate, and brief relative to contraction
what does an EKG measure
sum of electrical activity in myocardium., NOT A SINLE CELL
Describe P wave, QRS wave, and T wave
P: atria depolarize-
QRS: Ventricle depolarize
T: ventricle repolarize
Describe the 3 steps of the contractile cycle (6 stages <3)
1a. ventricular filling/ disastole: all chambers relaxed, ventricles fill passively
1b. P STEP: atrial contaction/systole: contraction moves blood to ventricles. AV valves open
2a. QRS STEP: FIRST HEART SOUND HEARD: isovolumetric contraction/ ventricle systole: AV valves close
2b. T STEP: ventricular ejection: SL + aortic valve open. blood moves to aorta and pulm art
3a. isovolumetric relaxation: SECOND HEART SOUND HEARD: SL and aortic valve close. blood flows into relaxed aorta
3b. back to ven diastole. all chambers relaxed, ven fill passively
Cardiac output definition + equation
volume of blood pumped by left ventricle in one minute
CO= HR x SV
CO = HR x (EDV-ESV)
Define EDV and ESV
end dias volume: volume just before contraction
end sys volume: volume after contraction
define SV
stroke volume: amount pumped out during systole
how is HR controlled through CV center in medulla?
NE release causes increase in HR
ACh release causes dec in HR
how is HR controlled through pacemaker cells/autonomic system
parasympathetic stim slows down depolarization
sympathetic stim speeds up depolarization
What changes EDV?
fill time (inc fill time, inc HR)
venous return (inc symp, inc vasocons, inc CO)
What changes ESV?
preload (inc fill load, inc CO)
contractility (inc contraction, inc CO)
afterload (force to eject blood) (inc afterload DEC CO)
What is the ejection fraction and what does a lower ejection fraction indicate
percent of EDV pumped out in one beat
lower EF, weaker heart
define blood flow
difference in blood pressure divided by peripheral resistance
in terms of BP, hypertension is
140/90
in terms of BP, hypotension is
90/60
define MAP and give avg
mean arterial pressure: 1/3 pulse pressure + diastolic BP
Local and systemic factors that affect resistance
Vasodilation; inc blood flow
local: high CO2, H+ K+, low O2
systemic: low sympathetic activity
Vasoconstriction; dec blood flow
local: stretch and endothelins
systemic: increase hormones and sympathetic activity
Why are capillaries optimized for exchange?
high cross section decreases flow, and gives time for material exchange
3 forces at work in capillary exchange, and their pressures
Diffusion: lipids, gases, some ions
Filtration: driven by capillary hydrostatic pressure
35mmHg at arterial, 18 at venous
Reabsorption: water drawn back by blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP). constant 25mmHg
Net filtration pressure at each capillary ends
arterial: 10mmHg , fluid moves into interstitial
venous: -7mmHg, fluid moves into capillary
Dif between local and systemic edema
local is just extra interstitial fluid in inflammation, a process to dilute toxins.
systemic indicates cardiovascular problem
3 factors that influence CO and BP
autoregulation: immediate localized changes
neural mechs: responds quickly to changes at specific sites
endocrine mechs: slowest, direct long term changes
Describe autoregulation
LOCAL vasodilators (high CO, H, K, low O2) increase blood flow in busy or inflamed tissue
LOCAL vasoconstrictors decrease blood flow in quiet damaged tissue
If autoreg is ineffective, goes to neural or endo mechs. Describe the general baroreceptor reflex response in CV center (neural mechs)
baroreceptors in aortic arch and carotid sinus detect stretch in vessel wall
CV center in medulla receives info
alters symp/parasymp output to heart (from cardiac center)
alters symp output to blood vessels (vasomotor center)
more descriptive: describe the baroreceptor reflex for high blood pressure
baroreceptor stimulated
vasomotor/sympathetic inhibited
cardioinhibitory/parasymp STIMULATED
cardioacceleratory/sympathetic inhibited
vasodilation and dec CO
more descriptive: describe the baroreceptor reflex for low blood pressure
baroreceptor stimulated
vasomotor/sympathetic STIMULATED
cardioinhibitory/parasympathetic inhibited
cardioacceleratory/symp STIMULATED
vasoconstriction and increase CO
What happens when you stand up? How does baroreceptor response help?
less blood to heart, BP CO SV decrease
to compensate
baroreceptors detect low BP
CV center in medulla activates sympathetic, inactivates parasympathetic
sympathetic causes vasoconstriction
increases BP
What happens during light exercise
increase in autoregulation- metabolites causes vasodilatoin
increase in EDV increases stretch
What happens during strenuous exercise
same autoreg, but also SYMP activity
What happens during hemorrhage
elevation of BP through baroreceptors (neural)
hormonal activation (Endo)
Define atherosclerosis and describe how its caused
stiffening of wall due to fat deposits. reduces blood flow and increases peripheral resistance
high LDL attract WBCs
causes inflammation and thickening of wall (PLAQUE)
What causes coronary artery disease and 2 treatments
atherosclerosis
treat with coronary artery bypass or stent into blood vessels
difference between atrial and ventricular fibrillations
atrial: atrial wall quivers, blood clots may form, leads to stroke
ventricular: ventricle quivers, doesnt pump blood, cardiac arrest
Difference between heart failure and congestive heart failure
heart failure: cannot pump enough blood to organs
congestive hf: blood backs up on venous side. edema in tissue, lungs fill with fluid.
3 ways the CV system changes with age
blood: decrease hematocrit, increases clot liklihood
blood vessels: arteries lose elasticity, plaques, pooling of blood
within heart: conducting cells, reduce elasticity, atherosclerosis, scar tissue