Kidneys: Basic Renal Processes- Tubular Secretion
1/5
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Tubular Secretion
Selective movement of non filtered substances from the peritubular capillaries into the tubular lumen
How are renal hydrogen ions secreted?
Secreted in the proximal tubules
Secreted or reabsorbed by special “intercalated cells” in the distal and collecting tubules depending on the acid balance in the plasma
Organic anion and cation secretion is controlled by what and what does it facilitate?
Controlled by tubular secretion
Facilitates rapid clearance of certain hormones (postaglandins, epinephrine)
Facilitates removal of organic ions that circulate in complex to carrier proteins (not filtered)
Elimination of foreign compounds
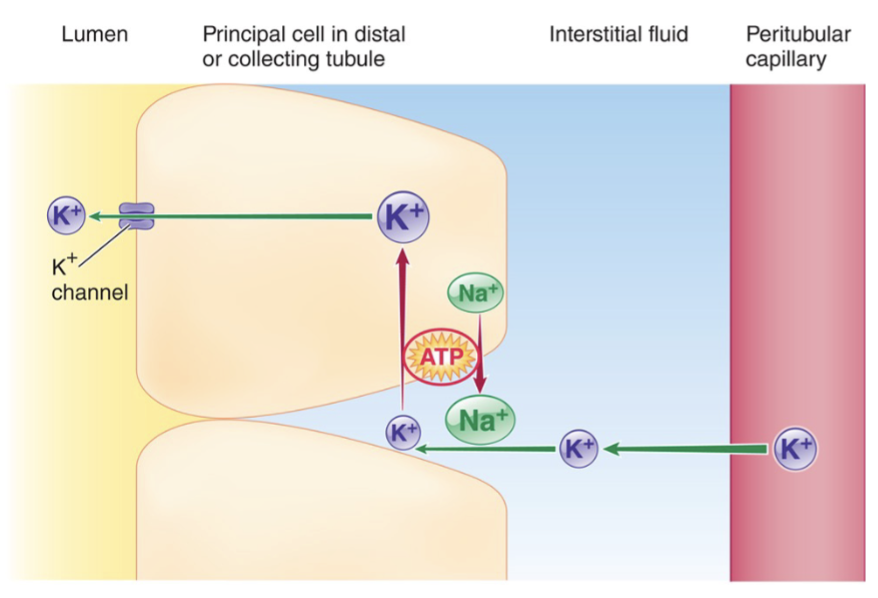
How is tubular secretion of K+ tightly regulated?
K+ is selectively moved in opposite directions along the tubules- K+ is low in the plasma and high in the cells
Most of the K+ in the filtrate is reabsorbed in the proximal tubules via leak channels in the basolateral membrane- tubular reabsorption
Tubular cels in the distal and collecting tubules have leak channels in the tubular membrane- tubular secretion
High plasma K+ directly stimulates aldosterone from the adrenal cortex which stimulates insertion of K+ leak channels in the luminal membrane of the distal and colelcting tubules, almost all K+ in urine is the result of secretion
Processes that promote Na+ reabsorption promote removal of K+
Urine Excretion
The kidneys can excrete urine in varying concentrations depending on body needs
Urine can range form more dilute or more concentrated than ECF/ plasma
How are kidneys able to produce urine of varying concentrations?
Long loops of Henle of juxtamedullary nephrons
Countercurrent multiplication
Hormonal control over water loss in the collecting tubules