Protostome General Structures & Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Three germ/tissue layers
Triploblast
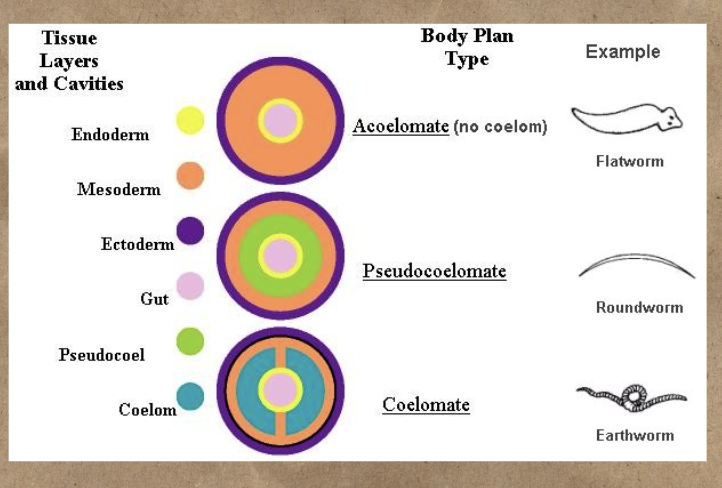
This tripoblast tissue type has “NO” body cavity between the gut and outer wall
Acoelomates ( ex: flatworm)
This tripoblast tissue type has “partially” lined body cavity with mesoderm
Pseudocoelomates (ex: Nematode)
This tripoblast tissue type has body cavity “Completely” lined with mesoderm
Coelomates (ex: Earthworm)
Concentration of sense organs, nervous control, etc are located at the anterior end of the body
Cephalization
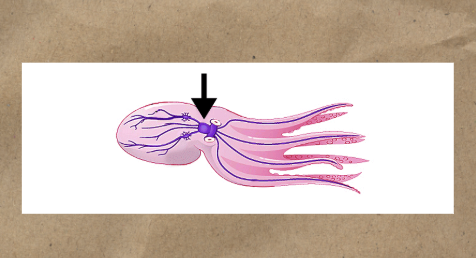
Benefits of Cephalization
Good for animals that move with the same end of the body forward
Better motor control
Better sensory
Better coordination
Fluid held under pressure in a closed body compartment that function as a skeleton
Hydrostatic Skeletons
Specialized excretory cells that regulate osmotic pressure and maintain ionic balance in organism (removing waste)
Flame Cells (Protonephridia)
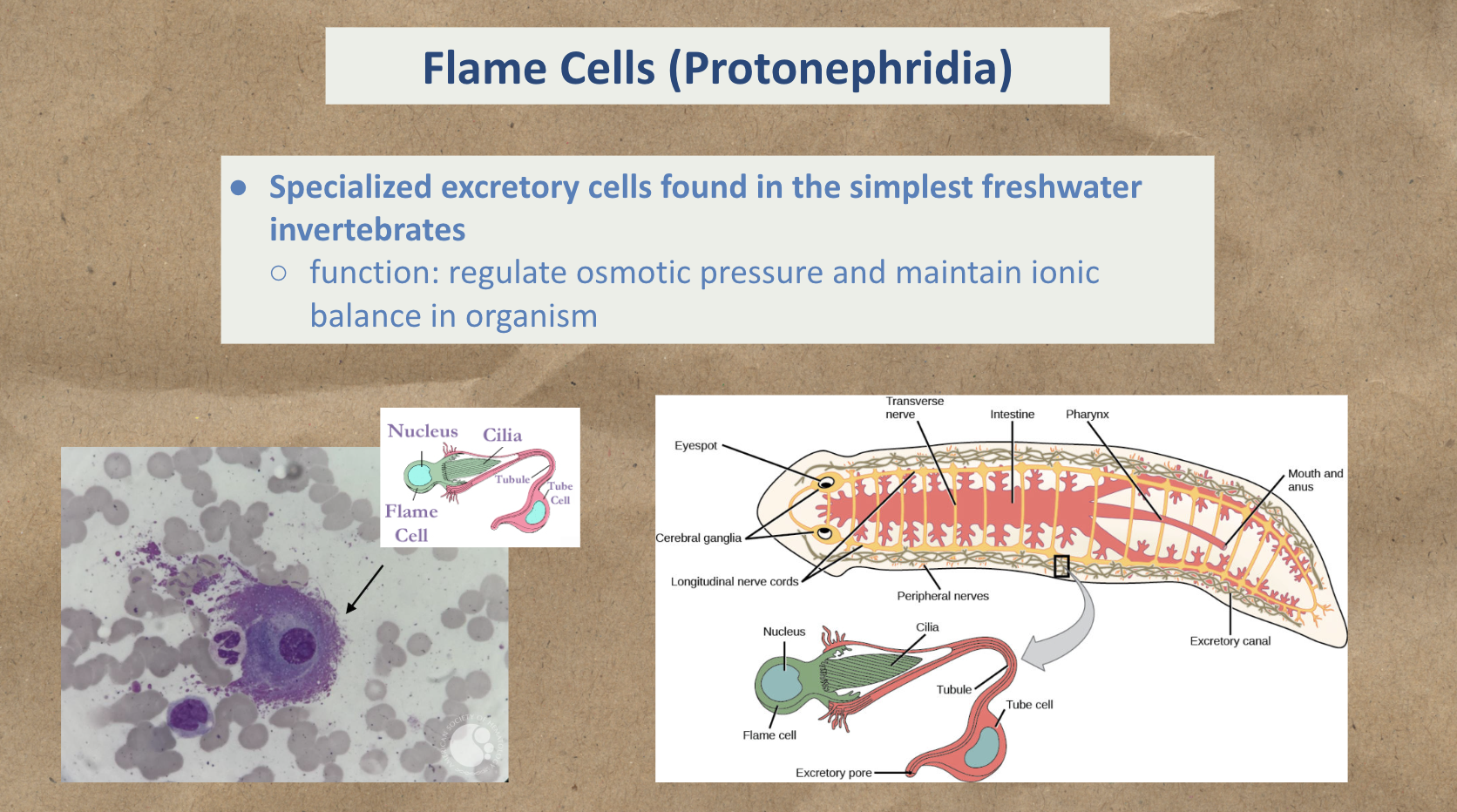
This group of protostome contains:
Triploblastic acoelomates
Hydrostatic skeleton
Bilateral symmetry
Incomplete digestive tract
Monoecious (containing both male and female reproductive organs)
Platyhelminthes - Flatworms
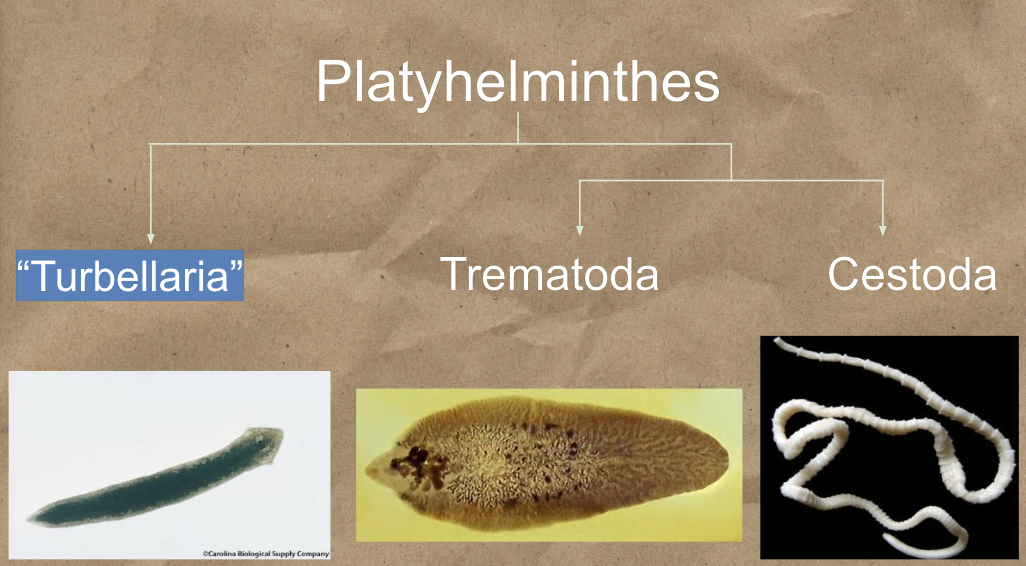
Platyhelminthes contains the following group
Turbellaria
Trematoda
Cestoda

This Platyhelminthes group has the following:
Free living flatworms
Move using ciliated epidermis & muscle contractions
Found in water & terrestrial
Carnivorous
Use chemoreception to find prey
Turbellaria
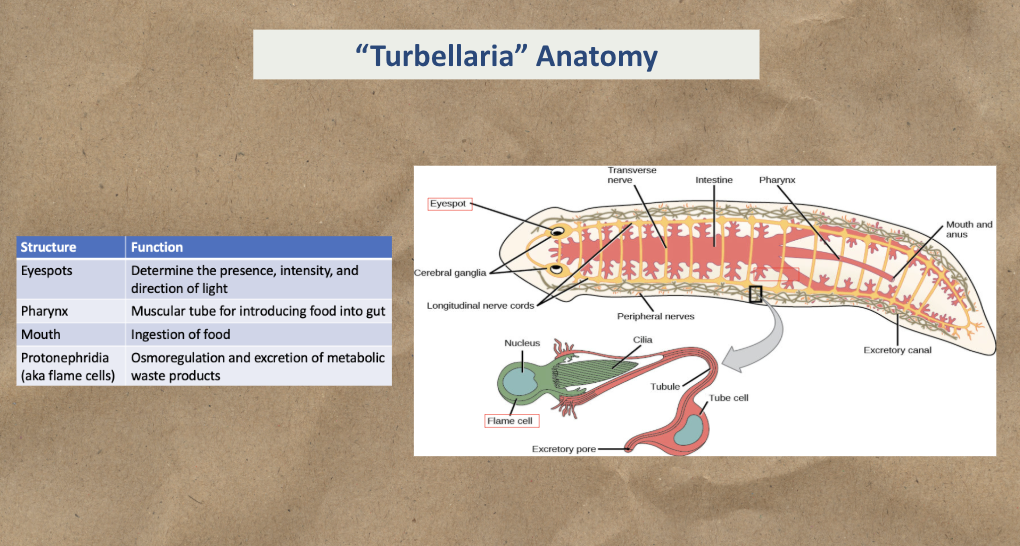
Know Turbellaria anatomy (Eyespot, Flame cell, Pharynx)
Study the diagram
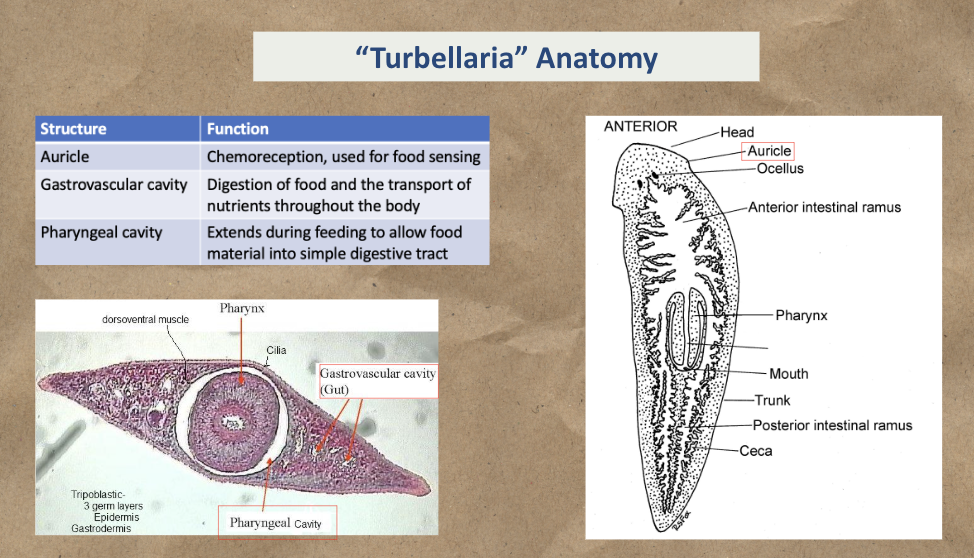
Know Turbellaria anatomy (Auricle, Gastrovascular cavity, pharyngeal cavity)
Study the diagram
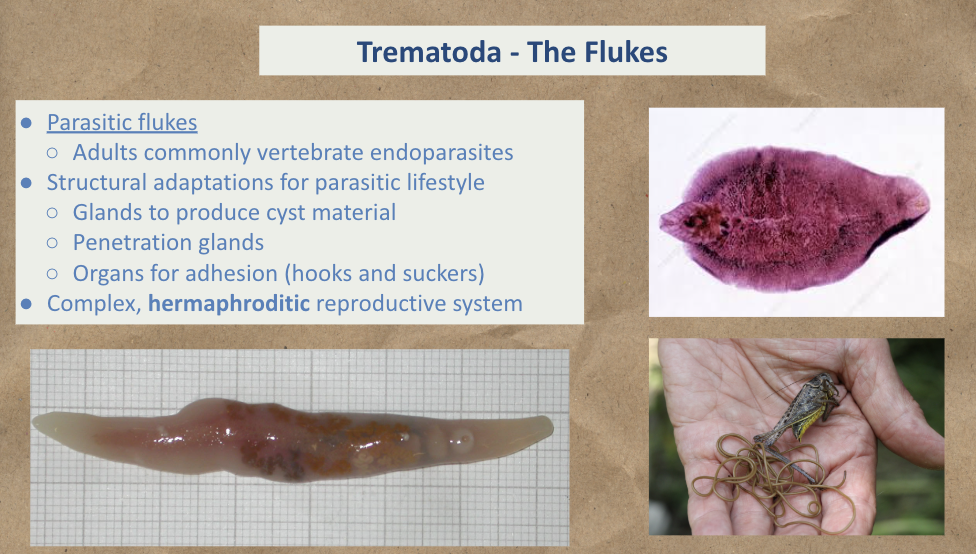
This Platyhelminthes group has the following:
Parasitic Flukes
Glands, penetration glands, hooks and suckers (parasitic lifestyle)
Complex, hermaphroditic reproductive system
Trematoda (The Flukes)
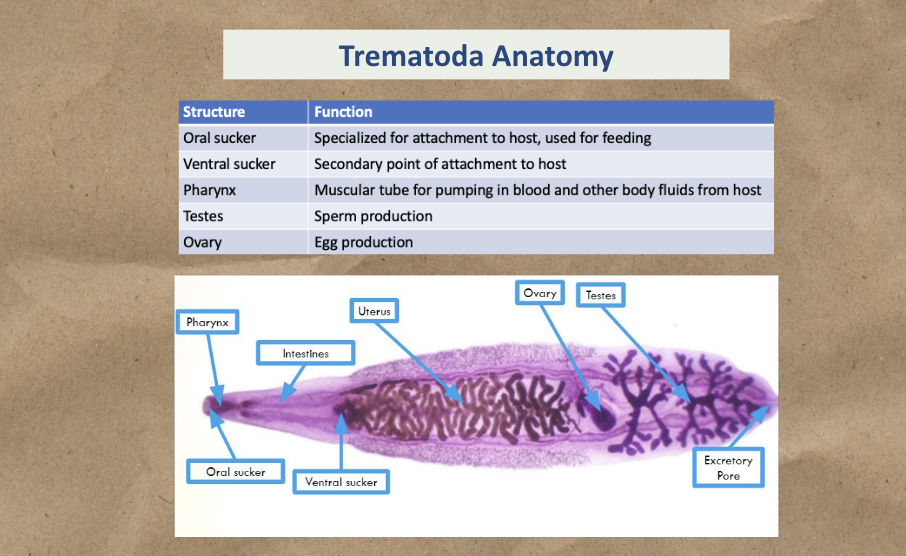
Know Trematoda Anatomy (Oral sucker, Ventral Sucker)
Study the image
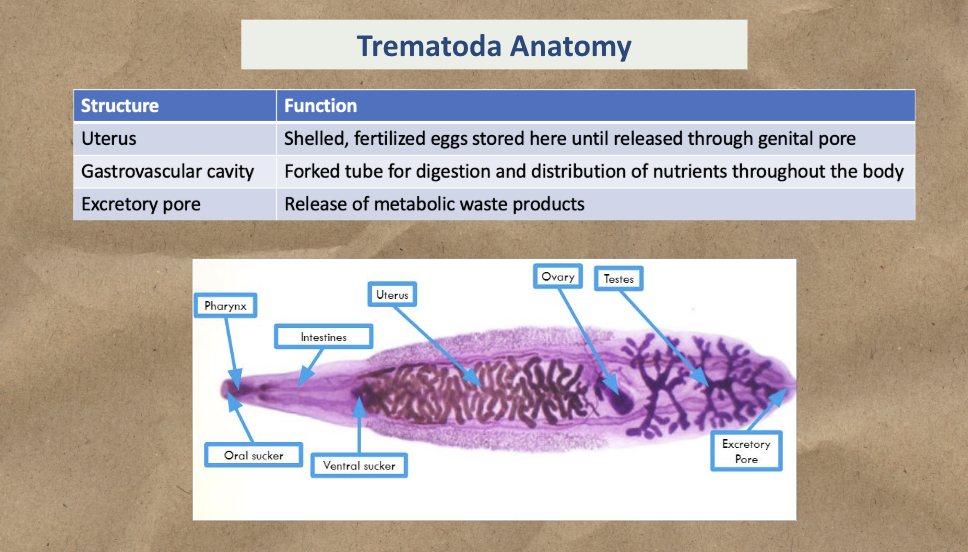
Know Trematoda Anatomy (Uterus, Gastrovascular cavity, Excretory pore)
Study the image
Liver Fluke Life Cycle
Study the image:
Sexually reproduce in human liver
Asexually reproduce in snails

This Platyhelminthes group has the following:
Mainly adults found as parasites in vertebrates
No digestive system
Absorb nutrients directly throughthe host’s intestine
Covered in microvilli
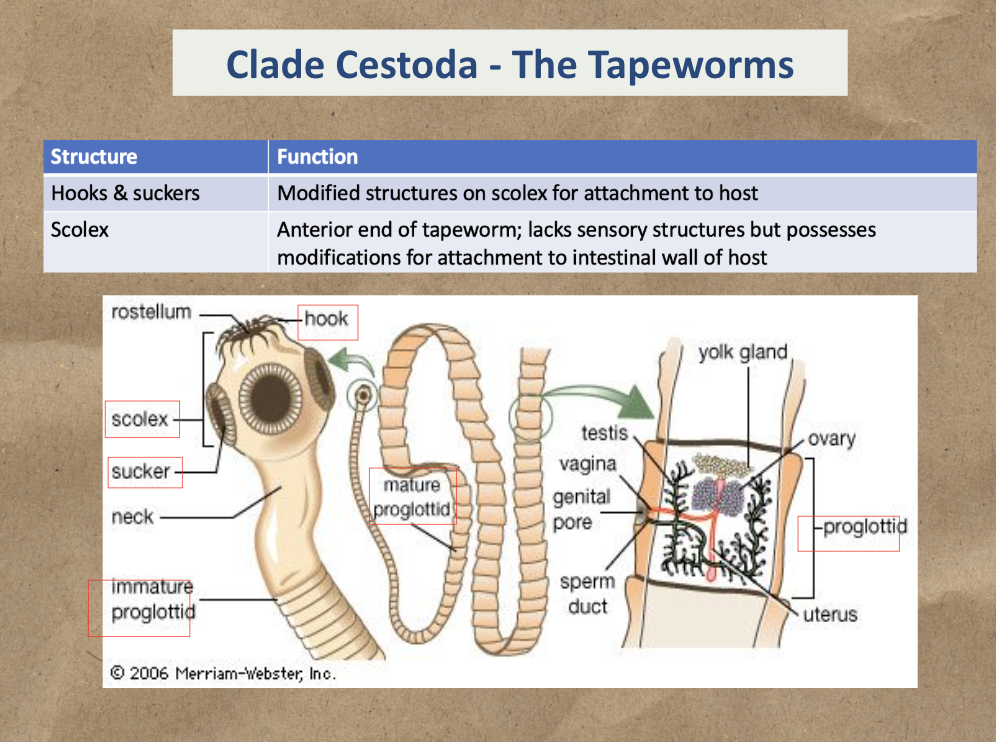
Scolex (head region) with hooks and suckers
No mouth
Cestoda (The tapeworms)
Cestoda: Body segments that contain gonads and mature as they move away from the scolex
Proglottids
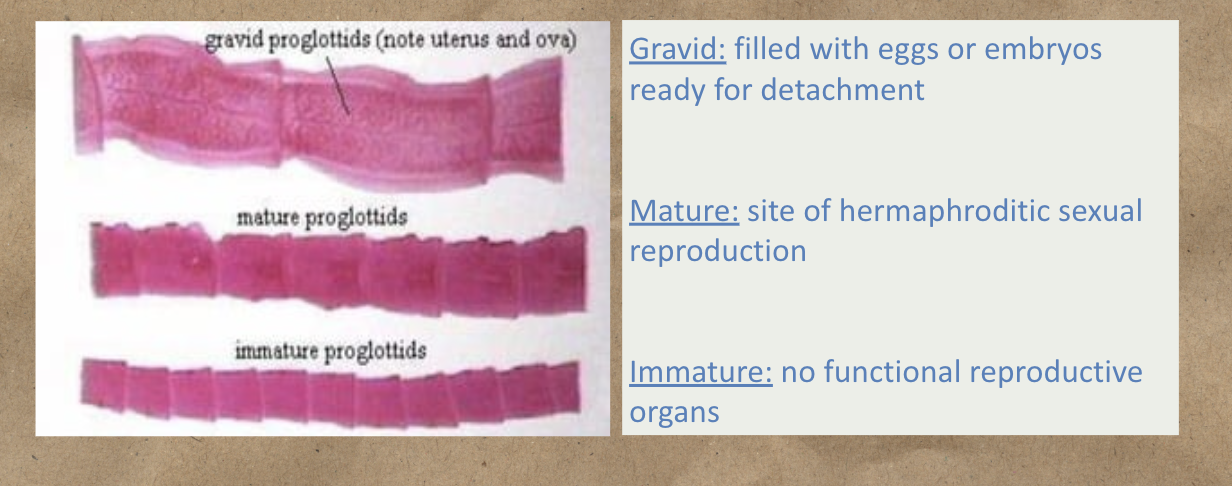
This proglottids are filled with eggs or embryos ready for detachment
Gravid
This proglottids are the site of hermaphroditic sexual reproduction
Mature
This proglottids has no functional reproductive organs
Immature
Structure and function of Cestoda
Study Hooks & Suckers and Scolex